Detailed guide on how to heal lower back pulled muscle injury using rest, anti-inflammatories, and physical therapy. Seven key steps for comprehensive back injury treatment, covering initial response through full recovery. A pulled lower back muscle, also known as lumbar strain, is a common issue. It affects millions of people worldwide. It happens when the muscles or tendons in the lower back get stretched or torn. This leads to pain, stiffness, and limited movement.
Dealing with a pulled muscle can be very painful and limiting. Our guide will help you through the recovery process. It will give you the knowledge and tools to heal and prevent future injuries.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes and symptoms of a pulled lower back muscle.
- Effective treatment options for lumbar strain.
- Prevention strategies to avoid future injuries.
- The importance of seeking professional medical guidance.
- Recovery timelines and what to expect.
Understanding Pulled Lower Back Muscles

It’s important to know about pulled lower back muscles for proper recovery. A pulled lower back muscle, or lumbar strain, happens when muscles or tendons stretch too far or tear. This can be due to sudden twisting, heavy lifting, or direct trauma.
What Is a Lumbar Strain?
A lumbar strain is an injury to the muscles or tendons in the lower back. The lower back, or lumbar region, supports the upper body and helps with movement. When these muscles or tendons get overstretched or torn, it’s called a strain.
The severity of a lumbar strain can range from mild to severe. Most people recover from a lumbar muscle strain in one month. Many get better in 2 weeks with rest and self-care.
How Common Is Lower Back Pain?
Lower back pain is very common and affects people of all ages. It’s estimated that many will experience lower back pain at some point. Causes can include muscle strain, poor posture, and serious conditions like herniated discs.
Things like lifestyle choices, job hazards, and health conditions can lead to lower back pain. Knowing these factors helps in preventing and treating it.
Anatomy of the Lower Back
The lower back, or lumbar region, has muscles, ligaments, and bones that support and move the body. It has five vertebrae cushioned by discs. Muscles like the latissimus dorsi and erector spinae are key in supporting the spine and enabling movement.
A series of muscles and ligaments keep the spinal bones in place. Straining these muscles can cause tiny tears in the tissue. Knowing the anatomy of the lower back helps understand how strains happen and how to treat them.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Lower Back Strain
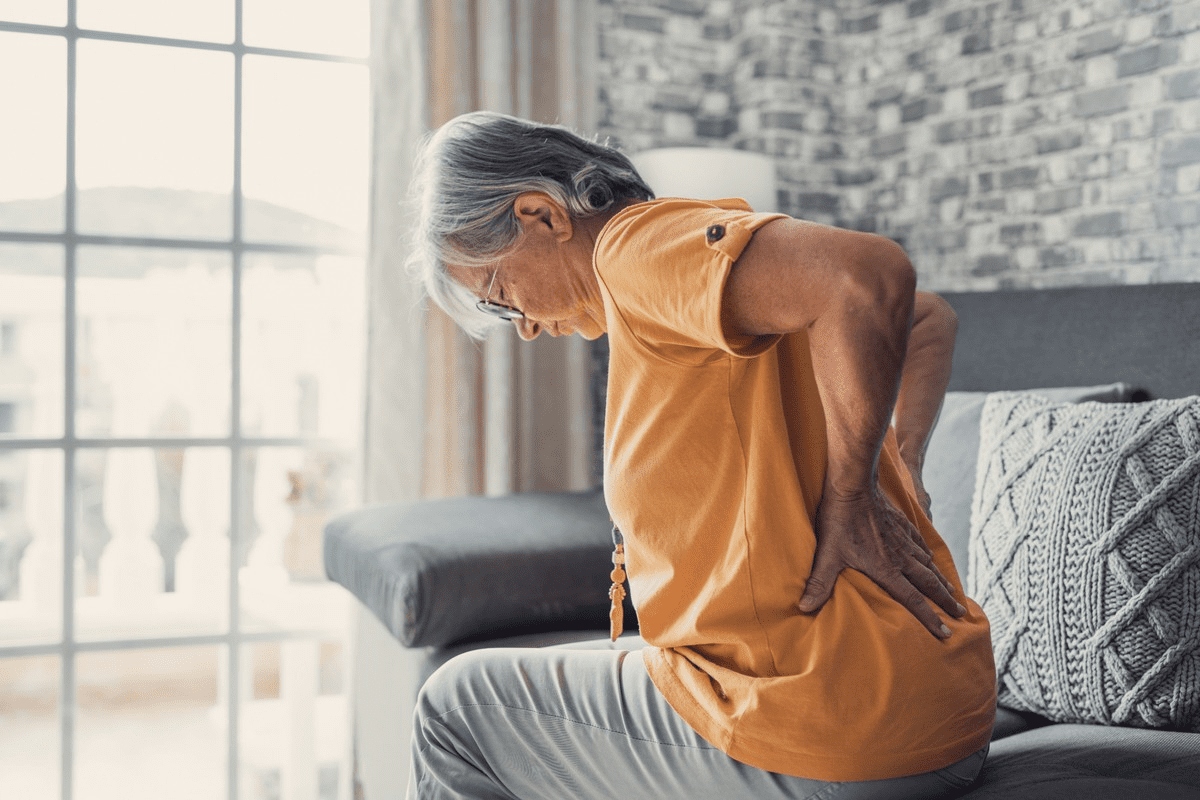

Knowing the symptoms of a lower back strain is key to getting better. When you pull a muscle in your lower back, the pain can hit you hard right away.
Common Signs of a Pulled Back Muscle
