Bone Marrow Harvesting: Stem Cell Collection and Transplant Guide
Stem cell transplantation is a lifesaving treatment for diseases like leukemia and lymphoma. A key part of this treatment is the bone marrow harvesting process, which involves collecting healthy stem cells for transplantation. This step is essential when doctors need to Harvest Bone Marrow safely and efficiently.
During the bone marrow harvesting process, stem cells are taken from the bone marrow usually from the iliac crest under general anesthesia. This procedure is carefully performed to ensure minimal discomfort and maximum cell collection, especially when the medical team needs to Harvest Bone Marrow in the most effective way.
At LivHospital, we guide you through every step of stem cell extraction from bone marrow. This complex procedure requires precision and care, and our medical team uses advanced techniques to ensure your safety and achieve the best possible results whenever we Harvest Bone Marrow for transplantation.
Key Takeaways
- The bone marrow harvest is typically performed under general anesthesia.
- Stem cells are usually extracted from the back of the hip bone (iliac crest).
- Patients may experience soreness and nausea after the procedure.
- Pain medication and anti-nausea medication are administered as needed.
- A well-balanced diet high in iron is recommended for 2 months after the procedure.
Understanding Bone Marrow and Its Importance
Bone marrow is a key part of our body. It’s the spongy tissue inside bones like hips and thighbones. It makes blood cells, which are vital for our health.
What is Bone Marrow and Its Function
Bone marrow is where blood cells are made. It’s filled with stem cells that turn into different blood cells. It also has many blood vessels to get oxygen and nutrients.
This tissue is essential for our health. It makes:
- Red blood cells to carry oxygen
- White blood cells for fighting infections
- Platelets for blood clotting
Types of Stem Cells in Bone Marrow
Bone marrow has two main stem cell types. Hematopoietic stem cells make all blood cells. Mesenchymal stem cells can become bone, cartilage, or fat cells.
| Stem Cell Type | Function | Differentiates Into |
| Hematopoietic Stem Cells | Produce blood cells | Red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets |
| Mesenchymal Stem Cells | Support bone and connective tissue health | Bone cells, cartilage cells, fat cells |
Medical Uses for Harvested Bone Marrow
Harvested bone marrow is used in medical treatments. It’s key in stem cell transplantation. This helps treat diseases like leukemia and genetic disorders.
The bone marrow harvesting is safe. Recovery is quick, with bone marrow levels back to normal in four to six weeks. This makes it a good option for patients needing stem cell transplants.
Medical Indications for Bone Marrow Harvesting
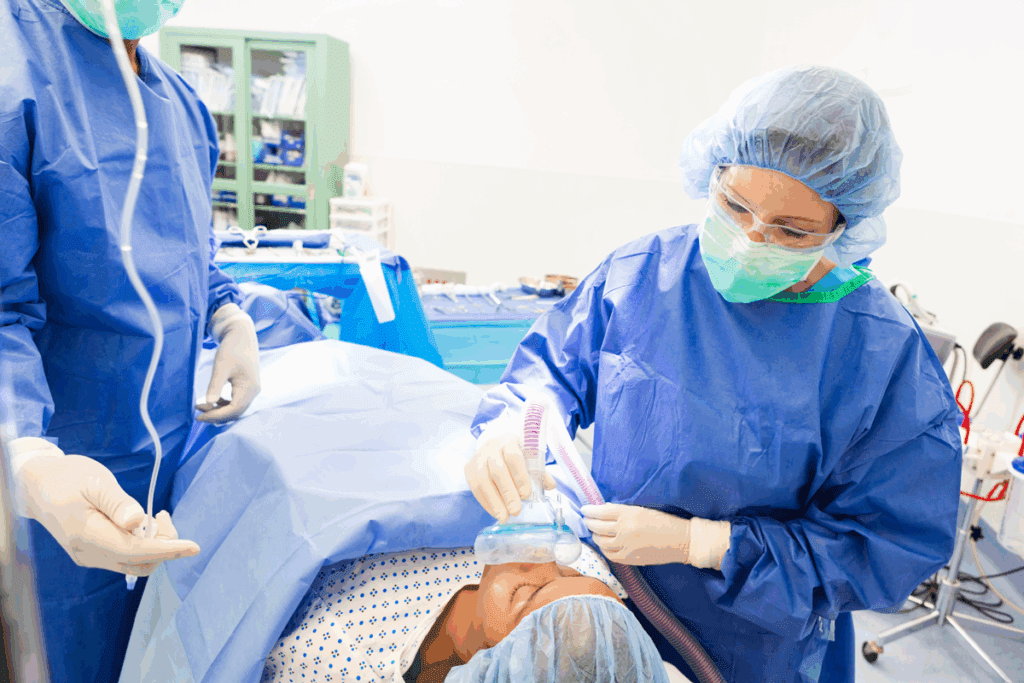
Bone marrow transplantation is a lifesaving treatment for many diseases. It involves harvesting bone marrow. We will look at the medical reasons for this procedure, the types of transplantation, and who can get it.
