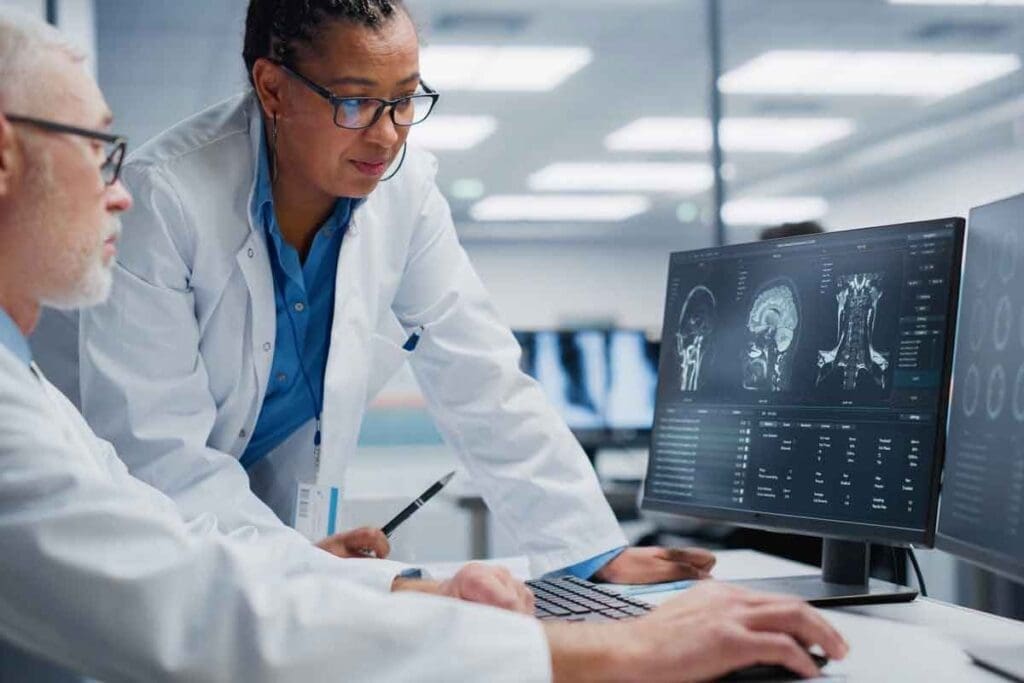
A brain aneurysm is a weak spot in an artery in the brain. It often shows up at the base of the skull. Fixing a brain aneurysm needs careful planning. This includes looking at the aneurysm’s size, where it is, and the patient’s health.
At Liv Hospital, we treat aneurysms with surgical clipping or endovascular coiling. We pick the best method for each patient. Our team aims to give top-notch care with full support for international patients.
Key Takeaways
- Repairing a brain aneurysm involves either surgical clipping or endovascular coiling.
- The choice of treatment depends on the aneurysm’s size, location, and patient factors.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to providing world-class healthcare with full support.
- Our team uses advanced medical techniques to treat brain aneurysms.
- Patient-centered care is our top priority in treating aneurysms.
Understanding Brain Aneurysms
It’s key for both patients and doctors to understand brain aneurysms. This condition is serious and affects many people each year.
What is a Brain Aneurysm?
A brain aneurysm is a bulge in a brain blood vessel. It can burst, causing serious problems. This condition often has no symptoms until it bursts, making it a hidden danger.
We’ll dive into what causes brain aneurysms, risk factors, and symptoms. This will help us understand this complex issue better.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Many things can lead to brain aneurysms. Genetics are a big factor, with a family history increasing risk. Other factors include:
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- Age, between 30-60 years
- Gender, with women more at risk
Knowing these risk factors helps in early detection and prevention. A medical expert notes,
“Identifying and managing risk factors can significantly reduce the likelihood of aneurysm rupture.”
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact |
| Smoking | Damages blood vessels | High |
| High Blood Pressure | Increases pressure on blood vessels | High |
| Family History | Genetic predisposition | Moderate to High |
Signs and Symptoms of Brain Aneurysms
Brain aneurysms usually don’t show symptoms until they burst. Symptoms include:
- Severe headache, often described as “the worst headache” ever experienced
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion or altered mental state
- Seizures
It’s important to recognize these symptoms quickly. We stress the need to seek medical help right away if these symptoms are seen.
