Last Updated on October 21, 2025 by mcelik
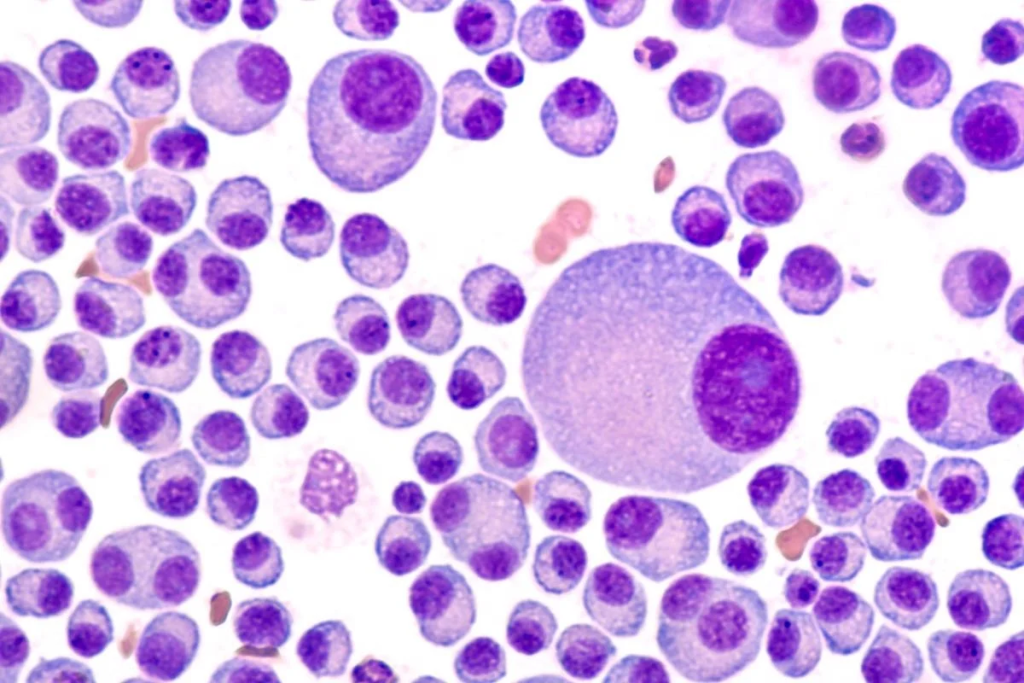
Multiple myeloma is a cancer that affects thousands worldwide. It causes a lot of suffering and death. The progression of the disease leads to various complications. So how does multiple myeloma kill you. Knowing how myeloma ends is key for both patients and doctors.
We will look into the final stages of multiple myeloma and what makes it deadly. The dying process is complex, involving the bone marrow and overall health.
To understand multiple myeloma, we need to know what it is and how it affects the body. It’s a cancer that starts in the plasma cells. These cells are key to our immune system.
Multiple myeloma happens when bad plasma cells build up in the bone marrow. This buildup can cause anemia, bone pain, and make infections more likely. It also messes with how the body makes antibodies, making it hard to fight off infections.
As the disease gets worse, it can cause many problems. The malignant plasma cells damage the bone marrow, leading to anemia and a weak immune system. It can also cause bone lesions, leading to pain and a higher risk of fractures.
The effects of multiple myeloma on the body are wide-ranging. It needs a detailed treatment plan to manage symptoms and slow the disease’s growth. Knowing how it works and its impact helps doctors find better ways to help patients.
Multiple myeloma’s causes are complex, involving genetics, environment, and demographics. While we don’t know the exact cause, research has found several risk factors. These factors increase the chance of getting this disease.
Age is a big risk factor, with most cases in people over 65. Family history also matters, as those with a relative with myeloma are at higher risk. Exposure to chemicals like pesticides and herbicides also raises the risk.
Other risk factors include:
Knowing these risk factors helps identify who’s at higher risk. This can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment.
Genetics play a big role in myeloma. Certain genetic changes, like those in the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene, are common in myeloma cells. Environmental factors, like chemical and radiation exposure, also play a part.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Risk |
| Age | Most diagnoses occur after age 65 | Significantly increases risk |
| Family History | Having a first-degree relative with myeloma | Increases risk |
| Chemical Exposure | Exposure to pesticides, herbicides, etc. | May increase risk |
Research is ongoing to understand how genetics and environment interact in myeloma. Knowing these factors is key to better prevention and treatment.
Multiple myeloma is a complex disease that goes through different stages. Each stage has its own challenges and characteristics. It’s important for patients and doctors to understand these stages to manage the disease well.