Conditions Requiring Bone Marrow Transplantation
Bone marrow transplantation treats life-threatening conditions like leukemia and lymphoma. It also helps with multiple myeloma and genetic disorders. These conditions often need healthy stem cells to replace damaged bone marrow.
“Bone marrow transplantation has revolutionized the treatment of hematological malignancies and certain genetic disorders, giving patients a chance at remission and improved survival rates.”
Hematologist
The process starts with harvesting bone marrow. This marrow is then used for transplantation. The marrow is usually taken from the pelvic bone because it has the most stem cells.
Autologous vs. Allogeneic Transplantation
There are two main types of bone marrow transplantation: autologous and allogeneic. Autologous uses the patient’s own stem cells. These cells are harvested, stored, and then reinfused after chemotherapy or radiation.
- Autologous Transplantation: Uses the patient’s own stem cells.
- Allogeneic Transplantation: Uses stem cells from another person, often a sibling or unrelated donor.
Allogeneic transplantation is used when the patient’s bone marrow is too damaged. The choice between autologous and allogeneic depends on the condition, the patient’s health, and donor availability.
Patient Selection Criteria
Choosing patients for bone marrow harvesting and transplantation involves several factors. These include medical history, disease status, and donor availability. A detailed evaluation is done to see if the patient is a good candidate for the procedure.
| Criteria | Description | Importance |
| Medical History | Previous treatments, comorbidities, and overall health. | High |
| Disease Status | Current state of the disease, including stage and response to previous treatments. | High |
| Donor Availability | Presence of a suitable donor for allogeneic transplantation. | High |
Healthcare professionals carefully evaluate these criteria. This helps determine the best treatment for patients needing bone marrow transplantation.
Pre-Procedure Preparation for Donors
To make bone marrow harvesting smooth, donors must meet certain criteria and get medical checks. This prep is key to reduce risks and make the donation go well.
Donor Screening and Eligibility Requirements
Donor screening checks the donor’s health history and current status. Eligibility criteria include age, health, and no certain medical conditions that could be risky.
We do detailed interviews and medical checks to see if a donor is right. This includes looking at their health history, doing physical exams, and lab tests for health issues.
Required Medical Evaluations and Tests
Donors go through medical checks and tests to make sure they’re eligible and safe. These include:
- Blood tests to check for diseases and health.
- Medical imaging to look at bone marrow and body structure.
- Physical exams to check overall health and find risks.
| Test/Evaluation | Purpose |
| Blood Tests | Check for infectious diseases and assess overall health. |
| Medical Imaging | Evaluate bone marrow and overall anatomy. |
| Physical Examination | Assess overall health and identify any risks. |
Physical and Dietary Preparation Instructions
Donors also get tips on physical and dietary prep for the procedure. They’re told to eat well, drink lots of water, and avoid certain meds that might affect the donation.
We also guide them on what to do after the procedure. This includes managing pain and avoiding too much activity to help with healing.
By carefully checking and preparing donors, we make sure the bone marrow harvesting is safe and successful. This prep is vital for both the donor and the recipient’s health.
