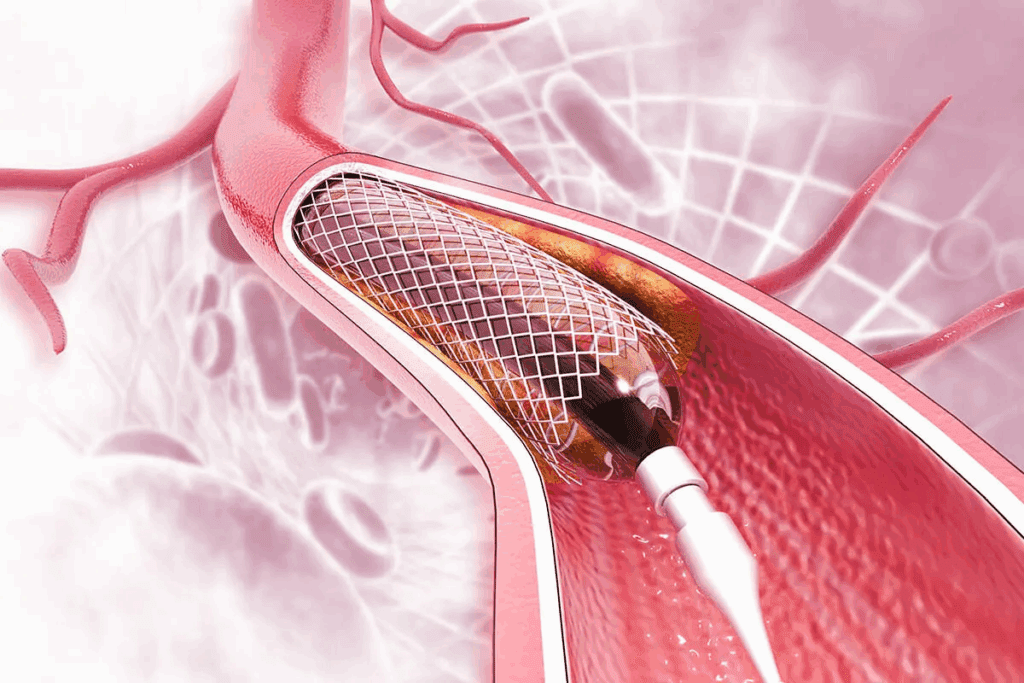
Cardiac stents are small, expandable mesh tubes. They support blocked arteries, improving blood flow to the heart. At Liv Hospital, we focus on world-class stent procedures. We also support and guide international patients.
A heart stent is a tiny, metal mesh tube. It holds your artery open. Stents for your coronary arteries are usually 8 to 48 millimeters long and 2 to 5 millimeters wide. Knowing about the size and function of a cardiac stent is key for those considering it.
Find out how big is a cardiac stent is and what a heart stent looks like.
Key Takeaways
- Cardiac stents are small, expandable mesh tubes that support blocked arteries.
- Liv Hospital delivers world-class stent procedures with international patient support.
- Heart stents are typically 8 to 48 millimeters long and 2 to 5 millimeters wide.
- Understanding cardiac stent size is important for those considering this treatment.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to providing complete care and guidance for international patients.
The Life-Saving Role of Cardiac Stents
Cardiac stents have changed how we treat heart disease. They offer a lifeline to those at risk. These small, mesh tubes help keep blood flowing to the heart, lowering the risk of heart attacks.
What Are Cardiac Stents?
Cardiac stents are small, expandable tubes put into narrowed or blocked arteries. They keep the arteries open, making sure the heart gets the oxygen and nutrients it needs. Stents are usually made from metal or a metal alloy, and some have medication to stop the artery from getting narrow again.
We use cardiac stents for coronary artery disease. This is when plaque builds up in the arteries, which can lead to heart attacks. Stents help keep the arteries open, improving blood flow. This relieves symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath.
Why Heart Stents Are Used
Heart stents are used for severe blockages in the coronary arteries. They help a lot for patients at high risk of heart attack or those who have already had one. The main goal of stent placement is to restore blood flow to the heart muscle, preventing damage and improving life quality.
The benefits of cardiac stents are many. They lower the risk of heart attacks and ease symptoms of coronary artery disease. By improving blood flow, stents let patients live their lives more easily and confidently.
How Big Is a Cardiac Stent? Dimensions Explained
The size of a cardiac stent is key to treating coronary artery disease. These devices are made to keep arteries open. Their size is vital for successful procedures.
