At Liv Hospital, we know how bad lumbar and cervical spine pain can be. That’s why we use advanced interlaminar epidural injection techniques to help. This method is key in managing spine pain, helping patients feel better and live better lives. Get the ultimate guide to the interlaminar epidural injection. We explain the procedure steps for both lumbar and cervical applications.
We mix the newest medical tech with care that puts patients first. The interlaminar epidural injection is a well-known way to tackle spine problems. We aim to do this procedure with great care and precision.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the role of interlaminar epidural injections in spine pain management
- The benefits of advanced techniques in epidural injections
- Overview of the step-by-step guide for lumbar and cervical procedures
- The importance of patient-focused care in medical procedures
- Liv Hospital’s commitment to international standards of care
The Fundamentals of Interlaminar Epidural Injection
Understanding interlaminar epidural injections is key for healthcare pros to help patients with spinal pain. We’ll look at what it is, how it’s used, and why it works. Plus, we’ll see how it helps manage pain.
Definition and Clinical Applications
An interlaminar epidural steroid injection puts corticosteroids and local anesthetics into the epidural space. It’s done through the interlaminar space. This method helps with spinal issues like herniated discs and spinal stenosis.
This technique is used for both lumbar and cervical spine pain. It targets pain relief by delivering medication directly to the epidural space.
Anatomical Basis of the Interlaminar Approach
The interlaminar approach targets the epidural space between the vertebral laminae. Knowing the spine’s anatomy is vital for this procedure. The epidural space has fat, veins, and nerve roots, making it perfect for pain relief.
Evidence-Based Outcomes for Pain Management
Many studies show interlaminar epidural steroid injections work well for spinal pain. They offer pain relief and help patients function better.
| Study | Outcome | Follow-up Period |
| Manchikanti et al. (2017) | Significant pain relief and functional improvement | 12 months |
| Cohen et al. (2012) | Improved pain scores and reduced medication use | 6 months |
| Bensler et al. (2018) | Effective pain management and reduced need for surgery | 24 months |
These studies prove interlaminar epidural steroid injections are a valuable treatment for spinal pain.
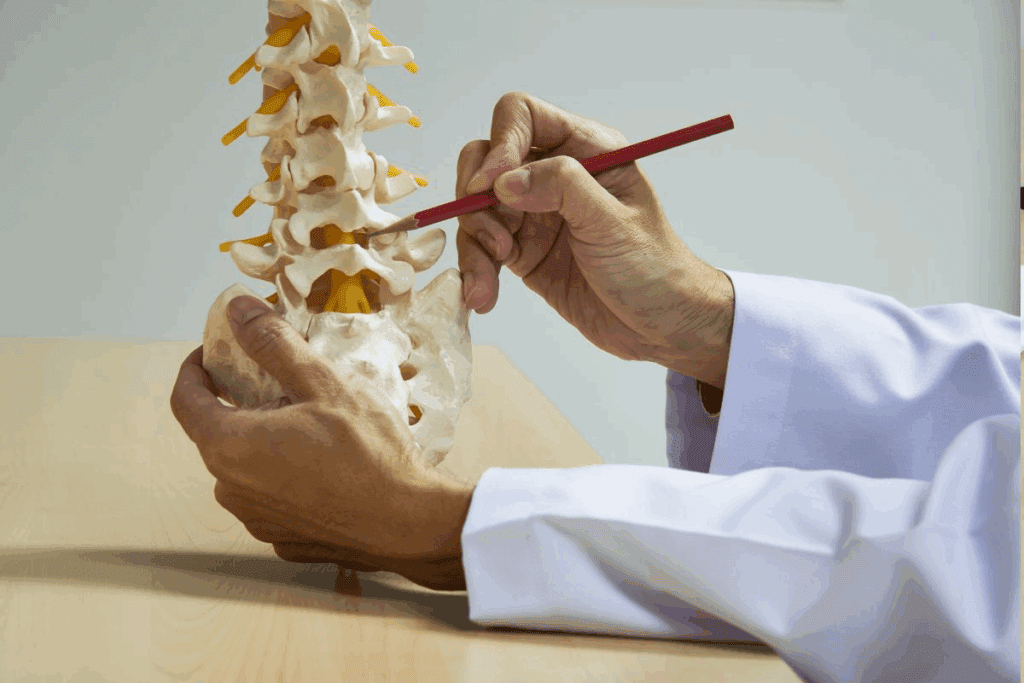
Anatomy of the Interlaminar Space
The anatomy of the interlaminar space changes a lot in different parts of the spine. This is important for doctors to know when they do interlaminar epidural injections. The interlaminar space is the area between the vertebrae’s laminae. It’s a key spot for epidural procedures.
