Uveitis is a serious eye condition that affects the uvea. This is the middle layer of the eye, including the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. If not treated, it can cause big vision problems.Identifying symptoms like one eye sensitive to light and watery which may indicate Uveitis or other serious issues. See a doctor for one eye sensitive to light and watery.
At Liv H, we know uveitis can cause pain, redness, and vision loss. It can harm not just the uvea but other parts of the eye too. It’s important to spot the symptoms early and get medical help fast to avoid lasting vision damage.
Key Takeaways
- Uveitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the uvea, a critical part of the eye.
- Symptoms include pain, redness, and vision loss, necessitating prompt medical attention.
- Early diagnosis is key to prevent long-term vision damage.
- Uveitis can affect people of all ages.
- Untreated uveitis can lead to serious vision issues.
Understanding Uveitis: An Overview
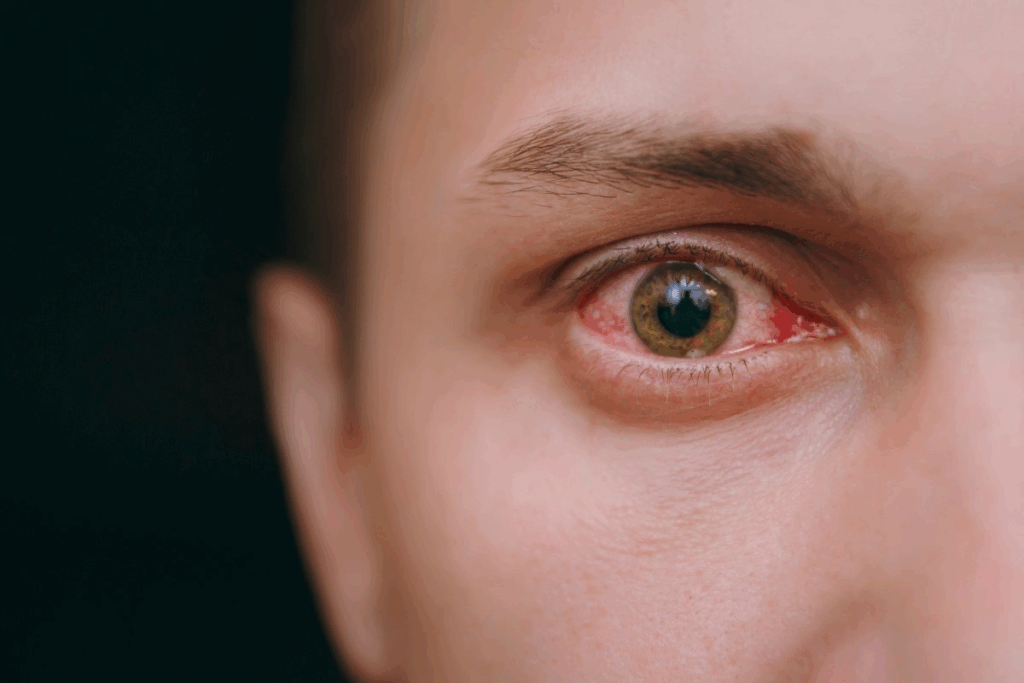
To understand uveitis, we need to know about the uvea and its role in eye health. Uveitis is when the uvea, a key part of the eye, gets inflamed. This can cause symptoms and problems, so it’s important to know what causes it and its effects.
Definition and Anatomy of the Uvea
The uvea is the middle layer of the eye, made up of the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. It’s essential for supplying blood to the retina and other eye parts. When the uvea gets inflamed, known as uveitis, it can disrupt this blood supply, leading to vision issues. Uveitis can be caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, or injuries.
Prevalence and Impact Statistics
Uveitis is a major cause of preventable blindness globally. It affects between 69 to 204 people per 100,000, with annual incidence rates from 17 to 52 per 100,000. In the developed world, uveitis is the third leading cause of preventable blindness. This highlights the need to understand and manage uveitis to avoid severe vision loss.
