High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a big health problem worldwide. It affects about 1.4 billion people. The World Health Organization (WHO) says hypertension is when blood pressure stays high, usually over 130 systolic or 80 diastolic mmHg.
It’s important to know the main hypertension symptoms and what high blood pressure can lead to. At Liv Hospital, we stress the need to spot the signs of high blood pressure early. This helps us give the right care on time.
Understand hypertension symptoms and how high blood pressure affects your body.
Key Takeaways
- Hypertension is a major global health issue affecting 1.4 billion people worldwide.
- High blood pressure is defined as 130/80 mmHg or higher.
- Understanding hypertension symptoms is key for early detection.
- Liv Hospital offers full care for managing high blood pressure.
- Spotting the warning signs of hypertension can lead to timely treatment.
Understanding Hypertension: A Silent Global Epidemic
Hypertension is a major global health issue. It’s a condition known as high blood pressure. If not treated, it can cause serious heart problems.
Medical Definition of High Blood Pressure
Hypertension is medically defined as high blood pressure. It’s when your systolic blood pressure is ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure is ≥90 mmHg. Knowing this helps doctors diagnose and treat it right.
The epidemiology of hypertension studies how it spreads in populations. It’s key for creating health plans to fight it.
Global Prevalence and Statistics
Worldwide, 1.4 billion people have hypertension. The World Health Organization (WHO) says this number went from 650 million in 1990 to 1.4 billion in 2019. This big increase shows we need to do more to fight hypertension.
| Year | Number of Adults with Hypertension (in millions) |
| 1990 | 650 |
| 2019 | 1,400 |
These numbers show hypertension’s growing problem worldwide. It’s why we must keep working on public health to tackle it.
It’s important to understand hypertension’s impact and scope. By knowing its prevalence and stats, we can tackle this silent global epidemic better.
How Blood Pressure Is Measured and Classified
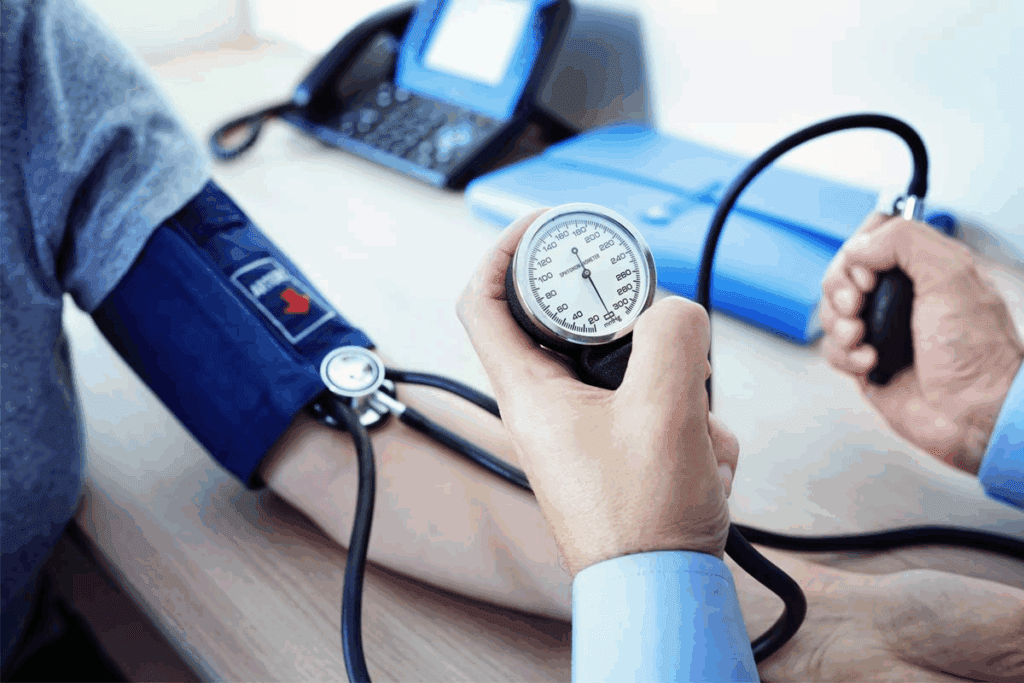

Blood pressure measurement is key in diagnosing and managing high blood pressure. We use a sphygmomanometer to measure it. This device shows two numbers: systolic (top number) and diastolic (bottom number).
