Managing heart valve narrowing requires a personalized approach to ensure optimal patient outcomes. Cardiovascular stenosis is when blood vessels or heart valves narrow. This can greatly affect health if not managed well.
Liv Hospital uses evidence-based protocols and focuses on the patient. They stay up-to-date with the latest research. This way, Liv Hospital provides top-notch medical care worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- Cardiovascular stenosis is a serious condition that requires proper management.
- Liv Hospital offers personalized treatment plans for optimal patient outcomes.
- Evidence-based protocols are used to ensure the best possible care.
- Patient-centered innovation is a key aspect of Liv Hospital’s approach.
- Internationally recognized medical care is delivered by Liv Hospital.
Understanding Cardiovascular Stenosis
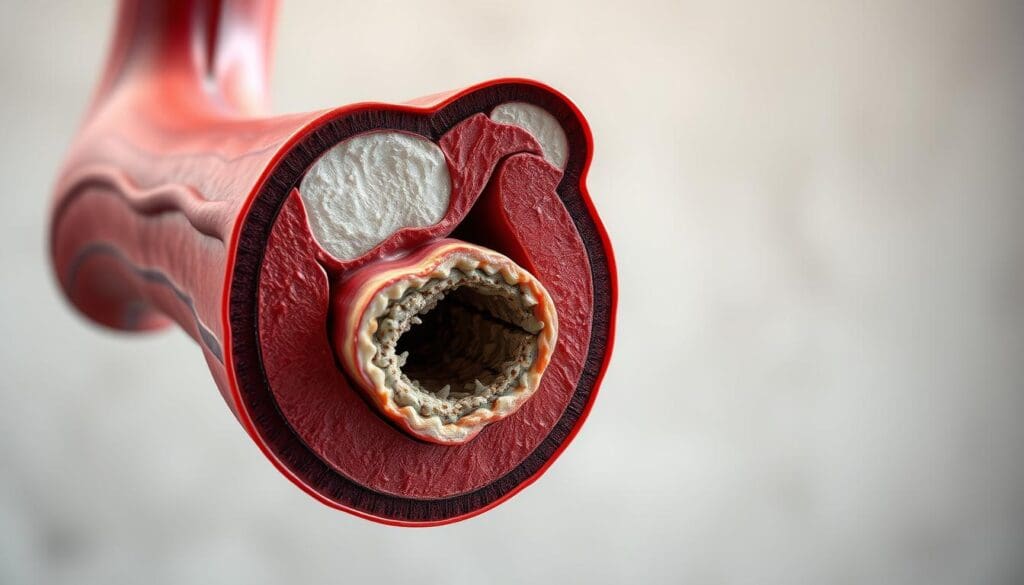

Cardiovascular stenosis is when the heart valves or blood vessels narrow. This can lead to serious health problems. The narrowing can cause different issues, depending on where and how severe it is.
Definition and Pathophysiology
Cardiovascular stenosis means the blood vessels or heart valves narrow. This blocks blood flow. It can happen in different parts of the heart and blood system.
The reasons for stenosis include atherosclerosis, calcification, and being born with it. For example, mitral stenosis often comes from rheumatic fever. Pulmonary stenosis might be something you’re born with. Knowing why it happens helps in treating it.
Impact on Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular stenosis can harm your heart health a lot. It makes the heart work harder, which can lead to heart failure if not treated. Studies show that surgery or less invasive methods are best for severe aortic stenosis.
The narrowing can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and tiredness. In bad cases, it can be deadly. So, knowing the causes of stenosis and its effects on the heart is key to good treatment.
Managing cardiovascular stenosis needs a full plan. This includes medicine, surgery, and changing your lifestyle. Understanding the condition helps doctors give better care and improve patient results.
Types of Cardiovascular Stenosis
Cardiovascular stenosis affects different parts of the heart and blood vessels. It’s important to understand each type to manage it well. Stenosis is when passages in the heart narrow down.
Coronary Artery Stenosis
Coronary artery stenosis narrows the arteries that feed the heart. This is often due to atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up. It can cause heart pain, reduced blood flow, and increase heart attack risk.
Aortic Valve Stenosis
Aortic valve stenosis narrows the valve that lets blood flow out of the heart. It can cause chest pain, fainting, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, surgery like valve replacement is needed.
