Computed Tomography (CT) scans have changed how we diagnose diseases. They give detailed images of a cat scan using X-rays and advanced computers.
The creation of CT scans was a big step forward in medical imaging. It helps doctors find and treat diseases better. Over time, CT scans have gotten faster and more precise.
It’s important to know about CT scans, from their invention to how they’ve improved. This article will dive into the tech behind CT scans and their use in medicine.
Key Takeaways
- CT scans use X-rays and computing technology to produce detailed body images.
- The invention of CT scans revolutionized medical diagnostics.
- CT scans have evolved to provide faster and more accurate diagnoses.
- Understanding CT scans is key to seeing their value in today’s medicine.
- CT scans have many uses in diagnosing and treating diseases.
What Are CT Scans: Defining Modern Medical Imaging
CT scans, also known ascomputed axial tomography, are key in modern medicine. They mix X-rays and computer tech to show detailed body images. Doctors use them to find and track many health issues.
The Difference Between CT Scans and Traditional X-rays
CT scans show three-dimensional images, unlike X-rays’ two-dimensional views. They take X-rays from many angles around the body. CT scans give a clearer view of inside structures, helping with complex health problems.
X-rays struggle to tell apart soft tissues. But CT scans can spot different tissues like organs and tumors. This is because they measure tissue density.
How Computerized Tomography Creates Cross-Sectional Images
Creating CT scan images involves a few steps. An X-ray tube sends X-rays through the body. Sensors on the other side catch these X-rays. A computer then makes the images from this data.
The images are very detailed. They can be seen in different views, like axial and sagittal. This helps doctors understand the body better and diagnose more accurately.
In short, CT scans are a big leap in medical imaging. They combine X-rays and computer tech to make detailed cross-sectional images. These images are key for doctors to diagnose.
The Groundbreaking Invention of CT Scanners
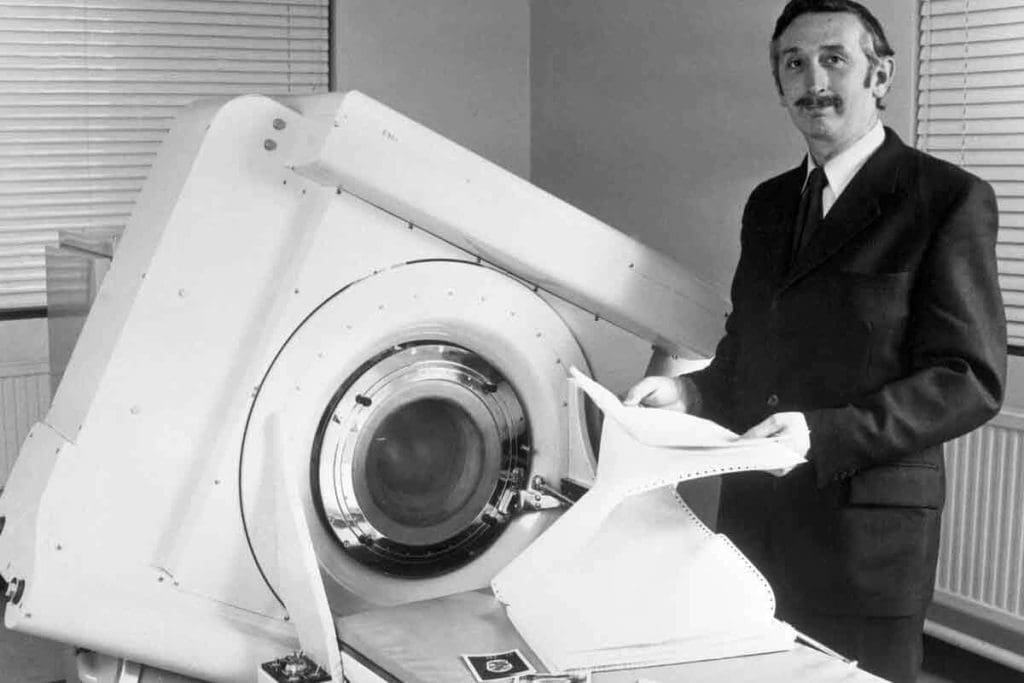

The CT scanner changed medical imaging. It lets doctors see inside the body without surgery.
Sir Godfrey Hounsfield, a British engineer, made the first working CT scanner. He worked at EMI Laboratories in the late 1960s and early 1970s. His invention could show images of the brain.
