
A pulled groin muscle, also known as a groin strain, happens when the muscles inside the thigh get stretched, injured, or torn. This injury can cause a lot of pain and tenderness in the groin area. It makes it hard to move freely and get back to sports.
At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to treat and recover from a groin strain properly. A groin strain is an injury to the area where the abdomen meets the leg. It affects the inner thigh muscles (adductors) that attach to the pubic bone. For more information on aftercare, you can visit trusted health resources.
Knowing how to treat a pulled muscle in the groin is key to getting better. We will show you the recovery steps. We aim to provide the best care to help you get back to your normal activities.
Key Takeaways
- Rest and protect the injured area for 1 to 2 weeks.
- Avoid intense activities while pain persists.
- Apply ice or heat as directed to reduce swelling and pain.
- Use crutches if prescribed and wear supportive clothing.
- Follow-up care is key for a successful recovery.
Understanding Groin Pull Injuries
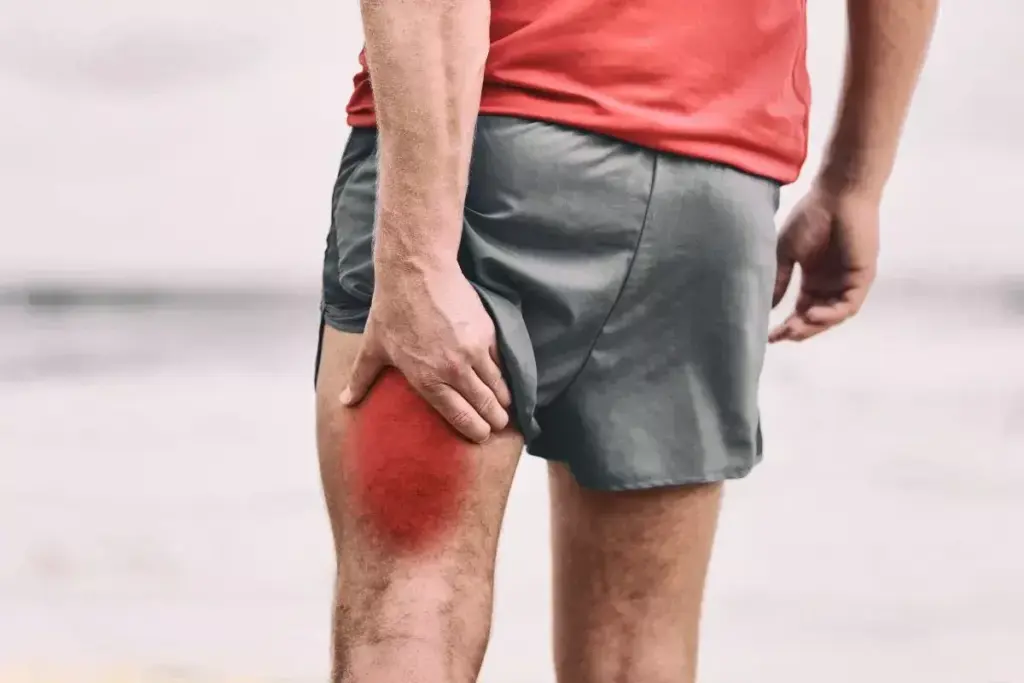
A groin pull injury, also known as a groin strain, happens when the muscles in the groin area get stretched or torn. This injury is common among athletes, mainly those in sports that need quick movements, sprinting, or sudden direction changes.
What Is a Groin Strain?
A groin strain affects the muscles of the inner thigh, the adductor group. These muscles help bring the legs together. When they get overstretched or torn, it causes pain and tenderness in the groin area. This pain can feel like a dull ache or sharp pain, depending on how severe the strain is.
The main signs include pain and tenderness in the groin area. In bad cases, there might be swelling or bruising. Knowing these symptoms is key to diagnosing and treating the injury right.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Groin strains often come from activities with sudden direction changes, sprinting, or kicking. Sports like soccer, hockey, and football are big culprits. Other risks include poor flexibility, not warming up enough, and muscle fatigue. Athletes who have had groin injuries before are more likely to get them again.
Prevention is important. Knowing these causes and risks helps us find ways to lower the chance of groin strains.
Sports with Highest Injury Rates
Certain sports have more groin injuries because of their physical demands. These include:
- Soccer
- Hockey (both field and ice)
- Football
- Rugby
- Basketball
Athletes in these sports need to watch their groin health closely. They should add preventive steps to their training.
Recognizing Groin Pull Symptoms

It’s important to know the signs of a pulled groin to avoid more harm and speed up healing. When we get a groin strain, we might notice several symptoms. These signs tell us we need to take care of ourselves and manage the injury right.
Primary Pain Indicators
The main sign of a groin pull is pain, usually in the groin or inner thigh. This pain can be mild or very strong. It often gets worse when we do things that move our hips, like walking or climbing stairs.