In the early stage, patients might not show any symptoms. This stage is marked by the presence of monoclonal protein (M-protein) in the blood or urine. Early detection and monitoring are key to manage the disease before it gets worse.
As the disease moves to the intermediate stage, patients may start feeling symptoms like bone pain, fatigue, or frequent infections. The M-protein levels are higher, and organs like the bone marrow and kidneys are affected more. Regular assessment and adjusting treatment plans are important to control the disease and improve quality of life.
In the advanced stage, multiple myeloma can severely damage bones, bone marrow, and other organs. This can lead to complications like anemia, kidney failure, and increased risk of infections. Aggressive management and supportive care are needed to ease symptoms and improve quality of life.
Relapsed myeloma happens when the disease comes back after a break. Refractory myeloma is when the disease doesn’t respond to treatment. Managing these types requires new treatment approaches and careful monitoring to get the best results.
The progression of multiple myeloma through its stages shows the need for personalized care and flexible treatment plans. By knowing the characteristics of each stage, patients and doctors can work together to create the best management plans.
| Stage | Characteristics | Management Strategies |
| Early Disease | Asymptomatic, presence of M-protein | Monitoring, early detection |
| Intermediate Disease | Emergence of symptoms, higher M-protein levels | Regular assessment, adjustment of treatment plans |
| Advanced Disease | Significant organ damage, complications | Aggressive management, supportive care |
| Relapsed/Refractory Myeloma | Disease recurrence or lack of response to treatment | Innovative treatment approaches, careful monitoring |
Multiple myeloma can cause death in several ways. It affects the bone marrow, causes systemic problems, and can lead to organ failure. This disease impacts important body functions, making the how does multiple myeloma kill you.
The bone marrow is key for making blood cells. Multiple myeloma harms it by growing bad plasma cells. This can cause:
“The bone marrow failure is a hallmark of multiple myeloma’s progression, leading to severe complications.”
Multiple myeloma also causes problems throughout the body. These include:
These issues show how complex the disease is and how it can harm many body systems.
Organ failure is a big part of why multiple myeloma is fatal. It can cause:
The way these mechanisms work together shows why treating multiple myeloma needs a full approach.
As we learn more about multiple myeloma, it’s clear that knowing how it kills is key to finding better treatments.
Advanced multiple myeloma can cause severe bone problems. These issues can greatly affect a patient’s life quality. As the disease gets worse, the bone marrow gets more affected, leading to various bone-related problems.
One major bone issue in advanced multiple myeloma is pathological fractures. These fractures occur when the bone weakens due to the disease. They can be very painful and limit a patient’s movement.
The risk of these fractures increases because myeloma cells destroy bone tissue. This destruction creates lytic lesions, visible on X-rays. To manage this risk, treatments aim to strengthen bones and reduce myeloma activity.
Spinal cord compression is another serious issue in advanced multiple myeloma. It happens when a tumor or broken bone presses on the spinal cord. This is a medical emergency that needs quick treatment to avoid permanent damage.
Symptoms include back pain, numbness or weakness in the legs, and problems with bladder or bowel control. It’s important to catch and treat this early to keep nerve function.
Managing bone pain is key in palliative care for advanced multiple myeloma. As the disease advances, pain can worsen. A mix of medicines and non-medical methods, like radiation, may be used.
Good pain management in the final stages of multiple myeloma is vital. Healthcare teams work with patients and families to create a pain plan that meets their needs.