Sir Godfrey Hounsfield: The Brilliant Mind Behind CT Scanning
Sir Godfrey Hounsfield’s work in medical imaging is huge. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1979. He shared it with Allan McLeod Cormack for their similar work.
- Hounsfield used X-rays to make cross-sectional images.
- His work built on earlier ideas, but he made CT scanning real.
When Was the CT Scan Developed: Timeline of Early Development
The CT scan’s development started in the late 1960s. Here are some important dates:
- 1967: Hounsfield began working on it at EMI.
- 1970: The first prototype was built and tested.
- 1971: The first clinical CT scanner was set up at Atkinson Morley Hospital in London.
The First Clinical Applications in 1971-1972
The first patient was scanned on October 1, 1971, with the EMI Mark I scanner. The scans were mainly for brain images.
The early use of CT scanners showed its power. It could tell different soft tissues apart. This was a big step up from X-rays.
CT scanners’ success in hospitals led to more tech improvements. They became a key part of medical care.
The Evolution of Images of a Cat Scan Through the Decades
Over the years, CT scan technology has changed a lot, making medical imaging better. The first simple images have turned into clear, detailed scans today. This shows how fast computed tomography has improved.
First-Generation CT Images: Limitations and Capabilities
The first CT scanner came out in the early 1970s, starting a new chapter in medical imaging. Early CT scans could show cross-sections of the body better than X-rays. But these early images were not as clear and took longer to get.
The first CT scanners moved in a straight line and then rotated a bit. This method made the images blurry and not very detailed.
Modern High-Resolution CT Imaging
Today’s CT scanners are much better, giving clear images quickly. Multi-detector CT (MDCT) scanners are key to this improvement. They can take many images at once, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
Now, CT scans help find tumors, vascular diseases, and guide treatments. Their clear images are vital in medical care.
| Feature | First-Generation CT | Modern CT |
| Scan Time | Several minutes | Seconds |
| Resolution | Lower | High |
| Detector Technology | Single detector | Multi-detector |
The Transition from 2D to 3D Visualization
Going from 2D to 3D images is a big step in CT imaging. Early CT scans were 2D, which was good but limited. Now, CT scanners can show images in 3D, giving a better view of inside the body.
This change has made diagnoses more accurate. It’s also helped in planning surgeries and tracking diseases.
CT Scan vs. Cat Scan: Understanding the Terminology
The terms “CT scan” and “CAT scan” are often used the same way. But, there’s a difference in history and use in medicine. Knowing this helps in clear talk in medical settings.
Origins of the Term “CAT Scan”
The term “CAT scan” came up early in the tech’s development. “CAT” means “Computed Axial Tomography.” It was used when the tech first came out in the 1970s. Both doctors and the public used “CAT scan” a lot.
As noted by
“The development of CAT scanning marked a significant milestone in medical imaging, giving us new views of the body’s inside.”
This quote shows how CAT scanning changed medical checks.
Why Medical Professionals Prefer “CT Scan” Today
Now, doctors mainly say “CT scan.” The switch from “CAT scan” to “CT scan” made the term simpler. It dropped “Axial” and “Tomography” for just “Computed Tomography.” This change is because the tech has grown, allowing scans in more ways than before.
| Term | Full Form | Usage |
| CT Scan | Computed Tomography | Doctors like it for being simple and clear about today’s scans. |
| CAT Scan | Computed Axial Tomography | It was used before; now, it’s less common in doctor talk but known by everyone. |
Doctors prefer “CT scan” because the tech has grown. It now does more than just axial tomography. As Computed Tomography gets better, so does the way we talk about it.
The Science Behind Computed Axial Tomography
To understand CT scans, you need to know about X-ray absorption and tissue density measurement. Computed Axial Tomography (CT scans) uses X-rays to see inside the body. They work by how much x-rays different tissues absorb.
X-ray Absorption and Tissue Density Measurement
X-rays go through the body differently. Bone absorbs more, while soft tissues absorb less. This difference helps create detailed images.
The CT scanner measures how much x-rays are blocked. It does this from many angles. Then, it makes a map of tissue densities in the body.
The Hounsfield Scale: Quantifying Tissue Density
The Hounsfield scale helps measure X-ray absorption in tissues. It gives each tissue a number, called Hounsfield Units (HU), based on its density.
Water is 0 HU, and air is about -1000 HU. Bone, being denser, has a higher HU value, often over +700 HU. This scale helps doctors see different tissues and structures.