The Bone Marrow Harvesting Process: A Detailed Look
Bone marrow harvesting is a team effort. Surgeons, anesthesiologists, and nurses work together for success. They need special skills, equipment, and a good choice of where to take the bone marrow.
Medical Team Members and Their Roles
Many medical experts are key to bone marrow harvesting. The team usually includes:
- Surgeons: They do the bone marrow extraction.
- Anesthesiologists: They give anesthesia to reduce pain and discomfort.
- Nurses: They help during the procedure and care for the patient after.
Every team member is vital for a safe and successful procedure.
Specialized Equipment and Materials
The bone marrow harvesting uses specialized equipment to reduce risks and get more stem cells. This includes:
- Needles and syringes made for bone marrow aspiration.
- Monitoring tools to watch the patient’s vital signs.
- Sterile items to keep everything clean and safe.
Optimal Harvesting Sites in the Body
The iliac crest is often chosen for bone marrow harvesting. It has a lot of stem cells. The procedure is done under general anesthesia to lessen pain. The team picks the best site for the best results.
Step-by-Step Bone Marrow Harvest Procedure
The bone marrow harvest procedure is a detailed process that needs careful attention. We will walk you through the main steps. This will help you grasp the complexity of extracting bone marrow.
Anesthesia Administration and Monitoring
The first step is giving anesthesia to reduce pain and discomfort. We choose local or general anesthesia based on the patient’s health and the doctor’s advice. Keeping an eye on the patient’s vital signs is key to their safety and comfort.
Proper Patient Positioning for Access
After giving anesthesia, the patient is placed in a way that makes it easy to reach the iliac crest. Proper positioning is vital for a smooth procedure and to avoid complications. We make sure the patient is comfortable and safe during the whole process.
Iliac Crest Identification and Marking
We find the iliac crest using anatomical landmarks and imaging. Once found, we mark the area where the needle will go. Accurate marking is key for a successful bone marrow aspiration.
Needle Insertion and Aspiration Technique
To harvest bone marrow, we insert a special needle into the iliac crest. We use a specialized needle and a precise technique to get the right amount of bone marrow stem cells. The method of how is bone marrow extracted is critical for the success of the transplant.
Explaining the bone marrow harvest procedure shows how complex and precise bone marrow stem cell extraction is. It requires skill and a dedicated medical team. Understanding this process highlights its importance in medical treatments.
How Bone Marrow is Extracted: Detailed Techniques
There are several ways to extract bone marrow, each with its own benefits. The method chosen depends on the patient’s health, the purpose of the extraction, and the doctor’s skills.
Traditional Needle and Syringe Aspiration
The most common method is using a needle and syringe. A needle is inserted into the bone marrow, usually in the iliac crest. The marrow is then sucked out with a syringe. This is done under local anesthesia or sedation to reduce pain. We find this method works well for getting enough marrow for transplants.
Volume Collection Requirements for Transplantation
The amount of bone marrow needed for a transplant varies. It depends on the recipient’s weight and health condition. Our team carefully determines the needed volume for the best results.
Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Collection Alternative
Another method is collecting stem cells from the blood. This involves using growth factors to move stem cells into the blood. Then, they are collected through apheresis. This method is less invasive and might be preferred by some. We consider it when looking for the best option for our patients.
Technological Advancements in Extraction Methods
New technologies have made bone marrow extraction safer and more efficient. Modern tools and techniques have lowered risks and improved marrow quality. We keep up with new tech to improve our procedures. Bone marrow harvesting is generally safe, and recovery is quick, with marrow levels returning to normal in four to six weeks.
Processing and Handling Harvested Bone Marrow
Processing and handling bone marrow is key to keeping stem cells alive. We take great care in every step, from filtering to storing, to keep the marrow quality high.
Filtering and Preparation Protocols
First, we filter the bone marrow to get rid of bone spicules, fat, and other stuff. We use special filters that catch stem cells but let other things go. Then, we get the marrow ready for more steps or storage.
