Finding out if you have plaque buildup in arteries is hard because it often doesn’t show symptoms early on. Atherosclerosis is when plaque builds up in the arteries, making them narrow and hard. This can block blood flow, leading to serious health problems like heart attacks.Find out how to know if you have plaque in your arteries and discover the key signs and tests for early detection.
Many people don’t notice anything until it’s too late, like when they have a heart attack. It’s important to know the signs and risk factors. At LivHospital, we use the latest technology to help you understand your heart health and what treatments are available.
Key Takeaways
- Detecting plaque buildup can be challenging due to the lack of symptoms in early stages.
- Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Recognizing signs and risk factors is key for early detection.
- LivHospital offers advanced medical care for heart health.
- Understanding the condition and modern treatment options is vital.
Understanding Arterial Plaque: What It Is and Why It Matters
Knowing about arterial plaque is key to keeping your heart healthy and avoiding heart disease. It’s when cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other stuff build up in artery walls. This is called atherosclerosis.
Definition of Plaque in the Heart and Arteries
Plaque in the heart and arteries is a mix of different substances. They stick to the inside of artery walls. This can make arteries narrow and hard, cutting off blood to important organs.
The Process of Atherosclerosis
The atherosclerosis process has a few main steps:
- Lipids get into the artery wall
- Inflammation and immune response happen
- A fibrous cap forms over the plaque
- The plaque can burst, causing a blood clot
Different Types of Arterial Plaque
There are a few kinds of arterial plaque, including:
- Stable plaque: Has a thick fibrous cap, so it’s less likely to burst
- Unstable plaque: Has a thin cap and is more likely to burst, causing heart problems
- Calcified plaque: Has calcium, making it more stable but can also block blood flow
It’s important to know about these plaque types to find the best treatments.
The Silent Danger: Why Arterial Plaque Often Goes Undetected
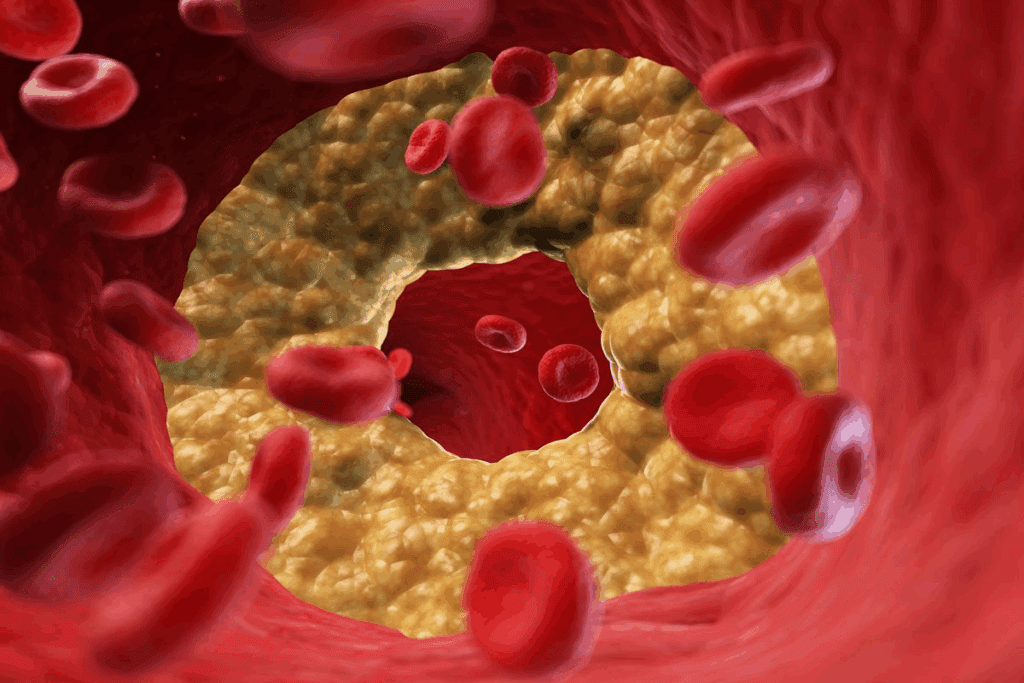
Arterial plaque can build up silently, without any symptoms. This silent growth can lead to serious heart problems before people even know they have an issue.
