How to boost platelets during chemo? Discover how to increase platelet count with amazing dietary and medical methods. Powerful tips for cancer patients and others!
Chemotherapy can cause a drop in platelet counts, affecting up to 30% of patients. Low platelet counts can lead to serious health issues. It’s important to find ways to manage them well.

Studies have found that recombinant human thrombopoietin (rhTPO) can help raise platelet counts. This article will look at the latest ways to boost platelets during chemo. We’ll cover medical treatments and changes in lifestyle.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the risks associated with low platelet counts during chemotherapy.
- Exploring medical interventions like rhTPO for managing CIT.
- Discussing lifestyle modifications to support platelet health.
- Reviewing the latest hospital protocols for patient care.
- Highlighting the importance of effective platelet count management.
Understanding Platelets and Their Function
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are tiny blood cells that help stop bleeding when we get hurt. They are made in the bone marrow and move through our blood. “Platelets are key for hemostasis, the body’s way to stop bleeding after an injury.”
What Are Platelets?
Platelets are small, colorless cell fragments that form clots to stop or prevent bleeding. They are vital for the blood, helping to prevent too much bleeding when a blood vessel is injured.
Normal Platelet Count Range
A normal platelet count is between 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. Counts below this range can mean thrombocytopenia, a condition that raises the risk of bleeding. Keeping a platelet count in the normal range is key, even more so during chemotherapy.
The Role of Platelets in the Body
The main job of platelets is to prevent and stop bleeding. When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets stick to the injury, clumping together to form a blood clot. This clot helps stop bleeding and starts the healing process. Knowing how platelets work is important for managing conditions like chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia (CIT).
By understanding platelets and their role, patients and healthcare providers can better handle the risks of low platelet counts during chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy-Induced Thrombocytopenia (CIT) Explained
Chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia, or CIT, is a condition that affects the body’s platelet production during chemotherapy. It can cause a big drop in platelet count. This can make cancer treatment harder.
How Chemotherapy Affects Platelet Production
Chemotherapy targets fast-growing cells, including those making platelets in the bone marrow. This can severely reduce platelet production, causing thrombocytopenia. The effect on platelet production varies with the type and intensity of chemotherapy.
Prevalence of CIT in Cancer Patients
CIT affects up to 25-30% of patients on certain chemotherapy regimens. This shows the importance of watching platelet counts during cancer treatment. Studies show a high risk of CIT in patients on intensive chemotherapy.
Risk Factors for Developing Low Platelet Counts
Several factors increase the risk of low platelet counts in cancer patients. These include:
- The type and dose of chemotherapy
- Previous radiation therapy
- Bone marrow involvement by cancer
- Pre-existing blood disorders
Knowing these risk factors is key to early detection and management of CIT.
Recognizing Signs of Low Platelet Count During Treatment
Knowing the signs of thrombocytopenia is key to staying proactive during treatment. This condition, caused by low platelet count, often occurs with chemotherapy. It can lead to serious issues if not handled correctly.
Common Symptoms of Thrombocytopenia
Chemotherapy patients should watch out for common thrombocytopenia symptoms. Look for easy bruising and prolonged bleeding from cuts. Also, keep an eye out for petechiae (small red or purple spots) and frequent nosebleeds.
In some cases, you might feel fatigue or shortness of breath. This is due to anemia linked to thrombocytopenia.
When to Alert Your Healthcare Team
It’s important to know when to tell your healthcare team about symptoms. If you have severe bleeding that won’t stop, or a severe headache or confusion, call them right away. Also, alert them if you see blood in your urine or stool.
Quick action can prevent serious problems.
Monitoring Platelet Levels During Chemotherapy
Keeping an eye on platelet levels is vital during chemotherapy. Your healthcare team will do regular blood tests to check your count. Knowing your platelet levels helps them adjust your treatment to lower bleeding risks.
Medical Interventions for How to Increase Platelet Count
Several medical treatments can help increase platelet count in patients receiving chemotherapy. These treatments are key for managing a condition called chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia (CIT). This condition can cause serious bleeding problems.
