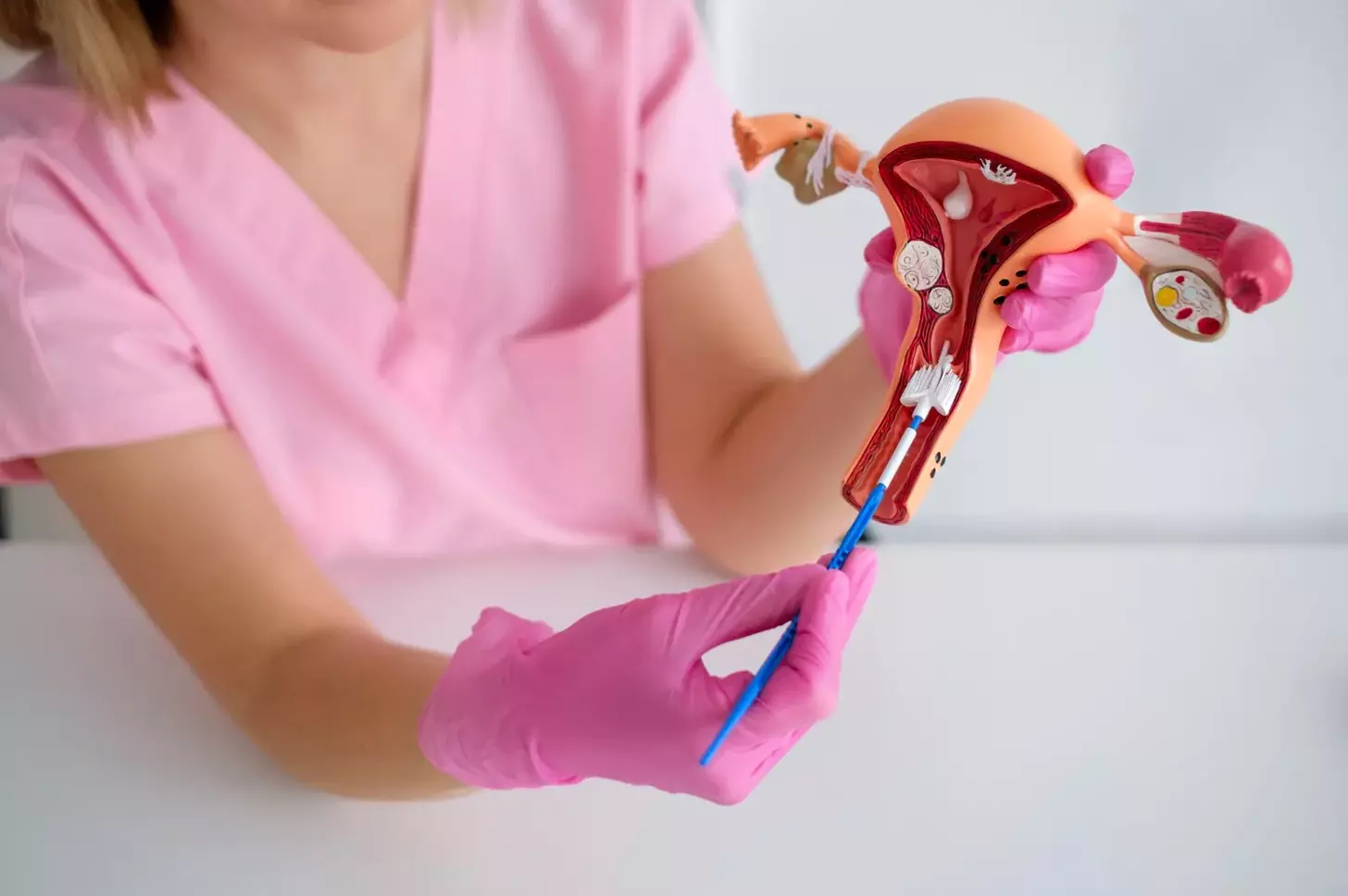
At Liv Hospital, we specialize in advanced surgical techniques that prioritize patient care and comfort. Laparoscopic surgery to remove fibroids is a minimally invasive procedure that has revolutionized the treatment of uterine fibroids.
