At Liv Hospital, we know that getting a diagnostic test can worry many patients. An angiogram, or angiography, is a key tool for doctors to check blood flow and vessel health. It uses X-rays and dye to see blood vessels, spotting blockages or narrowings.
We aim to give our patients all the details about an angiography. This includes what to expect, possible risks, and how long it takes. Knowing about this test helps patients get ready and feel more comfortable.
Key Takeaways
- An angiogram is a diagnostic procedure that uses X-rays and a special dye to visualize blood vessels.
- The procedure helps doctors assess blood flow and identify any blockages or narrowing.
- Understanding the basics of angiography can help patients prepare and feel more at ease.
- Liv Hospital is committed to providing international patients with top-notch healthcare services.
- Our team is dedicated to ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
Understanding Angiography: What Is an Angiogram?

Angiography helps us see how blood vessels work and if they’re healthy. It’s a way to look at blood vessels using X-rays. We do this by putting a special dye into the blood vessels.
Definition and Purpose
Angiography is a test that uses X-rays and dye to see inside blood vessels. It helps find problems like blockages or narrow spots. This test is key for diagnosing and treating blood vessel issues.
This test is very important for doctors to make the right decisions for patients. Studies show angiography is great for checking blood vessel health. It helps doctors take care of their patients better.
The Process of Recording X-rays of Blood Vessels
To take X-rays of blood vessels, a few steps are needed. First, a small incision is made, and a catheter is put in. Then, dye is injected through the catheter to make the blood vessels show up on the X-rays.
The dye makes the blood vessels visible on X-rays. This lets doctors see how blood flows and if there are any problems. It helps them find and fix issues.
When Is an Angiogram Necessary?
An angiogram is needed in many cases. It’s used to check for problems like heart disease or blockages in blood vessels. It’s also used for other vascular diseases.
- To find blockages or narrow spots in blood vessels
- To spot vascular issues like aneurysms or malformations
- To help with procedures like angioplasty or stenting
Knowing when you need an angiogram helps you get ready. It shows how important it is for your health care.
Types of Angiograms and Their Applications
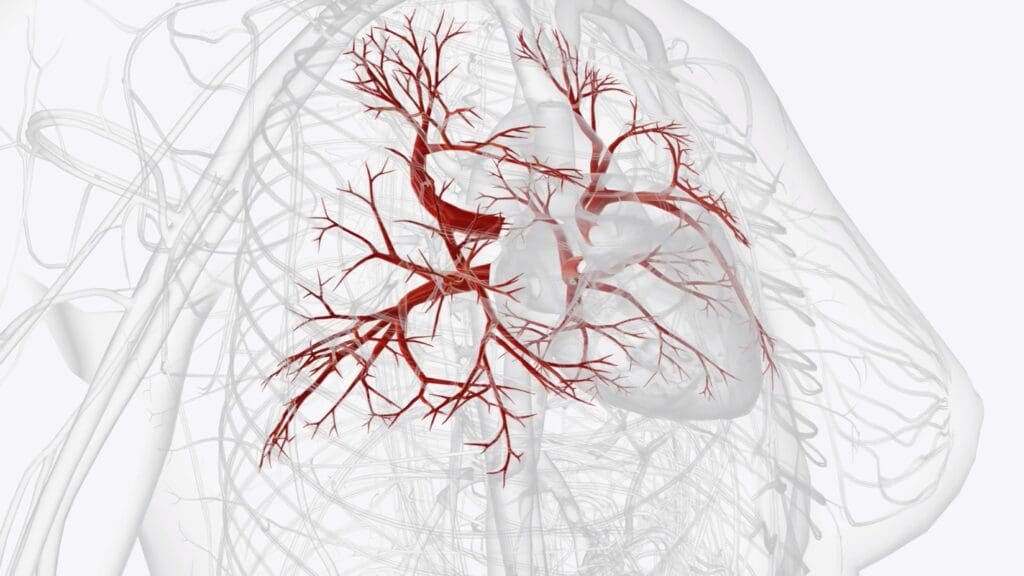
There are many types of angiograms, each for different blood vessels. They help diagnose conditions like coronary artery disease and cerebral vasculature disorders. Angiography is also used for peripheral artery disease and pulmonary embolism.