The common signs of a pulled back muscle include sharp pain, muscle spasms, stiffness, and less movement. These signs usually show up right after the injury.
- Sharp pain or tenderness in the lower back area
- Muscle spasms or stiffness
- Limited mobility or flexibility
- Pain that worsens with movement, coughing, or sneezing
Differentiating Muscle Strain from Other Back Injuries
It’s important to tell the difference between a muscle strain and other back problems like herniated discs or spinal fractures. Muscle strains usually hurt in one spot and feel stiff. But other injuries might hurt more in your legs or make you feel numb.
Condition | Common Symptoms |
Muscle Strain | Localized pain, stiffness, limited mobility |
Herniated Disc | Radiating pain, numbness, tingling sensations |
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you have really bad pain, numbness, or tingling, or if your symptoms get worse, you should seek medical attention. Also, if you’ve had back problems before or have other health issues, it’s a good idea to see a doctor.
- Severe or worsening pain
- Numbness or tingling sensations
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- History of back problems or underlying health conditions
Common Causes of Pulled Lower Back Muscles
Knowing why lumbar strains happen is key to avoiding and treating them. These strains occur when muscles and ligaments in the lower back face too much stress. This stress can come from many sources.
Improper Lifting Techniques
One big reason for lower back strain is bad lifting habits. When you lift heavy things without bending your knees or using your legs, you stress your back. This can lead to muscle strain.
Sudden Twisting Movements and Falls
Twisting suddenly, whether in sports or daily life, can hurt your lower back. Falls onto your back or buttocks can also harm the muscles and ligaments in this area.
Repetitive Motions and Overuse
Doing the same thing over and over, like in some jobs or hobbies, can cause overuse injuries. This strain on the lower back muscles can lead to pain and discomfort.
Sports-Related Injuries
Playing sports can also lead to pulled lower back muscles. Activities that involve heavy lifting, quick stops, or twists (like football, tennis, or gymnastics) raise the risk of lumbar strain.
Knowing these common causes helps in taking steps to prevent them. By understanding what leads to lumbar strain, people can adopt safer habits. This can help reduce injury risk and ease lower back pain.
Immediate Actions After Pulling a Lower Back Muscle
Pulling a lower back muscle can be really tough. But, knowing what to do right away can help a lot. The first steps you take are key to lessening pain, swelling, and avoiding more harm.
The First 24-48 Hours: Rest Protocol
The first 24 to 48 hours are super important. We suggest a rest plan to help the muscle heal. Stay away from things that make the pain worse and let the muscle rest.