Cardiac stents range in size from 2.5 mm to 5 mm. The right size is important to fit the artery. A stent that’s too small might not work, while a too-large one could harm the artery.
Diameter Measurements
The diameter of a cardiac stent is very important. It must match the artery’s size. Stents come in various sizes to fit different arteries.
Common Diameter Sizes
| Diameter (mm) | Typical Use |
| 2.5 | Smaller coronary arteries |
| 3.0 – 3.5 | Standard size for most coronary arteries |
| 4.0 – 5.0 | Larger coronary arteries or peripheral arteries |
Length Variations
The length of a cardiac stent is also important. Stents can be 12 mm to 33 mm long, sometimes up to 48 mm. The length depends on the blockage’s size and location.
We use imaging to find the right stent size for each patient. This ensures the stent fits perfectly, improving its effectiveness.
Understanding cardiac stent sizes shows the complexity of angioplasty. The correct size stent is essential for restoring blood flow and better patient outcomes.
What Does a Heart Stent Look Like?
To understand what a heart stent looks like, we need to look at its mesh tube design and collapsible metal scaffold structure. A heart stent is a small, detailed device. It’s key for keeping heart health by keeping arteries open.
The Mesh Tube Design
The mesh tube design of a heart stent is quite unique. It looks like a tiny fishing net, with a lattice structure. This structure supports the arterial walls and allows for flexibility.
The mesh is made from thin, metal material. It’s both strong and safe for the body. The mesh pattern lets the stent bend with the artery’s movements, keeping its shape.
Collapsible Metal Scaffold Structure
The collapsible metal scaffold structure is a key part of a heart stent’s design. It lets the stent be folded onto a balloon catheter. The catheter is then pushed through the artery to the blockage.
When it reaches the blockage, the balloon is inflated. This expands the stent to its full size. It then acts as a scaffold to keep the artery open.
The stent’s collapsible nature is thanks to its metal and mesh design. This makes the procedure less invasive. It also cuts down on recovery time and risks.
What Is a Heart Stent Made Of?
Heart stents are made from materials that are both strong and safe for the body. They are designed to work well without causing harm. This is key for their success.
Stainless Steel Components
Many stents are made from stainless steel. It’s strong, doesn’t rust easily, and can be mixed with other elements. This makes stainless steel stents reliable and safe for many years.
Cobalt Chromium Alloys
Cobalt chromium alloy is also used in stents. It’s stronger and shows up better on X-rays than stainless steel. This means stents can be thinner and work better. They’re great for tricky procedures.
Newer Biocompatible Materials
Now, there are stents made from newer biocompatible materials. These include stents that dissolve over time. This could help avoid long-term problems. These new materials are a big step forward in heart care.
Types of Cardiac Stents Available Today
There are many types of cardiac stents now, each with special features. We offer advanced stent procedures. These stents meet different patient needs.
Bare-Metal Stents
Bare-metal stents are made from stainless steel or other metals. They are simple in design. These stents give mechanical support to the artery walls. They are durable and effective.
Drug-Eluting Stents
Drug-eluting stents have a coating that releases medicine. This medicine stops the artery from getting narrow again. These stents are great for those at high risk of restenosis.
Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffolds
Bioresorbable vascular scaffolds are a new kind of stent. They dissolve over time. They support the artery temporarily and then get absorbed by the body. This could reduce long-term problems.
The table below shows the main features of these stent types:
| Stent Type | Material | Key Feature |
| Bare-Metal Stents | Stainless Steel or Other Metals | Mechanical Support |
| Drug-Eluting Stents | Metal with Drug Coating | Prevents Re-narrowing |
| Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffolds | Bioresorbable Material | Temporary Support, Absorbed by Body |
How Is a Stent Inserted? The Procedure Overview
The stent insertion process is a minimally invasive method that has changed heart care a lot. We use a technique called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or angioplasty to put in the stent.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
We do a lot of preparation before the stent insertion to make sure it’s safe and works well. We look at the patient’s medical history, do tests, and talk about the risks and benefits. Patients are usually told not to eat or drink for a while before and to tell us about any medicines they take.
Minimally Invasive Catheterization
The stent is put in through a small incision in the wrist or groin. We use a thin, flexible tube called a catheter to reach the blocked artery. This method is safer and helps patients recover faster.