Coronary Angiograms
Coronary angiograms check for coronary artery disease. They look at the coronary arteries. This is key to finding blockages or narrowing that affect heart blood supply.
We use these to see how bad the disease is. Then, we decide the best treatment.
Cerebral Angiograms
Cerebral angiograms help with brain blood vessel issues. They find problems like aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations. By seeing the brain’s blood vessels, we can plan the right treatment.
Peripheral Angiograms
Peripheral angiograms diagnose peripheral artery disease. This disease affects blood flow outside the heart and brain. It can cause pain and cramping in the limbs.
These angiograms help us find blockages. This guides our treatment choices.
Pulmonary Angiograms
Pulmonary angiograms are for pulmonary embolism. This is when a blood clot blocks lung blood vessels. The procedure is key for finding and treating the clot.
Case reports show angiography’s value in vascular conditions. Knowing about different angiograms helps us see their importance in medicine.
How Serious Is an Angiogram? Risk Assessment
Understanding the risks of an angiogram is key. An angiogram helps doctors see inside blood vessels and organs. It’s mostly safe, but knowing the risks is important.
Classification as a Minimally Invasive Procedure
An angiogram is a minimally invasive procedure. It involves a small skin puncture for a catheter. This makes it safer than open surgery. But, it’s not risk-free.
Safety Profile Compared to Other Diagnostic Tests
An angiogram is generally safe, with few serious side effects. It’s safer than many other tests. The benefits of a clear diagnosis often outweigh the risks.
Who Should Consider Alternative Tests
Some people might need other tests because of their health. Those allergic to dye or with kidney issues should talk to their doctor. Discussing individual risk factors with a healthcare provider is key.
Even though it’s mostly safe, an angiogram has some risks. These include dye allergies, bleeding, or damage to blood vessels. It’s important for patients to know these risks and talk to their doctor.
The Special Dye Used in Angiography
During an angiogram, a special dye is used to make blood vessels visible on X-ray images. This dye, known as contrast media, is key in the diagnostic process. It highlights blood vessels, helping doctors check their health and blood flow.
Composition of Contrast Media
Contrast media is made from iodine-based or gadolinium-based compounds. These substances absorb X-rays well, making blood vessels clear in images. They are safe for most patients, but some may have adverse reactions.
How the Dye Highlights Blood Vessels
When contrast media is injected into blood vessels, it absorbs X-rays. This creates a contrast between vessels and tissues. This contrast helps the X-ray machine capture detailed images of blood vessels, vital for diagnosing vascular conditions.
Potential Reactions to Contrast Media
While contrast media is generally safe, some patients may react. These reactions can be mild, like nausea and itching, or severe, like anaphylaxis. Some people are more likely to have allergic reactions to contrast media.
To better understand the possible reactions, let’s look at the following table:
| Reaction Type | Symptoms | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Reaction | Nausea, itching, mild rash | Common |
| Moderate Reaction | Urticaria, vomiting, mild respiratory distress | Less Common |
| Severe Reaction | Anaphylaxis, severe respiratory distress, cardiac arrest | Rare |
It’s important to know about the possible reactions to contrast media for patient safety. Doctors take steps to reduce risks, like checking patient history and watching during the procedure.
Preparing for Your Angiogram
An angiogram needs careful preparation. This includes following specific instructions and medical evaluations. Your healthcare team will guide you through these steps to ensure a smooth procedure.
Pre-Procedure Instructions
Before your angiogram, you’ll get pre-procedure instructions. These might include fasting, avoiding certain medications, and arranging a ride home. It’s important to follow these instructions to reduce risks and ensure success.
Necessary Medical Evaluations
You’ll need to have necessary medical evaluations before the angiogram. This might include blood tests, a physical exam, and a review of your medical history. These steps help identify any risks and make sure you’re healthy enough for the procedure.