Systolic vs. Diastolic Pressure
Systolic pressure is the pressure in arteries when the heart pumps blood. Diastolic pressure is the pressure when the heart rests. Both are important for understanding blood pressure.
Blood Pressure Categories
Blood pressure is divided into levels based on systolic and diastolic readings. Knowing these categories helps diagnose hypertension and plan treatment.
| Blood Pressure Category | Systolic Pressure (mmHg) | Diastolic Pressure (mmHg) |
| Normal | Less than 120 | Less than 80 |
| Elevated | 120-129 | Less than 80 |
| Stage 1 Hypertension | 130-139 | 80-89 |
| Stage 2 Hypertension | 140 or higher | 90 or higher |
White Coat Hypertension vs. Masked Hypertension
It’s important to know the difference between white coat hypertension and masked hypertension. White coat hypertension is high blood pressure in a doctor’s office but normal at home. Masked hypertension is normal in a doctor’s office but high at home.
Understanding these conditions helps in accurate diagnosis and treatment of hypertension. By knowing systolic and diastolic pressure, blood pressure categories, and white coat and masked hypertension, we can better care for those with high blood pressure.
Common Hypertension Symptoms to Watch For
It’s important to know the common symptoms of hypertension for early detection and management. Many people with hypertension don’t show symptoms. But, some symptoms can really affect their life quality.
Morning Headaches and Dizziness
Morning headaches can be a sign of high blood pressure. This happens because blood pressure goes up at night. It makes blood vessels in the brain swell, causing pain. Dizziness is another symptom that may accompany hypertension, as the increased pressure can affect blood flow to the brain, causing a feeling of lightheadedness or unsteadiness.
“High blood pressure is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and being aware of its symptoms can be lifesaving.”
Visual Disturbances
Hypertension can also cause visual disturbances, including blurred vision, double vision, or even loss of vision in severe cases. The increased pressure can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to these symptoms. Regular eye exams are essential for detecting any changes in vision that may be related to hypertension.
Chest Pain and Palpitations
Chest pain and palpitations are more severe symptoms that can be associated with hypertension. Chest pain may occur if the high blood pressure leads to coronary artery disease or if it causes the heart to work harder, potentially leading to angina. Palpitations, or irregular heartbeats, can also be a symptom, as hypertension can affect the heart’s rhythm.
It’s essential to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other conditions, making it vital to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. By being aware of these symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing their blood pressure and preventing complications.
Gender Differences: Hypertension Symptoms in Men vs. Women
Hypertension affects men and women differently. Each gender has its own symptoms and health risks. Research shows clear differences in how hypertension shows up and grows in men and women.
Male-Specific Manifestations
Men often face hypertension at a younger age than women. Hypertension symptoms in men include:
- Nosebleeds
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest pain
Men are more likely to have hypertensive crises, which are emergencies. It’s key for men, with a family history of hypertension, to watch their blood pressure closely.
Female-Specific Manifestations
Women, post-menopause, face a higher risk of hypertension. Hypertension symptoms in women can be less obvious and include:
- Shortness of breath
- Swollen ankles, feet, or legs
- Frequent urination
- Headaches
Women should keep an eye out for these signs, even more so if they’re overweight or don’t move much.
Hormonal Influences on Blood Pressure
Hormones greatly affect blood pressure. For example, estrogen helps keep blood vessels healthy. This might explain why younger women often have lower blood pressure than men. But, estrogen levels drop after menopause, which can raise blood pressure.
“The hormonal changes during menopause can significantly impact blood pressure, highlighting the need for women to be proactive about their cardiovascular health during this phase.”