Mitral Valve Stenosis
Mitral valve stenosis narrows the valve between the heart’s left chambers. It can block blood flow, leading to fatigue, shortness of breath, and palpitations. Treatment can range from medication to surgery.
Pulmonary Valve Stenosis
Pulmonary valve stenosis narrows the valve that lets blood flow to the lungs. It’s often present at birth and can be mild or severe. Symptoms include shortness of breath and fatigue, with severe cases leading to heart failure.
Liv Hospital and other top medical centers use proven treatments for these stenosis types. They tailor treatments to each patient’s needs.
| Type of Stenosis | Location | Common Causes | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coronary Artery Stenosis | Coronary Arteries | Atherosclerosis | Chest Pain, Heart Attack |
| Aortic Valve Stenosis | Aortic Valve | Age-related Degeneration, Congenital Issues | Chest Pain, Fainting, Shortness of Breath |
| Mitral Valve Stenosis | Mitral Valve | Rheumatic Fever, Congenital Issues | Fatigue, Shortness of Breath, Palpitations |
| Pulmonary Valve Stenosis | Pulmonary Valve | Congenital Heart Defect | Shortness of Breath, Fatigue |
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Cardiovascular stenosis can come from several sources. These include degeneration, atherosclerosis, and congenital conditions. Knowing these causes helps in preventing and managing the condition.
Age-Related Degeneration
Age is a big risk factor for cardiovascular stenosis. As we get older, our heart valves and arteries wear out. This can cause stenosis. Degenerative changes like calcification and thickening make valves stiff and more likely to cause stenosis.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is another major cause. It’s when plaque builds up in arteries. This can narrow arteries, including the coronary ones, leading to stenosis. Atherosclerotic plaque is made of fat, cholesterol, and other stuff that hardens and blocks blood flow.
Congenital Factors
Congenital heart defects also increase the risk of stenosis. People born with heart valve problems or other defects are more likely to get stenosis. Congenital conditions can make stenosis worse and often need early treatment.
Other Contributing Factors
Lifestyle choices and certain conditions also play a part. Smoking, eating too much saturated fat, high blood pressure, and diabetes can all increase the risk of stenosis.
“Managing these risk factors through lifestyle changes and medical treatment can greatly lower the chance of getting cardiovascular stenosis.”
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Stenosis |
|---|---|---|
| Age-Related Degeneration | Natural wear and tear on heart valves and arteries | Increased risk with age |
| Atherosclerosis | Plaque buildup in arteries | Narrowing of arteries |
| Congenital Factors | Heart defects present at birth | Potential for early onset stenosis |
It’s important to understand these causes and risk factors. This knowledge helps in creating good prevention and treatment plans for cardiovascular stenosis.
Recognizing Symptoms of Cardiovascular Stenosis
It’s important to know the symptoms of cardiovascular stenosis early. This condition can show itself in many ways, from mild to severe. Knowing these signs helps manage the condition better.
Early Warning Signs
The first signs of cardiovascular stenosis can be easy to miss. They might include fatigue, shortness of breath, and mild chest discomfort. These symptoms start slowly and can be confused with other, less serious issues.
Being aware of these early signs is key. This is true if you have a family history of heart disease or other risk factors.
Advanced Symptoms
As the condition gets worse, symptoms get more serious. You might feel severe chest pain (angina), dizziness, and fainting spells. These signs mean the blockage is more severe and need quick medical help.
These symptoms can really affect your daily life and how well you feel. Getting help right away is very important.
Emergency Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
In very bad cases, symptoms can be life-threatening. You might have acute chest pain, severe shortness of breath, and loss of consciousness. These need immediate medical care to avoid serious problems or death.
If you or someone else has these emergency symptoms, call for help right away. Go to the emergency room or call emergency services.
Knowing the different symptoms of cardiovascular stenosis is key to early treatment. By spotting the early signs and getting medical help when needed, you can greatly improve your health and life quality.
Diagnostic Approaches for Cardiovascular Stenosis
Diagnosing cardiovascular stenosis involves several steps. These include a physical check-up, imaging tests, and lab work. Getting the diagnosis right is key to choosing the right treatment and helping patients get better.
Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing cardiovascular stenosis is a thorough physical exam. Doctors look for signs like murmurs, abnormal heart sounds, and changes in pulse or blood pressure. These signs can show if stenosis is present and how severe it is.