Recombinant Human Thrombopoietin (rhTPO)
Recombinant human thrombopoietin (rhTPO) is a big step forward in treating CIT. rhTPO boosts platelet production by helping megakaryocytes grow and mature. Megakaryocytes are the bone marrow cells that make platelets. Research shows that rhTPO can raise platelet counts, lowering the chance of bleeding and the need for transfusions.
Romiplostim and Other Thrombopoietin Receptor Agonists
Romiplostim is a top treatment for CIT. It works by attaching to the thrombopoietin receptor on megakaryocytes, encouraging platelet production. Studies have found that romiplostim can increase platelet counts in patients with CIT, cutting down on bleeding risks. Other thrombopoietin receptor agonists, like eltrombopag, are also used to treat CIT.
Growth Factors for Platelet Production
Other growth factors can also help make more platelets. Interleukin-11 (IL-11) is one such factor used to treat low platelet counts. Though not as common, these growth factors offer more ways to manage CIT.
Using these medical treatments can greatly improve platelet counts in chemotherapy patients. This helps their overall health and lowers the risk of serious problems.
Accelerated Recovery Timelines with Platelet-Boosting Therapies
Platelet-boosting therapies have changed how we treat chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia. These treatments help patients recover faster. This is key to keeping their treatment effective.
3-5 Day Faster Recovery with Interventions
Research shows platelet recovery is 3-5 days faster with these therapies. This quick recovery greatly improves a patient’s treatment experience.
Impact on Treatment Schedules
Quick platelet recovery means treatment schedules can be adjusted. This helps patients stay on their chemotherapy plan. It could lead to better results.
Monitoring Response to Platelet-Boosting Therapies
It’s vital to watch how patients react to these therapies. Regular checks help doctors adjust treatments as needed.
Platelet Transfusions: When They’re Necessary
Platelet transfusions are key for patients with low platelet counts due to chemotherapy. They help increase platelet counts, reducing the risk of bleeding.
Indications for Platelet Transfusion
Transfusions are considered when platelet counts drop below 10,000/ µL or in active bleeding cases. Prophylactic transfusions prevent bleeding in low counts. Therapeutic transfusions stop active bleeding.
The Transfusion Process
The transfusion process involves giving platelet concentrates into the patient’s blood. It’s done through a vein in a clinical setting with healthcare supervision.
Potential Risks and Benefits
Platelet transfusions can save lives but come with risks. Complications include allergic reactions, TRALI, and infectious agent transmission. Yet, the benefits often outweigh these risks, preventing severe bleeding.
Healthcare providers must carefully consider each patient’s needs and risks. They tailor their approach to meet the individual’s specific situation.
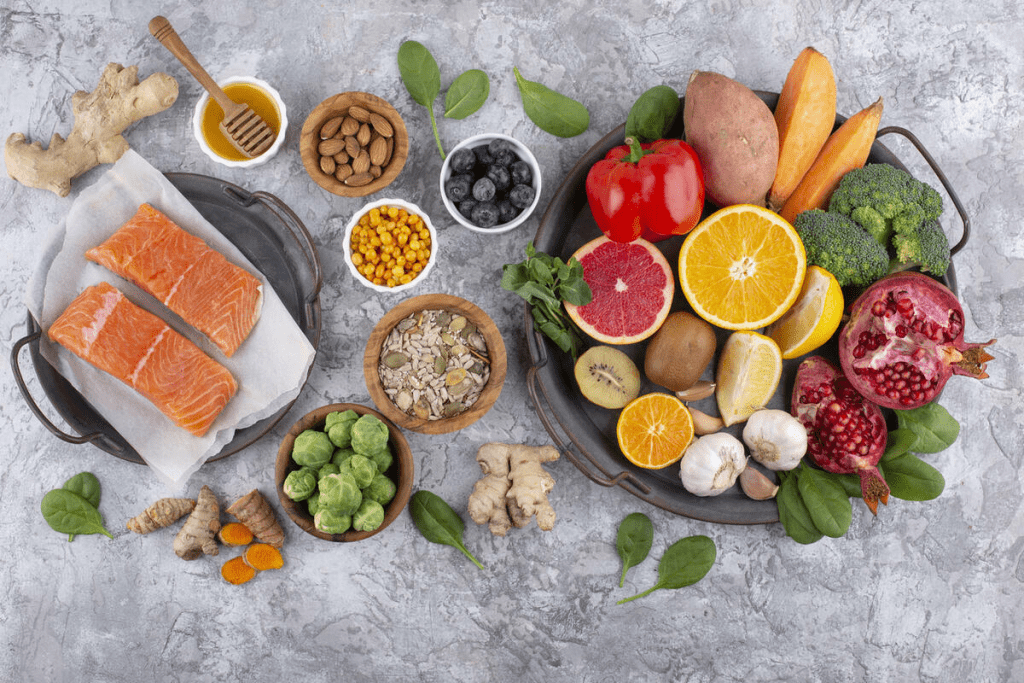
Dietary Approaches to Support Platelet Production
Eating the right foods can help increase platelet production and lessen thrombocytopenia’s effects. A balanced diet is key to meeting the body’s needs during chemotherapy.