Some people might feel sharp pain or muscle spasms in their groin or lower belly. This happens when they try to contract or stretch the muscles that are hurt.
Common pain indicators include:
- Pain or tenderness in the groin or inner thigh area
- Sharp pain or spasms during physical activities
- Discomfort when bringing the legs together or during hip movements
Visual and Physical Symptoms
Other signs can show up too. These include swelling, bruising, or a popping sound when we get hurt. In serious cases, we might see a visible deformity or not be able to move our leg right.
Additional symptoms to watch for:
- Swelling or inflammation in the groin area
- Bruising or discoloration
- A feeling of weakness or instability in the hip or groin
Grading the Severity of Strains
Groin strains are graded from 1 to 3 based on how bad the injury is. Knowing the grade helps us figure out the best treatment and recovery plan.
The grading system includes:
- Mild strain (Grade 1): A few muscle fibers are torn, causing mild pain and minimal loss of function.
- Moderate strain (Grade 2): A significant number of muscle fibers are torn, leading to moderate pain, swelling, and reduced strength.
- Severe strain (Grade 3): A complete tear of the muscle, resulting in significant pain, swelling, and loss of function.
By knowing these symptoms and the severity of the injury, we can get the right medical help. It’s also good to know that swimming can help in recovery. It’s low-impact and keeps our heart rate up without hurting our groin too much.
Immediate Treatment for Pulled Groin Muscles
When you get a pulled groin muscle, acting fast is key. The first steps you take can really help your recovery. They can also lower the chance of getting hurt again.
The RICE Method Explained
The RICE method is a well-known way to treat injuries like groin pulls. It stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Doctors say using RICE in the first 24 to 48 hours can help a lot.
- Rest: Stay away from things that make the pain worse.
- Ice: Use ice packs on the hurt area for 15-20 minutes, a few times a day.
- Compression: A compression bandage can help lessen swelling.
- Elevation: Keep the hurt leg higher than your heart to cut down swelling.
Doctors say the RICE method is key for managing pain and swelling early on. Learn more about groin pull treatment.
Pain Management Options
Controlling pain is a big part of treating a pulled groin muscle. You can use over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. They can help with pain and swelling.
Best Positions for Reducing Strain
Finding the right position to ease strain on the groin is important. Try lying down with your hurt leg a bit higher to help with swelling and pain. Also, stay away from positions that make it worse.
By taking these steps right away, you can manage your groin pull well. This helps you on the path to a full recovery.
Long-Term Recovery Process
Healing a pulled groin muscle takes time, depending on how bad the injury is. Knowing how long it will take and what steps to take can help you plan your recovery.
Timeline Expectations by Severity
The time it takes for a groin strain to heal changes with the injury’s severity. Mild to moderate strains usually need 4 to 8 weeks to heal. More serious injuries might take months. It’s important to be patient and not rush to avoid re-injury.
Doctors say a good recovery plan is key. It should match the injury’s needs. This helps the muscle heal right and get strong again.
Rehabilitation Exercises
Exercises are key in the recovery process. They help get flexibility, strength, and function back. A physical therapist can create a plan that fits your needs and updates it as you heal.
- First, you’ll do gentle stretches to get flexibility back.
- When you’re healing, you’ll start strengthening exercises to build muscle strength and stability.
- Later, you’ll do exercises that are like your daily activities or sports to get ready for them.
Safe Activities During Recovery
While you’re recovering from a groin strain, stay away from activities that might make it worse. But don’t stay completely inactive, as it can make your muscles stiff and weak. Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling are good choices if they don’t hurt.
Always listen to your body and stop if you feel pain or discomfort. Slowly getting back to full activity with a doctor’s help can prevent injury and help you recover well.
Conclusion
Treating a pulled groin muscle needs a full plan. This plan helps with both quick relief and long-term healing. We talked about knowing the signs of a groin pull, understanding how bad it is, and using the RICE method first.
It’s key to handle pain well and do exercises that match your healing stage. This helps the healing process go smoothly and quickly.
So, how do you treat a pulled groin muscle? We say be patient, take good care, and follow a solid rehab plan. If done right, these injuries can fully heal. This lets people get back to their usual activities without pain.
By following these steps and watching for groin pull signs, we can help people recover well. Our method mixes medical knowledge with caring support. It helps people on their way to getting better.
FAQ
What is a groin strain?
Is swimming good for a groin strain?
What is the best position for a groin strain?
How do you treat a pulled groin muscle?
What are the symptoms of a torn groin?
How long does it take to recover from a groin pull?
What are the best rehabilitation exercises for a groin strain?
Can I continue to exercise with a pulled groin muscle?
How can I prevent groin strains in the future?
References
The Lancet. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(98)03340-6/fulltext