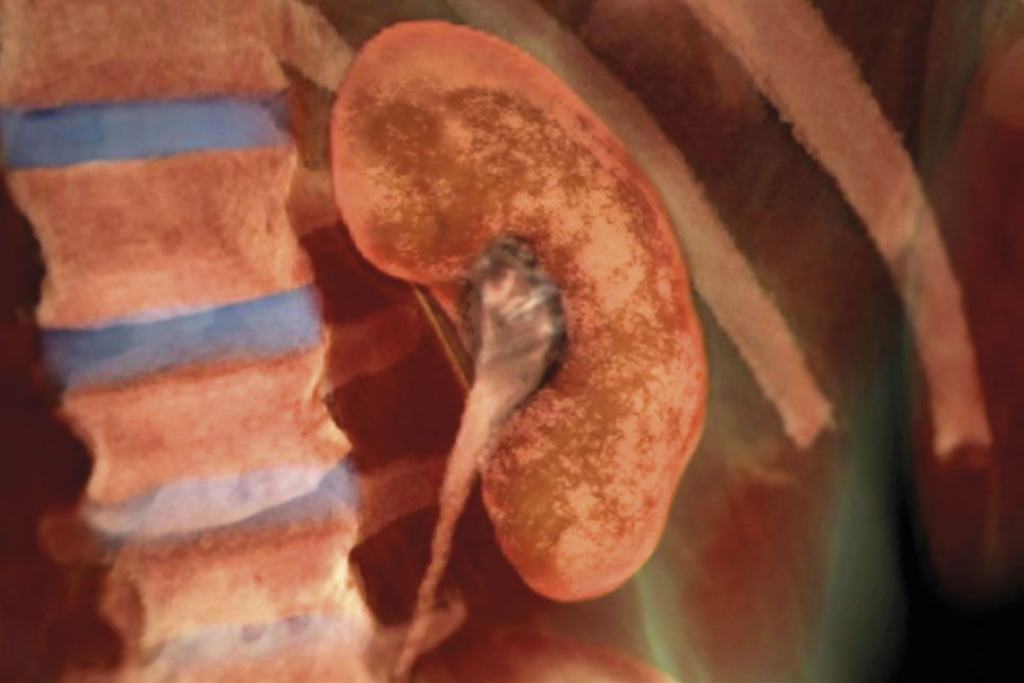
Kidney failure is a big problem in the late stages of multiple myeloma. It affects how well patients do. We will look at how renal damage happens, how myeloma kidney disease gets worse, and what it means for life expectancy.
Renal damage in multiple myeloma happens in a few ways. Light chain toxicity is a big reason, where too many light chains from myeloma cells hurt the kidneys. Other causes include high calcium levels, not enough water, and harmful medicines.
The disease gets worse as light chains build up in the kidneys. This causes damage to the tubules and leads to cast formation. Things like high calcium and not enough water can make it worse. Knowing how this works helps doctors take care of the kidneys in myeloma patients.
Kidney failure really cuts down on the life expectancy of multiple myeloma patients. How long someone lives depends on how bad the kidney damage is and their overall health. Getting help early is key to better results.
Many things can lead to kidney failure in multiple myeloma, including:
Understanding these causes helps doctors take better care of the kidneys. This can lead to better outcomes for patients.
Advanced multiple myeloma causes serious problems with blood and the immune system. These issues can be deadly. They happen because the disease affects the bone marrow and immune system.
Many with multiple myeloma face severe anemia. This is because cancer cells replace healthy bone marrow cells. This leads to fewer red blood cells, causing tiredness, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Bleeding problems are common in those with multiple myeloma. These issues come from low platelet counts or platelet problems. The disease also makes proteins that mess with blood clotting. This can cause easy bruising and nosebleeds.
People with multiple myeloma often get sick easily. This is because their immune system is weakened. They are more likely to get serious infections like pneumonia and sepsis.
| Complication | Cause | Effect |
| Severe Anemia | Replacement of normal bone marrow cells by malignant plasma cells | Fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath |
| Bleeding Disorders | Thrombocytopenia, platelet dysfunction, abnormal proteins interfering with blood clotting | Easy bruising, nosebleeds, bleeding complications |
| Recurrent Infections | Immunoglobulin production, impaired antibody production | Pneumonia, sepsis, life-threatening infections |
In the final stages of multiple myeloma, neurological symptoms become more common. These symptoms pose big challenges for patient care. As the disease gets worse, different neurological problems can happen, affecting the patient’s life quality and needing detailed care plans.
Spinal cord compression is a serious issue in terminal multiple myeloma. It happens when a tumor or broken bone presses on the spinal cord. This can cause severe back pain, weak limbs, and even paralysis if not treated quickly. We must handle spinal cord compression carefully to keep neurological function and improve patient results.
Managing spinal cord compression often includes radiation therapy, corticosteroids, and sometimes surgery. These steps help relieve the pressure and stabilize the spine.
Hypercalcemia, or high calcium levels in the blood, is another problem in terminal multiple myeloma. It can cause confusion, tiredness, and even coma in severe cases. It’s vital to manage hypercalcemia to stop these brain symptoms and make patients more comfortable.
Treatment for hypercalcemia includes drinking lots of water, diuretics, and medicines that slow down bone breakdown, like bisphosphonates.
Cognitive changes are common in the final stages of multiple myeloma. These can be from mild confusion to severe brain problems. Causes include high calcium levels, side effects from medicines, and the disease’s direct effect on the brain.
| Neurological Manifestation | Common Causes | Management Strategies |
| Spinal Cord Compression | Tumor or fractured bone compressing the spinal cord | Radiation therapy, corticosteroids, surgery |
| Hypercalcemia | Elevated calcium levels due to bone destruction | Hydration, diuretics, bisphosphonates |
| Cognitive Changes | Hypercalcemia, medication side effects, disease progression | Management of underlying causes, supportive care |
It’s key to understand and tackle these neurological symptoms for full care of patients with terminal multiple myeloma. By managing these issues well, we can better patient outcomes and improve their life quality in the disease’s final stages.