Lumbar and Sacral Interlaminar Anatomy
In the lumbar area, the spaces between the vertebrae are wider. This makes it easier to get to the epidural space. The lumbar spine has bigger spaces than the cervical or thoracic regions.
When doing a lumbar interlaminar epidural steroid injection (ILESI), knowing the anatomy is key. The njx interlaminar lmbr sac procedure needs exact knowledge of the lumbar and sacral anatomy for safe and effective needle placement.
The sacral area has its own unique features because of the sacrum’s fused structure. The sacral hiatus is a key landmark for caudal epidural injections. Knowing the sacral anatomy well is important for successful procedures in this area.
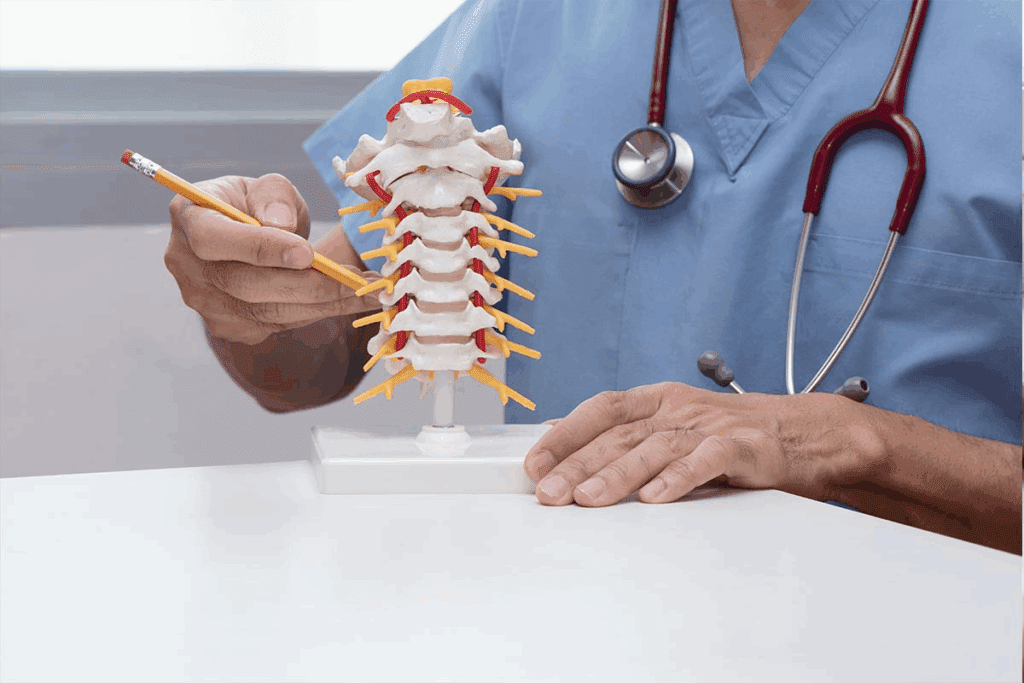
Cervical and Thoracic Interlaminar Considerations
The cervical and thoracic spine are different because of their anatomy. In the cervical area, the spaces are narrower, and there’s a higher risk of problems. Doing a cervical ILESI needs precise knowledge and careful technique to avoid issues.
The thoracic spine is more complex because of its shape and the rib cage. The spaces in the thoracic area are smaller, so careful technique is needed for safe access to the epidural space.
Epidural Fat Distribution and Clinical Relevance
Epidural fat distribution is key for the success of epidural injections. The amount and where the fat is can affect how the injectate spreads. In areas with more fat, the injectate might spread more, which can change the outcome of the procedure.
Knowing how epidural fat distribution affects the procedure is important for making it work better. This knowledge helps doctors choose the right amount and type of injectate. This can make the procedure more successful.
Indications and Patient Selection
Choosing the right patients for interlaminar epidural injections is key. It’s important to know when and when not to use this treatment. These injections help with many spinal problems.
Primary Indications for ILESI Procedures
These injections are mainly for people with radicular pain and neck pain from disc issues. They aim to cut down inflammation and ease pain by putting corticosteroids in the epidural space.
