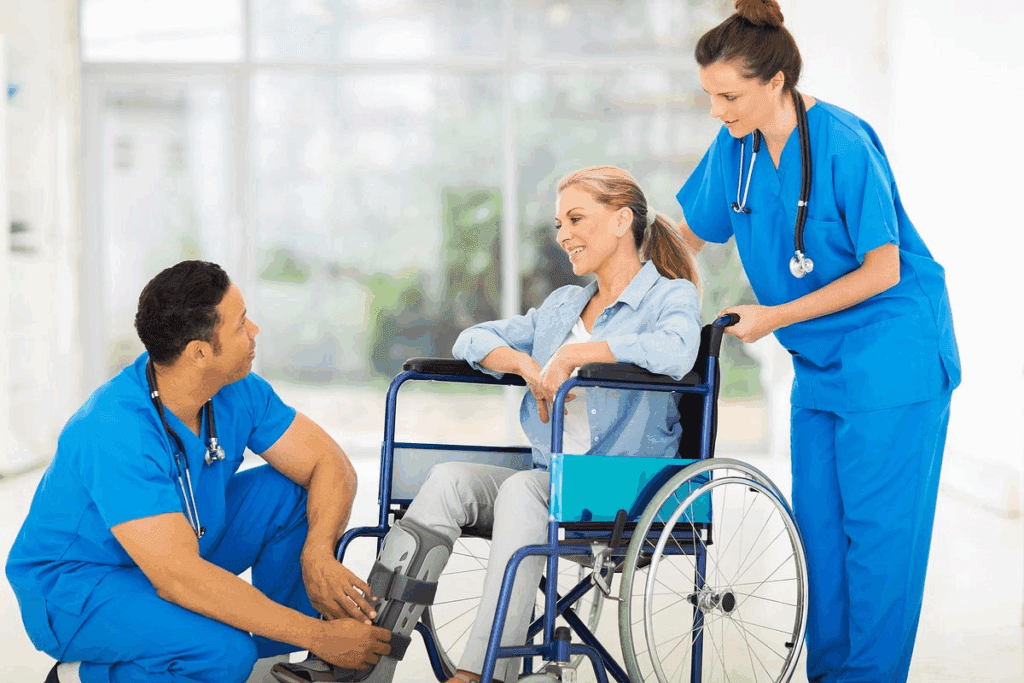
Studies reveal that 75% of patients who walk early after surgery recover faster. This shows how important walking is in recovery. By walking speeds up surgery recovery, people can leave the hospital sooner and avoid more problems.
Walking gently after surgery boosts improved circulation blood flow. This is key for healing tissues to get the oxygen and nutrients they need. This early ambulation post-op benefits speeds up recovery and improves overall health.
Key Takeaways
- Early ambulation significantly reduces recovery time post-surgery.
- Walking enhances circulation, aiding in the healing process.
- Gentle post-operative walking can minimize hospital stay.
- Improved circulation supports overall health and well-being.
- Patients who walk post-surgery often experience fewer complications.
The Science Behind Walking and Post-Surgical Recovery
Recent studies have shown how movement helps after surgery. Walking soon after surgery is now seen as key for recovery.
How Movement Affects Healing Processes
Movement, like walking, boosts healing. It enhances blood circulation, which is vital for healing tissues. This helps reduce inflammation and aids in tissue repair.
Walking also boosts the body’s healing powers. It boosts the immune system by increasing white blood cells. This helps fight off infections. Plus, it reduces the risk of complications like DVT and pulmonary embolism.
Research Evidence Supporting Early Ambulation
More research backs up the benefits of walking after surgery. Studies show patients who walk soon have better outcomes. For example, a Journal of Surgical Research study found walking early cuts down on complications.
A Journal study also found benefits. Patients who walked within 24 hours of surgery recovered faster and better than those who waited. This shows walking is essential in recovery plans.
Improved Circulation Blood Flow: The Primary Benefit
Walking after surgery boosts blood flow, helping your body heal. It improves circulation, which is key for delivering oxygen and nutrients to healing tissues. This is vital for recovery.