By making small incisions in the abdomen and using specialized instruments, our expert surgeons can excise uterine fibroids with precision and care. Studies have shown that this approach results in faster recovery times, lower pain scores, and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgery.
We understand the importance of providing comprehensive care to our patients, and our team is dedicated to delivering world-class healthcare services. In this guide, we will walk you through the step-by-step process of uterine fibroid laparoscopic surgery, highlighting the benefits and best practices for this innovative procedure.
Key Takeaways
- Minimally invasive procedure with smaller incisions
- Faster recovery times and lower pain scores
- Fewer complications compared to open surgery
- Expert surgeons with specialized training
- Comprehensive care for international patients
Understanding Uterine Fibroids and Their Impact
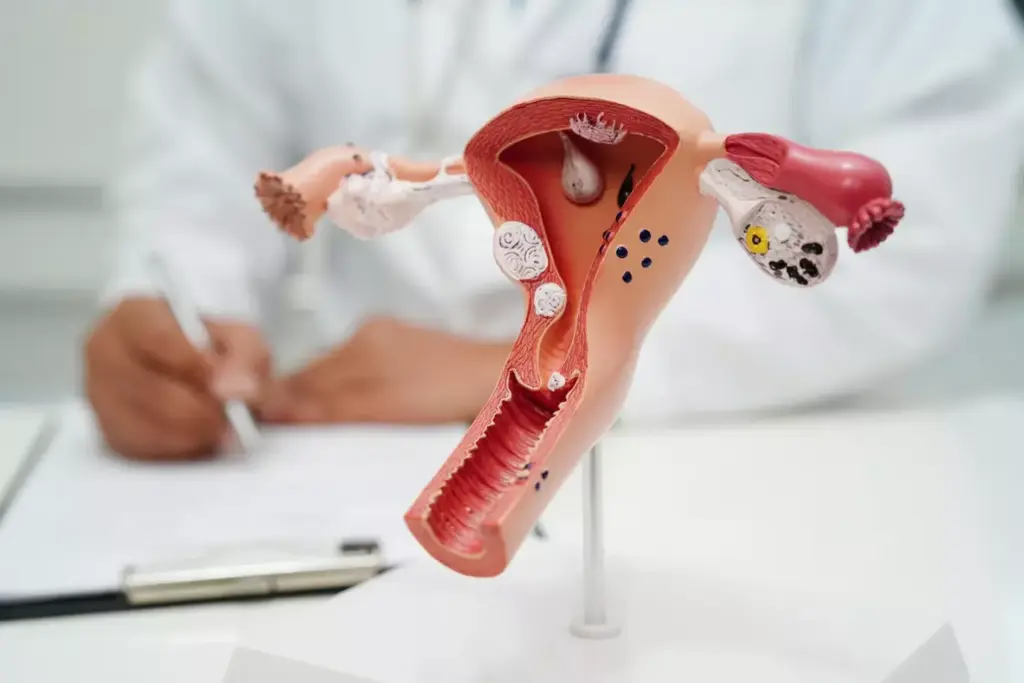
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are benign growths that develop in or around the uterus, presenting a range of challenges for women’s health. These growths are common among women of reproductive age and can cause a variety of symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and infertility.
Types and Classification of Fibroids
Fibroids are classified based on their location within or around the uterus. The main types include:
- Intramural Fibroids: These grow within the muscular uterine wall.
- Submucosal Fibroids: These project into the uterine cavity, potentially causing heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Subserosal Fibroids: These grow outward from the uterus into the pelvis.
- Pedunculated Fibroids: These are attached to the uterus by a stalk-like structure.