Image Reconstruction Algorithms and Processing
The CT scanner’s raw data is turned into images using image reconstruction algorithms. These algorithms combine data from many angles to create body slices.
Today’s CT scanners can make images in different planes, like sagittal and coronal views. This helps doctors see more clearly and understand the body better.
What Are Cat Scans For: Primary Medical Applications
Doctors use CT scans for many important reasons. They help diagnose injuries and plan surgeries. CT scans are key in modern medicine, used in many areas of healthcare.
Diagnosing Strokes, Tumors, and Vascular Conditions
CT scans are vital for spotting strokes, tumors, and blood vessel problems. They show detailed images of the brain. This helps doctors find where strokes or tumors are.
For blood vessel issues, CT angiography shows blood vessels. It helps find blockages or aneurysms.
Key Diagnostic Applications:
- Stroke diagnosis and assessment
- Tumor detection and characterization
- Vascular condition assessment
Detecting Internal Injuries and Trauma Assessment
In emergencies, CT scans quickly check for internal injuries. They find bleeding, organ damage, and fractures. This info is vital for emergency care.
| Trauma Assessment | CT Scan Capabilities |
| Internal Injuries | Detection of internal bleeding and organ damage |
| Fracture Detection | Identification of complex fractures |
Cancer Staging and Treatment Planning
CT scans are key in cancer staging. They show how far cancer has spread. This info is vital for planning treatments like surgery and radiation.
CT scans in cancer treatment:
- Tumor size and location assessment
- Identification of metastasis
- Guiding radiation therapy
CT-Guided Procedures and Interventions
CT-guided procedures are precise. They include biopsies and tumor treatments. This method is less invasive, leading to faster recovery and better results.
Thanks to CT scans, doctors can make more accurate diagnoses and treatments. This improves patient care greatly.
Types of CT Scans and Specialized Techniques
Today’s CT scans use many techniques, like contrast-enhanced imaging and low-dose scans. These methods have made diagnosis more accurate and safer for patients.
Contrast-Enhanced CT Imaging
Contrast-enhanced CT scans use a special dye to show certain body parts. It’s great for seeing blood vessels, tumors, and other issues.
Benefits of Contrast-Enhanced CT:
- It shows blood vessels better
- Helps find tumors and lesions
- Checks how well organs work
CT Angiography for Vascular Visualization
CT angiography focuses on blood vessels. It’s used to find problems like aneurysms and stenosis.
| Condition | Diagnostic Capability |
| Aneurysms | Accurate sizing and location |
| Stenosis | Assessment of narrowing severity |
| Vascular Malformations | Detailed visualization of abnormal vessel structures |
Low-Dose CT Protocols
Low-dose CT scans use less radiation but keep image quality high. This is key for patients needing many scans.
Advantages of Low-Dose CT:
- Less radiation risk
- Good for long-term monitoring
- Follows ALARA principles
Cardiac CT and Coronary Imaging
Cardiac CT scans look at the heart and coronary arteries. They help find heart disease and check how well the heart works.
Cardiac CT applications include:
- Checking for coronary artery disease
- Examining heart structure
- Planning for heart procedures
Technological Advancements in CT Scanning Equipment
CT scanning has changed a lot, helping doctors diagnose and treat patients better. We’ve seen big changes, like moving from single-slice to multi-detector CT scanners. Now, we have dual-energy and spectral CT technology too.
From Single-Slice to Multi-Detector CT Scanners
The move to multi-detector CT scanners was a big step. Multi-detector CT scanners scan faster and give clearer images. This makes it easier for doctors to make accurate diagnoses.
Old CT scanners could only take one slice at a time. This was slow and often had problems because of patient movement. But, with multi-detector tech, we can take many slices at once. This cuts down scan times and makes images better.
Dual-Energy and Spectral CT Technology
Dual-energy CT is a big improvement. It lets us tell different materials apart based on their atomic number and density. This helps doctors understand tissues and lesions better, even in tough cases.
Spectral CT goes even further. It takes data at different energy levels. This gives us detailed info on tissue makeup and helps spot certain conditions better.
Improvements in Speed, Resolution, and Radiation Dose Reduction
Today’s CT scanners are faster, clearer, and use less radiation. New algorithms and hardware have made these improvements possible.
