At Liv Hospital, we know how vital a coronary angiogram is for spotting heart disease.how is a coronary angiogram performedWhat techniques are used in nuclear cardiology? This test is key for our cardiologists to see the heart’s blood vessels. It helps them find any blockages.
A coronary angiogram procedure uses a thin catheter to put a dye that shows up on X-rays. This dye lets doctors see the coronary arteries clearly. Knowing the steps helps patients get ready and feel less worried.
We help our patients every step of the way. We aim to give them the best care and knowledge. Our goal is to make the whole process as easy as possible for them.
Key Takeaways
- A coronary angiogram is a key tool for finding heart disease.
- The procedure uses a thin catheter to put a dye that shows up on X-rays.
- These X-ray images help doctors spot any blockages in the heart’s blood vessels.
- Learning about the steps can help patients feel less anxious.
- Liv Hospital offers top-notch care and knowledge during the procedure.
Understanding Coronary Angiography
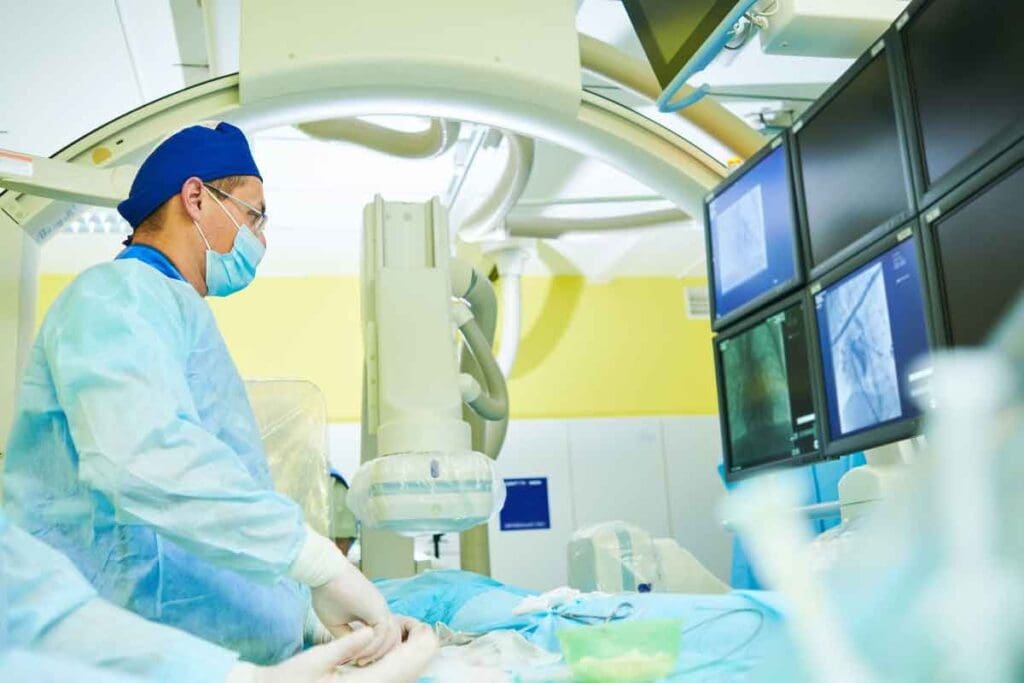
Coronary angiography is the top choice for finding coronary artery disease. It shows the coronary arteries in detail. This helps doctors know how to treat a patient’s heart.
We will look at what coronary angiography is, its purpose, and why it’s the best for diagnosing heart disease.
What Is a Coronary Angiogram?
A coronary angiogram uses dye and X-rays to see blood flow in the heart’s arteries. It helps doctors find blockages or problems in the arteries.
The Purpose of Cardiac Angiography
Cardiac angiography’s main goal is to find and check how bad the coronary artery disease is. It shows the arteries’ condition, helping doctors decide on treatment.
Coronary Angiography as the Gold Standard Diagnostic Tool
Coronary angiography is seen as the best tool because it accurately shows the arteries. The info it gives is key to making treatment plans, like angioplasty or bypass surgery.
| Diagnostic Tool | Accuracy | Information Provided |
| Coronary Angiography | High | Detailed images of coronary arteries |
| Stress Test | Moderate | Heart function under stress |
| CT Scan | High | Cross-sectional images of the heart |
Knowing about coronary angiography helps patients understand the diagnostic process. It shows how it helps doctors make treatment plans.
When Is a Coronary Angiogram Necessary?

A coronary angiogram is usually needed when other tests show problems or symptoms point to heart disease. It’s a key step in figuring out and treating heart issues.