Understanding the type and classification of fibroids is crucial for determining the best treatment approach.
Symptoms Warranting Surgical Intervention
While not all fibroids cause symptoms, some women experience significant discomfort or health issues that may necessitate surgical intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Fertility issues or recurrent miscarriages
- Urinary frequency or constipation due to pressure on adjacent organs
When these symptoms impact a woman’s quality of life, surgical options such as laparoscopic fibroid removal may be considered.
Evidence-Based Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Approaches
Minimally invasive surgical techniques, including laparoscopic fibroid removal, have been shown to offer several benefits over traditional open surgery. These include:
- Smaller incisions, resulting in less postoperative pain and scarring
- Shorter hospital stays and recovery times
- Reduced risk of complications and adhesions
- Preservation of fertility and uterine integrity
Advantages of Laparoscopic Fibroid Removal
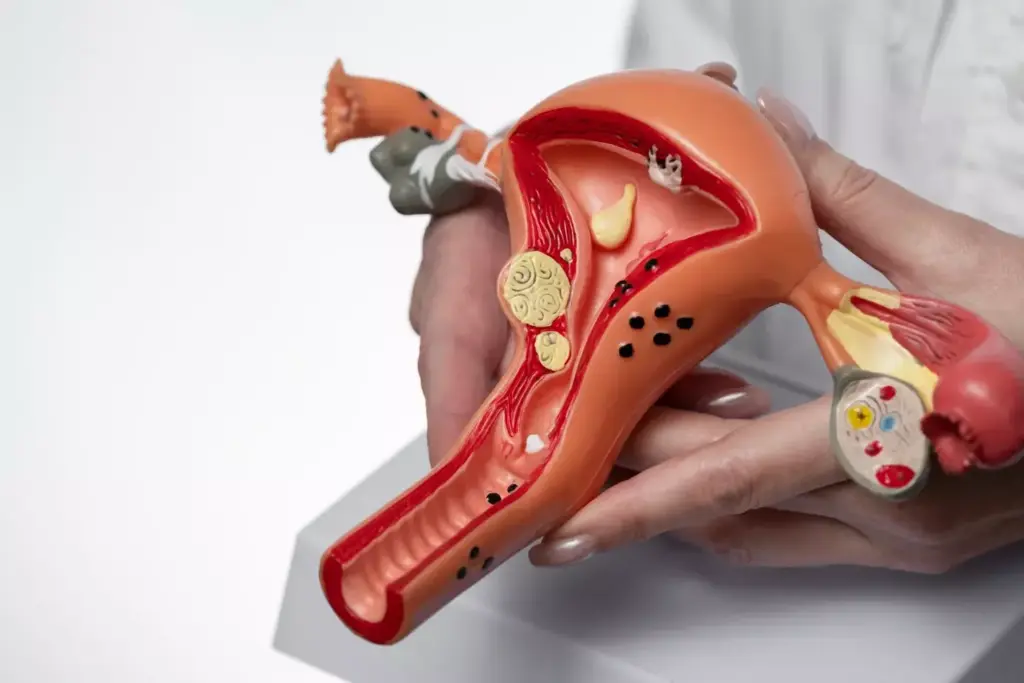
Laparoscopic fibroid removal has gained popularity due to its numerous benefits over traditional open myomectomy procedures. We will examine the key advantages of this minimally invasive approach, highlighting its benefits in terms of recovery, pain management, and cosmetic outcomes.
Comparison with Open Myomectomy Procedures
When comparing laparoscopic fibroid removal to open myomectomy, several significant differences emerge. Laparoscopic surgery involves smaller incisions, resulting in less tissue trauma and reduced risk of complications. In contrast, open myomectomy requires a larger abdominal incision, which can lead to increased postoperative pain and longer recovery times.