The main reasons for using ILESI include:
- Radiculopathy from herniated discs or spinal stenosis
- Pain from discs without big herniations
- Pain after surgery or failed back surgery syndrome
Specific Conditions Treated with Lumbar Interlaminar Approach
The lumbar interlaminar method is great for lower back and leg issues. It’s used for:
| Condition | Description | Symptoms |
| Lumbar Radiculopathy | Compression or irritation of nerve roots in the lumbar spine | Lower back pain, leg pain, numbness, tingling |
| Spinal Stenosis | Narrowing of the spinal canal, often causing nerve compression | Pain, weakness, numbness in legs, worse with walking |
| Disc Herniation | Protrusion of the intervertebral disc, potentially compressing nerves | Back pain, radiating pain to legs, neurological deficits |
Appropriate Candidates for Cervical Interlaminar Injections
Cervical interlaminar injections are for those with neck pain and nerve issues. It’s vital to pick the right patients because of the neck’s delicate structures.
Good candidates have:
- Cervical radiculopathy with arm pain and nerve symptoms
- Cervical disc herniation causing nerve symptoms
- Pain after cervical spine surgery
Contraindications and Risk Assessment
Interlaminar epidural steroid injections help many patients but have risks and contraindications. We must evaluate these carefully to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Absolute Contraindications
Certain conditions make interlaminar epidural steroid injections unsafe. These include active infections, where steroids could worsen the infection. Also, uncontrolled coagulopathy raises the risk of bleeding.
Progressive neurological decline is another absolute no-go. It may signal a serious condition needing different treatment.
Relative Contraindications
Relative contraindications are conditions that might not completely rule out the injections but need careful thought. These include poorly controlled chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension. Steroid injections could have big effects on these conditions.
Other relative contraindications are previous adverse reactions to steroid injections or a history of hard-to-manage side effects from corticosteroids.
Pre-Procedure Risk Stratification
Before an interlaminar epidural steroid injection, we do a detailed risk assessment. We look at the patient’s health, the condition being treated, and any procedure risks.
| Risk Factor | Assessment Criteria | Mitigation Strategy |
| Bleeding Risk | Coagulation status, anticoagulant use | Adjust anticoagulants, monitor coagulation |
| Infection Risk | Active infection, immunocompromised status | Delay procedure until infection resolved, prophylactic antibiotics |
| Neurological Risk | Progressive neurological decline, previous neurological conditions | Alternative diagnostic approaches, careful neurological monitoring |
By carefully looking at these factors, we can lower risks and improve outcomes for patients getting interlaminar epidural steroid injections.
Equipment and Medication Preparation
To make interlaminar epidural steroid injections work well, we must prepare everything carefully. This preparation boosts the procedure’s success and lowers the risk of problems.
Standard Equipment Setup for ILESI and LESI Procedures
For interlaminar epidural steroid injections (ILESI) and lumbar epidural steroid injections (LESI), we need a few key items. These include a low-resistance syringe, a Tuohy epidural needle, and equipment for fluoroscopic guidance. Fluoroscopic guidance is key for placing the needle accurately and seeing the injection in real-time.
We use a low-resistance syringe for a smooth medication delivery. The Tuohy epidural needle is chosen for its curved tip, making it easier to move through the epidural space.
Needle Selection and Specifications
Picking the right needle is vital for a successful procedure. The Tuohy needle is often used because it’s designed to avoid dural puncture. Needle length and gauge depend on the patient’s body and the procedure’s needs.
Medication Formulations and Dosing
The medications for ILESI and LESI usually mix corticosteroids and local anesthetics. Corticosteroids help reduce swelling, and local anesthetics give quick pain relief. We adjust the medication and dosage for each patient’s specific situation.
“The choice of medication and dosage should be carefully considered to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing possible side effects.” – Expert in Pain Management
By preparing the right equipment and medication, we can perform a safe and effective interlaminar epidural steroid injection. This helps our patients get the best pain relief possible.
Imaging Guidance Techniques for Interlaminar Epidural Steroid Injection
Effective imaging guidance is key for safe and effective interlaminar epidural steroid injections. We use advanced imaging to place the needle accurately and deliver the treatment.
Fluoroscopic Setup and Positioning
Fluoroscopic guidance is vital for these injections. Proper fluoroscopic setup and positioning are essential for seeing the target area. We start by placing the patient on a special table that lets us see clearly.
The fluoroscope is adjusted to show a clear view of the interlaminar space. Sometimes, we tilt the fluoroscope for a better view. This oblique view helps us avoid complications.
Anatomical Landmarks Identification
Finding the right anatomical landmarks is key for success. Under fluoroscopy, we spot the spinous processes and the interlaminar space. The middle of the interlaminar space is where we aim for the epidural space.
We watch the needle’s path on the fluoroscope to make sure it’s in the right place. This is important for safely delivering the steroids and avoiding problems.
Contrast Enhancement Protocols
Contrast enhancement is a big part of the procedure. It helps us see if the needle is in the right spot and if the treatment is spreading as it should. We use a safe contrast agent for this.