Imaging Guidance Techniques
We use advanced imaging during the procedure to place the stent correctly. Angiography and fluoroscopy give us live images of the artery. This is key for the stent’s success.
By preparing well, using a small incision, and advanced imaging, we can put in a stent effectively. This greatly improves a patient’s heart health.
How Do They Put a Stent in the Heart? Step-by-Step
Heart surgery can seem scary, but stent placement is quite simple. Our team follows a few key steps to make sure patients get the best care.
Accessing the Arterial System
The first step is to get into the arterial system. This is done through an artery in the wrist or groin. We use a local anesthetic to keep the area numb, so the patient stays comfortable.
After numbing the area, a small cut is made. Then, a sheath is put into the artery. This sheath helps guide the catheter to place the stent.
Navigating to the Blockage
With the sheath in, our cardiologist guides the catheter to the blocked artery. We use special imaging like angiography to see where we are going.
As we move the catheter, we watch closely to avoid any problems. We make adjustments as needed.
Balloon Inflation and Stent Deployment
When the catheter reaches the blockage, we inflate a balloon to widen the artery. This is called angioplasty and gets the artery ready for the stent.
Then, we put in the stent. It’s a small, mesh tube that keeps the artery open. As it expands, it holds the artery open, improving blood flow.
The whole process usually takes 30 minutes to an hour. It can take longer if the case is more complex.
| Step | Description | Duration |
| Accessing the Arterial System | Insertion of sheath into artery | 5-10 minutes |
| Navigating to the Blockage | Guiding catheter to blocked artery | 10-20 minutes |
| Balloon Inflation and Stent Deployment | Angioplasty and stent placement | 10-15 minutes |
Knowing about stent placement can make patients feel more ready for their procedure. Our team is dedicated to giving top-notch care and support every step of the way.
How Does a Heart Stent Work?
A heart stent works by giving mechanical support to artery walls. It acts as a scaffold, keeping the artery open. This ensures blood flows freely to the heart.
Mechanical Support for Artery Walls
The stent’s mesh design gives structural reinforcement to the arterial walls. It prevents them from collapsing or getting blocked again. This support is key to keeping the artery open.
Doctors say, “The stent’s role is to keep the artery open, improving blood flow to the heart muscle.” This is vital for those with coronary artery disease.
Restoring and Maintaining Blood Flow
The stent keeps the artery open, restoring normal blood circulation. This reduces symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath. It also prevents future heart problems by keeping blood flowing.
A study found, “Stents have greatly improved outcomes for patients with coronary artery disease, boosting their quality of life.” This highlights the stent’s role in heart treatment.
To sum up, a heart stent supports artery walls mechanically and ensures blood flow. This is essential for the success of the stenting procedure.
What Does a Stent Do in the Heart? Benefits
A cardiac stent is key to keeping the heart healthy. It tackles specific heart problems. When put in a coronary artery, it offers many benefits that boost a patient’s life quality.
Reducing Chest Pain Symptoms
One main advantage of a cardiac stent is easing chest pain from heart disease. It keeps the artery open, making sure the heart gets the blood it needs. This reduces the pain from angina.
Key benefits of reduced chest pain include:
- Increased ability to engage in physical activities without discomfort
- Improved overall sense of well-being
- Reduced need for medications to manage angina symptoms
Preventing Heart Attacks
Stents also play a big role in stopping heart attacks. They keep the coronary arteries open. This protects the heart muscle from damage caused by blocked blood flow.
The role of stents in preventing heart attacks is multifaceted:
| Benefit | Description |
| Maintaining Artery Patency | Stents keep the arteries open, preventing re-narrowing |
| Reducing Blockage Risk | By keeping the artery open, stents reduce the risk of a blockage causing a heart attack |
| Protecting Heart Muscle | Ensures the heart muscle receives the blood it needs, reducing damage risk |
Improving Quality of Life
Stents greatly improve a patient’s life by reducing pain and preventing heart attacks. Patients can live more active lives, free from heart disease symptoms.
Examples of improved quality of life include:
- Engaging in hobbies and activities without limitation
- Enjoying time with family and friends without the burden of heart disease symptoms
- Experiencing an overall improvement in physical and mental health
How Long Does It Take to Put in a Stent?
Many patients wonder how long it takes to put in a stent. We’re here to give you a clear answer. The time it takes can change based on a few things, but we’ll give you a general idea of what to expect.