- Smaller incisions result in less tissue damage
- Reduced risk of postoperative complications
- Less postoperative pain
Studies have shown that laparoscopic myomectomy offers significant advantages over open myomectomy in terms of reduced blood loss, fewer postoperative complications, and shorter hospital stays. We will explore these differences in more detail below.
Recovery Time and Pain Score Differences
One of the most significant advantages of laparoscopic fibroid removal is its impact on recovery time. Patients who undergo laparoscopic surgery typically experience faster recovery times compared to those who have open myomectomy. This is due in part to the smaller incisions used in laparoscopic procedures, which result in less tissue trauma and reduced postoperative pain.
| Procedure | Average Recovery Time | Average Pain Score |
|---|---|---|
| Laparoscopic Myomectomy | 2-4 weeks | 3-5/10 |
| Open Myomectomy | 6-8 weeks | 6-8/10 |
As shown in the table above, laparoscopic fibroid removal results in significantly shorter recovery times and lower pain scores compared to open myomectomy. These differences are crucial for patients who wish to return to their normal activities quickly and with minimal discomfort.
Cosmetic and Fertility Preservation Benefits
In addition to its benefits in terms of recovery and pain management, laparoscopic fibroid removal also offers significant cosmetic advantages. The smaller incisions used in laparoscopic surgery result in less scarring, which is an important consideration for many patients. Furthermore, by minimizing tissue trauma and preserving the integrity of the uterus, laparoscopic myomectomy can help preserve fertility.
We recommend laparoscopic fibroid removal for patients who are concerned about their cosmetic appearance and wish to preserve their fertility. By choosing this minimally invasive approach, patients can benefit from a quicker recovery, less postoperative pain, and improved cosmetic outcomes.
Patient Selection Criteria for Laparoscopic Surgery
The laparoscopic approach to fibroid removal is most effective when patients are carefully chosen based on specific criteria. Proper patient selection is crucial for the success of this minimally invasive procedure.
Ideal Candidates Based on Fibroid Size and Number
Typically, the procedure is reserved for women with fewer fibroids under 10 cm in size. The number and size of fibroids are critical factors in determining the suitability of a patient for laparoscopic fibroid removal. Patients with multiple large fibroids may not be ideal candidates due to the complexity of the procedure and potential risks.
We assess the fibroid size and number to determine if a patient can undergo laparoscopic surgery safely. The location of the fibroids is also a significant factor, as it affects the complexity of the procedure.
Contraindications and Risk Assessment
Certain conditions may contraindicate laparoscopic fibroid removal. We conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential contraindications, such as severe adhesions, significant medical comorbidities, or suspicion of malignancy.
Patients with a history of multiple abdominal surgeries or significant pelvic adhesions may require a more cautious approach. Careful evaluation of the patient’s overall health and previous surgical history is essential.
Preoperative Imaging and Evaluation
Preoperative imaging plays a vital role in planning the surgical approach. We use imaging techniques such as ultrasound or MRI to assess the size, number, and location of fibroids.
This information allows us to tailor the surgical plan to the individual patient’s needs, ensuring the best possible outcome. The use of advanced imaging techniques enhances our ability to select the most appropriate candidates for laparoscopic fibroid removal.
By carefully evaluating patient selection criteria, including fibroid size and number, contraindications, and preoperative imaging, we can ensure a safe and effective laparoscopic fibroid removal procedure.
Required Equipment and Operating Room Setup
Laparoscopic fibroid removal is a complex procedure that demands specialized equipment and a meticulously planned operating room setup. To ensure a successful surgery, we must have the right tools and a well-organized environment.
Essential Laparoscopic Instruments
The laparoscopic instruments used in fibroid removal are designed for precision and minimal invasiveness. These include:
- Trocars and cannulas for safe entry into the abdominal cavity
- Laparoscopes with high-definition cameras for clear visualization
- Grasping instruments for manipulating tissues and fibroids
- Dissecting instruments for careful separation of tissues
- Suturing instruments for uterine reconstruction
Laparoscopic instruments are crucial for the success of the procedure, allowing us to perform the surgery with minimal trauma to the patient.