Under fluoroscopy, we inject the contrast agent. This lets us see it spreading in the epidural space. It’s vital to make sure the treatment goes where it’s meant to.
Performing Lumbar Interlaminar Epidural Injection
The lumbar interlaminar epidural injection is key for managing chronic back pain. Its success depends on careful steps. We’ll walk you through the process, highlighting the need for precision and safety.
Patient Positioning for NJX Interlaminar LMBR SAC
First, we position the patient correctly for the procedure. They lie on their stomach on a table with X-ray guidance. We make sure their back is ready by finding the right spot with X-rays.
Sterile Field Preparation
Keeping the area clean is vital to avoid infections. We clean the skin and cover it to make a sterile area. This step helps keep the procedure safe.
Step-by-Step Needle Advancement Technique
Getting the needle in the right spot is key. We use a special technique to find the epidural space. The steps are:
- Insert the needle into the skin at the chosen spot.
- Slowly move the needle until it hits the ligamentum flavum.
- Use a special syringe to feel when the needle is in the epidural space.
- Check the needle’s position with X-rays and contrast.
Medication Administration Protocol
With the needle in place, we give the medication. It usually includes a steroid and a painkiller. We make sure the right amount goes into the right space.
| Medication | Dosage | Purpose |
| Corticosteroid (e.g., triamcinolone) | 40-80 mg | Reduce inflammation |
| Local Anesthetic (e.g., lidocaine) | 1-2 ml of 1% | Provide immediate pain relief |
By following these steps, we ensure a safe and effective procedure. It helps patients with chronic back pain find relief.
Cervical Interlaminar Epidural Injection Technique
The cervical interlaminar epidural injection technique requires specialized positioning and careful attention to detail. We must consider the patient’s anatomy and the procedure’s specific needs. This ensures both safety and effectiveness.
Specialized Positioning for NJX Interlaminar CRV THRC
Positioning is key for cervical interlaminar epidural injections. Patients are usually placed in a prone position. The neck is slightly flexed to open the interlaminar space.
This setup needs careful adjustment to prepare the space for the needle.
Safety Considerations Specific to Cervical Approach
Safety is the top priority for cervical interlaminar epidural injections. We must be aware of risks like spinal cord injury and intravascular injection. To reduce these risks, we use imaging guidance and monitor patient feedback closely.
“The use of fluoroscopic guidance is essential for safe and effective cervical interlaminar epidural steroid injections.” –
A respected medical journal
Procedural Steps for Cervical ILESI
The steps for cervical interlaminar epidural steroid injections include:
- Preparing the patient with proper sterile technique
- Using fluoroscopic guidance to find the target interlaminar space
- Advancing the needle with caution, watching for loss of resistance
- Confirming correct needle placement with contrast media
Medication Delivery and Volume Considerations
When delivering medication, we consider the volume and type of injectate. We aim for effective pain relief with minimal risk of complications. A mix of corticosteroids and local anesthetics is used, adjusting the volume to avoid harm to nearby neural structures.
By following these steps and considering each patient’s unique needs, we can improve the outcomes of cervical interlaminar epidural injections.
Managing Complications and Adverse Events
Complications and adverse events can happen during or after interlaminar epidural injections. It’s important to know how to handle them. This ensures patient safety and the best possible outcomes.
Common Complications During Procedure
Several complications can occur during the procedure. These include dural puncture and vasovagal reactions. Dural puncture can cause severe headaches due to cerebrospinal fluid leakage. Vasovagal reactions, marked by bradycardia and hypotension, need quick attention to avoid syncope or worse.
To tackle these issues, we use different strategies. For dural puncture, we often start with bed rest, hydration, and sometimes an epidural blood patch. Vasovagal reactions are managed with atropine or other medications to keep the patient stable.
Post-Procedure Complications
After the procedure, complications can include infection, bleeding, and nerve root injury. Infection is rare but serious, needing quick antibiotic treatment. Bleeding can range from minor bruising to serious hematomas, requiring monitoring and sometimes intervention.
Nerve root injury can happen from trauma or the injected solution. We assess the injury’s severity and may use corticosteroids or other treatments to help symptoms and aid recovery.
| Complication | Management Strategy |
| Dural Puncture | Conservative management (bed rest, hydration), epidural blood patch |
| Vasovagal Reaction | Atropine administration, vital sign stabilization |
| Infection | Prompt antibiotic treatment |
| Nerve Root Injury | Corticosteroids, symptom management |
Emergency Protocols and Management
Having strong emergency protocols is key for managing complications. This means having quick access to needed medications and equipment for resuscitation. It also means having a trained team ready to act in emergencies.