How Walking Enhances Blood Circulation
Walking is a simple yet effective way to boost blood circulation. When you walk, your muscles contract and relax. This action helps pump blood more efficiently throughout your body.
This increased circulation is vital for recovery. It ensures your body’s tissues get the nutrients and oxygen they need to heal.
The enhancement of blood circulation through walking comes from several factors:
- Increased heart rate, which pumps blood more efficiently
- Muscle contractions that help push blood upwards towards the heart
- Improved vascular function, allowing for better blood flow regulation
Oxygen and Nutrient Delivery to Healing Tissues
Improved circulation means better delivery of oxygen and nutrients to healing tissues. Oxygen is key for repairing damaged cells. Nutrients provide the building blocks for tissue regeneration. Walking ensures these vital components reach the healing areas efficiently.
The process involves several steps:
- Increased blood flow delivers oxygen to healing tissues
- Nutrients are transported to the areas needing repair
- Efficient removal of waste products, which can impede healing
Reducing Inflammation Through Better Blood Flow
Better blood flow also helps reduce inflammation, a common issue after surgery. Inflammation can slow healing and cause complications. Walking helps your body manage and reduce inflammation more efficiently.
The benefits of reduced inflammation include:
- Faster recovery times
- Less risk of complications
- Improved overall health outcomes
In conclusion, walking improves blood circulation, which is key for post-surgical recovery. It enhances oxygen and nutrient delivery and reduces inflammation. Walking plays a vital role in ensuring a smooth and effective healing process.
Preventing Complications Through Movement
Moving around after surgery is key to avoiding many complications. It helps prevent issues that can slow down recovery. Early walking is important to avoid problems linked to staying in bed too long.
DVT and Blood Clot Prevention
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a big risk after surgery, more so for those having orthopedic or abdominal surgeries. Walking boosts blood flow, which lowers the chance of blood clots in deep veins. Early walking is advised to prevent DVT.
| Risk Factors for DVT | How Walking Helps |
| Prolonged immobility | Improves blood circulation |
| Surgery type (orthopedic, abdominal) | Reduces blood stasis |
| Age and obesity | Enhances overall circulation |
Reducing Pulmonary Complications and Pneumonia Risk
Pulmonary issues, like pneumonia, can happen after surgery, more so for thoracic or abdominal surgery patients. Walking boosts lung health and aids in coughing, lowering the risk of lung problems. Regular movement can greatly reduce pneumonia risk.
Stimulating Bowel Function and Reducing Constipation
Constipation is common after surgery, caused by anesthesia and pain meds. Walking can help get bowel function back to normal and lower constipation risk. Early movement helps restore normal bowel function, easing discomfort and avoiding complications.
Knowing the benefits of movement after surgery helps patients play a big role in their recovery. It reduces complications and speeds up healing.
Physical Benefits Beyond Circulation
Walking after surgery does more than just improve blood flow. It plays a big role in recovery. It helps keep muscles strong, prevents them from wasting away, and boosts joint mobility.
Maintaining Muscle Strength and Preventing Atrophy
Muscle wasting is common after surgery, mainly if you’re not moving much. Walking fights this by keeping muscles strong and stopping them from wasting. It works many muscles at once, keeping them active and strong.
Research shows early walking after surgery can stop muscle weakness. A study in a Journal of found early walkers after orthopedic surgery had stronger muscles than those who didn’t.
Enhancing Joint Mobility and Flexibility
Walking also improves joint mobility and flexibility. It keeps joints moving smoothly, reducing stiffness. This is great for those who’ve had orthopedic surgery, where moving joints well is key to getting better.
A good walking plan can really help joints work better. Here are some ways walking helps joints:
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Recovery |
| Improved Range of Motion | Walking keeps or improves joint movement. | Makes it easier to do daily tasks by reducing stiffness. |
| Reduced Joint Stiffness | Walking helps keep joints flexible by moving synovial fluid. | Boosts mobility and cuts down on pain. |
| Increased Flexibility | Walking makes joints more flexible. | Helps maintain good posture and lowers injury risk. |
Adding walking to your recovery plan can bring these benefits. It makes recovery more complete and effective.