Medication Adjustments
Some medications might need to be adjusted or stopped before the angiogram. This includes blood thinners and other medications that could affect the procedure or increase bleeding risk. Tell your doctor about all your medications and follow their advice on medication adjustments.
What to Bring to the Hospital
On the day of your angiogram, bring important documents like insurance cards and identification. Also, bring a list of your medications and any relevant medical records. For more detailed guidance, check out this guide on angiogram preparation.
| Item to Bring | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Insurance Cards | For billing and insurance purposes |
| Identification | To verify patient identity |
| List of Medications | To inform medical staff about current medications |
| Relevant Medical Records | To provide medical history and context |
The Angiogram Procedure: Step by Step
We’ll walk you through the angiogram procedure, from start to finish. This test is key for checking your blood vessels. Knowing what to expect can make it less scary.
Arrival and Initial Preparation
When you arrive, our team will welcome you. They’ll go over your medical history and explain the test. You’ll change into a gown and lie down on a table.
Getting ready is important for a smooth angiogram. Our team will make sure you’re comfortable and know what’s happening.
Catheter Insertion Process
The next step is putting a catheter into a blood vessel. This is usually in the groin or arm. You’ll get local anesthesia to make it less painful.
Dye Injection and Imaging
With the catheter in place, a dye is injected. This dye makes the blood vessels show up on X-rays. The X-rays then capture images of your blood flow and any blockages.
| Step | Description | Key Elements |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arrival and Preparation | Medical history review, patient education |
| 2 | Catheter Insertion | Local anesthesia, X-ray guidance |
| 3 | Dye Injection and Imaging | Contrast dye, X-ray imaging |
| 4 | Completion and Catheter Removal | Catheter removal, wound care |
Completion and Catheter Removal
Once the images are taken, the catheter is removed. Pressure is applied to stop bleeding. The whole process usually takes 20 to 60 minutes.
Most patients find the angiogram procedure okay. Our team is here to keep you safe and comfortable.
How Long Does an Angiogram Take?
Knowing how long an angiogram takes is important for patients. We’ll explain the usual time, what can change it, and what to expect at the hospital.
Typical Procedure Duration
An angiogram usually lasts from 20 to 60 minutes. The exact time depends on the case’s complexity and the type of angiogram. For example, a coronary angiogram might be quicker than a cerebral one.
Factors That May Extend Procedure Time
Several things can make an angiogram longer. These include the patient’s health, any complications, and if more tests or treatments are needed. Patients with complex vascular conditions often need more time.
Total Hospital Stay Duration
The angiogram itself is short, but you’ll stay in the hospital longer. Plan to spend at least a few hours. This lets our team watch for complications and keep you safe.
Timing for Combined Diagnostic and Treatment Procedures
Sometimes, an angiogram is done with other tests or treatments. This makes your hospital stay longer. We’ll tell you how long it will take and what you need to do beforehand.
Studies show that procedure times vary. We adjust our approach for each patient. Knowing what can affect your angiogram’s length helps us prepare you better for your visit.
Anesthesia and Comfort During an Angiogram
Choosing the right anesthesia is key to making sure you’re comfortable during an angiogram. We know that medical procedures can make you anxious. So, we aim to make your experience as comfortable as possible.
Local Anesthesia vs. Sedation Options
Most angiograms use local anesthesia to numb the area where the catheter goes in. This is usually in the groin or arm. It lets you stay awake and alert but feel less pain. Sometimes, sedation is offered to help you relax. Sedation can be light, where you’re awake but calm, or deeper, where you might almost sleep.
We’ll talk to you about the best anesthesia and sedation options. This will depend on your needs and the details of your procedure.
What Sensations to Expect
You might feel a pinch when the local anesthetic is given. But once it numbs the area, you shouldn’t feel much pain. Some people might feel a bit of pressure or a sharp feeling when the catheter moves. These feelings are usually short-lived and not too bad.
| Sensation | Description | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Pinch | Brief discomfort when local anesthetic is administered | Local anesthetic numbs the area |
| Pressure | Mild feeling when catheter is moved | Adjustments made by medical team |
| Sharp feeling | Temporary sensation during catheter placement | Medical team monitors and adjusts as needed |
Communication With Your Medical Team
Talking openly with your medical team is important for a good experience during your angiogram. If you have any worries or feel uncomfortable, let us know. Our team is ready to help and make sure you’re comfortable during the procedure.
