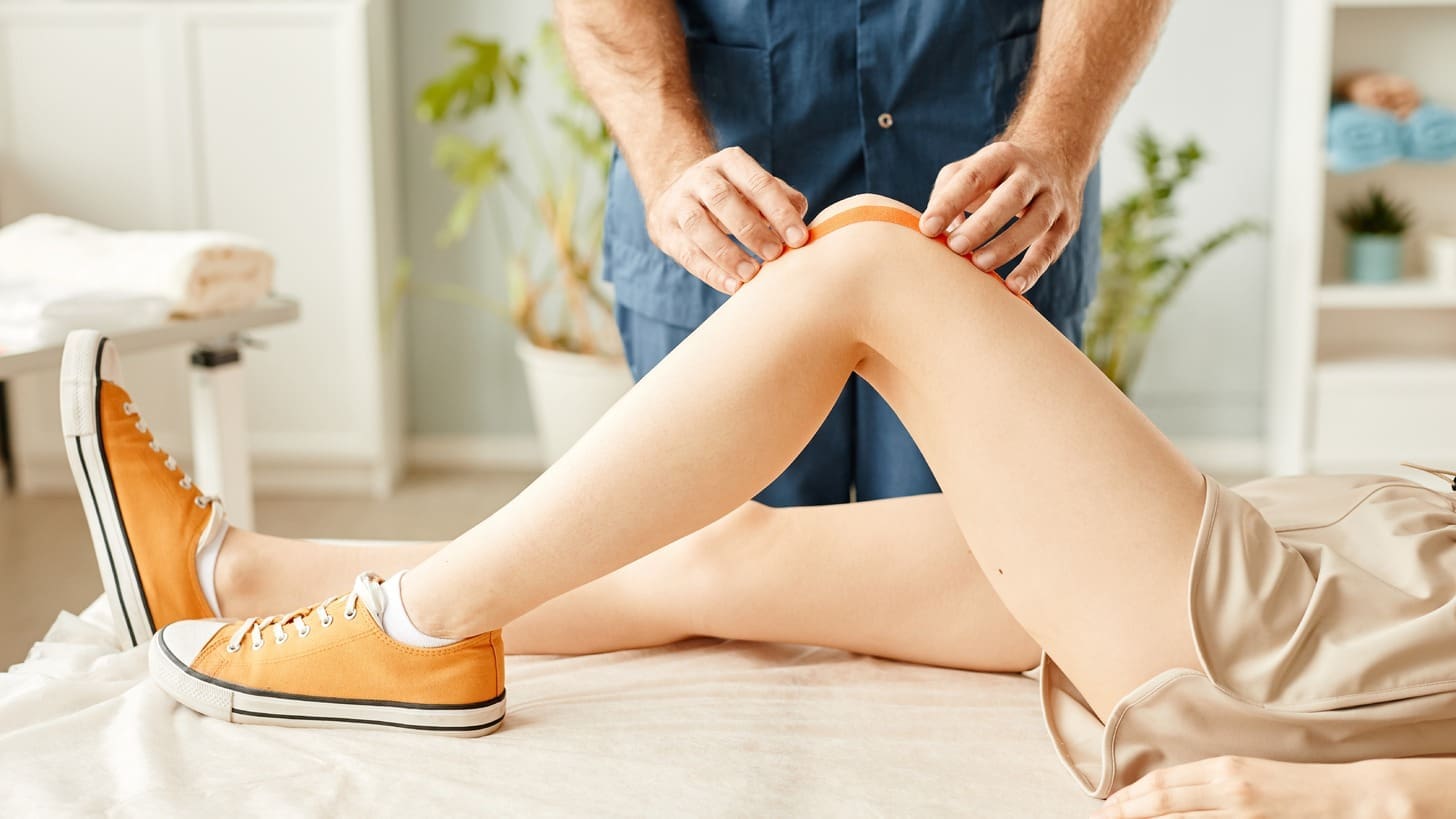
Knee pain in young athletes is a big worry. It can affect their health and how well they do in sports. At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to help them with care that works.
Tibial apophysitis, or Osgood-Schlatter disease, is a common problem in teens who play sports a lot.
This condition causes pain and discomfort in the knee. It happens because of inflammation at the tibial tubercle apophysis. Our team at Liv Hospital is here to help with care that’s just right for each patient.
We use the latest treatments to help young athletes get better. By knowing what causes it, how it feels, and how to treat it, we can help them feel better and get back to their sports.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes and symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter disease is key to treating it well.
- Personalized care and the latest treatments can really help young athletes get better.
- Liv Hospital is all about top-notch healthcare for everyone, including international patients.