Advanced Energy Devices for Hemostasis
Advanced energy devices play a vital role in achieving hemostasis during laparoscopic fibroid removal. These devices include:
- Electrosurgical units (ESUs) for cutting and coagulation
- Ultrasonic dissectors for precise tissue dissection and hemostasis
- Bipolar sealing devices for effective vessel sealing
The use of advanced energy devices helps minimize bleeding and ensures a clear surgical field, enhancing the safety and efficacy of the procedure.
Surgical Team Positioning and Ergonomics
Proper positioning of the surgical team and ergonomic setup of the operating room are essential for the success of laparoscopic fibroid removal. The surgical team should be positioned to allow for optimal visualization and access to the surgical site.
We ensure that the operating room is set up to promote ergonomic working conditions, reducing fatigue and improving the precision of the surgical team. This includes the strategic placement of monitors, the positioning of the patient, and the arrangement of surgical instruments.
By combining the right equipment with a well-planned operating room setup and ergonomic considerations, we can ensure a safe and efficient laparoscopic fibroid removal procedure.
Preoperative Preparation Protocol
A well-planned preoperative preparation protocol is vital for the success of laparoscopic fibroid removal surgeries. Proper preoperative preparation involves careful consideration of several key factors to ensure a smooth and successful procedure.
Anesthesia Considerations
Anesthesia plays a crucial role in the comfort and safety of the patient during laparoscopic fibroid removal. General anesthesia is typically used, as it allows for complete control over the patient’s airway and ensures they remain comfortable throughout the procedure. We also consider the patient’s overall health, including any pre-existing medical conditions that may affect anesthesia administration.
“The choice of anesthesia technique can significantly impact the patient’s surgical experience,” as noted by experts in the field. Our team works closely with anesthesiologists to tailor the anesthesia plan to each patient’s needs.
Patient Positioning and Draping
Proper patient positioning is essential for optimal access to the surgical site. The patient is typically placed in a lithotomy position with legs supported in stirrups, allowing for easy access during the procedure. We ensure that the patient is securely positioned to prevent any movement during surgery.
Preoperative Medication Management
Effective preoperative medication management is critical to minimize risks and ensure a successful outcome. We review the patient’s current medications, adjusting or discontinuing them as necessary to prevent complications during surgery. Anticoagulant medications, for instance, are often stopped several days before the procedure to reduce the risk of bleeding.
By carefully managing preoperative medications, we can significantly reduce the risk of complications and promote a smoother recovery for our patients.
Step 1: Port Placement and Initial Access Techniques
The success of laparoscopic fibroid removal surgery hinges on the initial port placement and access techniques. This critical step sets the stage for the entire procedure, influencing both the surgeon’s ability to perform the operation effectively and the patient’s safety and recovery.
Veress Needle vs. Direct Entry Methods
The technique used for initial access can vary, with options including the Veress needle and direct entry methods. The Veress needle technique involves using a specialized needle to create pneumoperitoneum before inserting the trocar. This method is traditionally used to minimize the risk of injury to underlying structures.
Direct entry methods, on the other hand, involve inserting the trocar directly into the abdomen without prior insufflation. This approach can be faster but may carry a slightly higher risk of complications if not performed correctly.
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Veress Needle | Creates pneumoperitoneum before trocar insertion | Reduces risk of injury to underlying structures | Requires additional step for insufflation |
| Direct Entry | Inserts trocar directly into the abdomen | Faster procedure time | Potentially higher risk of complications |
Strategic Port Positioning for Optimal Access
Strategic port positioning is crucial for optimal access during laparoscopic fibroid removal. The placement of ports should be planned carefully to provide the surgeon with the best possible angles for visualization and manipulation of instruments.