Knowing your anesthesia options and talking with your medical team can make your angiogram experience better. It can be less stressful and more comfortable.
Potential Risks and Complications
It’s important for patients to know about the risks of angiography. This test is useful but can have side effects. Knowing these can help patients make better choices about their health.
Common Minor Side Effects
Most people don’t have big problems after angiography. But, some might feel:
- Discomfort or pain where the catheter was put in
- Bruising or swelling at the site
- Mild allergic reactions to the dye, like rash or itching
These issues usually go away in a few days.
Allergic Reactions to Contrast Dye
Some might have an allergic reaction to the dye used in angiography. Telling your doctor about any allergies is key. Symptoms can be mild (like hives) or severe (anaphylaxis). For more on preparing for an angiogram, check out our guide on angiogram preparation.
Bleeding and Vascular Complications
Bleeding and vascular problems can happen, but they’re rare. These might include:
- Hematoma at the catheter site
- Bleeding that needs a blood transfusion
- Vascular damage, like dissection or perforation
People on blood thinners or with vascular disease are at higher risk.
Rare Serious Complications
Though rare, serious problems can happen. These might include:
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Heart attack or other heart issues
- Kidney damage from the dye
Talking to your doctor about your risks can help you understand angiography better.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision About Angiography
Knowing what an angiography is and how it works is key for patients. It helps them understand their treatment options better. This knowledge lets them make choices that fit their health needs.
Research shows that informed patients handle their care better. They make smarter decisions about their treatment. It’s vital to talk to your doctor about any worries or questions you have. This way, you’ll be ready for what’s ahead.
Choosing angiography means looking at your health needs and what the procedure can do for you. We aim to give top-notch care to all our patients, including those from abroad. We want to make sure you get the best care possible.
When you know about angiography, you can decide on your treatment with confidence. You’ll know you’re in the hands of our skilled medical team.
What is an angiogram?
An angiogram is a test that uses X-rays and dye to see blood vessels. It helps doctors check blood flow and if vessels are okay.
How long does an angiogram procedure take?
An angiogram usually takes 20-60 minutes. But, you might stay in the hospital longer for getting ready and recovering.
Is an angiogram a serious procedure?
Angiography is usually safe and not very invasive. But, it’s not risk-free. Talk to your doctor about your own risks.
What kind of dye is used in angiography?
Angiography uses a special dye to show blood vessels on X-rays. This helps doctors see how blood flows and if vessels are healthy.
How is the dye injected during an angiogram?
The dye goes through a catheter in a blood vessel. Then, X-rays are taken to see the blood vessels.
What are the possible risks and complications of angiography?
Risks include minor side effects and allergic reactions to the dye. There’s also a chance of bleeding or vascular problems. Rarely, serious complications can happen.
What type of anesthesia is used for an angiogram?
You might get local anesthesia or sedation for an angiogram. Talk to your doctor to find out what’s best for you.
How do I prepare for an angiogram?
Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. This includes pre-procedure steps, medical checks, and adjusting medications. It helps make the procedure go smoothly.
What are the different types of angiograms?
There are many types of angiograms. These include coronary, cerebral, peripheral, and pulmonary angiograms. Each is used for different reasons.
How long does it take to recover from an angiogram?
Recovery from an angiogram is usually quick. But, you might stay in the hospital longer. Follow your doctor’s advice for aftercare.
References
- Coronary angiography. Retrieved from: https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/tests/coronary-angiography
- Coronary angiogram. Retrieved from: https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/coronary-angiogram
- Coronary angiography. Retrieved from: https://www.pennmedicine.org/treatments/coronary-angiography
- CT angiography. Retrieved from: https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/angioct?PdfExport=1




