The Asymptomatic Nature of Early Plaque Buildup
In the beginning, arterial plaque doesn’t show symptoms. This makes it hard for people to find out they have it without a doctor’s test. This asymptomatic nature means many don’t find out until it’s too late.
Why Early Detection Matters
Finding arterial plaque early is key. It lets doctors act fast to stop it from getting worse. Understanding the causes of plaque formation, like high cholesterol, helps manage risks.
Statistics on Undiagnosed Arterial Plaque
Studies show up to 40 percent of people might have plaque without knowing it. This shows how important it is to get checked and stay aware. Many people don’t show symptoms until it’s too late, making regular health checks critical.
Common Symptoms That May Indicate Plaque in Your Arteries
It’s important to know the signs of plaque buildup in your arteries. This can lead to heart diseases. Spotting these signs early can save lives.
Chest Pain (Angina)
Chest pain, or angina, is a common sign. It happens when the heart doesn’t get enough blood and oxygen. People often feel a tight or squeezing feeling in their chest.
Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath is another symptom. It can happen when plaque limits blood flow. This can happen even when you’re not moving much.
Weakness and Fatigue
Feeling weak and tired can also be a sign. Reduced blood flow can make you feel unwell and lacking in energy.
Symptoms Based on Affected Arteries
The symptoms change based on which arteries are affected. For example, plaque in the heart arteries can cause chest pain. But plaque in the leg arteries can lead to pain when walking.
Medical Expert, “Plaque in arteries is a silent killer, often showing no symptoms until it’s too late.” Understanding these symptoms is key to catching it early and preventing heart problems.
Knowing these symptoms and talking to a doctor can help catch problems early. This can prevent heart attacks and strokes.
How to Know if You Have Plaque in Your Arteries: Diagnostic Methods
Healthcare professionals use several tests to find out if you have plaque in your arteries. These tests show if you have plaque and how much. This is important to stop heart problems.
Non-Invasive Tests
First, doctors use non-invasive tests. These include:
- CT Calcium Score: This test shows how much calcium is in your coronary arteries. It tells how much plaque you have.
- Carotid Ultrasound: This ultrasound looks for plaque in the carotid arteries. These arteries supply blood to your brain.
- Doppler Ultrasound: It checks blood flow in arteries. It finds any narrowing or blockages.
These tests are great for finding plaque early and keeping an eye on it.
Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
For a closer look, doctors might suggest more tests. These include:
- Angiogram: This test uses dye and X-rays to see inside your arteries. It finds blockages.
- Cardiac MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging shows detailed pictures of your heart and blood vessels. It checks plaque and how well your heart is working.
These tests give important info for diagnosing and treating plaque in arteries.
When to See a Doctor for Arterial Plaque Screening
If you worry about plaque in your arteries, see a doctor. They will check your risk and suggest tests. Early detection is key to managing and preventing the progression of arterial plaque.
Knowing about these tests is the first step to caring for your arteries. By working with doctors and using these tests, you can understand your risk. Then, you can take steps to keep your arteries healthy.
The Relationship Between Cholesterol and Plaque
It’s key to know how cholesterol and plaque are connected for heart health. Cholesterol, a fatty substance in blood, is a big part of forming arterial plaque.
Understanding “Good” vs. “Bad” Cholesterol
Cholesterol moves through blood with lipoproteins, which are sorted by density. Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), or “bad” cholesterol, sticks to artery walls, causing plaque. On the other hand, High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL), or “good” cholesterol, helps clear out extra cholesterol, which might lower plaque risk.
How LDL Cholesterol Contributes to Plaque Formation
Too much LDL cholesterol can cause cholesterol to build up on damaged artery walls. This starts atherosclerosis. Over time, this buildup hardens and forms plaques, which can narrow arteries and block blood flow.
Cholesterol Testing and What Your Numbers Mean
Cholesterol tests are vital for checking heart risk. They measure LDL, HDL, and triglycerides in blood. Knowing these numbers helps both you and your doctor manage cholesterol and prevent plaque.
Triglycerides and Their Role in Plaque Development
Triglycerides, a blood fat, can also help plaque form when levels are high. Keeping triglycerides in check through diet, exercise, and sometimes medicine is key to heart health.
What Causes Plaque to Build Up in Arteries
It’s important to know what causes plaque buildup in arteries to prevent heart disease. Plaque buildup, or atherosclerosis, is a complex process. It’s influenced by many factors. Let’s look at the main causes.