Types of Uveitis and Their Characteristics
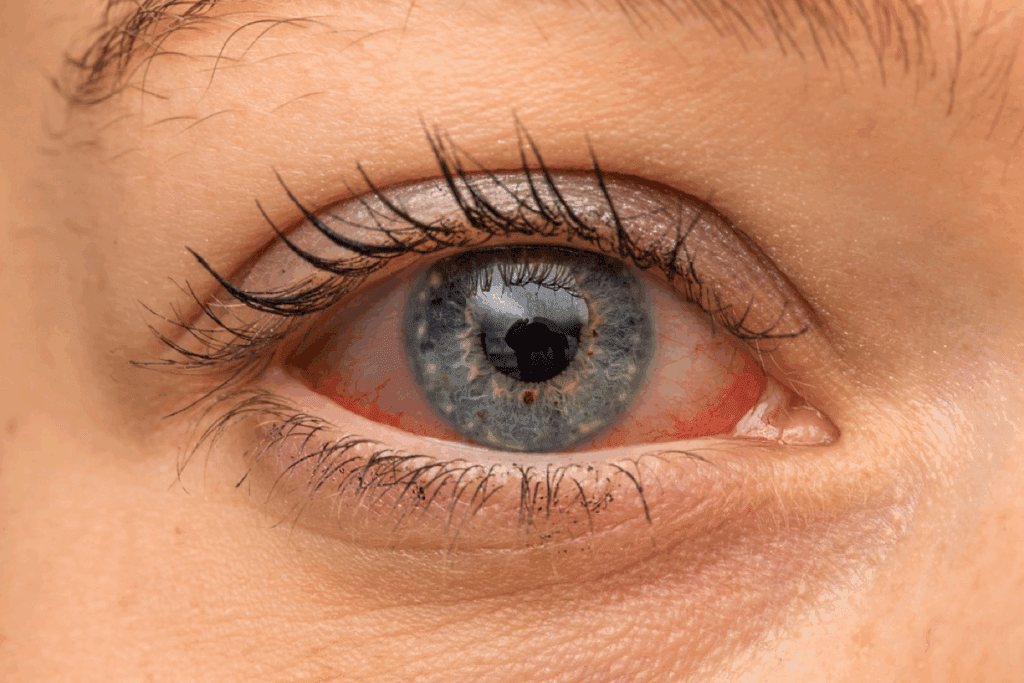
Uveitis can be divided into several types based on where the uvea is inflamed. Knowing this helps us understand the symptoms and how to treat it.
Anterior Uveitis (Iritis)
Anterior uveitis, or iritis, is the most common type. It affects the front part of the uvea, mainly the iris. Symptoms include eye pain, redness, and light sensitivity. Treatment usually involves anti-inflammatory meds to reduce inflammation and ease symptoms.
Intermediate Uveitis
Intermediate uveitis involves inflammation of the vitreous humor and the peripheral retina. It can cause floaters and blurred vision. Patients may need corticosteroids or immunosuppressive therapy to manage it.
Posterior Uveitis
Posterior uveitis affects the back part of the uvea, including the retina and choroid. Symptoms include vision problems and floaters. Prompt treatment is key to prevent retinal damage.
Panuveitis
Panuveitis is a severe form that affects all layers of the uvea. It can cause eye pain, vision loss, and light sensitivity. Treatment often involves a mix of medications to control inflammation and prevent complications.
Type of Uveitis | Area Affected | Common Symptoms |
Anterior Uveitis | Front part of the uvea (iris) | Eye pain, redness, sensitivity to light |
Intermediate Uveitis | Vitreous humor and peripheral retina | Floaters, blurred vision |
Posterior Uveitis | Back part of the uvea (retina and choroid) | Vision disturbances, floaters |
Panuveitis | All layers of the uvea | Eye pain, vision loss, sensitivity to light |
Common Causes and Risk Factors of Uveal Inflammation
Knowing what causes uveitis is key. It can come from autoimmune disorders, infections, and environmental factors. Uveitis is complex, so finding the cause is vital for the right treatment.
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune diseases are a big risk for uveitis. In these diseases, the body attacks itself. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and multiple sclerosis raise the risk. An overactive immune system can cause inflammation in the uvea, leading to uveitis.