Mental and Emotional Benefits of Post-Surgery Walking
Walking after surgery helps with physical recovery and boosts mental and emotional health. It releases endorphins, which help manage pain and improve mood.
Endorphin Release and Pain Management
Walking after surgery releases endorphins, known as “feel-good” hormones. These hormones interact with the brain’s opioid receptors, reducing pain. This natural method can lower the need for opioid pain meds, reducing side effects.
Key benefits of endorphin release include:
- Reduced pain perception
- Improved mood
- Enhanced sense of well-being
A study in a Journal of found that exercise-induced endorphin release improves mood and reduces pain in surgery recovery patients.
“The psychological benefits of post-surgery walking should not be underestimated. It’s a simple yet effective way to improve mental health outcomes.”
Mood Enhancement and Depression Reduction
Walking after surgery also boosts mood and reduces depression. It increases serotonin and dopamine, key for mood regulation. Regular walking can lessen depression and anxiety symptoms in post-surgery patients.
The relationship between walking and mood enhancement can be summarized in the following table:
| Aspect | Benefit |
| Neurotransmitter Production | Increased serotonin and dopamine levels |
| Mood Regulation | Improved mood stability |
| Depression Symptoms | Reduced symptoms of depression |
Regular walking in recovery improves mental well-being. It’s key to include walking in the recovery plan for these benefits.
Walking Protocols for Different Types of Surgeries
Different surgeries need special walking plans for safe recovery. The surgery type, how big it is, and the patient’s health decide the walking plan.
Orthopedic Surgeries
Orthopedic surgeries, like knee or hip replacements, have specific walking plans. Patients might start with walkers or crutches. Early walking is key to avoid stiffness and help bones heal.
Knee replacement patients start with short walks, then walk more as their knee gets stronger. Hip surgery patients walk gently at first, focusing on avoiding dislocation.
Abdominal and Thoracic Procedures
Abdominal or thoracic surgery patients benefit from walking to prevent lung problems and aid in gut recovery. Gentle walking helps the bowels and reduces constipation risk.
Abdominal surgery patients start with short walks, then walk more as their muscles heal. Thoracic surgery patients do deep breathing exercises and walk to boost lung health.
Cardiac and Vascular Surgeries
Cardiac or vascular surgery patients walk to improve heart health and aid in healing. Walking should get gradually longer and harder to avoid too much strain.
Cardiac surgery patients start walking a day or two after surgery, with short walks. Vascular surgery patients also start walking early, watching for any signs of trouble at the surgery site.
Timeline and Progression: What to Expect
Knowing the recovery timeline helps patients set realistic goals and follow doctor’s orders. The journey to full recovery is split into stages, each with its own goals and rules.
Days 1-3: Initial Movements
Right after surgery, it’s important to start moving to avoid serious issues like blood clots. These first steps are small and gentle. They might be just sitting up or standing with help.
- Short, gentle movements
- Assistance from healthcare providers or caregivers
- Monitoring for any signs of complications
Week 1: Short, Frequent Walks
In the first week, patients are told to walk short distances often. This means walking for a few minutes every hour. As you get stronger, you can walk longer and more often.
Key aspects include:
- Starting with short walks (2-3 minutes)
- Gradually increasing duration and frequency
- Monitoring pain and discomfort levels
Weeks 2-4: Building Distance and Speed
By weeks 2-4, you’ll start to walk farther and faster. You might walk longer hallways or around the block. The walks will get more intense over time.
- Increasing walking distance
- Improving walking speed
- Incorporating gentle stretches or exercises
Months 1-3: Returning to Normal Activity
By months 1-3, you’ll likely be back to your usual activities. This stage means walking more and possibly starting other exercises. Always check with your doctor first.
Expectations include:
- Resuming most daily activities
- Increasing exercise intensity and duration
- Continuing to monitor progress and adjust as necessary
Walking Aids and Support Systems
Choosing the right walking aids and support systems is key for a smooth recovery after surgery. These tools offer stability and help regain confidence in walking.