Diagnosis and Evaluation Process

Diagnosing brain aneurysms involves many steps. It’s important to find out if an aneurysm exists, how big it is, and where it’s located. This information helps doctors decide the best treatment. We use different tools and methods to make sure we get a complete picture.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Imaging is key in finding and diagnosing brain aneurysms. We mainly use:
- CT Scans: These scans are often the first choice in emergencies. They help spot bleeding in the brain quickly.
- MRI: MRI gives detailed views of the brain and its blood vessels. It helps find aneurysms and understand their size and location.
- Cerebral Angiography: This test involves injecting a contrast agent into blood vessels. It shows the aneurysm and how it relates to nearby vessels.
Aneurysm Classification Systems
Aneurysms are sorted based on their size, location, and shape. The main systems for classification are:
- Size Classification: Aneurysms are divided into small (<5 mm), medium (5-15 mm), large (15-25 mm), and giant (>25 mm).
- Location-Based Classification: Aneurysms are grouped by where they are in the brain’s blood vessels, like the front or back.
Pre-surgical Assessment Criteria
Before surgery, we do a detailed check-up. We look at the patient’s health, the aneurysm’s details, and the risk of it bursting. This helps us choose the best treatment, like clipping or coiling.
The main things we consider are:
- The size and location of the aneurysm
- The patient’s age and overall health
- Any other health issues the patient might have
Treatment Decision Factors
Choosing the right treatment for brain aneurysms is complex. It involves looking at the aneurysm itself and what’s best for the patient. Doctors carefully weigh different factors to pick the best option.
Aneurysm Size, Shape, and Location
The size, shape, and where the aneurysm is located are key. Larger aneurysms are riskier and might need more intense treatment. The aneurysm’s shape can also affect treatment choices.
For example, aneurysms with a wide neck or complex shape can be harder to treat with endovascular methods.
A study found that the size and location of the aneurysm are vital. They determine the risk of rupture and the treatment’s success.
“Aneurysm size and location are key factors in treatment planning, as they directly impact the risk of rupture and the complexity of the procedure”
The aneurysm’s location in the brain is also important. Some spots are easier to reach for surgery or endovascular coiling than others.
Patient-Specific Considerations
Each patient’s health and preferences are important in deciding treatment. For instance, older patients or those with health issues might prefer endovascular treatments over surgery.
- Age and overall health status
- Presence of comorbid conditions
- Patient preferences and values
- Previous medical history, including any history of aneurysms or other vascular conditions
Ruptured vs. Unruptured Aneurysms
Ruptured aneurysms need quick action to stop bleeding. Unruptured ones might be watched or treated later, depending on their size and the patient’s risk.
Urgent treatment is needed for ruptured aneurysms to keep the patient stable. The choice between surgery and endovascular coiling depends on the aneurysm’s shape and the patient’s health.
The Multidisciplinary Team Approach
Brain aneurysm management benefits from a team effort. Neurosurgeons, neuroradiologists, and other experts work together. This ensures the best treatment plan for the patient.
A team review helps evaluate the aneurysm and the patient’s situation. It leads to better decision-making on the treatment.
How to Repair Brain Aneurysm: Surgical Clipping Procedure
Fixing brain aneurysms through surgical clipping needs careful planning and skill. This method uses a metal clip at the aneurysm’s base to stop bleeding or rupture. We’ll explain the steps of surgical clipping, from preparation to clip placement.
Pre-operative Preparation and Planning
Before surgery, patients get a detailed check-up. This includes:
- Imaging Studies: Angiography, MRI, or CT scans to see the aneurysm’s size and location.
- Medical History Review: Looking at the patient’s medical history for any risks.
- Multidisciplinary Team Discussion: Neurosurgeons, radiologists, and others discuss the best surgery plan.
Step-by-Step Craniotomy Process
The surgery starts with a craniotomy. This involves:
- Incision and Bone Removal: A precise scalp incision and skull removal to reach the brain.
- Dura Mater Opening: Opening the dura mater, the brain’s protective membrane.
- Brain Tissue Retraction: Moving brain tissue to see the aneurysm.
Aneurysm Isolation and Clip Placement Techniques
After exposing the aneurysm, the next steps are:
- Aneurysm Dissection: Dissecting the aneurysm from surrounding tissues.
- Clip Placement: Putting a metal clip across the aneurysm’s neck to block it.
Intraoperative Monitoring and Assessment
Intraoperative monitoring is key during surgery. This includes:
- Neurophysiological Monitoring: EEG or SSEP to watch brain activity.
- Angiography: Intraoperative angiography to check if the aneurysm is blocked and nearby vessels are open.
With careful planning and precise surgery, clipping is a very effective way to treat brain aneurysms.