Infections
Infections are a common cause of uveitis. Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can start uveitis. For example, toxoplasmosis, a parasitic infection, can cause posterior uveitis. Knowing how infections lead to uveitis is key for managing it well.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also affect uveitis. Trauma to the eye can start uveitis. Exposure to chemicals or toxins might also play a part. But, more research is needed to understand their full impact.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics also play a big role in uveitis. People with a family history of autoimmune diseases or uveitis are at higher risk. Certain genes can increase this risk, making genetic screening important for those with a family history.
By knowing these causes and risk factors, we can improve diagnosis and treatment of uveitis. This can help reduce complications and improve patient outcomes.
Recognizing Inflammatory Eye Disease Symptoms
It’s important to know the signs of uveitis early. This is because uveitis can harm your sight if not treated right away. Knowing the common symptoms helps patients get help fast.
Eye Pain and Discomfort
Eye pain or discomfort is a key sign of uveitis. This pain can be mild or very strong. It might feel like there’s pressure in your eye.
In some cases, the pain can make it hard to do everyday things.
Vision Changes
Vision problems are another sign of uveitis. You might see things blurry, have trouble seeing colors, or see less clearly. These vision changes can happen suddenly or slowly.
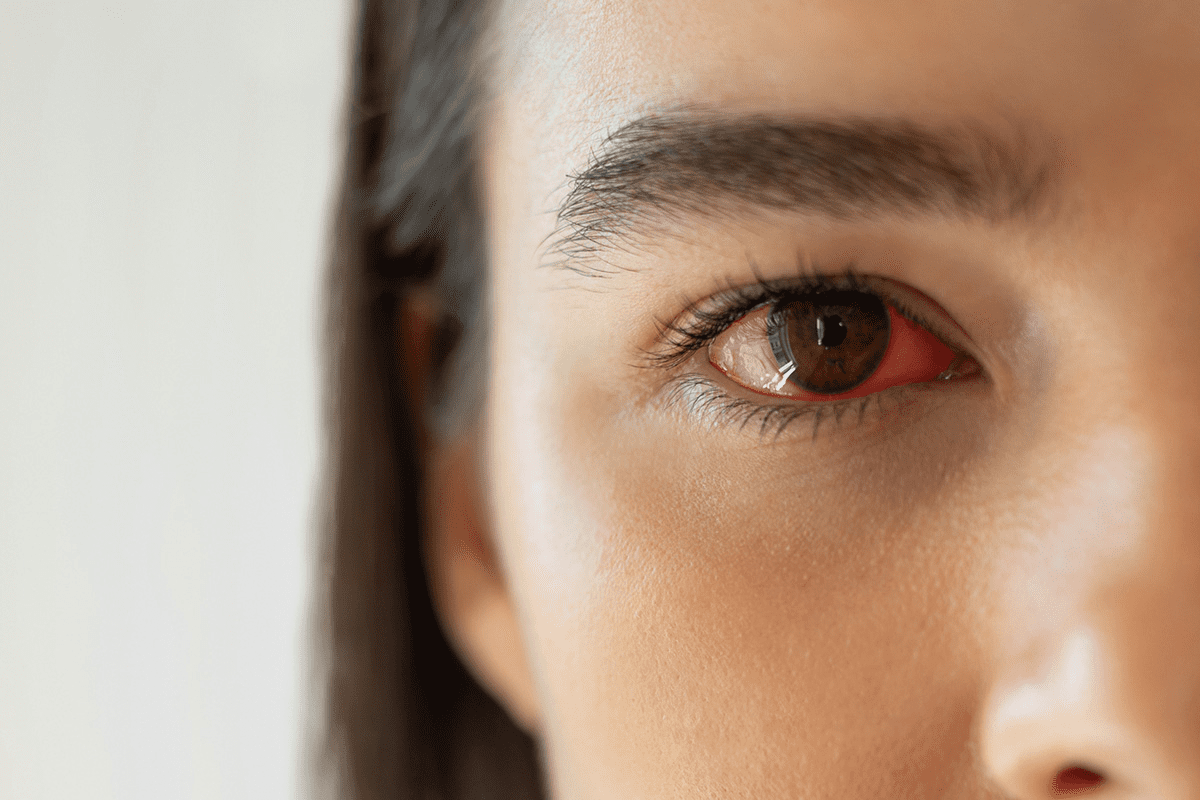
Redness and Inflammation
Red or pink eyes are signs of uveitis. The inflammation makes the eye look different. Sometimes, the eye can swell or feel sore.