Typically, the laparoscope is inserted through a port at or near the umbilicus, while additional ports are placed in the lower quadrants to allow for instrument manipulation. The exact positioning may vary depending on the patient’s anatomy and the location of the fibroids.
Establishing Pneumoperitoneum Safely
Establishing pneumoperitoneum is a critical step in laparoscopic surgery, including fibroid removal. This involves inflating the abdomen with carbon dioxide to create a clear visual field and working space.
Safety considerations during this step include monitoring the pressure of the pneumoperitoneum to avoid excessive pressure that could lead to complications. The use of a Veress needle or direct entry method must be done with caution to minimize the risk of injury to underlying structures.
By carefully managing the initial access and port placement, surgeons can significantly enhance the safety and efficacy of laparoscopic fibroid removal procedures.
Step 2: Systematic Laparoscopic Assessment and Fibroid Localization
To ensure the effective removal of fibroids, a meticulous laparoscopic examination is necessary. This step is crucial for identifying the location, size, and number of fibroids, which in turn guides the surgical approach.
Comprehensive Abdominal Survey
A comprehensive abdominal survey is the first step in the laparoscopic assessment. This involves a thorough examination of the abdominal cavity to identify any adhesions, abnormalities, or other structures that may impact the surgery.
We use a laparoscope to visualize the abdominal cavity, allowing us to inspect the uterus, ovaries, and surrounding tissues. This survey helps us to identify any potential challenges and plan the most effective approach for fibroid removal.
Uterine Manipulation Techniques
Uterine manipulation is a critical component of laparoscopic fibroid removal. We use specialized instruments to mobilize the uterus, allowing for better visualization and access to the fibroids.
Effective uterine manipulation enables us to identify the fibroids more accurately and facilitates their removal. This technique also helps in reducing the risk of complications during the surgery.
Mapping Multiple Fibroids for Sequential Removal
When multiple fibroids are present, mapping their location is essential for sequential removal. We create a mental or visual map of the fibroids, noting their size, location, and depth within the uterine wall.
| Fibroid Characteristics | Surgical Considerations |
|---|---|
| Size: Large (>5 cm) | May require multiple incisions or advanced energy devices for hemostasis |
| Location: Intramural | Requires careful dissection to avoid damaging surrounding uterine tissue |
| Number: Multiple | Sequential removal is necessary to avoid excessive bleeding and ensure complete removal |
By following a systematic approach to laparoscopic assessment and fibroid localization, we can ensure that all fibroids are identified and removed effectively, minimizing the risk of complications and promoting optimal outcomes.
Step 3: Performing Laparoscopic Fibroid Removal Technique
The third step in laparoscopic fibroid removal involves a precise technique to minimize bleeding and ensure effective fibroid enucleation. We employ a combination of methods to achieve this, starting with vasopressin injection to reduce blood loss during the procedure.
Vasopressin Injection for Hemostasis
Vasopressin injection is a critical step in laparoscopic fibroid removal, as it helps to minimize bleeding by inducing vasoconstriction. We typically inject vasopressin into the uterus around the fibroid to reduce blood flow to the area. This not only reduces the risk of significant blood loss but also provides a clearer surgical field, allowing for more precise dissection and enucleation of the fibroid.
The use of vasopressin has been shown to be effective in reducing blood loss during myomectomy. Studies have demonstrated that vasopressin injection can significantly decrease the need for blood transfusions and reduce the risk of postoperative complications.
Uterine Incision and Exposure Methods
Following vasopressin injection, we proceed with a strategic uterine incision to access the fibroid. The incision should be carefully planned to avoid damaging surrounding tissues and to ensure adequate exposure of the fibroid. We use a combination of laparoscopic instruments and energy devices to make a precise incision and to maintain hemostasis.
The choice of incision technique may vary depending on the size, location, and number of fibroids. For example, a linear incision may be used for a single, large fibroid, while multiple small incisions may be necessary for several smaller fibroids.