- Seeing a doctor early can help ease knee pain and stop more serious problems later.
- Our team is all about helping teens with tibial apophysitis get back to their sports.
Understanding Tibial Apophysitis and Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Tibial apophysitis, or Osgood-Schlatter disease, is a big worry for young athletes. It causes knee pain and discomfort. This happens because of inflammation at the tibial tubercle apophysis.
Definition and Pathophysiology
Osgood-Schlatter disease is when the tibial tubercle gets inflamed. This is where the patellar tendon meets the tibia. It’s a form of juvenile osteochondrosis that affects the growth plate at the tibial tuberosity.
The tibial tuberosity apophysis is very important during growth. It’s a spot that changes a lot during adolescence. The condition happens because this growth plate is weak during rapid growth periods.
Prevalence in Adolescent Athletes
Osgood-Schlatter disease is common in young athletes, mainly those who run, jump, and change direction quickly. It’s more common in sports like soccer, basketball, and gymnastics.
- Soccer players are often affected because of the knee stress.
- Gymnasts get hurt from high-impact landings.
- Basketball players jump and land a lot, stressing the tibial tubercle.
Impact on Daily Activities and Sports
Osgood-Schlatter disease can really hurt a young person’s sports and daily life. The pain can make it hard to move and play sports well. Even simple things like kneeling or climbing stairs can hurt.
It’s important to manage this condition well. This means resting, doing physical therapy, and sometimes using supports.
Knowing about Osgood-Schlatter disease helps us treat and manage it better. This way, we can help young athletes recover and keep playing sports.
Anatomy of the Tibial Tubercle and Knee Mechanics

Understanding the tibial tubercle’s anatomy is key to understanding Osgood-Schlatter disease. The tibial tubercle, or tibial tuberosity, is where the patellar tendon meets the tibia.
The Tibial Tuberosity Apophysis Structure
The tibial tuberosity apophysis is a cartilage growth area at the tibia’s top. It’s very sensitive during adolescence because of fast growth.
The apophysis is where tendons and ligaments attach. For the tibial tubercle, it’s where the patellar tendon connects. This tendon links to the quadriceps tendon, which covers the kneecap.
Patellar Tendon Attachment
The patellar tendon is vital for knee function. It helps transmit forces from the quadriceps to the tibia, allowing the knee to extend.
The tendon’s attachment to the tibial tubercle is under a lot of stress. This is true for activities like running, jumping, and quick turns.
Growth Plate Vulnerability During Development
Growth spurts in adolescence make the tibial tuberosity apophysis more prone to injury. This is a major reason for Osgood-Schlatter disease.
The condition causes inflammation of the patellar tendon and surrounding tissues. This leads to pain and swelling below the kneecap.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
It’s important to know what causes Osgood-Schlatter disease. This knowledge helps in managing and preventing it. We will look at the different factors that lead to this condition.
Rapid Growth Spurts in Adolescents
Adolescents going through rapid growth are at high risk for Osgood-Schlatter disease. Their bones, muscles, and tendons change fast. This can put extra stress on the tibial tubercle.
This stress can cause inflammation and pain, which are signs of Osgood-Schlatter disease. Keeping an eye on growth spurts and adjusting activities can lower this risk.
High-Impact Sports and Activities
Playing high-impact sports and activities also raises the risk. Sports like soccer, basketball, and gymnastics put a lot of stress on the knee and tibial tubercle.
Players in these sports should know the risks. They should warm up properly and wear the right gear to prevent injuries.
Biomechanical Factors Contributing to Stress
Biomechanical issues, like poor lower extremity alignment, can also cause Osgood-Schlatter disease. These issues can put more stress on the tibial tubercle, leading to pain and inflammation.
People with biomechanical problems should see a healthcare professional. They can help reduce the risk of Osgood-Schlatter disease.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics also play a part in Osgood-Schlatter disease. If your family has a history of it, you might be more likely to get it.
Knowing your genetic risk can help you take steps to prevent or manage the condition.
Recognizing Symptoms of Tibial Apophysitis
Knowing the signs of Osgood-Schlatter disease is key to treating it well. We’ll cover the common signs to help you know when to see a doctor.
Tibial Tubercle Pain and Inflammation
The main sign is pain and swelling at the tibial tubercle, just below the kneecap. This pain comes from repeated stress and strain.
Swelling and Tenderness Below the Kneecap
Swelling and tenderness below the kneecap are also signs. The area might feel warm and hurt when pressed. This swelling is the body’s way of reacting to injury.
Pain Patterns During and After Activity
Pain from Osgood-Schlatter disease often happens during and after sports like running, jumping, or quick turns. The pain can be mild or severe and get worse if not treated.