Floaters and Visual Disturbances
Floaters are small spots that seem to move in your eye. They can be a sign of uveitis. You might also see flashes of light or feel very sensitive to light.
These symptoms can be scary and disrupt your daily life.
If you notice these symptoms, see a doctor right away. Early treatment can help prevent serious problems and keep your vision safe.
One Eye Sensitive to Light and Watery: A Primary Warning Sign
Uveitis often shows up with symptoms like being sensitive to light and having watery eyes in one eye. These signs can be very uncomfortable and are key warning signs that something is wrong.
Understanding Photophobia in Uveitis
Photophobia, or being sensitive to light, is a common symptom of uveitis. This makes the eye very sensitive to light, causing discomfort or pain. The inflammation in uveitis irritates the eye, leading to this sensitivity.
Photophobia can really disrupt daily life. It can make simple tasks like reading, watching TV, or going outside on a sunny day hard.
Why Uveitis Causes Excessive Tearing
Excessive tearing is another symptom of uveitis. The inflammation and irritation of the eye make the lacrimal gland produce more tears. This results in a watery eye. The eye is trying to soothe and protect itself with these extra tears.
While tears can be comforting, persistent or severe tearing needs a doctor’s check-up. This is true, even if it’s accompanied by other symptoms.
Differentiating from Other Eye Conditions
Sensitivity to light and watery eyes are big signs of uveitis. But, these symptoms can also show up in other eye problems. For example, conjunctivitis or dry eye syndrome can cause similar symptoms. Yet, the way symptoms come together can help tell uveitis apart from other conditions.
If you’re having trouble with sensitivity to light or watery eyes, see an eye specialist. This is true, even if you have other symptoms like eye pain or vision changes. Getting the right diagnosis is key to effective treatment.
Eyeball Pain and Blurred Vision: The Connection
Uveitis, a form of eye inflammation, can cause blurred vision and eye pain. When the uvea gets inflamed, it can harm different parts of the eye. This leads to symptoms that can really affect your daily life.
How Inflammation Affects Vision Clarity
Inflammation in uveitis can mess with your vision clarity. When the uvea is inflamed, it makes the eye hurt and vision blurry. This is because the inflammation messes with how the eye handles visual info.
The uvea is key for the eye, bringing blood and nutrients to other parts. When it’s inflamed, it can mess up the eye’s normal work. This leads to vision problems.
The Relationship Between Pain and Visual Disturbances
The link between eyeball pain and blurred vision in uveitis comes from the inflammation. When the uvea gets inflamed, it causes both pain and vision issues. The pain comes from the inflammation irritating the eye’s nerves. The blurred vision is from the inflammation messing with the eye’s focus.
It’s important to understand this link to manage uveitis well. By tackling the inflammation, you can reduce both pain and vision problems.
Tracking Vision Changes
Keeping an eye on vision changes is key in managing uveitis. By watching for changes, you can spot flare-ups early. This means you can act fast. Keeping a vision diary or checking your vision regularly helps.
Regular eye exams are also vital. They help track uveitis’s impact on your vision. Working with an eye care pro helps you manage your condition and protect your sight.
Sudden Eye Pain in Children and Adults
Eye pain from uveitis can happen suddenly and affects both kids and adults. It shows up in different ways. Uveitis is a condition that can happen at any age, so it’s important to know about it and get medical help fast.
Age-Specific Symptoms
Uveitis symptoms change with age. Adults might feel sudden eye pain, redness, and light sensitivity. Kids might not show clear signs, so it’s key to get their eyes checked often.
Some common symptoms by age include:
- In children: lack of obvious symptoms, requiring regular eye check-ups.
- In adults: sudden onset of eye pain, redness, and photophobia.