Foods Rich in Vitamins K, B12, C, and Folate
Some vitamins are key to healthy platelet counts. Vitamin K is vital for blood clotting. You can find it in spinach and kale. Vitamin B12 is important for making platelets and is in animal products like meat and fish. Vitamin C helps iron absorption, which is key for platelets. It’s in citrus fruits and bell peppers. Folate is in dark greens and beans, helping prevent low platelet counts.
The Role of Iron and Protein in Platelet Health
Iron is essential for making hemoglobin, which carries oxygen. This supports health and platelet production. Iron is in red meat, fish, and beans. Protein is vital for platelet building. Eating enough protein from lean meats and legumes helps platelet health.
Foods to Avoid During Thrombocytopenia
Some foods can help platelet counts, while others may increase bleeding risk. It’s best to avoid foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats. Also, foods that cause allergies or interact with treatments should be avoided.
Making smart food choices can help those with chemotherapy support their platelet health and overall well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications to Protect Low Platelets
Lifestyle changes are key to protecting low platelets during chemo. By making smart choices, patients can lower their risk of bleeding and injury. This helps keep their health safe.
Preventing Injuries and Bleeding
For those with low platelet counts, preventing injuries and bleeding is a big concern. Simple steps like using a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoiding contact sports can help. Also, be careful with sharp objects and avoid heavy lifting or bending.
Exercise Considerations
Exercise is good for health, but those with low platelet counts need to be careful. Gentle activities like yoga or short walks are best. They help circulation without risking injury. High-impact activities should wait until platelet counts are safe.
Managing Daily Activities Safely
It’s important to manage daily activities safely with low platelet counts. Be aware of fall hazards at home, like loose rugs or wet floors. Take steps to reduce these risks. Also, rest often and avoid overdoing it.
The Impact of Platelet Levels on Chemotherapy Scheduling
Chemotherapy is a complex treatment that needs careful planning and monitoring. The impact of platelet levels on chemotherapy scheduling is key for oncologists. It affects when and how much treatment is given.
Platelet counts are vital for safe and effective chemotherapy. Low platelet levels increase the risk of bleeding. This might mean changing the treatment plan.
When Treatment Delays May Be Necessary
If a patient’s platelet count is very low, treatment delays might be needed. The oncologist will decide based on the patient’s health and platelet count.
Delaying chemotherapy can affect the treatment schedule. It might make treatment last longer. But it’s often necessary to avoid serious problems.
Dose Modifications Based on Platelet Counts
Dose modifications help manage patients with low platelet counts. Adjusting the chemotherapy dosage can reduce bleeding risks. It also keeps the treatment effective.