The table below shows how CT scanning has gotten better:
| Feature | Early CT Scanners | Modern CT Scanners |
| Scan Time | Several minutes | Seconds |
| Resolution | Lower resolution | High resolution |
| Radiation Dose | Higher doses | Lower doses with dose modulation |
Benefits and Limitations of CT Imaging
Computed Tomography (CT) imaging is known for its detailed cross-sectional images. It’s a key tool in modern medicine. Yet, it also has some limitations to consider.
Diagnostic Advantages Over Other Imaging Modalities
CT scans have many benefits. They give high-resolution images that help diagnose many conditions. A study on the National Institutes of Health website saysCT scans are vital in emergencies for quick injury assessment.
Key benefits include clear images of the brain, spine, and organs. This is very helpful in emergencies where fast diagnosis is needed.
Radiation Exposure Concerns and Safety Considerations
CT imaging’s main drawback is radiation exposure. CT scans use X-rays, which carry some risk. Healthcare providers must balance the benefits against the risks, mainly for those needing many scans.
Safety considerations include using the least amount of radiation needed. New CT technology helps reduce doses, making scans safer.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility Factors
CT imaging’s cost and accessibility are also key. CT scanners are pricey and need regular upkeep. But, they can lead to better treatment plans, saving money in the long run.
Access to CT imaging varies by location. Urban areas usually have more scanners than rural ones. Efforts are being made to make CT technology more portable and affordable.
Conclusion: The Future of CT Imaging in Modern Medicine
Medical imaging is always getting better, and CT scans are no exception. New technologies like dual-energy and spectral CT are making images clearer and helping doctors diagnose better. This is a big step forward.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also changing the game. They help doctors analyze images faster and more accurately. This means patients can get the right treatment sooner. CT scans will play a bigger role in treating cancer and diagnosing strokes, among other things.
The future of CT imaging is bright, thanks to ongoing improvements. We can expect even sharper images, less radiation, and more comfort for patients. CT scans will keep being a key part of healthcare, helping doctors give the best care possible.
FAQ
What is a CT scan?
A CT scan, or computed tomography scan, is a medical test. It uses computer-processed x-rays to create detailed images of the body. These images are cross-sectional, showing different parts of the body.
Who invented the CT scan?
Sir Godfrey Hounsfield, a British engineer, invented the CT scan in the early 1970s.
What is the difference between a CT scan and a traditional X-ray?
Traditional X-rays show 2D images. But CT scans create detailed 3D images. They do this by combining multiple x-ray images from different angles.
What are CT scans used for?
CT scans help diagnose many medical conditions. They are used for strokes, tumors, vascular conditions, internal injuries, and guiding medical procedures.
What is the Hounsfield scale?
The Hounsfield scale measures tissue density in CT scans. It ranges from -1000 (air) to +1000 (dense bone). Water is 0 on this scale.
What is contrast-enhanced CT imaging?
Contrast-enhanced CT imaging uses a contrast agent. This agent highlights specific areas or structures in the body. It improves diagnostic accuracy.
How have CT scans evolved over time?
CT scans have changed a lot. They started with single-slice scanners. Now, we have multi-detector CT scanners. These advancements mean faster scans, higher resolution, and less radiation.
What are the benefits of CT scans?
CT scans have many benefits. They provide high-resolution images quickly. They also help guide medical interventions.
What are the limitations of CT scans?
CT scans involve radiation, which is a concern. They may not be right for all patients. This includes those with certain medical conditions or allergies to contrast agents.
What is the difference between a CT scan and CAT scan?
CT scan and CAT scan are often used in the same way. But “CT scan” is the preferred term. It accurately describes the technology used.
How have advancements in CT technology improved patient care?
Advances in CT technology have made diagnosis more accurate. They have also reduced radiation doses. This has improved patient safety and outcomes.
What is the future of CT imaging?
The future of CT imaging looks bright. We can expect better image resolution, less radiation, and new uses in diagnosis and treatment.
References
- Tozzi, L., Zhang, X., Pines, A., et al. (2024). Personalized brain circuit scores identify clinically distinct biotypes in depression and anxiety. Nature Medicine, 30(7), 2076“2087.https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03057-9
- Liang, S., Wang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2020). Biotypes of major depressive disorder: Neuroimaging evidence from resting-state default mode network patterns. NeuroImage: Clinical, 28, 102514.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S221315822030351X
- Dinga, R., Marquand, A. F., & Penninx, B. W. J. H. (2019). Evaluating the evidence for biotypes of depression. NeuroImage: Clinical, 22, 101797.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213158219301469

