Hypercalcemia is a big problem in multiple myeloma. It happens when bone tissue gets destroyed, raising blood calcium levels. This can make patients feel very sick.
Multiple myeloma makes calcium levels go up in a few ways. The disease causes too many bad cells in the bone marrow. This messes up bone health, leading to more calcium in the blood.
Many factors, like special proteins from myeloma cells, help break down bones. This makes more calcium get into the blood.
| Mechanism | Description |
| Osteoclast Activation | Myeloma cells produce factors that activate osteoclasts, leading to increased bone resorption. |
| Bone Destruction | The imbalance in bone remodeling results in the destruction of bone tissue, releasing calcium. |
| Impaired Renal Function | Hypercalcemia can impair kidney function, further complicating calcium excretion. |
Severe hypercalcemia can cause many symptoms. These include feeling confused, having trouble going to the bathroom, and being very thirsty. In bad cases, it can even hurt the heart and brain.
“Hypercalcemia of malignancy is a serious complication that can significantly affect patient outcomes. Managing this condition requires a thorough approach to ease symptoms and improve comfort.”
Dealing with hypercalcemia in late-stage multiple myeloma is tough. Doctors try to make patients feel better and live more comfortably. They might use water, special drugs, and medicines like bisphosphonates to help.
Every patient reacts differently to treatment. So, doctors need to tailor plans for each person. They aim to make the rest of the patient’s life as good as it can be.
In summary, hypercalcemia is a big problem in multiple myeloma. Knowing how it happens, what symptoms it causes, and how hard it is to treat helps us help patients better.
Patients with multiple myeloma often have weakened immune systems. This makes them more likely to get infections. The disease and treatments can both weaken the immune system.
As a result, these patients face a higher risk of severe infections. Some of these infections can be life-threatening.
Multiple myeloma patients are more likely to get infections. The disease makes it hard for the body to fight off germs. Treatments like chemotherapy also weaken the immune system.
We need to take steps to prevent and treat infections in these patients. This is important for their care.
Key factors contributing to infection vulnerability include:
In the late stages of multiple myeloma, patients are very vulnerable to infections. These can include pneumonia, sepsis, and other serious infections. Their weakened immune system makes it hard for them to recover.
| Infection Type | Common Pathogens | Clinical Features |
| Pneumonia | Bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae), Viruses (e.g., Influenza) | Cough, Fever, Shortness of breath |
| Sepsis | Various bacteria, fungi | Fever, Tachycardia, Hypotension |
Sepsis is a serious problem in late-stage multiple myeloma. It happens when the body’s response to an infection gets out of control. Sepsis can cause organ failure and is often fatal.
We must quickly recognize and treat sepsis. This is hard in patients with weak immune systems.
“Sepsis remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with hematologic malignancies, including multiple myeloma.”
We need to watch for signs of sepsis and start treatment right away. This includes using broad-spectrum antibiotics and supportive care for organ problems.
Multiple myeloma often becomes resistant to treatment, making it hard to manage. This resistance can come from genetic changes in cancer cells and changes in the bone marrow.
Drug resistance in multiple myeloma comes from many sources. Genetic changes in myeloma cells can make them resistant to certain treatments. The bone marrow environment also helps myeloma cells survive, making them less likely to respond to treatment.
Managing refractory multiple myeloma needs a detailed plan. We look at the patient’s health, past treatments, and any other health issues. Treatment strategies might include trying new therapies or joining clinical trials.
When all treatments fail, we focus on improving the patient’s quality of life. This includes managing symptoms, easing pain, and supporting patients and their families emotionally and psychologically.
Multiple myeloma’s end stage shows clear signs. These include physical, lab, and functional changes. Patients face many symptoms that hurt their quality of life.
End-stage multiple myeloma brings many physical problems. These can be very hard to deal with. Some common symptoms are:
Severe bone pain is a big problem in advanced myeloma. It needs good pain management.
Labs are key in diagnosing and tracking end-stage multiple myeloma. Important lab signs include:
| Laboratory Test | Significance in End-Stage Myeloma |
| Serum Calcium Levels | High calcium means bone damage |
| Hemoglobin Levels | Low hemoglobin shows bone marrow failure |
| Serum Creatinine | High levels mean kidney problems |
| Monoclonal Protein Levels | Changes in M-protein show disease progress or treatment response |
Labs give vital info on disease progress and patient health.