Murmurs are important clues. They are sounds heard over the heart when blood flow is turbulent. This usually happens because of stenotic valves or narrowed arteries. The type and loudness of the murmur can tell doctors more about the condition.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is a big part of diagnosing cardiovascular stenosis. Tools like echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and CT angiography give detailed pictures of the heart and blood vessels. They help spot narrowing or stenosis.
Echocardiography is great for checking valve function and finding stenosis in heart valves. Cardiac MRI and CT angiography give detailed views of the heart’s anatomy, including the coronary arteries, aorta, and other major vessels.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are also vital for diagnosing cardiovascular stenosis. They include blood lipid profiles, troponin levels, and other biomarkers. These tests show if the heart is stressed or damaged.
These tests help understand why stenosis happens, like because of atherosclerosis. They also help track the patient’s health over time. They guide doctors in deciding on treatments, like medicines or procedures.
By using information from physical exams, imaging, and lab tests, doctors can accurately diagnose cardiovascular stenosis. This helps them create a good treatment plan for patients.
Medical Management of Cardiovascular Stenosis
Managing cardiovascular stenosis is key and includes medicines, lifestyle changes, and check-ups. These steps can greatly improve life for those with this condition.
Pharmacological Treatments
Medicines are a big part of treating cardiovascular stenosis. Medicines like beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and statins help manage symptoms and slow the disease. Beta-blockers ease the heart’s work, ACE inhibitors relax blood vessels, and statins lower cholesterol.
The right medicine depends on the stenosis type and the patient’s health. For example, those with coronary artery stenosis might need antiplatelet therapy to stop clots.
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle is key in managing cardiovascular stenosis. Eating a heart-healthy diet full of fruits, veggies, and whole grains helps control cholesterol and blood pressure. Regular exercise, like walking or swimming, is also good.
Quitting smoking and drinking less alcohol are also important. These changes help manage stenosis and lower the risk of serious problems.
Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Regular check-ups and monitoring are vital for managing cardiovascular stenosis. Seeing your healthcare provider regularly helps track the disease and treatment success.
Patients often get tests like echocardiograms to check their heart valves or arteries. This care ensures treatments are adjusted as needed for the best results.
Combining medicines, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups helps people with cardiovascular stenosis live well. It’s a complete approach that boosts heart health from all sides.
Surgical Interventions for Stenosis Treatment
Surgical procedures are key in treating cardiovascular stenosis. Studies show that both surgical and minimally invasive methods are effective.
The main surgeries for cardiovascular stenosis are Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG), Valve Replacement Surgery, and Valvuloplasty. Each surgery targets different stenosis issues. They are chosen based on the patient’s condition and health.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
CABG improves heart blood flow by bypassing blocked arteries. It’s often for coronary artery stenosis. A graft from another body part is used to bypass the blockage, helping the heart muscle get blood again.
Valve Replacement Surgery
Valve replacement surgery replaces a sick valve with a new one. It’s needed for aortic or mitral valve stenosis. The choice between a mechanical or bioprosthetic valve depends on age, lifestyle, and health.
Valvuloplasty
Valvuloplasty is a less invasive surgery. It uses a balloon to open a stenotic valve. It’s good for those at high surgery risk or with complex conditions.
Patient Selection Based on Age and Risk
Choosing patients for surgery depends on age, health, and risk factors. Older patients or those with many health issues need careful consideration. A team decides the best treatment plan for each patient.
In summary, surgery is a vital part of treating cardiovascular stenosis. Knowing the different surgeries helps doctors create personalized treatment plans. This improves patient results.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive procedures have changed how we treat cardiovascular stenosis. They offer safer options than traditional surgery. These new methods help patients recover faster, face fewer complications, and have better results.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI)
TAVI is a new way to treat aortic valve stenosis. It puts a new valve in the heart through a catheter, usually from the leg. This method avoids open-heart surgery, which is good for high-risk patients.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
PCI is a non-surgical way to treat blocked arteries. It uses a balloon to open the artery and may include a stent. PCI is great for patients with acute coronary syndrome.
Balloon Valvuloplasty
Balloon valvuloplasty is a minimally invasive method for heart valve problems. It uses a balloon catheter to widen the valve. But, it’s not right for everyone, like those with calcified valves.