Rest is the first part of the R.I.C.E. method for treating pulled muscles. Resting the area helps prevent more damage and lets the muscle start fixing itself.
Proper Positioning and Body Mechanics
Even when resting, it’s important to keep the right position and body mechanics. Find a comfy way to lie down that doesn’t hurt your lower back more. A supportive mattress or a pillow under your knees when lying on your back can help ease the pain.
“Proper posture and body mechanics are fundamental in reducing strain on the lower back, both during recovery and in daily activities.”
Ice Therapy for Inflammation Reduction
Ice therapy is also key in the early stages. Ice on the affected area cuts down on swelling and pain. Ice for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, is recommended in the first 48 hours.
When to Transition to Heat Therapy
After 48 hours, we often switch to heat therapy. Heat relaxes the muscle, boosts blood flow, and aids in healing. But, only switch to heat when the swelling has gone down.
Therapy Type | Application Time | Benefits |
Ice Therapy | First 48 hours | Reduces inflammation and pain |
Heat Therapy | After 48 hours | Relaxes muscle, increases blood flow |
How to Heal Lower Back Pulled Muscle: Treatment Options
To heal a pulled lower back muscle, a good treatment plan is key. It should tackle pain, inflammation, and help you get back to normal. Rest, pain management, and physical therapy are all important steps to take.
Over-the-Counter Pain Management
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain meds are vital for managing pain and swelling. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen are often used. They help reduce pain and swelling, making them a top choice for treating acute lower back pain.
Always follow the dosage instructions and talk to a doctor before starting any medication. This is important, even if you have other health conditions or take other meds.
Prescription Medications When Needed
If OTC meds don’t work, prescription medications might be needed. Muscle relaxants can help with muscle spasms and pain. But, they should only be used as directed by a doctor due to possible side effects.
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is a big part of recovering from a pulled muscle. A physical therapist will create a plan to strengthen your back, improve flexibility, and posture. They might use manual therapy, stretching, and strengthening exercises.
Physical therapy not only helps you recover but also teaches you how to move better to avoid future injuries, experts say.
Alternative Treatments and Their Effectiveness
There are also alternative therapies like acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy. They might help some people manage pain and relax. But, the evidence is not always clear.
- Acupuncture uses fine needles to stimulate healing and pain relief.
- Chiropractic care focuses on spinal adjustments to improve alignment and reduce muscle and nerve pressure.
- Massage therapy can relax muscles, improve blood flow, and reduce pain.
Always talk to a doctor before trying alternative treatments to make sure they’re right for you.
Rehabilitation Exercises for Lower Back Recovery
Rehabilitation exercises are key for healing and preventing injuries in the lower back. They help strengthen muscles and improve back health. These exercises are important as we recover.
Gentle Stretching Techniques
Gentle stretches are a great start for lower back recovery. Knee-to-chest stretches and pelvic tilts improve flexibility and reduce stiffness. Start with gentle movements and slowly increase intensity as your back heals.
“Stretching is vital for recovery,” as it boosts flexibility and lowers muscle tension. Consistency is key in stretching exercises.