It’s important for doctors to understand these gender differences. This way, they can give better care. By knowing the specific symptoms and risks for each gender, we can manage hypertension better and lower the risk of serious problems.
The Silent Danger: Why Hypertension Often Goes Undetected
Hypertension is a silent killer because it often doesn’t show symptoms. This makes it hard to catch without regular check-ups.
Asymptomatic Progression
Hypertension is called a “silent killer” because it progresses without symptoms. This makes it hard for people to know they have it without medical tests.
Many people don’t know they have hypertension. It usually doesn’t show symptoms until it has harmed the body a lot.
Importance of Regular Screening
Regular blood pressure checks are key to catching hypertension early.
The World Health Organization says people with high blood pressure might not feel any symptoms. So, regular blood pressure tests are important to find those at risk.
Benefits of Regular Screening:
- Early detection of hypertension
- Prevention of cardiovascular complications
- Reduced risk of kidney damage
| Screening Frequency | Risk Category | Recommended Action |
| Every 2 years | Low risk | Continue routine check-ups |
| Annually | Moderate risk | Monitor lifestyle factors |
| Every 6 months | High risk | Consult a healthcare provider |
Knowing the risks of hypertension and the need for regular screening helps. It lets people manage their blood pressure and lower the risk of serious problems.
Severe Symptoms That Require Immediate Medical Attention
Knowing when to seek medical help for high blood pressure is key. Severe hypertension can cause heart attacks, strokes, and kidney damage. We’ll cover the signs of a hypertensive crisis and what to do.
Hypertensive Crisis Warning Signs
A hypertensive crisis happens when blood pressure hits 180/120 mmHg or higher. Look out for these signs:
- Severe headache
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Blurred vision or other visual disturbances
- Anxiety or confusion
- Seizures
When to Call 911
If you see any of these, call 911 right away:
- Chest pain or tightness
- Severe difficulty breathing
- Severe headache with confusion or blurred vision
- Seizures or convulsions
Quick action can save lives.
Emergency Treatment Protocols
Emergency care for high blood pressure includes:
| Treatment | Description |
| Intravenous medications | To quickly lower blood pressure |
| Monitoring | Watching vital signs and organ function closely |
| Hospitalization | For more evaluation and care |
Knowing these steps can help you prepare for emergencies.
Quick action on severe hypertension symptoms is vital. It helps avoid serious problems and improves health outcomes.
Major Health Complications Caused by Untreated Hypertension
Untreated hypertension can cause severe health problems. It affects many parts of the body. High blood pressure is a big risk for serious conditions like cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Cardiovascular Complications
Cardiovascular problems are big risks with untreated hypertension. High blood pressure can lead to heart failure. The heart works too hard and can weaken over time.
Hypertension can also cause coronary artery disease. This is when arteries narrow or block, leading to heart attacks. Other heart problems include left ventricular hypertrophy and cardiac arrhythmias. These can be dangerous and even life-threatening.
Cerebrovascular Complications
Cerebrovascular problems are also serious for those with untreated hypertension. High blood pressure is a leading cause of stroke. It can cause blood vessels in the brain to burst or block, leading to brain damage.
Hypertension can also lead to transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), or “mini-strokes.” These are temporary but can warn of a bigger stroke. It can also cause vascular dementia, where brain blood flow reduces, leading to cognitive decline.
Managing hypertension is key to avoiding these serious problems. By controlling blood pressure through lifestyle changes and, if needed, medication, people can lower their risk of these conditions.
Organ Damage: Long-term Effects of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure can cause serious damage to organs if not treated. It can harm many parts of the body, leading to serious health issues. We will look at how high blood pressure affects the kidneys, eyes, and arteries.
Kidney Damage and Failure
The kidneys filter waste from our blood. High blood pressure can damage the kidneys’ blood vessels. This can make the kidneys work poorly. Kidney damage can lead to chronic kidney disease and even kidney failure, needing dialysis or a transplant.
