A swollen knee without pain might seem less serious than one with pain. But, it’s important to get it checked by a doctor right away. This swelling happens when fluid builds up in the joint. It can mean there’s something going on under the surface.
Knee effusion is when too much fluid gathers in or around the knee. It can come from small injuries, long-term health issues, or inflammation. At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch, focused care for your knee problems.
It’s key to know why your knee swells without pain and how to handle it. We tailor our care to meet your specific needs.
Key Takeaways
- Swollen knee without pain can be a sign of an underlying condition.
- Knee effusion is caused by abnormal fluid accumulation within or around the knee joint.
- Various factors can lead to knee effusion, including minor injuries and chronic health conditions.
- Liv Hospital offers personalized orthopedic care for patients with knee effusion.
- Early evaluation and treatment are key to avoiding serious problems later.
Understanding Puffy Knee No Pain Condition
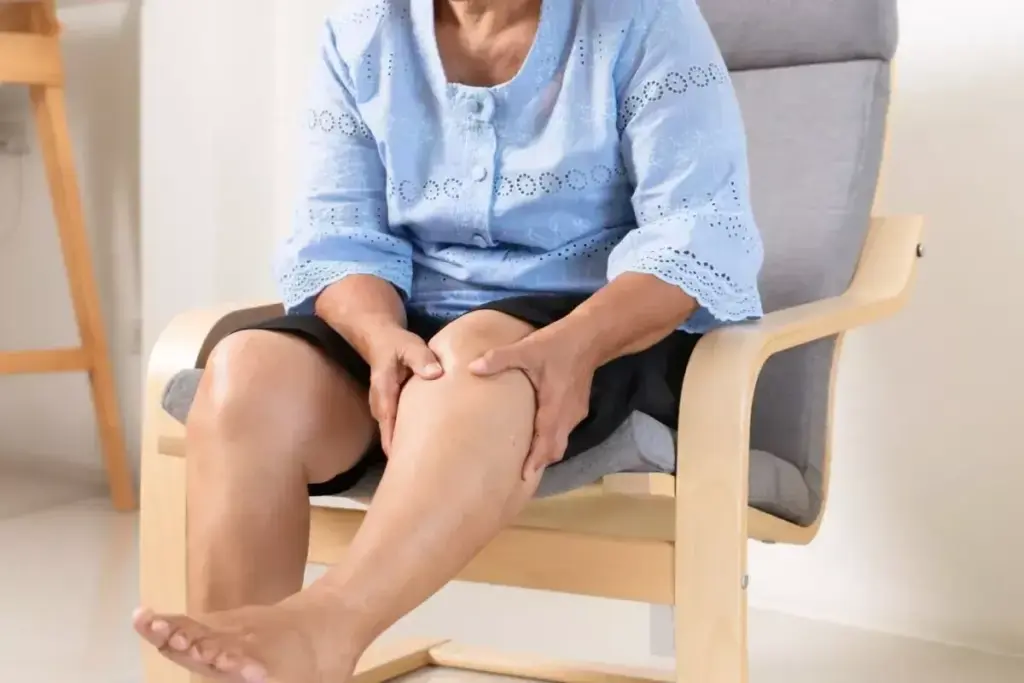

When your knee swells without pain, finding the cause is key. Knee effusion, or extra fluid in the knee, needs attention. Some fluid helps the knee move smoothly, but too much causes swelling.
What is Knee Effusion?
Knee effusion happens when too much fluid builds up in the knee. It can come from infections, inflammation, or injuries. This extra fluid can press on tissues, causing swelling. Remember, knee effusion is a sign of something else, not a disease itself.
To understand knee effusion better, let’s look at why it happens. Here’s a table of common causes:
| Cause | Description |
| Infection | Bacterial or viral infections can cause fluid accumulation in the knee. |
| Inflammation | Conditions like arthritis can lead to inflammation and subsequent effusion. |
| Overuse or Injury | Trauma or repetitive strain on the knee can cause swelling. |
| Tumors | In rare cases, tumors can cause knee effusion. |
Common Causes of Painless Knee Swelling
Painless knee swelling can come from many things. Overuse or injury is a big reason. Conditions like osteoarthritis can also cause swelling without pain. Sometimes, tumors or cysts can swell the knee. Knowing these causes helps find the right treatment.