Core Stabilization Exercises
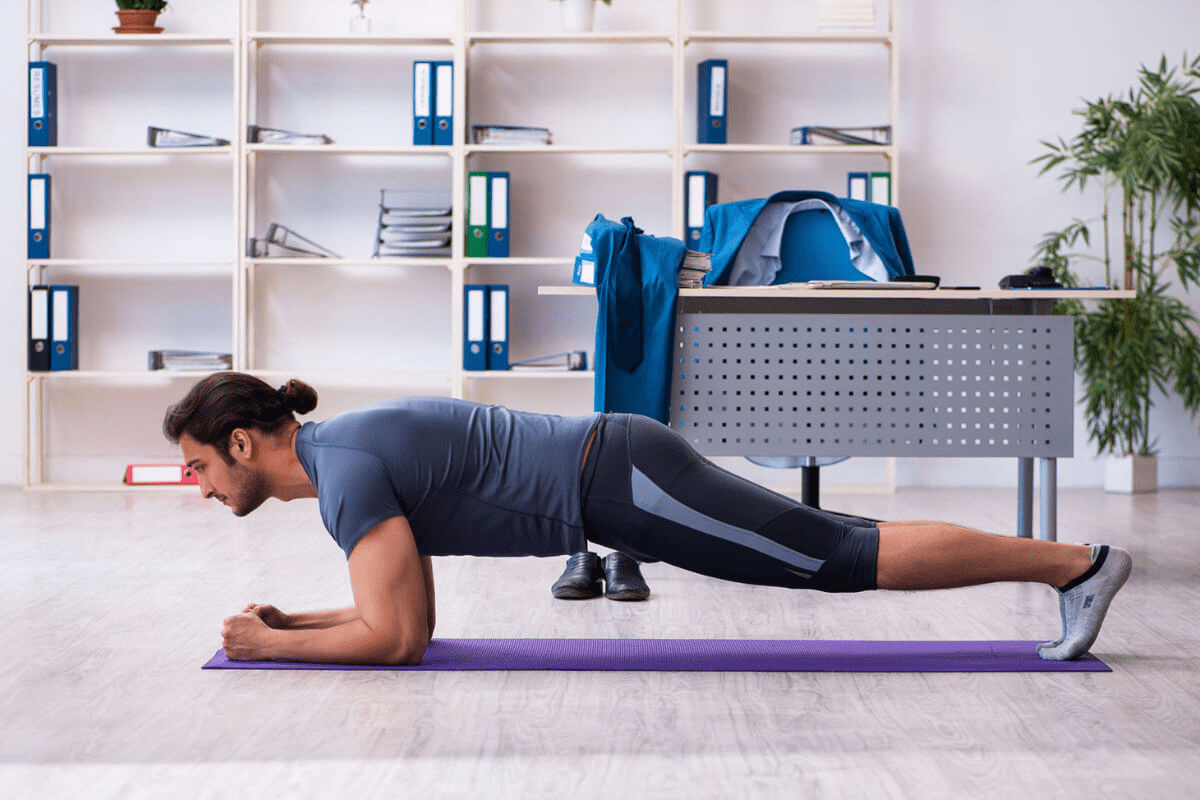
Core exercises are essential for supporting the lower back and improving spinal stability. Planks and bridges target core muscles, aiding recovery. Proper form is vital to avoid worsening the condition.
- Planks: Strengthens abdominal and back muscles
- Bridges: Targets gluteal and lower back muscles
- Bird Dog: Enhances core stability and balance
Progressive Strength Building
As recovery advances, adding strength-building exercises is beneficial. Gradually increase workout intensity to challenge muscles. Listen to your body and don’t overdo it.
“The goal of rehabilitation is not just to heal the current injury but to strengthen the back to prevent future issues.”
Proper Form and Technique
Proper form and technique are critical in rehabilitation exercises. Incorrect form can cause further injury. Work with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to ensure correct exercise performance.
By focusing on gentle stretches, core exercises, and strength building, you can recover from a pulled lower back muscle. This improves your overall back health.
Recovery Timeline and Expectations
Knowing how long it takes to heal a pulled lower back muscle is key. The time it takes can change based on how bad the injury is, your age, and how active you are. Most pulled muscles in the back heal in about two weeks with the right care. But, if the injury is severe, it might take longer.
Mild Strains
Mild strains usually heal in 1-2 weeks. It’s important to keep up with gentle stretching and strengthening exercises during this time.
Moderate Strains
Moderate strains can take 3-4 weeks to heal. It’s best to slowly start doing more activities, but avoid heavy lifting or bending.
Severe Strains
Severe strains or muscle tears can take 4-6 weeks to heal. During this time, sticking to a rehabilitation program that includes physical therapy is very important. This helps regain strength and flexibility.
Factors Affecting Healing Time
Several things can affect how long it takes for a pulled lower back muscle to heal. These include:
- Age: Older people may heal slower.
- Overall health: Having other health issues can slow healing.
- Activity level: Coming back to activity too soon can slow healing.