Advantages and Limitations
These procedures have big benefits like shorter recovery times and less pain. They also have fewer risks than traditional surgery. But, they can have downsides like valve problems over time with TAVI, or artery blockage again after PCI. Choosing the right patient is key to success.
Choosing between these procedures depends on many things. These include the type and severity of stenosis, the patient’s health, and what they prefer. A team of doctors is important in picking the best treatment.
Multidisciplinary Approach to Stenosis Care
Liv Hospital takes a team effort to treat cardiovascular stenosis. This means many healthcare experts work together. They create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
Team-Based Treatment Protocols
Managing cardiovascular stenosis needs a team. Cardiologists, surgeons, and radiologists are all part of it. This team makes sure every part of a patient’s health is looked at when planning treatment.
A study in Nature shows this team effort can really help patients with heart diseases.
Evidence-Based Care Pathways
Using the latest research, Liv Hospital makes sure patients get the best care. These pathways are based on the newest studies and guidelines. This way, care is always up-to-date and effective.
Patient-Centered Innovation
Liv Hospital puts patients first in treating cardiovascular stenosis. They focus on what each patient needs and wants. This approach makes care more personal and improves results.
International Standards and Ethical Practices
Liv Hospital follows global standards and ethics in treating heart diseases. This promise means patients get safe and top-notch care.
| Aspect of Care | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Team-Based Treatment | Involves multiple healthcare professionals | Comprehensive care, improved outcomes |
| Evidence-Based Pathways | Guided by latest research and guidelines | Standardized, optimized care |
| Patient-Centered Innovation | Focuses on individual patient needs | Personalized care, improved satisfaction |
Conclusion: Living with and Preventing Cardiovascular Stenosis
Managing cardiovascular stenosis well means taking steps to prevent it, finding it early, and treating it right. Knowing what causes it, its signs, and how to diagnose it helps a lot. This way, people can act early to lower the risks.
Preventing stenosis is key. Eating right, exercising often, and not smoking can really help. Also, keeping high blood pressure and high cholesterol in check is very important.
If you already have stenosis, you need to keep up with your care. See your doctor regularly, follow your treatment plan, and make healthy lifestyle changes. This way, you can manage your condition better and live a fuller life. By focusing on prevention and care, you can avoid serious problems and keep your heart healthy.
What is cardiovascular stenosis?
Cardiovascular stenosis is when a heart valve or blood vessel narrows. This can block blood flow and cause heart problems.
What are the common causes of cardiovascular stenosis?
It can happen due to aging, atherosclerosis, or being born with it. Other reasons include rheumatic fever and calcification.
What are the symptoms of cardiovascular stenosis?
Symptoms start with shortness of breath and feeling tired. Later, you might have chest pain and swollen legs. Severe cases include intense chest pain and trouble breathing.
How is cardiovascular stenosis diagnosed?
Doctors use physical exams, imaging like echocardiography, and lab tests. These help figure out how severe it is and its impact on your heart.
What are the treatment options for cardiovascular stenosis?
Treatments include medicines and lifestyle changes. Surgery like bypass grafting and valve replacement are also options. Minimally invasive procedures like TAVI and PCI are available too.
What is the difference between valvuloplasty and valve replacement surgery?
Valvuloplasty uses a balloon to open a narrowed valve. Valve replacement surgery replaces the valve with a new one, either mechanical or bioprosthetic.
Can cardiovascular stenosis be prevented?
Some risks like age and birth defects can’t be changed. But, managing high blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol can lower your risk.
How does Liv Hospital approach the treatment of cardiovascular stenosis?
Liv Hospital uses a team approach. They follow evidence-based care and focus on the patient. This ensures a well-rounded treatment plan.
What are the benefits of minimally invasive procedures for cardiovascular stenosis?
Procedures like TAVI and PCI have less recovery time and less body trauma. They also might have fewer complications than open-heart surgery.
How can patients with cardiovascular stenosis manage their condition effectively?
Effective management means following treatment plans and making lifestyle changes. Regular check-ups are also key to monitoring the condition and adjusting treatment as needed.
References
AHA Journals (Circulation): Aortic Stenosis: Recent Progress and Future Challenges (Specific DOI)
PubMed (NCBI): Unspecified Article on Valvular Heart Disease (Specific PubMed ID)



