Enucleation Strategies by Fibroid Type
The enucleation strategy is tailored to the type and characteristics of the fibroid. For example, intramural fibroids require careful dissection to separate the fibroid from the surrounding myometrium, while subserosal fibroids may be more easily enucleated due to their location on the surface of the uterus.
We use a range of techniques to enucleate fibroids, including sharp dissection, blunt dissection, and the use of energy devices to facilitate separation of the fibroid from the surrounding tissue. The choice of technique depends on the specific characteristics of the fibroid and the surgeon’s preference.
| Fibroid Type | Enucleation Strategy | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Intramural | Sharp dissection, careful separation from myometrium | Avoid damaging surrounding myometrium |
| Subserosal | Blunt dissection, potentially easier enucleation | Be cautious of adhesions to surrounding structures |
| Submucosal | Careful dissection to avoid entering the uterine cavity | Minimize risk of uterine cavity breach |
By employing the right techniques and strategies, we can ensure safe and effective removal of fibroids during laparoscopic surgery. The combination of vasopressin injection, precise uterine incision, and tailored enucleation strategies allows for optimal outcomes and minimizes the risk of complications.
Step 4: Uterine Reconstruction for Future Fertility
Uterine reconstruction is a pivotal step in laparoscopic fibroid removal, directly influencing future fertility. This critical phase involves not only repairing the uterus but also ensuring that the reconstruction supports the patient’s reproductive goals.
Multi-Layer Closure Techniques
Effective uterine reconstruction begins with multi-layer closure techniques. This approach involves closing the uterine incision in multiple layers to ensure hemostasis and restore the uterine architecture. By doing so, we minimize the risk of complications and promote optimal healing.
The first layer typically involves closing the endometrium, followed by the myometrium, and finally, the serosa. Each layer requires precise suturing to ensure that the uterus heals properly and maintains its integrity.
Suturing Methods and Materials
The choice of suturing methods and materials plays a crucial role in uterine reconstruction. Absorbable sutures are commonly used as they reduce the risk of complications and eliminate the need for suture removal. The type of suture material used can affect the healing process, with some materials promoting better tissue repair than others.
Barbed sutures, for instance, have gained popularity for their ability to provide secure closure without the need for knot tying, reducing operative time and enhancing the security of the closure.
Preventing Adhesion Formation
Preventing adhesion formation is another critical aspect of uterine reconstruction. Adhesions can lead to complications such as bowel obstruction, chronic pain, and infertility. To mitigate this risk, surgeons often employ techniques such as meticulous hemostasis, gentle tissue handling, and the use of adhesion barriers.
By combining these strategies, we can significantly reduce the risk of adhesion formation and promote a healthier recovery for our patients.
Step 5: Specimen Retrieval and Extraction Methods
After carefully removing the fibroids, the next crucial step is specimen retrieval and extraction. This phase is critical in ensuring the success of the laparoscopic procedure and maintaining patient safety.
Contained Morcellation Techniques
Contained morcellation is a technique used to extract the removed fibroids through the laparoscopic ports. This method involves placing the specimen in a containment bag to prevent tissue dissemination within the abdominal cavity. Contained morcellation techniques have evolved to minimize the risk of tissue spillage and potential complications.
- Power morcellation within a bag
- Manual morcellation techniques
- Use of specialized morcellation devices
These techniques require precision and adherence to safety protocols to avoid complications.
Safety Considerations During Extraction
Safety during specimen extraction is paramount. Potential risks include tissue spillage, bleeding, and injury to surrounding structures. To mitigate these risks, we employ careful planning and execution.
- Careful inspection of the containment bag for integrity
- Minimizing the size of the extraction incision
- Using hemostatic agents to control bleeding
By prioritizing safety, we can reduce the risk of complications and ensure a smoother recovery for the patient.
Alternative Retrieval Approaches
In some cases, alternative retrieval approaches may be necessary. These can include extending the port site or using a posterior colpotomy for specimen extraction. The choice of retrieval method depends on various factors, including the size and number of fibroids, patient anatomy, and surgeon preference.