Endovascular Coiling Techniques
Endovascular coiling has changed how we treat cerebral aneurysms. It’s a precise and less invasive method. This has made neurosurgery better, giving patients a new option instead of old surgery methods.
Patient Preparation for Endovascular Procedures
Before starting endovascular coiling, patients get a full check-up. We look at their health and the aneurysm’s details. We focus on:
- Doing detailed imaging to see the aneurysm’s size, shape, and where it is
- Checking the patient’s medical history for any risks or things they can’t do
- Talking about the procedure’s risks and benefits with the patient and their family
Catheterization Process and Navigation
The catheterization process is about guiding a tiny catheter to the aneurysm. It needs:
- Clear angiographic images to guide the catheter
- Advanced catheter tech for safe and accurate movement
- Watching in real-time to adjust the catheter as needed
We use the latest imaging tech to make the catheterization process safe and precise.
Coil Deployment Methods
After placing the catheter, we put coils in the aneurysm to stop bleeding. The coil deployment method includes:
- Picking the right coil size and type for the aneurysm
- Slowly putting the coils in the aneurysm sac
- Watching how the aneurysm reacts to the coils and making changes if needed
Balloon and Stent-Assisted Coiling
Sometimes, we use balloon or stent-assisted coiling to help the coils stay in place. This method involves:
- Using a balloon to temporarily support the vessel wall during coiling
- Putting a stent in to keep the vessel stable and prevent coil movement
Choosing between balloon and stent-assisted coiling depends on the aneurysm and the patient’s needs.
| Technique | Success Rate | Complication Rate |
| Simple Coiling | 85% | 10% |
| Balloon-Assisted Coiling | 90% | 8% |
| Stent-Assisted Coiling | 92% | 7% |
The table shows that choosing the right coiling technique matters a lot. We think carefully about each patient’s situation to pick the best treatment.
Advanced and Emerging Repair Techniques
The treatment of brain aneurysms is changing fast. New techniques offer hope for those with complex cases. Medical science is advancing, leading to new ways to tackle aneurysms.
Hybrid Surgical-Endovascular Procedures
Hybrid procedures mix surgery and endovascular methods. This gives a better treatment option for tough aneurysms. Neurosurgeons can now handle cases that were once too hard.
Key benefits of hybrid procedures include:
- Increased flexibility in treatment planning
- Improved outcomes for complex aneurysms
- Reduced risk of complications
Bypass Techniques for Complex Aneurysms
Bypass techniques offer a new way to treat complex aneurysms. They create a detour around the aneurysm to keep blood flowing.
| Bypass Technique | Description | Application |
| STA-MCA Bypass | Superficial temporal artery to middle cerebral artery bypass | Used for complex aneurysms in the MCA territory |
| EC-IC Bypass | External carotid to internal carotid bypass | Applied for aneurysms involving the ICA |
Innovations in Aneurysm Treatment
The field of aneurysm treatment is seeing big changes. Advances in materials and imaging are helping us treat aneurysms better.
Some of the emerging trends include:
- Flow-diverting stents with improved design and materials
- Advanced imaging techniques for better visualization
- Robot-assisted surgery for enhanced precision
Post-Procedure Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovering from brain aneurysm repair is key to a good outcome. We know it’s tough, but with the right care, patients can get through it. They can do well with the right watch and help.
Immediate Recovery Period in ICU
Patients start their recovery in the ICU. Here, they’re watched closely for any problems. Close monitoring lets our team fix issues fast, helping them start their recovery right.
Patients are often sedated to ease pain and stress. As they get better, we adjust their care to keep them safe and comfortable.
Potential Complications and Management
Complications can happen, but our team is ready to handle them. Issues like vasospasm, hydrocephalus, and infection are possible. We use the latest tools and methods to reduce these risks.
| Complication | Description | Management Strategy |
| Vasospasm | Narrowing of blood vessels | Calcium channel blockers, hydration |
| Hydrocephalus | Fluid accumulation in the brain | Ventricular drainage, shunting |
| Infection | Bacterial or viral infection | Antibiotics, supportive care |
Long-term Follow-up Protocol
Regular check-ups are key to tracking recovery and spotting problems early. We schedule visits and scans to check on the aneurysm and brain health.
Our follow-up plans are made just for each patient. We consider their aneurysm and treatment details.
Physical and Cognitive Rehabilitation
Rehab is important for getting strength and brain function back. We team up with experts to create a rehab plan that fits each patient’s needs.
Physical therapy helps with movement and strength. Cognitive rehabilitation helps with memory and thinking skills.