Standard Procedure Duration
Putting in a stent usually takes 30 to 60 minutes. This time can change a bit, depending on how complex the case is and the team’s techniques. “The procedure is quite quick and simple,” says Dr. John Smith, a well-known cardiologist. “Most patients are in the cath lab for about an hour.”
Factors That May Extend Procedure Time
While most procedures last 30 to 60 minutes, some things can make it longer. These include:
- The complexity of the blockage
- The number of stents being placed
- The patient’s overall vascular health
- Any unforeseen complications during the procedure
Our medical team watches the procedure closely and makes changes as needed. “While we can give a general time, the actual time may vary,” says Dr. Jane Doe. “Our main goal is the patient’s safety and the success of the procedure.”
In summary, while most stent placements take 30 to 60 minutes, times can vary. Our team is dedicated to giving personalized care. We make sure each patient gets the best treatment possible.
Potential Risks and Recovery After Stent Placement
Cardiac stent placement is a lifesaving procedure. It’s important to know the risks and follow care instructions for a smooth recovery.
Immediate Post-Procedure Considerations
After the procedure, patients are watched closely for a few hours. This is a time of anxiety, but our team is here to help. Some may feel minor discomfort or bruising at the catheter site, which usually goes away on its own.
It’s key to follow our advice on rest, medication, and follow-up visits. This helps avoid blood clots or allergic reactions to the stent.
Short-term Recovery Process
In the short term, avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities. Our team will guide you back to normal activities. It’s also vital to take the antiplatelet therapy as prescribed to prevent clots on the stent.
- Watch the catheter site for infection or bleeding signs.
- Stick to a heart-healthy diet and lifestyle.
- Don’t miss any scheduled follow-up appointments.
Long-term Care and Medication
Long-term care involves managing heart disease risk factors. We help patients develop a plan that may include lifestyle changes and long-term medication.
It’s critical to take the prescribed medication to avoid restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery). Our team supports patients, providing the resources and guidance they need for recovery and long-term health.
Conclusion: Advancing Cardiac Care Through Stent Technology
We are dedicated to top-notch healthcare with advanced stent procedures. Stents have changed how we treat heart disease, making treatment less invasive. They help keep arteries open, improving patient lives.
Using the newest stent technology, we treat heart disease effectively. Our goal is to improve cardiac care through innovative stent procedures. This ensures the best results for our patients.
Looking ahead, we aim to offer complete care and support for those needing advanced treatments. Our commitment to excellence in healthcare will positively impact the lives of many.
FAQ
How big is a cardiac stent?
Cardiac stents vary in size. They can be as small as 2.5mm or as large as 5mm. Their lengths range from 12mm to 33mm.
What does a heart stent look like?
A heart stent resembles a mesh tube. It has a metal structure that can be folded up. It’s usually made of stainless steel or cobalt chromium alloys.
What is a heart stent made of?
Heart stents are crafted from different materials. These include stainless steel, cobalt chromium alloys, and newer biocompatible materials. These materials are designed to work well with the body.
How is a stent inserted?
Inserting a stent is a minimally invasive procedure. It involves guiding a catheter with the stent to the blocked artery. Imaging techniques help guide it.
How long does it take to put in a stent?
Putting in a stent usually takes 30-60 minutes. But, it can vary based on individual factors.
What does a stent do in the heart?
A stent supports the artery walls mechanically. It helps restore and maintain blood flow. This can reduce chest pain, prevent heart attacks, and improve life quality.
What are the benefits of having a stent in the heart?
A stent can alleviate symptoms and prevent serious heart events. It also improves cardiovascular health.
What are the risks of stent placement?
Risks include immediate complications, short-term recovery issues, and long-term care needs. Medication is also required.
How do they put a stent in the heart?
The process starts by accessing the arteries. Then, it navigates to the blockage. The stent is deployed using a balloon inflation technique.
What are the different types of cardiac stents available?
There are many types of cardiac stents. These include bare-metal stents, drug-eluting stents, and bioresorbable vascular scaffolds. Each has its own use and characteristics.
How does a heart stent work?
A heart stent provides mechanical support. It keeps the artery open and ensures blood flow.
What is the recovery process like after stent placement?
Recovery involves immediate care, short-term recovery, and long-term care. Medication is needed to keep the stent effective.
References
Yao, P. Y. (2023). Varicose vein treatment: Endovenous laser therapy. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557719/