Common Indications for the Procedure
We suggest a coronary angiogram for those showing signs of heart trouble. This includes:
- Angina or chest pain
- Abnormal stress test results
- Other heart-related issues that require detailed imaging of the coronary arteries
Medical guidelines say a coronary angiogram is often the next step when non-invasive tests don’t give clear answers. It’s also used when there’s a strong belief in coronary artery disease. “Coronary angiography remains the gold standard for diagnosing coronary artery disease,” say heart specialists.
Diagnostic Benefits of Coronary Angiography
The procedure of angiography for the heart gives detailed views of the coronary arteries. It helps spot blockages, narrowings, or other issues. This info is key for:
- Finding out how bad coronary artery disease is
- Deciding on the right treatment, like angioplasty or bypass surgery
- Figuring out the risk for future heart problems
Most angiography procedures for the heart take 30-60 minutes. It’s a fast and effective way to diagnose.
Alternatives to Consider
Though coronary angiography is very useful, other imaging methods might be looked at too. These include:
- Coronary CT angiography
- Cardiac MRI
- Stress echocardiography
We talk with our patients about these options to find the best test for their situation.
Preparing for Your Coronary Angiogram
Getting ready for a coronary angiogram is important. Your doctor will tell you what to do before the test.
Pre-Procedure Instructions
You’ll get instructions on how to prepare for your coronary angiogram. You might need to skip eating and drinking for a while before it. It’s very important to follow these instructions to make sure the test is safe and works well.
Your doctor might also check your blood to see how it clots. This is a common step to lower the chance of bleeding during and after the test.
Medication Considerations
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you’re taking, including blood thinners. They will tell you if you should keep taking them or stop before the test.
What to Bring to Your Appointment
On the day of your test, bring important documents like your insurance cards and ID. Also, have a list of your medicines and any past health issues.
Discussion with Your Healthcare Provider
You’ll get to talk to your doctor before the test. This is a chance to ask any questions or share concerns. You can learn more about the test, its risks, and what to expect when you’re recovering.
| Pre-Procedure Preparation | Details |
| Fasting | Avoid eating and drinking for a specified period before the procedure. |
| Medication Management | Inform your healthcare provider about all medications, especially blood thinners. |
| Documents to Bring | Insurance cards, identification,a list of medications, and relevant medical history. |
The Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory
The coronary angiography procedure happens in a special place called the cardiac catheterization laboratory. This area has the latest technology and a team of experts. They are trained to do the dye test for the heart with great care.
Equipment and Technology Used
The lab has top-notch gear for the coronary angiogram. It includes high-resolution imaging systems for clear views of the arteries. There’s also monitoring equipment to watch the patient’s health and specialized catheters for safe artery travel.
The Medical Team Involved
A team of skilled professionals works together during the procedure. The team has a cardiologist who does the angiogram, nurses and technicians for patient care, and sometimes an anesthesiologist for sedation. Each team member is key to a safe and successful procedure.
Safety Protocols in Place
Safety is the top priority in the lab. To keep risks low, strict safety rules are followed. These include sterilizing equipment, watching patient vital signs during the test, and being ready for emergencies. The team is ready to act fast if needed.
How Is a Coronary Angiogram Performed: The Procedure Step by Step
Getting a coronary angiogram involves several steps to get accurate results. It’s key to seeing the coronary arteries and finding heart disease.
Initial Setup and Monitoring
First, patients are hooked up to machines to watch their heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. An IV line is also put in for medicine.
Catheter Insertion Techniques
The area for the catheter is numbed with local anesthesia. A needle is used to get to the blood vessel. Then, a wire and catheter are threaded through.
Contrast Dye Injection Process
With the catheter in, a contrast dye is injected. This dye makes the arteries show up on an X-ray. It helps find any blockages.
Imaging the Coronary Arteries
The X-ray machine takes pictures of the arteries from different angles. These pictures show how healthy the arteries are. They help find heart disease.
| Step | Description |
| Initial Setup | Patient monitoring and IV insertion |
| Catheter Insertion | Numbing the area and assessing the blood vessel |
| Contrast Dye Injection | Injecting dye to visualize the coronary arteries |
| Imaging | Capturing X-ray images of the coronary arteries |
The coronary angiogram is a detailed test for the heart’s blood vessels. Knowing the steps helps patients get ready for it.
What to Expect During the Dye Test for the Heart
Going through a coronary angiogram can seem scary, but knowing what to expect helps a lot. The dye test is a key part of coronary angiography. It helps show clear images of your heart’s blood vessels.
Sensations During the Procedure
When the dye is injected, you might feel a flushing or warm sensation all over. This is normal and usually goes away fast. Some people might feel pressure or discomfort where the catheter is, but it’s usually mild and short-lived.