Development of Tibial Protuberance
A tibial protuberance or bony bump might appear below the kneecap. This bump comes from long-term inflammation and stress on the tibial tubercle.
Knowing these symptoms helps diagnose Osgood-Schlatter disease. If you notice any, seeing a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment is important.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Tibial Tubercle Pain | Pain and inflammation at the tibial tubercle |
| Swelling and Tenderness | Swelling and tenderness below the kneecap |
| Pain Patterns | Pain during and after activity, specially in sports |
| Tibial Protuberance | Development of a bony lump below the kneecap |
“Early recognition of Osgood-Schlatter disease symptoms is key for effective management and avoiding long-term damage.”
Diagnosing Osgood-Schlatter Disease Accurately
To diagnose Osgood-Schlatter disease, doctors use a mix of clinical checks and imaging tests. This method helps ensure patients get the right diagnosis and treatment.
Clinical Evaluation and Physical Examination
The diagnosis of Osgood-Schlatter disease starts with a detailed patient history and physical check. We look at the patient’s symptoms, like knee pain location and severity. We also check for swelling, tenderness, and inflammation in the knee.
A physical exam is key. We check for pain and tenderness at the tibial tubercle. We also examine the patient’s gait, knee movement, and lower limb alignment.
Imaging Studies: X-rays, Ultrasound, and MRI
Imaging tests are used to rule out other knee pain causes. X-rays can spot bone issues like fractures. Ultrasound helps with soft tissue injuries like tendinopathy or bursitis.
MRI is used when the diagnosis is unsure or when complex knee issues are suspected. It shows detailed images of bones and soft tissues, helping with diagnosis.
Ruling Out Other Knee Conditions
It’s important to rule out other knee pain causes in teens. This includes patellofemoral pain syndrome, meniscal injuries, or ligament sprains. We must consider these to accurately diagnose Osgood-Schlatter disease.
| Condition | Characteristics | Diagnostic Clues |
|---|---|---|
| Osgood-Schlatter Disease | Localized pain and swelling at the tibial tubercle | Tenderness on palpation, pain with kneeling or jumping |
| Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome | Retropatellar pain, often related to activity | Pain with squatting, climbing stairs; patellar maltracking |
| Meniscal Injuries | Pain, locking, or catching sensation in the knee | Positive McMurray’s test, joint line tenderness |
By carefully looking at symptoms and using clinical checks and imaging tests, we can accurately diagnose Osgood-Schlatter disease. This helps us tell it apart from other knee issues.
When to Seek Medical Help for Tibial Tubercle Pain
Knowing when to seek medical help for tibial tubercle pain is key. Tibial apophysitis, or Osgood-Schlatter Disease, is common in teens, mainly in sports players. While it often heals on its own, persistent or severe pain means you should see a doctor to check for other issues.
Warning Signs Requiring Professional Evaluation
Here are signs you need to see a doctor:
- Severe pain that makes it hard to do daily tasks or play sports
- Swelling or tenderness below the kneecap that doesn’t get better with rest or pain meds
- Pain that persists or gets worse even with trying to manage it on your own
- Any deformity or abnormality around the knee or tibial tubercle
Choosing the Right Healthcare Provider
It’s important to pick the right doctor for tibial tubercle pain. You might want to:
- Start with your primary care doctor for a first check-up and referral
- See an orthopedic specialist or sports medicine doctor for a detailed look and treatment
- Talk to a physical therapist for advice on exercises and getting better
Going to a doctor who knows about sports injuries or treating teens can help a lot.
What to Expect During Your Medical Visit
At your doctor’s visit for tibial tubercle pain, you’ll get a full check-up:
- A detailed medical history to understand your symptoms and how active you are
- A physical exam to check pain, swelling, and how well your knee works
- Possibly, imaging studies like X-rays or an MRI to confirm what’s going on and rule out other problems
Knowing what to expect can help you get ready for your visit. It ensures you get the best care for your tibial tubercle pain.
Conservative Treatment Approaches for Tibial Apophysitis
Managing Tibial Apophysitis starts with conservative treatments. These methods help ease symptoms and aid in recovery. We’ll look at the key strategies for managing this condition.
Rest and Activity Modification Strategies
Rest is key in treating Osgood-Schlatter disease. We suggest avoiding activities that stress the knee. This helps reduce pain and inflammation.