How Children May Express Eye Discomfort
Children with uveitis show eye discomfort in their own way. They might:
- Rub their eyes a lot.
- Talk about general eye discomfort without saying it’s painful.
- Change their behavior, like staying away from bright lights.
Parents and caregivers should watch for these signs and get medical help if they think something’s wrong.
Differences in Presentation Across Age Groups
Uveitis shows up differently in different ages. Adults might feel sharp pain and see things blurry. Kids might just seem uncomfortable or not want to do things because of their eyes.
Key differences include:
- Adults: more likely to say they have pain and blurry vision.
- Children: might not say they’re uncomfortable, so watching their behavior is important.
Knowing these differences helps get a diagnosis and treatment on time. We stress the need for regular eye exams, mainly for kids, to catch uveitis early and avoid problems.
Diagnosis of Uveitis
To find out if you have uveitis, doctors use many tools and methods. They do a detailed eye check to see if you have it, what kind, and how bad it is.
Initial Eye Examination
The first step is a detailed eye check. We use a slit-lamp to look at the front part of your eye for signs of inflammation. This helps us see how bad the uveitis is and if there are any other problems.
We also check how well you can see and your eye pressure. These tests tell us a lot about your eye’s health and help us decide how to treat you.
Specialized Diagnostic Tests
After the first eye check, we might do more tests. These include:
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Gives us detailed pictures of your retina to see if there are any changes.
- Fluorescein Angiography: Helps us see your retinal blood vessels and find any problems.
- Ultrasound Biomicroscopy: Looks at the front part of your eye to find things like tumors or cysts.
Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
Slit-Lamp Examination | Inspect the anterior segment for signs of inflammation |
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) | Provide detailed images of the retina |
Fluorescein Angiography | Assess the retinal vasculature and detect abnormalities |
Differential Diagnosis
It’s important to tell uveitis apart from other eye problems that look similar. A careful check helps us make the right diagnosis and plan the best treatment.
By using the results from eye exams, special tests, and figuring out what else it could be, we can accurately diagnose uveitis. Then, we start the right treatment to keep your vision safe.
Treatment Approaches for Uveitis
The main goal in treating uveitis is to lessen inflammation and ease symptoms. We use different treatments based on the type and severity of the condition.
Medication Options
Medicines are key in managing uveitis. The right medicine depends on the inflammation’s location and the patient’s health.
Corticosteroid eye drops are often the first choice for anterior uveitis. They help reduce inflammation and ease pain. For more severe cases or posterior uveitis, oral corticosteroids or injectable corticosteroids may be needed.
Steroid Therapy
Steroid therapy is vital in treating uveitis, mainly for acute inflammation. Yet, long-term use can lead to side effects like cataracts and high eye pressure.
Immunosuppressive Treatments
For those not helped by steroids or needing long-term treatment, immunosuppressive drugs are used. These drugs lower the immune system’s abnormal response causing uveitis. Examples include methotrexate, cyclosporine, and azathioprine.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery may be needed for uveitis complications or conditions caused by chronic inflammation. This can include cataract, glaucoma, or vitreoretinal surgery for retinal detachment or persistent inflammation.
We tailor each treatment plan to the patient’s unique situation. By using these approaches together, we can manage uveitis well. This helps prevent complications and keeps vision safe.
Complications of Untreated Uveitis
Uveitis can cause serious problems if not treated. It’s a condition that needs quick and proper care to avoid eye damage. We’ll look at the possible issues that can happen if uveitis isn’t treated right.
Vision Loss and Blindness
Untreated uveitis can lead to vision loss or even blindness. The inflammation can harm the eye’s structures, causing permanent vision problems. The extent of vision loss can vary, but it can be severe, even leading to total blindness.
Secondary Glaucoma
Uveitis can cause secondary glaucoma, where the eye pressure goes up. This high pressure can damage the optic nerve, making vision worse. Secondary glaucoma is a serious issue that needs quick medical help to avoid more vision loss.
Cataracts
The inflammation from uveitis can also lead to cataracts. Cataracts cloud the lens, making vision blurry. If not treated, cataracts can badly affect vision, needing surgery.