Changing the dose depends on the patient’s platelet count, health, and the chemotherapy type.
Balancing Cancer Treatment and Platelet Health
It’s a challenge to balance cancer treatment and platelet health. Oncologists must consider the benefits and risks of chemotherapy. They also think about how it affects platelet counts.
By watching platelet levels and adjusting treatment, healthcare providers aim to give the best care. They try to avoid complications.
Modern Multidisciplinary Approaches to Thrombocytopenia Management
Multidisciplinary care is changing how we manage thrombocytopenia in cancer patients. It brings together different specialties for a more complete care plan. This helps tackle the complex issues of thrombocytopenia.
Evidence-Based Protocols in Leading Hospitals
Top hospitals, like Liv Hospital, lead in using evidence-based protocols for managing thrombocytopenia. These protocols are based on the latest research and guidelines. This ensures patients get the best care possible.
Integrated Care Teams
The heart of multidisciplinary care is integrated care teams. These teams include hematologists, oncologists, nurses, and more. They work together to create treatment plans tailored for each patient.
Innovative Solutions for Enhanced Patient Safety
New solutions, like advanced diagnostic tools and treatments, are being used to keep patients safe. For example, thrombopoietin receptor agonists are showing great promise in boosting platelet production.
Case Studies of Successful Platelet Management
Many case studies show the success of these approaches in managing thrombocytopenia. For instance, a patient with severe thrombocytopenia due to chemotherapy was treated with platelet transfusions and thrombopoietin receptor agonists. This allowed them to keep up with their cancer treatment without major delays.
By using these modern, multidisciplinary methods, healthcare providers can greatly improve patient outcomes and quality of life during chemotherapy.
Conclusion: Navigating Chemotherapy with Optimal Platelet Management
Managing chemotherapy side effects is key, including low platelet counts. Keeping platelet levels healthy is vital for avoiding treatment delays and keeping patients safe.
Patients can work with their healthcare teams to keep platelet counts up. This includes medical treatments, diet, and lifestyle changes. These steps help in making more platelets and lowering bleeding risks.
Medical treatments like recombinant human thrombopoietin can speed up platelet recovery. Eating well and managing daily activities also help. These actions support platelet production and reduce bleeding risks.
By using these strategies, patients can handle chemotherapy better. This means less worry about low platelet counts. It helps doctors keep treatment on track, improving patient results.
FAQ
How can I increase my platelet count during chemotherapy?
You can use treatments like recombinant human thrombopoietin (rhTPO) and romiplostim to raise your platelet count. Eating foods rich in vitamins K, B12, C, and folate also helps.
What are the common symptoms of thrombocytopenia?
Symptoms include bruising, petechiae, nosebleeds, and bleeding gums. If you notice these, tell your healthcare team right away.
How do I know if I need a platelet transfusion?
You might need a transfusion if your platelet count is very low. Your healthcare team will decide based on your situation.
Can lifestyle modifications help protect low platelets?
Yes, avoiding injuries and bleeding, exercising carefully, and managing daily activities safely can help protect your platelets.
How do platelet levels impact chemotherapy scheduling?
Low platelet levels can affect when you get chemotherapy. You might need to delay or adjust your treatment.
What foods should I avoid during thrombocytopenia?
Avoid foods that can make bleeding more likely, like those with a lot of sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats. Your healthcare team can give you specific advice.
How can I boost my platelet count quickly?
While quick increases are hard, treatments like rhTPO and romiplostim can help. Also, making dietary changes and lifestyle adjustments can support platelet production.
What is the minimum WBC count for chemotherapy?
The minimum WBC count for chemotherapy depends on your treatment and health. Your healthcare team will decide what’s right for you.
How can I increase my platelet count in 2 days?
Increasing platelet count in 2 days is tough. But, medical treatments like transfusions or rhTPO o,r romiplostim might help. Talk to your healthcare team for advice.
Reference
Al-Samkari, H. (2023). Optimal management of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with solid tumors. Blood Reviews, 57, 100937. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10872905/