- Avoid high-impact activities such as running and jumping
- Modify sports techniques to reduce stress on the knee
- Gradually return to full activity to prevent re-injury
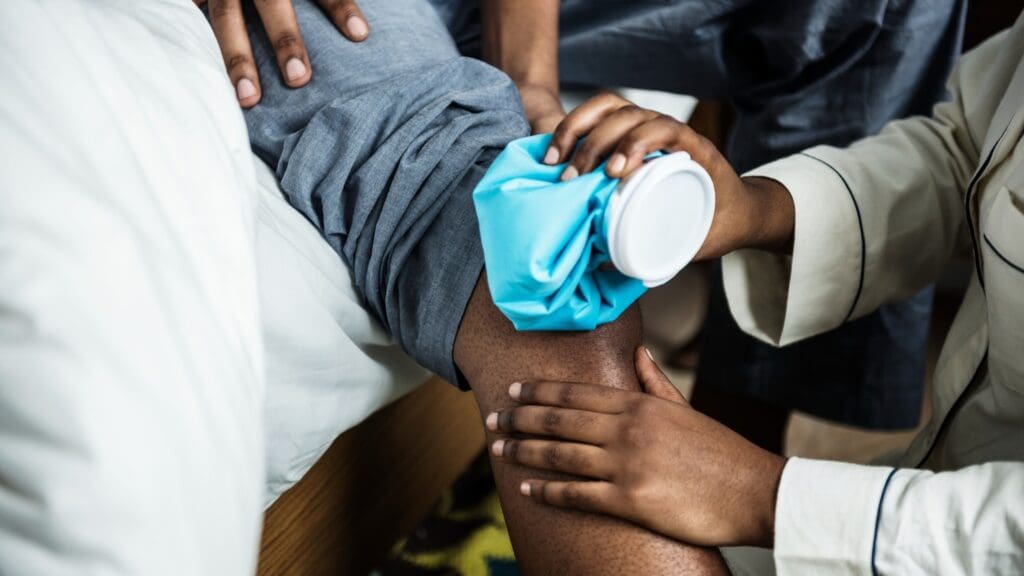
Effective Ice Therapy Techniques
Ice therapy is a simple yet effective method for reducing pain and inflammation associated with Osgood-Schlatter disease. We advise applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, after activities.
Key ice therapy tips:
- Use a barrier between the ice and skin to prevent ice burns
- Apply ice for 15-20 minutes, 3-4 times daily
- Monitor skin color and sensation during application
Appropriate Pain Management Options
Pain management is vital in treating Tibial Apophysitis. We often suggest over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. It’s important to follow the dosage and talk to a healthcare provider if pain doesn’t go away.
Elevation and Compression Methods
Elevation and compression can also help. Elevating the leg above heart level can reduce swelling. Compression bandages or sleeves provide support and reduce pain during activities.
By using these conservative treatments, we can manage Osgood-Schlatter disease effectively. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to create a treatment plan that fits your needs.
Comprehensive Physical Therapy Protocols
Managing Osgood-Schlatter disease through physical therapy is a detailed process. We create treatment plans that meet each patient’s unique needs.
Targeted Stretching Exercises for Quadriceps and Hamstrings
Stretching exercises are key in improving muscle flexibility and reducing tension around the knee. Quadriceps and hamstring stretches are vital. They directly affect the stress on the tibial tubercle.
- Quadriceps stretches help reduce tension on the patellar tendon.
- Hamstring stretches improve flexibility and reduce stress on the knee.
Progressive Strengthening Programs
Our strengthening programs aim to boost the muscles around the knee. We focus on exercises for the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip stabilizers.
Progressive resistance exercises help increase muscle strength. This reduces stress on the tibial tubercle.
Core and Hip Stabilization Techniques
Core and hip stabilization are key in physical therapy. Strengthening these areas improves lower limb mechanics and reduces knee stress.
- Core exercises improve overall stability and balance.
- Hip stabilization exercises reduce abnormal movement patterns.
Proper Movement Pattern Training
Teaching proper movement is vital for symptom prevention and recovery. We educate patients on correct techniques for daily and sports activities.
Movement pattern training lowers the risk of injury and enhances function.
Supportive Devices and Bracing Options
Supportive devices and bracing are key in treating Tibial Apophysitis. They offer extra support and stability. This helps ease the pain and discomfort of Osgood-Schlatter disease.
Infrapatellar Straps and Their Application
Infrapatellar straps are often used for Osgood-Schlatter disease. They apply pressure below the kneecap. This reduces tension on the patellar tendon and tibial tubercle.
By redistributing stress, infrapatellar straps can significantly reduce pain during activities. To use one, wear it snugly around your knee, just below the kneecap. Always check with a healthcare professional for the right fit.
Knee Braces for Activity Support
Knee braces offer stability and protection for the knee. By providing extra support, knee braces can help reduce irritation to the tibial tubercle. There are many types of knee braces, from simple sleeves to complex hinged ones. The right choice depends on your needs and how much support you need.