Retinal Damage
Retinal damage is another risk of untreated uveitis. The retina is key for seeing, and damage can cause vision problems like floaters and flashes. Retinal damage can be permanent, making early treatment of uveitis very important.
We stress the need to see a doctor if you think you have uveitis. Early treatment can greatly lower the risk of these problems, keeping your vision and eye health safe.
When to Seek Medical Help for Eye Symptoms
Eye symptoms can be a sign of a serious condition. It’s important to know when to seek medical help. Figuring out how serious your symptoms are can be tough. But knowing the warning signs can help you make good choices for your eye health.
Emergency Warning Signs
Certain eye symptoms need immediate attention. If you have any of these, get help right away:
- Sudden severe eye pain
- Vision loss or blurred vision
- Increased sensitivity to light
- Eye redness or swelling
- Floaters or flashes of light
Quick Sharp Pain in Eye: When to Visit the ER
A quick sharp pain in the eye can be scary. Not all sharp pains are emergencies. But some situations need a trip to the emergency room. If your sharp eye pain comes with:
- Vision changes
- Eye trauma
- Severe headache
Symptoms That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Some eye symptoms might seem minor but can be serious. Don’t ignore:
- Persistent eye discomfort
- Changes in vision
- Unusual eye discharge
Finding the Right Eye Specialist
If you’re worried about your eye symptoms, finding the right specialist is key. Look for an ophthalmologist or optometrist who:
- Has experience with your specific condition
- Is affiliated with a reputable medical institution
- Offers complete care and support
By knowing the warning signs and when to seek help, you can protect your eye health. This can prevent long-term damage.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Eye Health
Understanding uveitis is key to managing it. We’ve looked into the details of this inflammatory eye disease. This includes its different types, causes, symptoms, and treatments.
By knowing the signs, like eye pain and sensitivity to light, people can get help fast. This is important for early treatment and better outcomes.
Early treatment is vital for those with uveitis. It helps prevent serious problems like vision loss. Taking care of your eye health is essential.
Managing uveitis well means using medicine, making lifestyle changes, and keeping an eye on your health. It’s important to work with your doctor to create a treatment plan that’s right for you. By doing this, you can control uveitis and keep your life quality high.
FAQ
What is uveitis and how does it affect the eye?
Uveitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the uvea, the middle layer of the eye. It can cause vision problems, eye pain, and sensitivity to light. If left untreated, it can lead to vision loss and blindness.
What are the different types of uveitis?
There are four main types of uveitis: anterior, intermediate, posterior, and panuveitis. Each type affects different parts of the uvea and has distinct characteristics.
What causes uveitis?
Uveitis can be caused by various factors. These include autoimmune disorders, infections, environmental factors, and genetic predisposition. Understanding the cause is key for effective treatment.
What are the common symptoms of uveitis?
Common symptoms include eye pain, vision changes, redness, floaters, and sensitivity to light. Some people may also experience watery eyes or blurred vision.
How is uveitis diagnosed?
Diagnosing uveitis involves a thorough eye examination. This includes a review of medical history, visual acuity tests, and specialized tests like OCT or fluorescein angiography.
What are the treatment options for uveitis?
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of uveitis. Options include medications, steroid therapy, immunosuppressive treatments, and surgery.
Can uveitis cause blindness?
Yes, if left untreated or undertreated, uveitis can cause vision loss and blindness. Prompt medical attention is essential to prevent damage.
How can I manage my uveitis symptoms?
Managing symptoms involves medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring. This includes avoiding triggers, using protective eyewear, and attending follow-up appointments.
When should I seek medical help for eye symptoms?
Seek medical help immediately for sudden or severe eye pain, vision changes, or symptoms like flashes of light or increased sensitivity to light.
Can children develop uveitis?
Yes, children can develop uveitis, which may present differently than in adults. If your child complains of eye pain or vision problems, consult an eye specialist.
Is uveitis contagious?
Uveitis is not contagious, but it can be a sign of an underlying condition that may require medical attention.
What is the prognosis for uveitis?
With prompt and proper treatment, many people with uveitis can manage symptoms and prevent complications. Regular follow-up care is essential for maintaining eye health.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK540993/