Inflammatory Processes
Inflammation is a big player in arterial plaque development. Chronic inflammation damages the inner artery lining. This makes arteries more likely to collect lipids and other substances.
Endothelial Dysfunction
The endothelium, a thin layer of cells, is key to artery health. When it’s not working right, arteries can’t function properly. This leads to plaque formation.
Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress happens when free radicals overwhelm the body’s defenses. This stress damages artery walls. It makes them more likely to build up plaque.
Metabolic Factors
Metabolic factors, like high LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, play a big role. These substances can stick to artery walls. Over time, this leads to plaque buildup.
The table below shows the main factors that cause plaque buildup in arteries:
| Factor | Description | Impact on Arteries |
| Inflammatory Processes | Chronic inflammation damaging arterial lining | Increased susceptibility to plaque accumulation |
| Endothelial Dysfunction | Imbalance in normal arterial functioning | Promotes plaque formation |
| Oxidative Stress | Damage to arterial walls due to free radicals | Increased plaque buildup |
| Metabolic Factors | High LDL cholesterol and triglycerides | Accumulation on arterial walls |
Understanding these factors helps us see how complex plaque buildup is. It shows why we need to tackle these risk factors to avoid heart disease.
Risk Factors That Increase Your Chances of Developing Arterial Plaque
Arterial plaque forms due to many factors. Some can be changed, while others can’t. Knowing these factors helps prevent and manage plaque.
Modifiable Risk Factors
Many lifestyle choices and health conditions can be changed to lower plaque risk. These include:
- High Cholesterol: Too much LDL cholesterol can cause plaque.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure damages arteries, making them prone to plaque.
- Smoking: Smoking harms the heart and increases plaque risk.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes face higher risks due to blood sugar damage.
- Obesity and Physical Inactivity: Being overweight and inactive can lead to high blood pressure and diabetes.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Arterial Plaque |
| High Cholesterol | Elevated LDL cholesterol levels | Increases plaque formation |
| Hypertension | High blood pressure | Damages arterial walls |
| Smoking | Tobacco use | Damages cardiovascular system |
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
Some risk factors can’t be changed, but knowing them helps manage risk. These include:
- Age: Arterial plaque risk grows with age.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease raises risk.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some genes affect cholesterol and plaque risk.
Understanding both changeable and unchangeable risk factors helps prevent plaque. This knowledge lets people make better health choices, reducing plaque risk.
The Progression of Arterial Plaque: From Formation to Blockage
Arterial plaque starts with small changes in the artery walls. It can grow and block the artery if not treated.
Early Stage Development
High cholesterol, high blood pressure, and smoking start plaque formation. These cause endothelial dysfunction. This leads to lipids and inflammatory cells in the arteries.
Advanced Plaque and Arterial Narrowing
More plaque means the arteries narrow, known as atherosclerosis. This limits blood to organs, causing symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath.
Complications: Rupture and Thrombosis
Advanced plaque can rupture, causing a blood clot or thrombosis. This clot can block the artery, leading to heart attacks or strokes.
Common Locations for Plaque Body Formation
Plaque forms where blood flow is turbulent, like at artery branches. It often occurs in coronary, carotid, and peripheral arteries.
| Location | Potential Complication |
| Coronary Arteries | Heart Attack |
| Carotid Arteries | Stroke |
| Peripheral Arteries | Peripheral Artery Disease |
Knowing how plaque progresses shows why early detection and prevention are key. They help avoid serious heart and stroke risks.
Prevention Strategies: How to Reduce Plaque Formation and Progression
To fight plaque buildup, focus on diet, exercise, and heart health. A well-rounded approach can greatly lower the risk of getting arterial plaque.
Heart-Healthy Dietary Approaches
Eating lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins is key. The Mediterranean diet is great because it’s full of healthy fats and antioxidants.
“The Mediterranean diet has been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by improving lipid profiles and lowering blood pressure.”
Here are some diet tips:
- Eat a variety of colorful fruits and veggies.
- Add whole grains to your meals.
- Choose lean proteins like poultry and fish.
- Stay away from saturated and trans fats.
| Dietary Component | Recommended Intake | Benefit |
| Fruits and Vegetables | 5 servings/day | Rich in antioxidants and fiber |
| Whole Grains | 3-5 servings/day | High in fiber, vitamins, and minerals |
| Lean Proteins | Varies by individual needs | Supports heart health |
Exercise Recommendations
Regular exercise keeps your heart healthy and prevents plaque. Aerobic exercises like walking, cycling, or swimming are best. Aim for at least 150 minutes a week at moderate intensity.