Appropriate Footwear and Orthotics
Proper footwear and orthotics are also important for Osgood-Schlatter disease. Good footwear can reduce knee stress by promoting correct biomechanics and alignment. Orthotics, like shoe inserts, can be made to fit your foot’s specific needs. Look for shoes with good arch support and cushioning. For personalized orthotics, see a podiatrist or orthotist.
Using these supportive devices and bracing in a treatment plan can help a lot. People with Osgood-Schlatter disease can feel better and move more easily during daily activities and sports.
Conclusion: Long-Term Management and Prevention Strategies
Managing Osgood-Schlatter disease well means using both non-surgical and surgical methods. We’ve talked about treatments like rest, ice, physical therapy, and using supports. It’s also key to prevent it from coming back by using prevention strategies. These include not specializing too early, watching over kids, and teaching them about training.
Kids who play different sports and take breaks are less likely to get tibial apophysitis. It’s also good to have training programs before and during the season. These programs should help with muscle control and strength. Knowing why it happens and using these steps can help kids stay healthy while playing sports.
FAQ
What is Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a common issue in teens. It causes knee pain and swelling due to inflammation at the tibial tubercle.
What are the typical symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Symptoms include knee pain, swelling, and tenderness below the kneecap. You might also feel pain during and after sports. A bump may appear on the tibia.
What causes Osgood-Schlatter disease?
It’s caused by rapid growth, high-impact sports, and biomechanical stress. Genetics might also play a role, leading to tibial tubercle inflammation.
How is Osgood-Schlatter disease diagnosed?
Doctors use a physical exam and imaging like X-rays or MRI to diagnose it. This helps rule out other knee problems.
What are the treatment options for Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Treatment includes rest, ice, and pain relief. Elevation and compression are also used. Physical therapy and supportive devices like straps and braces are recommended.
How can I manage Osgood-Schlatter disease long-term?
Long-term management includes ongoing physical therapy and proper movement training. Using supportive devices and preventing recurrence are also key.
Can Osgood-Schlatter disease be prevented?
While prevention is not guaranteed, proper training and using the right footwear can help. Avoiding overuse is also important.
When should I seek medical help for tibial tubercle pain?
Seek medical help for persistent or severe pain, swelling, or tenderness. A noticeable tibial protuberance or bump is also a reason to visit a doctor.
What can I expect during a medical visit for Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Expect a thorough evaluation and possibly imaging studies. The doctor will then create a treatment plan tailored to you.
Are there any specific exercises for Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Yes, exercises like stretching for quadriceps and hamstrings are helpful. Strengthening and core stabilization can also alleviate symptoms.
How does Osgood-Schlatter disease affect daily activities and sports?
It can limit sports participation and daily activities due to pain. But, with proper management, you can continue your usual activities.
What is Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a common issue in teens. It causes knee pain and swelling due to inflammation at the tibial tubercle.
What are the typical symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Symptoms include knee pain, swelling, and tenderness below the kneecap. You might also feel pain during and after sports. A bump may appear on the tibia.
What causes Osgood-Schlatter disease?
It’s caused by rapid growth, high-impact sports, and biomechanical stress. Genetics might also play a role, leading to tibial tubercle inflammation.
How is Osgood-Schlatter disease diagnosed?
Doctors use a physical exam and imaging like X-rays or MRI to diagnose it. This helps rule out other knee problems.
What are the treatment options for Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Treatment includes rest, ice, and pain relief. Elevation and compression are also used. Physical therapy and supportive devices like straps and braces are recommended.
How can I manage Osgood-Schlatter disease long-term?
Long-term management includes ongoing physical therapy and proper movement training. Using supportive devices and preventing recurrence are also key.
Can Osgood-Schlatter disease be prevented?
While prevention is not guaranteed, proper training and using the right footwear can help. Avoiding overuse is also important.
When should I seek medical help for tibial tubercle pain?
Seek medical help for persistent or severe pain, swelling, or tenderness. A noticeable tibial protuberance or bump is also a reason to visit a doctor.
What can I expect during a medical visit for Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Expect a thorough evaluation and possibly imaging studies. The doctor will then create a treatment plan tailored to you.
Are there any specific exercises for Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Yes, exercises like stretching for quadriceps and hamstrings are helpful. Strengthening and core stabilization can also alleviate symptoms.
How does Osgood-Schlatter disease affect daily activities and sports?
It can limit sports participation and daily activities due to pain. But, with proper management, you can continue your usual activities.
References
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS). Osgood-Schlatter disease. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/osgood-schlatter-disease-knee-pain



