Communication with Your Medical Team
Talking openly with your medical team is very important during the procedure. If you feel any discomfort or have worries, tell them. They are trained to make sure you’re comfortable and safe during the cardiovascular angiography.
Duration of the Procedure
The dye test itself only takes a few minutes. But the whole coronary angiogram process, including getting ready and recovering, can take 30 to 60 minutes. Your team will give you a better idea based on your situation.
Managing Anxiety During the Test
It’s normal to feel anxious during a medical test. To calm down, try deep breathing or visualization. Having someone you trust there can also help. Your medical team is ready to support you and answer any questions, making sure you’re as comfortable as possible.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
After your coronary angiogram, we focus on your care to keep you safe and comfortable. The care you get is key for a smooth recovery. It helps avoid any problems.
Recovery in the Observation Area
You’ll go to an observation area after the test. Our team will watch you closely there. This is important to catch any problems early and make sure you’re okay before you go home.
Monitoring Vital Signs
We keep an eye on your heart rate, blood pressure, and the catheter site. This lets us act fast if anything changes.
Managing the Catheter Insertion Site
The catheter is taken out, and pressure is applied to stop bleeding. Your doctor will bandage the site. They’ll tell you how to care for it at home to avoid infection and help it heal.
Initial Activity Restrictions
You’ll be told not to lift heavy, bend, or do strenuous activities for a while. We’ll tell you when it’s okay to start doing things again.
| Care Aspect | Description | Importance |
| Monitoring | Continuous monitoring of vital signs and the catheter insertion site. | High |
| Catheter Site Care | Applying pressure and dressing the site after catheter removal. | High |
| Activity Restrictions | Avoiding strenuous activities to prevent complications. | Medium |
By following these care tips, you can lower the risk of problems. This helps you recover better after your coronary angiogram.
Recovery After Coronary Angiography
The time after a coronary angiography is key to watching and healing to avoid problems. We’ll help you through this important time. It’s vital to know the steps for a smooth recovery.
Hospital Discharge Instructions
After the coronary angiogram, patients stay for a few hours before going home. We give detailed instructions on wound care, medicine, and signs of trouble.
It’s important to follow these instructions closely to avoid complications. We also tell patients how to handle any pain or discomfort at the catheter site.
Activity Restrictions
After going home, avoid heavy lifting, bending, or hard work for a couple of days. Don’t lift anything heavier than 10 pounds or do activities that make you bend or stoop.
These rules help prevent bleeding and let the site heal. We’ll tell you what activities are safe and when you can go back to your usual routine.
When to Resume Normal Activities
The time it takes to get back to normal varies. Most people can start their usual activities in a few days.
But it’s important to listen to your healthcare team. They can give you advice based on your health and the angiogram.
Follow-up Appointments
Follow-up visits are key to your recovery. They let us check on you, solve any problems, and change your treatment if needed.
We’ll set up a follow-up visit before you leave the hospital. This ensures you know when and where to go for your next appointment.
| Activity | Recommendation |
| Lifting | Avoid lifting anything over 10 pounds for 2 days |
| Bending/Stooping | Avoid bending or stooping for 2 days |
| Strenuous Activities | Avoid for 2-3 days or as advised by your healthcare provider |
| Follow-up | Attend scheduled follow-up appointments |
By following these guidelines and your healthcare team’s advice, you can have a safe and effective recovery after your coronary angiography.
Potential Risks and Complications
Coronary angiography is a key tool for diagnosing heart issues. Yet, it’s important to know about the possible risks and complications. For many, the benefits of this procedure outweigh the risks.
Common Minor Side Effects
Most people have little to no side effects from coronary angiography. Some minor side effects include:
- Bruising or bleeding at the catheter insertion site
- Pain or discomfort where the catheter was inserted
- Allergic reactions to the contrast dye used during the procedure
These side effects are usually short-lived and go away on their own. Following post-procedure care can help minimize these risks.
Serious Complications
Though rare, serious complications can happen during or after the procedure. These may include:
- Heart attack or stroke
- Severe allergic reactions to the contrast dye
- Infection at the catheter insertion site
- Damage to the blood vessels or heart
It’s good to know that serious complications are rare. This is true when the procedure is done by skilled healthcare professionals.
Patient Statistics and Complication Rates
Research shows that coronary angiography complications are low. In experienced centers, the rate is under 1%. Here’s a summary of complication rates from various studies:
| Complication Type | Frequency |
| Minor bleeding | 2-5% |
| Major bleeding | 0.5-1.5% |
| Allergic reactions | 0.1-0.3% |
| Serious complications | <1% |
The table shows that while complications can happen, most are minor and short-lived.