The National Kidney Foundation says high blood pressure is a top cause of kidney failure in the U.S. “Hypertension is a major risk for kidney disease,” the American Heart Association notes. Managing blood pressure can prevent kidney damage.
Eye Damage and Vision Loss
Hypertension can harm the eyes’ blood vessels, causing eye problems. Hypertensive retinopathy damages the retina, potentially causing vision loss. It also raises the risk of other eye diseases like glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration.
Peripheral Artery Disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) happens when high blood pressure damages blood vessels outside the heart, usually in the legs. This can cause pain when walking, known as intermittent claudication. If not treated, PAD can lead to severe leg pain, even at rest, and increase the risk of gangrene and amputation.
The CDC says managing high blood pressure can prevent PAD and other heart conditions. Controlling blood pressure is essential for keeping the heart and blood vessels healthy.
Risk Factors That Amplify Hypertension Symptoms
Knowing what increases hypertension symptoms is key to managing it. Many things can make high blood pressure worse. Finding out what these are is important for controlling it.
Salt Sensitivity and Dietary Factors
About 50-60 percent of adults are salt sensitive, which raises their risk of high blood pressure. This means their blood pressure changes with salt intake. Eating too much sodium can cause high blood pressure in these people. Dietary factors are very important in managing hypertension, and cutting down on sodium is often the first step.
Eating a lot of processed foods, which are high in sodium, can make hypertension symptoms worse. On the other hand, eating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help. The DASH diet is a good example of a plan that helps manage blood pressure.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics also play a big role in hypertension. If your family has a history of high blood pressure, you’re more likely to get it. Scientists have found many genes that help control blood pressure, and changes in these genes can affect your risk.
Even though you can’t change your genes, knowing your family history is important. It means you should check your blood pressure more often. This can help catch and manage hypertension early.
Lifestyle Contributors
Lifestyle choices also affect hypertension. Things like unhealthy diets, not being active, and smoking or drinking too much alcohol are risks. Regular exercise can help lower blood pressure and prevent hypertension.
| Lifestyle Factor | Impact on Hypertension | Recommended Change |
| Physical Inactivity | Increases risk of hypertension | Engage in regular aerobic exercise |
| Unhealthy Diet | Contributes to high sodium intake | Adopt a balanced diet like DASH |
| Tobacco and Alcohol Consumption | Can raise blood pressure | Reduce or eliminate consumption |
By understanding and tackling these risk factors, people can manage their blood pressure better. This can help prevent serious problems linked to hypertension.
Diagnostic Approaches for Identifying Hypertension
Accurate diagnosis of hypertension is key to controlling this global health issue. We use different methods to find out if someone has high blood pressure. This ensures they get the right care and treatment.
In-Office Blood Pressure Measurements
In-office blood pressure checks are a common way to find out if someone has hypertension. These tests are done in a doctor’s office with a special device called a sphygmomanometer. It’s important to take several readings to get accurate results.
Key considerations for in-office measurements include:
- Ensuring the patient is seated comfortably with their back supported
- Using the correct cuff size to avoid inaccurate readings
- Avoiding caffeine and tobacco for at least 30 minutes before measurement
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) uses a portable device to track blood pressure over 24 hours. This method gives a detailed view of blood pressure patterns. It helps diagnose hypertension and understand its severity.
The benefits of ABPM include:
- Detecting white coat hypertension and masked hypertension
- Assessing blood pressure variability and nocturnal dipping
- Guiding treatment decisions with more accurate data
Home Blood Pressure Monitoring
Home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) lets patients check their blood pressure at home. It provides valuable insights for managing hypertension. HBPM can spot patterns and changes in blood pressure that office tests might miss.
Tips for effective HBPM include:
- Using a validated and calibrated blood pressure monitor
- Taking readings at the same time each day
- Recording readings in a log for review by healthcare providers
Treatment Strategies to Control Hypertension and Prevent Complications
Managing high blood pressure needs a mix of lifestyle changes and, if needed, medicine. At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch healthcare for international patients. We focus on creating treatment plans that fit each person’s needs.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes is key to controlling high blood pressure. These changes can lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of serious problems. Important lifestyle changes include:
- Dietary Changes: Eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help lower blood pressure. The DASH diet is often recommended.