We’ll look at treatments later. For now, it’s important to see a doctor for painless knee swelling. They can find the cause and suggest how to manage it.
Diagnosing Swollen Knee Without Pain
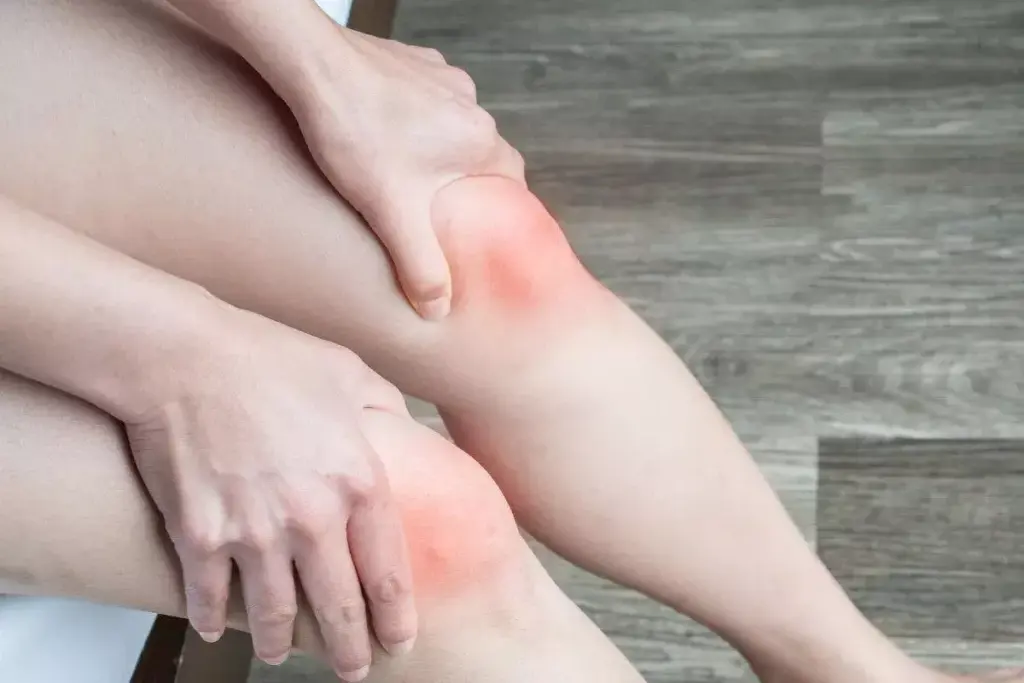
Diagnosing a swollen knee without pain is tricky. We use a mix of self-checks and doctor’s tests to find the cause.
Self-Assessment Techniques
Start by checking your knee for swelling. Look for any changes in how it moves or feels. Try bending and straightening your knee to see how far it goes.
Also, watch for warmth or redness, signs of inflammation. Remember any recent activities or injuries that might have caused the swelling.
Professional Diagnostic Methods
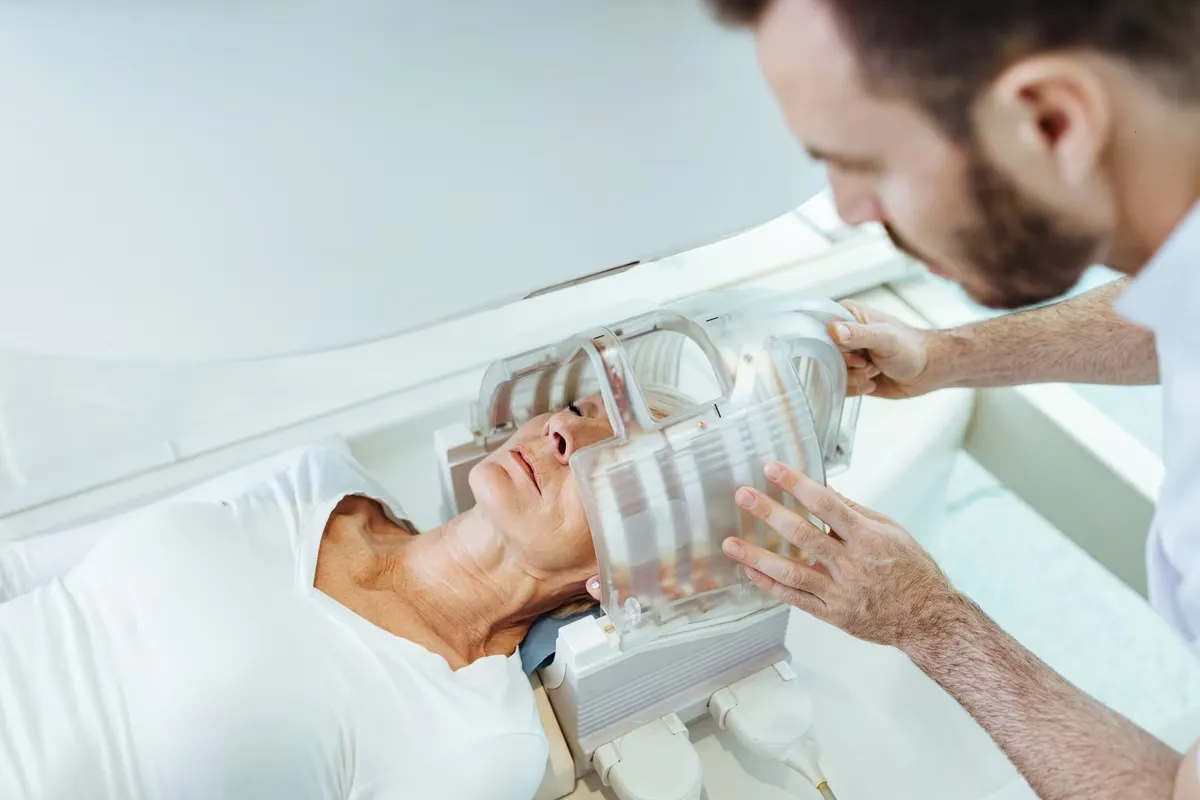
Doctors use special tests to figure out why your knee is swollen. Imaging tests like X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI show the inside of your knee. They can spot fluid buildup, cysts, or other problems.
Doctors also ask about your health history and do a physical check. Talking about recent travel, infections, or family health helps them understand more.
They might do blood tests to find other health issues that could be causing the swelling.
Effective Treatment Options for Knee Swelling
Managing knee swelling without pain needs a full treatment plan. The treatment for knee effusion changes based on the cause and how bad it is.
Home Remedies and Self-Care
For mild knee swelling with no pain, simple home remedies and self-care can help.
Resting the knee is key. Stay away from activities that might have caused the swelling.
Also, compression is important. A compression bandage can lessen swelling.
Medical Treatments
For serious or ongoing swelling on the knee but no pain, medical help is needed.
Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs can reduce swelling.
Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can teach exercises to strengthen knee muscles.
Arthrocentesis: If there’s a lot of fluid, arthrocentesis might be done.
| Treatment Option | Description | Benefits |
| Rest and Elevation | Resting the knee and elevating it | Reduces swelling |
| Ice Therapy | Applying ice packs | Reduces inflammation |
| Compression | Using a compression bandage | Provides support |
| Physical Therapy | Exercises to strengthen muscles | Improves joint stability |
| Arthrocentesis | Draining excess fluid | Relieves pressure |
Conclusion: When to Seek Medical Help
If your knee is swollen but you don’t feel pain, keep a close eye on it. Swelling without pain can have many causes. Knowing the reason is key to treating it right.
If your knee swelling doesn’t go away and you have symptoms like fever or trouble moving, see a doctor. At Liv Hospital, our team is ready to help with knee problems.
Wondering why your knee is swollen but not painful? Check your overall health and watch for any changes. Some cases might get better on their own, but others need medical help to avoid more problems.
Knowing when to seek medical help is important for your knee’s health. If you’re not sure why your knee is swollen or if you notice any worrying signs, talk to a doctor.
FAQ
What is knee effusion, and what causes it?
How can I diagnose a swollen knee without pain?
What are the treatment options for knee swelling?
Can knee swelling resolve on its own?
What is the role of arthrocentesis in treating knee effusion?
How can I prevent knee swelling?
When should I seek medical help for knee swelling?
Can knee swelling be a sign of an underlying serious condition?
How is knee effusion treated at Liv Hospital?
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27036390/