Walkers, Crutches, and Canes
Walkers, crutches, and canes are common post-surgery aids. They help prevent falls and support recovery. The right choice depends on the surgery type, health, and mobility.
- Walkers give the most support, perfect for those needing balance help.
- Crutches are good for those who can bear some weight but need balance support.
- Canes offer minimal support, ideal for those needing a bit of extra help.
Supportive Footwear and Proper Equipment
Supportive footwear is also vital for recovery. Shoes with good arch support and cushioning can ease discomfort and prevent issues.
It’s important to ensure walking aids fit well and meet the patient’s needs. Using the wrong equipment can cause more harm.
Using the right walking aids and support systems can greatly improve recovery. It reduces complications and boosts mobility.
Nutrition and Hydration to Support Your Walking Program
Nutrition and hydration are key to better recovery and walking after surgery. Good nutrition gives your body what it needs to heal. Hydration helps with circulation and keeping your body temperature right.
Pre-Walk Nutrition for Energy
Eating the right foods before walking can give you energy and prevent tiredness. A meal or snack with carbs, protein, and fats is best. Try:
- Oatmeal with fruits and nuts
- Whole-grain toast with avocado and eggs
- Greek yogurt with berries and honey
Timing is key. Eat 1-3 hours before walking to digest properly.
Hydration Before, During, and After Walking
Staying hydrated is vital for good performance and avoiding dehydration. Here’s how to stay hydrated:
- Drink water or a hydrating drink 30 minutes before walking.
- Keep drinking during your walk, more so for long or hard walks.
- Drink water after walking to help your body recover.
Check your urine color. It should be pale yellow or clear.
Recovery Nutrition to Support Healing
After walking, eat carbs and protein to help muscles recover and heal. Good choices include:
| Nutrient | Examples | Benefits |
| Carbohydrates | Whole-grain crackers, fruits | Replenish energy stores |
| Protein | Lean meats, nuts, eggs | Support muscle repair |
| Healthy Fats | Nuts, seeds, avocados | Support overall health |
Eating well and staying hydrated can really help your walking program and recovery. Focus on good nutrition before walking, staying hydrated, and eating right after. This will help your body heal and improve your walking.
Tracking Progress and Setting Goals
Setting realistic goals and tracking progress are key to a post-surgery walking program. They help patients regain strength and mobility. By watching their progress, patients stay motivated and adjust their walks as needed.
Step Count Goals and Gradual Increases
Setting step count goals is a good way to track progress. Start with small goals that match the patient’s current health and mobility. As they get better, increase these goals to keep them moving forward without overdoing it.
For example, a patient might aim for 500 steps a day and then increase it as they get stronger. This slow increase keeps them motivated and avoids burnout.
Wearable Trackers and Mobile Apps
Wearable trackers and mobile apps are great for tracking activity. Devices like Fitbits or smartwatches track steps, distance, and heart rate. They give patients a clear view of their progress.
Apps like MyFitnessPal or Strava offer more features. They help plan routes, track calories, and connect with others. These tools make tracking progress easier and help set achievable goals.
Journaling Your Recovery Journey
Journaling is also a powerful way to track recovery. By writing down daily activities, pain levels, and feelings, patients understand their healing better.
Journaling lets patients see their progress, spot patterns, and make better walking plans. It’s also a way to share their journey with healthcare providers to improve their recovery plan.
Special Considerations for Different Populations
Different patient groups face unique challenges during post-surgical recovery. These challenges include age, health conditions, and mobility issues. Each factor can affect the recovery process differently.
Elderly Patients: Safety and Adaptation
Elderly patients need extra support during recovery. They have less physical strength and may have other health problems. Key considerations include:
- Fall prevention measures
- Adjustments to medication regimens
- Monitoring for signs of delirium or cognitive decline
Healthcare providers may suggest physical therapy that fits the patient’s abilities. This helps in recovery and keeps them independent.
Patients with Obesity or Diabetes
Patients with obesity or diabetes face extra challenges in recovery. These include slow wound healing and a higher risk of infection. Management strategies include:
- Optimizing blood glucose control
- Implementing nutritional support tailored to their metabolic needs
- Monitoring for signs of wound complications
These patients might benefit from multidisciplinary care. This care involves endocrinologists, nutritionists, and other specialists.