In case of an adverse event, we follow a structured plan. This includes initial assessment, stabilizing the patient, and specific interventions based on the complication.
Being ready for complications and having clear protocols helps us minimize risks. This way, we can give our best care to patients getting interlaminar epidural injections.
Post-Procedure Care and Patient Instructions
After an interlaminar epidural injection, proper care is key to avoid complications and aid in recovery. We stress the need for a detailed care plan to achieve the best results.
Immediate Recovery Monitoring
Patients are watched closely in a recovery area right after the procedure. We check their vital signs and overall health, including pain and neurological status. This early check helps spot any issues quickly.
We also teach patients what to expect during recovery. This includes possible side effects and how to handle them. Knowing what to expect helps reduce anxiety and ensures they follow instructions well.
Discharge Criteria and Documentation
Before leaving, patients must meet certain criteria. This includes stable vital signs, the ability to walk, and no major complications. We record these checks in their medical file.
We give clear instructions in both words and writing. These cover how to take medication, when to come back for follow-ups, and what to watch for in case of emergencies.
| Discharge Criteria | Description |
| Stable Vital Signs | Heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation within normal limits. |
| Ability to Ambulate | Patient can walk without significant assistance or dizziness. |
| Absence of Complications | No signs of infection, neurological deficit, or other significant adverse effects. |
Patient Education for Optimal Outcomes
Teaching patients is a big part of our care after the procedure. We give them clear instructions on what to do next, including activity levels and medication use. We encourage them to ask questions and clear up any doubts.
For more details on care after the procedure, patients can visit our post-procedure care page. It has lots of helpful information and support.
By focusing on post-procedure care and education, we aim to improve patient outcomes and satisfaction after interlaminar epidural injections.
Conclusion
Interlaminar epidural injections are a key method for treating back and neck pain. We’ve looked at the basics, the body parts involved, and how these injections are done. Knowing how these injections work helps doctors give better pain relief to their patients.
Doing these injections right is very important. We talked about choosing the right patients, checking them before the procedure, and being careful during it. By getting better at these steps, doctors can help people with back and neck pain feel better.
We aim to give top-notch health advice. We hope this guide has given you useful knowledge and tips. It’s for doctors who want to improve their skills in giving these injections.
FAQ
What is an interlaminar epidural injection?
An interlaminar epidural injection is a small procedure. It puts medicine around the spinal cord. This helps people with back and neck pain feel better.
What conditions are treated with lumbar interlaminar epidural steroid injections?
This treatment helps with lower back and leg pain. It’s for conditions like radiculopathy, spinal stenosis, and disc herniations.
What are the benefits of using fluoroscopic guidance during interlaminar epidural injections?
Using fluoroscopy makes sure the needle goes in the right. This makes the treatment work better and lowers the chance of problems.
What are the contraindications for interlaminar epidural injections?
You shouldn’t get this treatment if you have an active infection or severe allergies. Also, if you have uncontrolled diabetes or high blood pressure, it’s not recommended.
How is the interlaminar space accessed during the procedure?
A needle is put between the vertebrae. Fluoroscopy helps place it correctly.
What are the possible complications of interlaminar epidural injections?
Risks include dural puncture and bleeding. Infections and allergic reactions can also happen. But, these are rare and can be handled.
What is the role of epidural fat distribution in interlaminar epidural injections?
The fat in the epidural space is key. It helps spread the medicine evenly.
How are patients prepared for interlaminar epidural injections?
Patients get a full check-up first. They learn what to do before and after the procedure. This helps them understand what to expect.
What is the difference between lumbar and cervical interlaminar epidural injections?
Lumbar injections help with lower back pain. Cervical injections treat neck and arm pain. The techniques and medicines used are different.
What is the importance of patient education after interlaminar epidural injections?
Teaching patients is vital. It helps them manage their pain and follow instructions. This leads to better results.
What is NJX DX/THER SBST INTRLMNR LMBR/SAC W/IMG GDN?
NJX DX/THER SBST INTRLMNR LMBR/SAC W/IMG GDN is a specific procedure. “NJX” is the medicine, “DX/THER” means it’s for diagnosis or treatment. “SBST” is the substance, “INTRLMNR” is the area, and “LMBR/SAC” is the location. “W/IMG GDN” means it uses imaging guidance.
Reference
ScienceDirect. (2012). Minimally invasive treatment of varicose veins. Galanopoulos, G. (2012). Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1743919112000313