Exercise boosts HDL (good) cholesterol and lowers LDL (bad) cholesterol. This helps prevent plaque.
Stress Management
Too much stress can harm your heart. Try mindfulness meditation, deep breathing, or yoga. These can reduce stress and improve your well-being.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking greatly increases the risk of plaque. Quitting can greatly lower this risk. Look for counseling, support groups, and nicotine replacement therapy to help quit.
By using these prevention strategies, you can fight plaque buildup. This can help lower your risk of heart disease.
Treatment Options for Existing Arterial Plaque
Managing arterial plaque needs a detailed plan. This plan must tackle the root causes and risk factors. We will look at the different treatments for those with existing plaque.
Medication-Based Treatments
Medicines are key in managing plaque. Statins help lower LDL cholesterol. Antiplatelet agents stop blood clots. Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors manage high blood pressure.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is sometimes needed to improve blood flow. Angioplasty and stenting widen narrowed arteries. Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) bypasses blocked arteries. These are for severe plaque or when meds don’t work.
“The goal of treatment is not only to manage symptoms but to slow or halt the progression of arterial plaque.”
— American Heart Association
Emerging Therapies for Plaque Regression
New treatments aim to reverse plaque buildup. These include new medicines and therapies targeting plaque formation. More research is needed to confirm their safety and effectiveness.
Knowing the treatment options helps those with plaque. They can work with their doctors to create a plan that fits their needs and risks.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Arterial Health
Understanding and managing plaque buildup is key to keeping your heart healthy. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatments for plaque in arteries helps us act early. This can lower the risk of heart disease.
To see if you have plaque, know the risk factors like high cholesterol. Regular screenings are also important. Tests can spot plaque early, helping us act fast.
Keeping your arteries healthy means living a heart-healthy lifestyle. This includes eating right and exercising often. By doing this, we can lower the risk of heart problems caused by plaque.
We suggest talking to a doctor to check your risk and make a plan for your heart health. This way, you can keep your heart in top shape.
FAQ:
What is arterial plaque, and how does it form?
Arterial plaque is a buildup of fatty deposits and cholesterol in arteries. It forms when the artery’s inner lining gets damaged. This damage lets plaque accumulate.
What are the symptoms of plaque buildup in the arteries?
Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, and fatigue. The symptoms depend on the arteries affected. Sometimes, there are no symptoms at all.
How is plaque in the arteries diagnosed?
Tests like ultrasound, CT scans, and stress tests can diagnose it. Advanced procedures like angiography are also used.
What is the relationship between cholesterol and plaque?
High “bad” cholesterol (LDL) can lead to plaque. “Good” cholesterol (HDL) helps remove excess cholesterol. Triglycerides also play a role in plaque development.
What causes plaque to build up in arteries?
Inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and oxidative stress cause plaque buildup. High blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol also contribute.
What are the risk factors for developing arterial plaque?
Risk factors include smoking, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Diabetes, age, family history, and genetics are also risk factors.
How can I reduce my risk of developing arterial plaque?
Eat heart-healthy foods, exercise regularly, manage stress, and quit smoking. These actions can help prevent plaque buildup.
What are the treatment options for existing arterial plaque?
Treatments include medications, surgeries, and new therapies aimed at reducing plaque.
Can arterial plaque be reversed?
Lifestyle changes and medical treatment can reverse some plaque buildup. But, advanced plaque may need more aggressive treatment.
How can I manage my arterial health?
Understand your risk factors, make lifestyle changes, and work with your healthcare provider. This helps monitor and treat plaque buildup.
What is the definition of plaque in the heart?
Plaque in the heart is atherosclerotic plaque in the coronary arteries. These arteries supply blood to the heart muscle.
What causes plaque to form in arteries?
Plaque forms due to high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes. These factors damage the artery’s inner lining, allowing plaque to accumulate.
References:
Morgado-Brajones, D., et al. (2022). “Inflammation in atherosclerosis: pathophysiology and mechanisms.” Atherosclerosis. published online.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39528464/



