Those with Pre-Existing Mobility Issues
Patients with mobility issues, like neurological conditions or chronic arthritis, need careful planning. Considerations include:
- Modifying physical therapy to accommodate their condition
- Using assistive devices to enhance mobility and safety
- Coordinating care with specialists to manage their underlying condition
By tailoring the recovery plan to their specific needs, these patients can achieve better outcomes. They can regain their functional abilities more effectively.
Potential Challenges and Warning Signs
Knowing the challenges and warning signs during recovery is key. It helps ensure a smooth healing process. As patients follow their walking program, being alert to these signs can prevent issues and speed up recovery.
Recognizing When to Slow Down or Stop
It’s important for patients to know when to slow down or stop walking. Severe pain, trouble breathing, or sudden dizziness mean it’s time to stop. If these symptoms happen, patients should rest before walking again at a slower pace.
Managing Pain and Swelling
Controlling pain and swelling is a big part of recovery. Using elevation, ice packs, and compression can help with swelling. For pain, talking to a healthcare provider is best. They might suggest medication or other treatments.
Keeping an eye on pain and swelling is important. If pain gets worse or swelling grows, it might be time to change the walking plan or get medical advice.
When to Contact Your Healthcare Provider
Knowing when to call a healthcare provider is critical. Signs of infection, like redness, warmth, or pus around the surgical site, or symptoms like fever, chills, or severe pain that doesn’t get better with medication, need immediate attention.
Also, watch for other warning signs. Chest pain, severe headache, or sudden numbness or weakness could mean serious problems that need quick medical help.
Conclusion: Walking as a Cornerstone of Surgical Recovery
Walking is key in recovering from surgery. It boosts physical and mental health, helping patients heal faster. It improves blood flow, reduces risks, and boosts overall health.
Walking offers many benefits in surgical recovery. It helps blood flow better and lowers the chance of blood clots and lung problems. These are all important for a smooth recovery.
Adding walking to a recovery plan helps patients heal quicker. With the right help, walking can lead to better recovery results. It’s a vital part of getting back to full health.
FAQ
How soon after surgery can I start walking?
Most doctors say you can start walking in 1-2 days after surgery. But, it depends on your surgery type and health.
What are the benefits of walking after surgery?
Walking helps your body in many ways. It improves blood flow, lowers the risk of blood clots, and helps your bowels work better. It also keeps your muscles strong and joints flexible.
How does walking improve circulation and blood flow?
Walking makes your heart beat faster and blood flow better. This brings oxygen and nutrients to your healing tissues. It helps reduce swelling and speeds up recovery.
Can walking help manage pain after surgery?
Yes, walking releases endorphins. These are natural painkillers that can help manage pain and improve your mood.
What type of walking aid should I use after surgery?
The right walking aid depends on your surgery and how mobile you are. You might need a walker, crutches, cane, or supportive shoes.
How can I track my progress while walking after surgery?
You can track your progress with step count goals, wearable trackers, or mobile apps. Keeping a journal can also help you see how far you’ve come.
Are there any special considerations for elderly patients or those with pre-existing mobility issues?
Yes, elderly patients and those with mobility issues need special care. They might need adapted walking programs and safety measures to ensure a safe recovery.
What are the signs that I should stop walking and contact my healthcare provider?
If you experience increased pain, swelling, dizziness, nausea, or trouble breathing, stop walking and call your doctor.
How can nutrition and hydration support my walking program after surgery?
Eating right and staying hydrated before, during, and after walking gives you energy. It also supports your healing and recovery.
Can I walk outdoors after surgery?
Yes, but be careful. Consider the weather, terrain, and safety when walking outside after surgery.
How long does it take to return to normal activity after surgery?
It varies based on your surgery and recovery. Generally, it can take weeks to months to get back to normal.
Reference:
Early mobilization after surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PubMed Central (PMC). https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8974232/



