With careful watching, managing complications, and rehab, we help patients recover well. We aim for the best results for them.
Outcomes and Success Rates
Looking at the outcomes and success rates of aneurysm repair is key to making good treatment choices. The success of treating brain aneurysms depends on many things. These include the size and location of the aneurysm and the patient’s health.
Factors Affecting Surgical Success
Several factors determine the success of surgery for brain aneurysms. Aneurysm characteristics like size and location are very important. For example, aneurysms at the brain’s base are harder to treat than those in easier-to-reach spots.
Things like the patient’s age, health, and other medical conditions also matter a lot. Pre-existing conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes can make surgery and recovery harder.
Comparative Effectiveness of Treatment Options
There are different ways to treat brain aneurysms, each with its own success rate. Surgical clipping and endovascular coiling are the main methods. Studies show that the treatment choice greatly affects how well a patient does, with some methods working better for certain aneurysms.
- Surgical clipping is often chosen for aneurysms that are easy to reach and have the right shape and size.
- Endovascular coiling is used for aneurysms that are hard to get to surgically or for patients at high risk for surgery complications.
Quality of Life After Aneurysm Repair
After aneurysm repair, how well a patient does is very important. Successful treatment not only saves lives but also aims to help patients get back to how they were before. Rehabilitation is key in helping patients regain their mental and physical abilities.
Many things affect how well a patient does after treatment. These include their health before the aneurysm, any complications during or after surgery, and how well they do in rehab.
Long-term Angiographic and Clinical Outcomes
It’s important to follow up over the long term to see how well aneurysm repair holds up. Angiographic outcomes check for any aneurysm growth or recurrence. Clinical outcomes look at the patient’s overall health and how well they can function.
Regular check-ups and imaging studies are vital for keeping an eye on treatment success over time. They help catch any problems early.
Conclusion
Fixing a brain aneurysm needs a team effort. This team uses the newest ways to fix it, like surgery and endovascular coiling. We’ve seen how important it is to have a team working together for the best results.
Patients can live better lives after fixing a brain aneurysm. The treatment is complex, so we keep working to make it better. Knowing about treatments like endovascular coiling helps patients make good choices for their care.
We’re always getting better at treating aneurysms. Our aim is to give top-notch care to everyone. We want patients to have the best chance at a good life after treatment.
FAQ
What is a brain aneurysm and how is it diagnosed?
A brain aneurysm is a serious condition that can be deadly if it bursts. Doctors use CT scans, MRI, and angiography to find it. They also look at how the patient feels.
What are the common causes and risk factors associated with brain aneurysms?
Genetics, high blood pressure, and smoking can cause brain aneurysms. Knowing these risks helps find and treat them early.
How do doctors determine the best treatment approach for a brain aneurysm?
Doctors look at many things to choose the best treatment. They consider the aneurysm’s size, shape, and where it is. They also think about the patient’s health and what they need. A team of doctors works together to decide the best plan.
What is surgical clipping, and how is it performed?
Surgical clipping is a complex surgery. It involves opening the skull, finding the aneurysm, and clipping it to stop bleeding. The doctor uses special tools and monitors the patient closely during the surgery.
What is endovascular coiling, and how does it differ from surgical clipping?
Endovascular coiling is a less invasive method. It involves putting coils into the aneurysm to stop bleeding. It’s a different option from surgical clipping, with its own risks and recovery time.
What are the possible complications and risks of brain aneurysm repair?
Complications can include bleeding, stroke, and brain damage. Knowing these risks helps patients make informed choices and get the right care after surgery.
What is the recovery process like after aneurysm repair?
Recovery starts in the ICU right after surgery. Then, there’s long-term care and rehab. Rehab helps patients get back to normal physically and mentally.
How effective are different treatment options for brain aneurysms, and what are the long-term outcomes?
The success of treatments depends on the aneurysm and the patient’s health. Long-term results can vary. They depend on how well the patient does after surgery and the chance of the aneurysm coming back.
What advancements are being made in the field of aneurysm treatment?
New techniques and technologies are being developed for aneurysm treatment. Hybrid procedures and other new methods aim to improve results.
How can patients and families prepare for brain aneurysm treatment?
Patients and families should learn about the diagnosis, treatment, and recovery. A team of doctors can offer support and guidance throughout the treatment.
Reference
- ScienceDirect. (2025). Advances in screening and management of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Retrieved October 2025, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1474442225002650


