Key steps in filtering and preparation include:
- Initial filtration to remove large debris
- Further processing to concentrate stem cells
- Quality checks to ensure the marrow meets required standards
Stem Cell Concentration Techniques
Getting stem cells to concentrate is a big deal in bone marrow processing. We use top-notch methods to isolate and boost these cells for transplant. This includes centrifugation, density gradient separation, or other ways to get the right amount of stem cells.
Storage and Transportation Methods
Storing and moving bone marrow right is essential for keeping it good. We keep it in cryogenic freezers to keep stem cells alive. When it’s time to send it to the recipient, we use special containers that keep it at the right temperature.
| Storage Method | Temperature | Duration |
| Cryogenic Freezing | -196°C | Long-term |
| Refrigeration | 2-8°C | Short-term |
Quality Control and Testing Measures
We check the bone marrow quality closely to make sure it’s up to par. This includes tests for bacteria and viruses, cell health checks, and more. We do this to make sure the marrow is safe and works well for transplant.
Our quality control process involves:
- Microbiological testing for bacterial and viral contaminants
- Cell viability and count assessments
- Functional assays to evaluate stem cell potency
Post-Procedure Care for Bone Marrow Donors
Good care after a bone marrow donation is key for a full recovery. We know recovery can be tough. Our goal is to help you get better smoothly and safely.
Immediate Recovery Monitoring Parameters
Donors are watched closely right after the procedure. Things like blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen levels are checked often. We also keep an eye on pain and comfort to make sure you’re okay.
This watching continues until you’re fully awake and stable. This usually happens in a recovery room where medical staff can quickly help if needed.
Pain Management and Comfort Strategies
Managing pain is very important after the procedure. We use medicines and other ways to help with pain. It’s important for you to tell us how much pain you’re in so we can adjust your care.
“Effective pain management is key for your comfort and can really help your recovery.”
Bone Marrow Transplant Specialist
Rest, staying hydrated, and gentle movement are also good for managing pain and healing.
Activity Restrictions and Recommendations
It’s best to rest and avoid hard activities for a bit after the procedure. Don’t do heavy lifting, bending, or exercise for 24 to 48 hours. You can start doing normal things again when you feel ready and we say it’s okay.
| Activity | Recommended Restriction Period |
| Heavy Lifting | 3-5 days |
| Bending or Strenuous Exercise | 2-3 days |
| Driving | 24-48 hours |
Potential Complications and Their Management
Even though rare, problems like infection, bleeding, or reaction to anesthesia can happen. We teach donors about these risks and the need to get help right away if they see any signs.
We also watch for any signs of trouble during recovery. We have plans ready to deal with these issues quickly and well.
By following these care tips, bone marrow donors can lower risks and have a good recovery. Our team is here to support and care for you every step of the way.
Recovery Timeline and Bone Marrow Regeneration
Knowing how long it takes to recover is key for bone marrow donors. The journey includes several steps, from right after donation to when the bone marrow is fully back.
First 24-48 Hours After Donation
The first 24-48 hours are very important after donating bone marrow. Donors often feel tired, in pain, and uncomfortable where they donated. Rest and managing pain well are advised during this time.
First Week of Recovery Milestones
In the first week, donors start to feel better. They notice less pain and more energy. It’s important to stick to the care plan after donation to recover smoothly.
Complete Bone Marrow Regeneration Process
Bone marrow usually gets back to normal in four to six weeks after donation. This time can vary, but most donors get better in a few weeks.
To show the recovery timeline, we’ve made a table:
| Recovery Stage | Timeline | Expected Symptoms |
| Immediate Post-Donation | 0-48 hours | Fatigue, pain, discomfort |
| Early Recovery | 2-7 days | Gradual improvement, reduced pain |
| Complete Regeneration | 4-6 weeks | Normal bone marrow levels restored |
It’s vital to follow the care plan and go to follow-up appointments. This helps ensure a good recovery.
Safety Considerations and Risk Management
Bone marrow harvesting is mostly safe, but donors should know about some risks. It’s important to understand the possible problems and side effects of the procedure.