- Severity of the strain: More severe strains take longer to heal.
As Medical Expert, a renowned orthopedic specialist, notes, “The key to a successful recovery is patience and sticking to a well-structured rehabilitation program.”
“Recovery from a lower back strain is not just about healing the immediate injury but also about preventing future occurrences through proper exercise and body mechanics.”
Strain Severity | Recovery Time | Recommended Actions |
Mild | 1-2 weeks | Gentle stretching, self-care |
Moderate | 3-4 weeks | Gradual increase in activity, physical therapy |
Severe | 4-6 weeks | Comprehensive rehabilitation program, physical therapy |
Understanding the recovery timeline and expectations helps individuals manage their healing journey better. This ensures a more effective and lasting recovery.
Preventing Future Lower Back Strains
To prevent lower back strains, we need to take action. This includes using the right techniques, exercising regularly, and making smart lifestyle choices. Knowing why lower back strains happen and how to stop them can greatly lower the risk.
Proper Lifting Techniques
Improper lifting is a big cause of lower back strains. To avoid this, we should bend at the knees, keep the object close, and lift with our legs. This method lessens the strain on our lower back and helps prevent injuries.
Core-Strengthening Routine
A strong core is key for supporting our lower back and keeping good posture. Doing a regular core-strengthening routine can help prevent lower back strains. Exercises like planks, bridges, and pelvic tilts are great for building core strength.
Ergonomic Considerations
Our daily environments, both at work and at home, are important for preventing lower back strains. Making sure our workspaces are ergonomically designed can lower the risk of lower back injuries. This means using chairs with proper lumbar support, positioning computer monitors at eye level, and taking breaks to stand and stretch.
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing our lifestyle can also help prevent lower back strains. Keeping a healthy weight, exercising often, and avoiding smoking are all good. Also, being mindful of our posture during daily activities, like sitting and standing, can help reduce lower back strain.
By adding these preventive steps to our daily lives, we can greatly reduce the risk of lower back strains. This helps us stay healthy and active.
Conclusion
Healing a pulled lower back muscle needs a full plan. This includes rest, managing pain, physical therapy, and exercises to get better. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and how to treat them helps. It also keeps you active and healthy.
As we’ve shown, taking care of yourself is key to getting better from a lower back strain. The right treatment and steps to avoid injuries help most people. They can get back to doing what they love.
This guide shows why treating and preventing lower back injuries is important. It gives a clear way to keep your back in top shape.
FAQ
What is a lumbar strain?
A lumbar strain is an injury to the muscles or tendons in the lower back. It can happen from overstretching, sudden twisting, or heavy lifting.
How long does it take to recover from a pulled lower back muscle?
Recovery time for a pulled lower back muscle varies. It depends on the injury’s severity, age, and activity level. It usually takes 1-6 weeks.
What are the common symptoms of a lower back strain?
Signs of a pulled back muscle include sharp pain, muscle spasms, stiffness, and limited mobility.
How can I alleviate pain and inflammation after pulling a lower back muscle?
The R.I.C.E. method helps. It includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation. These steps can ease pain and aid healing.
What are the most effective treatment options for a pulled lower back muscle?
Effective treatments include over-the-counter pain management and physical therapy. Alternative options like acupuncture and chiropractic care also help.
What exercises can help promote healing and prevent future injuries?
Gentle stretching, core stabilization exercises, and progressive strength building are beneficial. They aid in healing and prevent future injuries.
How can I prevent future lower back strains?
To prevent lower back strains, maintain good posture and exercise regularly. Avoid heavy lifting and use proper lifting techniques.
What are the causes of lumbar strain?
Lumbar strain can be caused by improper lifting, sudden twisting, repetitive motions, and sports injuries.
When should I seek medical attention for a lower back strain?
Seek medical help if you have severe pain, numbness, tingling, or trouble controlling your bladder or bowels.
Can I continue to exercise with a pulled lower back muscle?
Rest the affected area first. Then, introduce gentle exercises to aid healing and prevent future injuries.