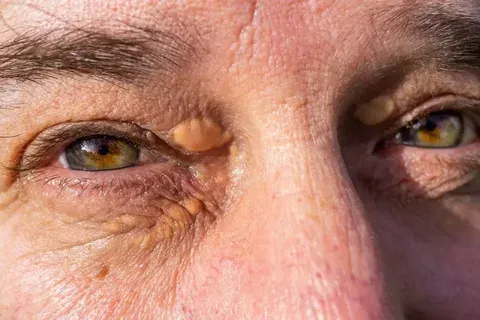
Eruptive xanthomas are harmless skin spots that warn of a serious health issue. They show up when triglyceride levels get too high. This can lead to serious problems like pancreatitis or heart disease.
Understanding the cause and implementing an effective treatment plan is key. We’ll show you how to manage eruptive xanthomas step by step. We’ll focus on fixing the lipid disorder at the root.
By tackling the cause, we can stop more problems and boost health. Our guide will cover the newest treatments and lifestyle changes. These will help you manage xanthoma eruptive conditions well.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the link between eruptive xanthomas and hypertriglyceridemia is vital for treatment.
- A step-by-step guide can help manage the condition and prevent complications.
- Addressing the underlying lipid disorder is key to treating xanthoma eruptive conditions.
- Latest medical treatments and lifestyle changes can significantly improve health outcomes.
- Early intervention is critical to preventing life-threatening conditions such as pancreatitis.
Understanding Eruptive Xanthomas and Their Causes

To tackle eruptive xanthomas, we first need to comprehend their causes. These skin lesions are linked to metabolic disorders, like high triglycerides.
What Are Eruptive Xanthomas?
Eruptive xanthomas are sudden skin eruptions. They appear as dome-shaped papules, often on the elbows, knees, and buttocks. These papules are yellowish and may have an erythematous halo. They are often seen in people with high triglycerides.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can lead to eruptive xanthomas, including:
- Hypertriglyceridemia: High triglycerides in the blood.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Uncontrolled diabetes can cause high triglycerides.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of high triglycerides.
- Alcohol Consumption: Drinking too much alcohol can raise triglyceride levels.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some genetic conditions can affect lipid metabolism.
Recognizing the Symptoms
It’s important to recognize the symptoms of eruptive xanthomas early. The main symptom is the sudden appearance of small, dome-shaped papules on the skin. These papules are usually on the extensor surfaces and may be itchy or tender.
If you notice unusual skin lesions or symptoms, see a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can manage the condition and address metabolic disorders.
Step-by-Step Treatment Plan for Eruptive Xanthomas
Treating eruptive xanthomas needs a detailed plan. It includes medical treatments and lifestyle changes. We suggest starting with managing high triglycerides, a common cause.
Lipid-lowering drugs are often used. Eating less fat and more omega-3 fatty acids can also help. In serious cases, plasmapheresis may be needed to clear excess lipids.
We also recommend lifestyle changes. These include staying at a healthy weight, exercising, and not drinking too much alcohol. Following this plan can help manage the condition and prevent complications.
For more details on xanthomas causes and photos, check out trusted medical sources. Knowing about the condition and its treatments is key to managing xenthoma and zanthoma effectively.
FAQ
What are eruptive xanthomas?
Eruptive xanthomas are small, yellowish bumps on the skin. They happen when lipids build up. High triglycerides in the blood often cause them.
What causes eruptive xanthomas?
They usually come from a lipid disorder like high triglycerides. Diabetes, obesity, and some genetic disorders can also play a part.
How are eruptive xanthomas treated?
Treatment focuses on the lipid disorder. This might mean changing your diet and exercising more. Medications can also help lower triglycerides.
Can eruptive xanthomas be prevented?
Yes, you can prevent them by managing your metabolism. Eat well, exercise, and check your lipid levels regularly.
Are eruptive xanthomas a sign of a serious health condition?
They can signal a lipid disorder. If not treated, this can lead to heart disease and other serious issues.
How can I manage my lipid levels to prevent eruptive xanthomas?
To manage lipids, eat healthy, exercise, and take your meds. Also, keep an eye on your lipid profiles.
What is the role of diet in managing eruptive xanthomas?
A good diet is key. Cut down on saturated fats, cholesterol, and simple carbs to lower triglycerides.
Can eruptive xanthomatosis be treated with medication?
Yes, drugs like fibrates, statins, and omega-3s can help control triglycerides and manage the condition.
What are the symptoms of eruptive xanthomatosis?
Symptoms include small, yellowish bumps on the skin. They often appear on the buttocks, thighs, or knees.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11927605/






