Common Side Effects and Their Duration
Donors might face several common side effects after bone marrow harvesting. These include:
- Pain at the harvest site, which is typically managed with pain medication
- Fatigue, a feeling of tiredness that can last for several weeks
- Bruising around the harvest site, which usually resolves on its own
These side effects are usually short-term and go away in a few weeks. It’s key for donors to follow the post-procedure care to lessen their impact.
Rare but Serious Complications
Though rare, serious complications can happen. These include:
- Infection at the harvest site, which requires prompt medical attention
- Nerve damage, potentially causing numbness or tingling
- Reaction to anesthesia, though this is rare with proper screening
Knowing about these risks helps donors make informed choices about donating.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Donors should watch for signs that mean they need to see a doctor right away. These include:
- Severe pain not managed by prescribed medication
- Signs of infection, such as fever, redness, or swelling at the harvest site
- Unusual bleeding or bruising
Being alert to these symptoms can help avoid serious problems.
Long-term Health Considerations for Donors
Studies on the long-term health effects of bone marrow donation are ongoing. Most donors don’t face long-term health issues from donating. But, it’s important to keep an eye on their health and get follow-up care.
We stress the need for careful monitoring and management of risks and complications from bone marrow harvesting. By understanding these, donors can make smart choices and get the best care.
Conclusion: The Impact and Importance of Bone Marrow Donation
Bone marrow donation is a lifesaving act that greatly impacts patients with serious diseases. The process of harvesting bone marrow is complex. It requires careful preparation, precise technique, and thorough care after the procedure. This ensures donors can recover quickly and safely.
The role of bone marrow donation is huge. It’s a key part of stem cell transplantation, helping treat serious conditions. By understanding its impact, we see how it saves lives and improves patient outcomes.
Bone marrow donation is a vital part of medicine, changing lives. As a key part of stem cell transplantation, it continues to be essential in treating patients with different diseases.
FAQ
What is bone marrow harvesting?
Bone marrow harvesting is a medical process. It takes stem cells from the bone marrow, usually from the iliac crest. This is done under general anesthesia.
Where is bone marrow most commonly harvested from?
The iliac crest is the top choice for bone marrow harvesting. It has a high concentration of stem cells.
How is bone marrow extracted?
Bone marrow extraction uses different methods. The most common is traditional needle and syringe aspiration.
Can bone marrow grow back after donation?
Yes, bone marrow fully regenerates in four to six weeks after donation.
What are the common side effects of bone marrow donation?
Side effects include pain, fatigue, and bruising. These usually go away in a few weeks.
What are the rare but serious complications of bone marrow donation?
Serious complications are rare but can include infection and nerve damage. They need immediate medical care.
How long does it take to recover from bone marrow donation?
Recovery usually takes a few weeks. The first 24-48 hours are critical. Full recovery takes four to six weeks.
What is the difference between autologous and allogeneic transplantation?
Autologous uses the patient’s own stem cells. Allogeneic uses stem cells from another person.
How is harvested bone marrow processed and handled?
Bone marrow is handled carefully to keep stem cells quality and viable. This includes filtering and preparation.
What are the medical indications for bone marrow harvesting?
It’s used for conditions needing stem cell transplant. This includes leukemia and genetic disorders.
How do you get bone marrow for transplantation?
Bone marrow is obtained through a harvesting procedure. This involves extracting stem cells under general anesthesia.
Will bone marrow grow back after harvesting?
Yes, bone marrow fully regenerates in four to six weeks after harvesting.
How is bone marrow extracted for stem cell transplantation?
Bone marrow extraction uses techniques like needle and syringe aspiration. This gets stem cells for transplant.
What is the role of the medical team in bone marrow harvesting?
The medical team ensures a safe procedure. This includes surgeons, anesthesiologists, and nurses.
How are stem cells extracted from bone marrow?
Stem cells are extracted using techniques like needle and syringe aspiration. Peripheral blood stem cell collection is also used.