End-stage multiple myeloma causes big problems with daily activities. Common issues include:
Early recognition of these problems helps doctors improve patient care and comfort.
Understanding physical symptoms, lab signs, and functional decline helps doctors give better care. This care is more effective and caring for patients.
The emotional and psychological effects of terminal multiple myeloma on patients and their families are huge. As the disease gets worse, both patients and their loved ones face many challenges. These challenges affect their emotional and psychological well-being.
Patients with terminal multiple myeloma often feel anxious, depressed, and scared of the unknown. The disease’s progression can make them feel hopeless and desperate. This greatly affects their quality of life.
We know these patients need more than just medical treatment. They also need emotional and psychological support. Effective coping mechanisms and supportive care are key to helping them deal with these challenges.
Terminal multiple myeloma affects not just the patient but also their family and caregivers. Caregivers often feel emotionally strained and burdened as they try to meet their loved one’s needs while taking care of themselves.
It’s important for families and caregivers to get the support they need. This includes counseling and respite care to help manage the caregiver burden.
Good communication is key in supporting patients and their families through terminal multiple myeloma. It’s important to have open and honest talks about the disease, treatment options, and end-of-life care. This helps everyone understand what’s happening.
We stress the need for patients to be involved in decision-making. This ensures their wishes are respected and their quality of life is maintained as much as possible.
Palliative care is key in managing symptoms and improving life quality for those with terminal multiple myeloma. As the disease advances, patients face many challenging symptoms. These symptoms can greatly affect their daily lives.
Managing pain is a major focus in palliative care for terminal multiple myeloma patients. We use a mix of medicines and non-medical methods to tackle pain. Opioid analgesics are used for severe pain, and adjuvant therapies like bisphosphonates help with bone pain.
We also suggest non-medical ways like physical therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy. These help patients deal with pain and enhance their well-being.
Palliative care aims to boost the quality of life for patients with terminal multiple myeloma. We focus on their physical, emotional, and social needs. We work with patients and their families to create care plans that meet their specific needs and wishes.
Supportive care is a vital part of palliative care for terminal multiple myeloma patients. It helps manage symptoms, enhance quality of life, and support patients and their families.
Examples include nutritional support, respiratory therapy, and psychological counseling. By addressing patients’ complex needs, we aim to improve their care experience and help them live with dignity.
As we keep pushing forward in multiple myeloma research, we give hope to patients and their families. New studies are revealing important details about the disease. This leads to better treatments and outcomes for patients.
The outlook for treating multiple myeloma is bright. Many new treatments are being looked into. These developments offer hope to myeloma patients, giving them more care options.
By investing in research, we can make managing and treating multiple myeloma better. This will improve patients’ lives. We are dedicated to providing top-notch healthcare and support to patients worldwide.
Multiple myeloma is a cancer that starts in plasma cells, a key part of our immune system. It can cause problems like anemia, bone damage, and weaken our immune system.
Risk factors include age, genetics, and exposure to certain toxins.
The disease can start as early, asymptomatic myeloma and progress to advanced stages. Each stage has its own challenges and needs specific care plans.
It can damage the bone marrow, causing anemia, infections, and bleeding issues. As it gets worse, it can also harm organs, leading to fatal complications.
The disease weakens bones, leading to fractures and spinal cord compression. Managing pain is key in the final stages.
It can damage kidneys through several ways, leading to failure. Understanding this is vital for managing the disease’s late stages.
Severe anemia, bleeding disorders, and infections are common. These can greatly affect a patient’s quality of life and survival.
Symptoms include spinal cord compression, hypercalcemia, and cognitive changes as the disease advances.
Elevated calcium levels can occur due to bone destruction. Symptoms include confusion, constipation, and increased thirst.
The disease weakens the immune system, making patients more susceptible to infections. Common infections and sepsis are major concerns in the end stages.
The disease can become resistant to treatments, making management difficult. Understanding drug resistance and managing refractory disease is critical for healthcare providers.
Patients and healthcare providers need to watch for physical symptoms, lab signs, and functional decline patterns in the final stages.
Patients face many psychological challenges. The disease also affects families and caregivers. Effective communication and decision-making are key in supporting them.
Pain management, improving quality of life, and supportive care are essential. These approaches can greatly enhance patient care and comfort in the final stages.
Currently, multiple myeloma is not curable, but ongoing research offers new treatments and better outcomes.
Life expectancy varies based on disease stage, treatment response, and overall health
Fonseca, R. (2014). Staging and prognostication of multiple myeloma. Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America, 28(3), 495-505. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4201368/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us