By understanding the various techniques and considerations for specimen retrieval and extraction, surgeons can optimize their approach to laparoscopic fibroid removal, ensuring the best possible outcomes for their patients.
Conclusion: Postoperative Care and Recovery Timeline
After undergoing laparoscopic fibroid removal, patients can expect a quicker recovery compared to open surgery. Proper postoperative care is essential for optimal recovery and outcomes. Studies have shown that laparoscopic myomectomy offers a shorter hospital stay and faster recovery, with more than 95% of patients undergoing the procedure in under 3 hours.
We emphasize the importance of postoperative care in achieving favorable outcomes, as highlighted in a study on laparoscopic myomectomy outcomes. Pregnancy outcomes after laparoscopic myomectomy are generally favorable, with a pregnancy rate comparable to or even higher than that associated with abdominal myomectomy.
By choosing laparoscopic fibroid removal, patients can benefit from a minimally invasive approach that reduces postoperative pain and promotes a faster return to normal activities. Our team is committed to providing comprehensive care and support throughout the recovery process.
What is laparoscopic fibroid removal?
Laparoscopic fibroid removal is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove uterine fibroids. It involves making small incisions in the abdomen to insert a laparoscope and surgical instruments, allowing for the removal of fibroids with less postoperative pain and quicker recovery times.
What are the benefits of laparoscopic fibroid removal compared to open myomectomy?
Laparoscopic fibroid removal offers several benefits, including less postoperative pain, quicker recovery times, and improved cosmetic outcomes. It also preserves fertility by minimizing damage to the uterus.
Who is a candidate for laparoscopic fibroid removal?
Ideal candidates for laparoscopic fibroid removal are patients with symptomatic fibroids, particularly those who wish to preserve their fertility. The size and number of fibroids, as well as the patient’s overall health, are factors considered when determining candidacy.
What is the role of preoperative imaging in laparoscopic fibroid removal?
Preoperative imaging, such as ultrasound or MRI, is crucial for planning and executing a successful laparoscopic fibroid removal. It helps identify the size, number, and location of fibroids, allowing surgeons to develop an effective surgical strategy.
How is laparoscopic fibroid removal performed?
The procedure involves several steps, including port placement and initial access, systematic laparoscopic assessment and fibroid localization, laparoscopic fibroid removal, uterine reconstruction, and specimen retrieval and extraction.
What is the recovery time for laparoscopic fibroid removal?
Recovery times vary, but most patients can expect to return to normal activities within a few weeks. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure typically results in less postoperative pain and quicker recovery compared to open surgery.
Are there any risks or complications associated with laparoscopic fibroid removal?
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks and potential complications, including bleeding, infection, and adhesions. However, these risks are minimized with proper patient selection, surgical technique, and postoperative care.
Can laparoscopic fibroid removal preserve fertility?
Yes, laparoscopic fibroid removal is designed to preserve fertility by minimizing damage to the uterus and surrounding tissues. The procedure involves careful removal of fibroids and reconstruction of the uterus to promote optimal healing and fertility.
What is the difference between laparoscopic myomectomy and laparoscopic fibroid removal?
Laparoscopic myomectomy and laparoscopic fibroid removal are often used interchangeably to describe the surgical removal of uterine fibroids using a minimally invasive approach.
How are fibroids removed during laparoscopic surgery?
Fibroids are removed using a combination of laparoscopic instruments and techniques, including enucleation and morcellation. The goal is to safely and effectively remove the fibroids while preserving the surrounding uterine tissue.
What is contained morcellation?
Contained morcellation is a technique used to remove fibroids or other specimens from the body in a contained manner, minimizing the risk of tissue dissemination and potential complications.




