When to Seek Medical Attention
After coronary angiography, watch for any unusual signs. Seek immediate medical help if you notice:
- Severe pain or swelling at the catheter insertion site
- Signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, or fever
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Weakness or numbness in your limbs
Knowing the risks and when to seek help can greatly improve your recovery.
Advancements in Coronary Angiography
The field of coronary angiography has seen big changes in recent years. These changes have made the procedure safer and more accurate. New research and technology have changed how we diagnose and treat heart disease.
Recent Research and Technological Improvements
Studies have focused on making coronary angiography better. A big improvement is 3D coronary angiography. It gives a clearer view of the heart’s arteries. Also, new catheter technology makes the procedure less invasive and more comfortable for patients.
New contrast agents have also been developed. These agents are safer, with fewer side effects. They work well for patients with allergies or sensitivities.
Enhanced Safety Protocols
Safety is a top concern in coronary angiography. Medical centers like Liv Hospital have strict safety rules. These include detailed checks before the procedure, constant monitoring during it, and thorough care after.
The use of radial access has also improved safety. It’s safer than traditional methods and allows for quicker recovery. This makes the experience better for patients.
International Standards and Best Practices
Coronary angiography follows international standards and best practices. These ensure quality and consistency worldwide. These standards are based on research and clinical trials.
Following these standards is key to patient trust and the best outcomes. It helps us reduce risks and increase benefits for our patients.
Future Directions in Cardiac Imaging
The future of coronary angiography looks bright. Ongoing research explores new technologies and techniques. For example, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning could improve accuracy and make procedures smoother.
We’re always looking to improve cardiac imaging. Our goal is to provide the best care possible. The advancements in coronary angiography are a big step towards that goal.
Conclusion
A coronary angiogram is a key tool for diagnosing heart disease. It shows how healthy your heart’s arteries are. This helps doctors figure out what’s wrong and how to fix it.
Learning about the angiogram can make you feel less nervous. Knowing what happens during the test helps you take part in your care. This way, you can make choices about your treatment.
This guide should have helped you understand the angiogram better. It’s important to talk to your doctor if you have more questions. This ensures you get the best care for your heart health.
FAQ
What is a coronary angiogram?
A coronary angiogram is a test that uses a thin catheter. It delivers a dye that shows up on X-rays. This helps doctors see the coronary arteries clearly and diagnose coronary artery disease.
Why is coronary angiography considered the gold standard for diagnosing coronary artery disease?
Coronary angiography is the top choice because it gives detailed views of the coronary arteries. This allows doctors to spot blockages and narrowings accurately.
What are the common indications for a coronary angiogram?
Common reasons for a coronary angiogram include chest pain and abnormal stress test results. A history of heart attack or cardiac arrest is also a sign.
How do I prepare for a coronary angiogram?
To prepare, follow the instructions given before the procedure. Manage your medications and know what to bring to your appointment. Discuss your preparation with your healthcare provider.
What happens during a coronary angiogram procedure?
The procedure starts with setup and monitoring. Then, a catheter is inserted, and contrast dye is injected. The arteries are imaged in a cardiac catheterization laboratory.
What sensations can I expect during the dye test for the heart?
You might feel warmth or flushing when the dye is injected. These feelings are usually short-lived.
How long does a coronary angiogram procedure take?
The procedure usually takes 30-60 minutes. But you should plan to spend several hours at the hospital.
What are the possible risks and complications of coronary angiography?
Risks include minor side effects like bruising or discomfort at the catheter site. Serious complications like bleeding or allergic reactions are also possible.
What is the recovery process like after a coronary angiogram?
Recovery starts with immediate care after the procedure. This includes monitoring and managing the catheter site. You’ll also get hospital discharge instructions and activity restrictions.
When can I resume normal activities after a coronary angiogram?
You can usually go back to normal activities in a few days. Always follow the specific instructions from your healthcare provider.
Are there any alternative diagnostic methods to coronary angiography?
Yes, there are non-invasive tests like stress tests and cardiac CT scans. But, coronary angiography is the best for diagnosing coronary artery disease.
How has coronary angiography technology advanced in recent years?
Recent advancements include better imaging tech and safer protocols. These changes make procedures more accurate and safer.
What are the benefits of being informed about the coronary angiogram procedure?
Being informed reduces anxiety and prepares you for the procedure. It also helps you make informed decisions about your care.
References
- Tavakol, M., Ashraf, S., & Brener, S. J. (2012). Risks and complications of coronary angiography: A comprehensive review. Global Journal of Health Science, 4(1), 65–93. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4777042/