- Physical Activity: Doing regular exercise, like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, for at least 150 minutes a week can help manage high blood pressure.
- Weight Management: Keeping a healthy weight reduces heart strain and can help lower blood pressure.
- Limiting Alcohol and Quitting Smoking: Drinking less alcohol and quitting smoking are key steps in managing high blood pressure.
“Lifestyle changes are the cornerstone of hypertension management. By making informed choices, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of cardiovascular complications.”
— Medical Expert, Cardiologist
Medication Options
If lifestyle changes alone are not enough to control high blood pressure, medicine may be needed. There are different types of blood pressure medicines, each working in its own way to lower blood pressure.
| Medication Class | Mechanism of Action | Examples |
| Diuretics | Help the kidneys remove excess fluid from the body, reducing blood pressure. | Hydrochlorothiazide, Furosemide |
| ACE Inhibitors | Block the production of a chemical that constricts blood vessels, allowing blood vessels to relax and widen. | Lisinopril, Enalapril |
| Calcium Channel Blockers | Prevent calcium from entering the cells of the heart and blood vessel walls, leading to lower blood pressure. | Amlodipine, Verapamil |
The right medicine depends on the person’s specific needs and health. Often, a mix of medicines is used to control blood pressure well.
By combining lifestyle changes with the right medicine, people can manage their high blood pressure well. This reduces the risk of serious problems and improves their quality of life.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Blood Pressure
It’s important to understand hypertension, its symptoms, and complications. Recognizing high blood pressure signs and taking action early can greatly reduce health risks.
Controlling blood pressure is key to avoiding heart and brain problems. At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch healthcare for international patients.
Managing hypertension involves monitoring, a healthy diet, stress control, and following treatment plans. By managing blood pressure, you can protect your kidneys, heart, and eyes from damage.
We aim to help international patients manage their hypertension effectively. Working with healthcare experts, you can create a plan to control your blood pressure and avoid complications.
FAQ
What is hypertension?
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is when your blood pressure stays high. It’s a big risk for heart and brain diseases.
What are the symptoms of hypertension?
Often, there are no symptoms. But some people might feel morning headaches, dizziness, or see things differently. They might also feel chest pain or have a fast heartbeat.
How is blood pressure measured and classified?
Doctors use a special tool to check blood pressure. It’s divided into levels based on the numbers. These levels are normal, elevated, stage 1, and stage 2 hypertension.
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure?
Systolic is the top number, showing pressure when the heart beats. Diastolic is the bottom number, showing pressure between beats.
What is white coat hypertension?
White coat hypertension is when blood pressure is high in a doctor’s office but normal at home.
What are the complications of untreated hypertension?
If not treated, high blood pressure can cause serious problems. These include heart disease, brain damage, kidney damage, eye problems, and artery disease.
How can hypertension be diagnosed?
Doctors can diagnose it with office checks, 24-hour monitoring, or home checks.
What are the treatment options for hypertension?
Treatments include changing your diet and exercise, and taking medicines. These can be diuretics, beta blockers, or ACE inhibitors.
How can I reduce my risk of developing hypertension?
To lower your risk, live a healthy lifestyle. Eat well, exercise regularly, and manage stress.
What is the global prevalence of hypertension?
Worldwide, about 1.4 billion people have hypertension. It’s a big health problem globally.
Why is regular blood pressure screening important?
Regular checks are key for catching hypertension early. It often doesn’t show symptoms until it’s serious.
What are the warning signs of a hypertensive crisis?
Signs of a crisis include very high blood pressure, chest pain, trouble breathing, and neurological issues. These need immediate doctor help.
References
World Health Organization. (2025). 9 Key Hypertension Symptoms and What High Blood. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension