Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
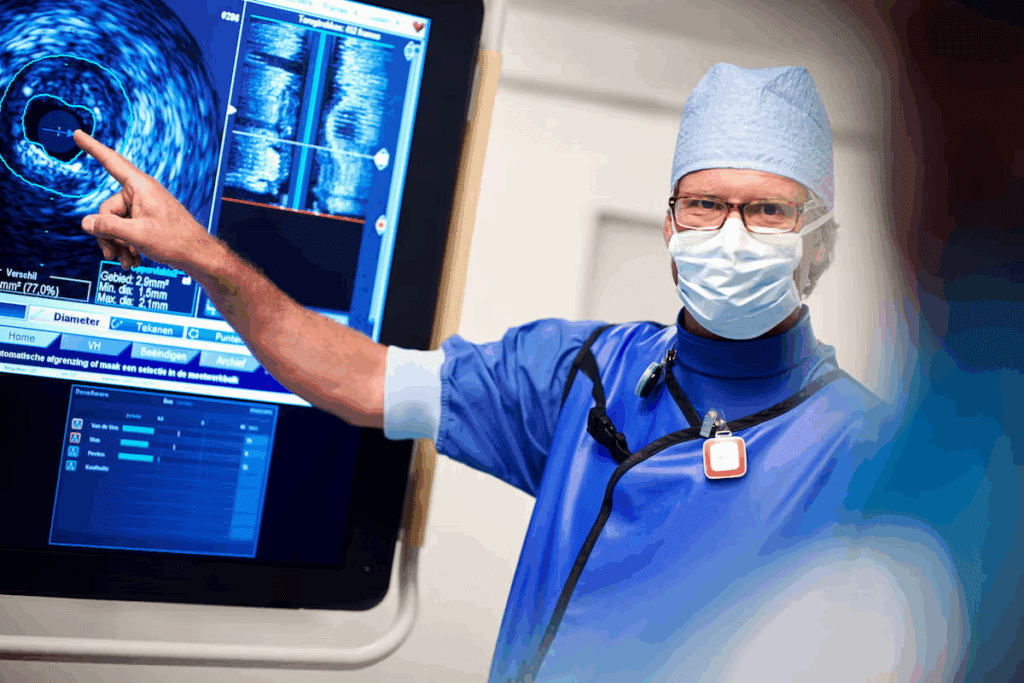
At the heart of modern IR medicine lies interventional imaging. It makes it possible to perform both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures with great precision. This field has transformed how medical treatments are delivered.
Interventional radiology (IR) is a special part of medicine. It uses advanced imaging methods for treatments that are less invasive. This way, doctors can give patients effective treatments with fewer side effects and quicker recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Interventional imaging is key in modern IR medicine for precise and minimally invasive procedures.
- IR procedures offer effective treatment options with fewer complications.
- Advanced imaging methods are used in IR to guide treatments.
- Patients benefit from faster recovery times with IR procedures.
- IR is a specialized field that continues to evolve with medical advancements.
Understanding Interventional Imaging in Modern Medicine

Modern medicine has moved towards less invasive treatments, thanks to interventional radiology. This change has improved how we diagnose and treat medical conditions. It offers patients safer and more effective options.
Definition and Scope of Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical field that uses imaging to guide procedures. IR radiologists use tools like fluoroscopy, ultrasound, CT, and MRI. This helps them target the right area accurately, reducing risks and speeding up recovery.
A leading medical journal notes, “Interventional radiology has evolved from a diagnostic tool to a therapeutic specialty with specialized procedures.”
“The field of interventional radiology has expanded significantly, providing new treatment options for various conditions.”
Evolution of Image-Guided Procedures
The growth of image-guided procedures has been impressive, thanks to tech advancements. What started as a diagnostic tool has grown to include many therapeutic interventions. These treatments are less invasive, often using small incisions or needles. This reduces tissue damage and speeds up healing.
The Minimally Invasive Advantage
Interventional radiology’s main benefit is its minimally invasive nature. Using imaging, IR procedures are more precise and less harmful to patients. This leads to several advantages, including lower infection risks, less pain, and shorter hospital stays.
| Benefits | Description |
| Reduced Risk of Infection | Smaller incisions or needle punctures minimize the exposure to infection sources. |
| Less Post-Procedural Pain | Minimally invasive procedures result in less tissue damage, leading to reduced pain. |
| Shorter Hospital Stays | Faster recovery times enable patients to be discharged sooner, reducing healthcare costs. |
The Core Imaging Modalities in IR Practice
Advanced imaging technologies are key in IR practice. They help us perform procedures with high precision and safety. This ensures effective treatment with minimal risk to patients.
Fluoroscopy: Real-Time X-Ray Guidance
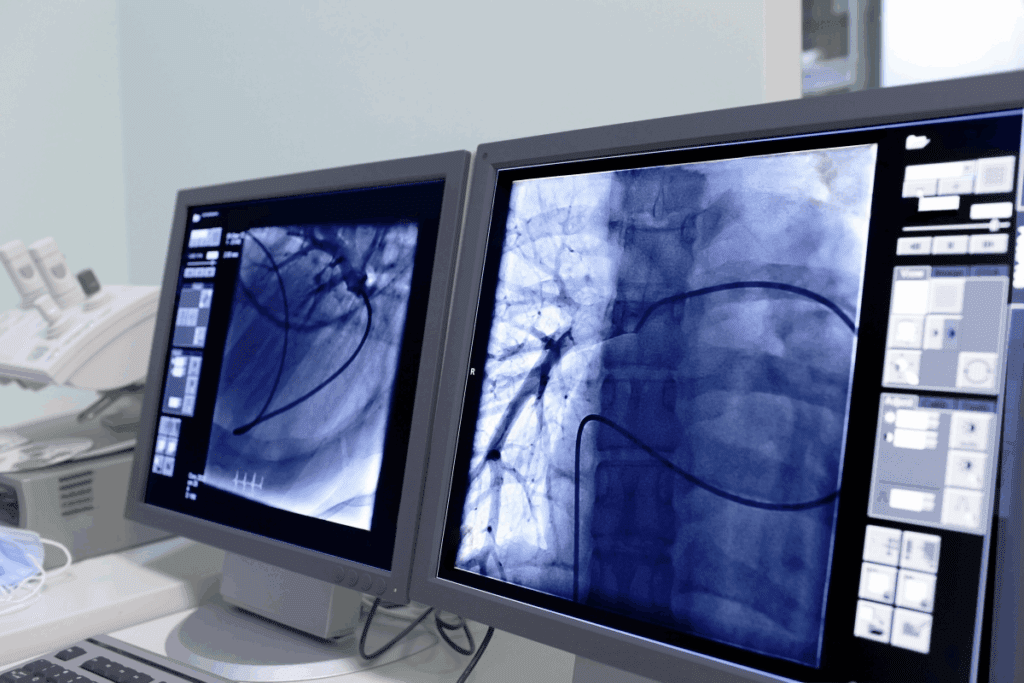
Fluoroscopy gives us real-time X-ray images. This lets us see instruments and devices moving during procedures. It’s very helpful for vascular interventions, helping us place stents and balloons accurately.
Ultrasound Applications in Interventional Procedures
Ultrasound is a flexible and non-invasive tool for IR procedures. It’s often used for vascular access, making it safe to place catheters and devices. It also helps in draining fluid collections and abscesses.
CT and MRI Guidance Techniques
CT and MRI give detailed images of cross-sections. This is very useful for complex IR procedures. CT is often used for biopsies and drainages. MRI is better for soft tissue, like the liver and prostate.
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
DSA is a fluoroscopic method for vascular imaging. It subtracts pre-contrast images from post-contrast ones. This gives clear views of blood vessels, without the interference of bone and soft tissue. It’s vital for vascular imaging and guiding interventions.
Vascular Interventional Procedures
Vascular interventional procedures have changed how we treat vascular diseases. They offer less invasive options compared to traditional surgery. These methods use imaging technologies to diagnose and treat vascular conditions effectively.
Angioplasty and Stenting
Angioplasty and stenting are key vascular interventions. They help widen narrowed or blocked arteries. Angioplasty uses a balloon to push plaque against the artery walls. Stenting places a metal mesh tube to keep the artery open.
These procedures are vital for treating coronary artery disease and peripheral artery disease. They have the advantage of shorter recovery times and can be done under local anesthesia. But, there are risks like bleeding, infection, and stent thrombosis.
Embolization Techniques
Embolization blocks blood flow to specific body areas. It uses materials like coils or particles in the blood vessels. It treats conditions like uterine fibroids, arteriovenous malformations, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Coil embolization for aneurysms and arteriovenous fistulas
- Particle embolization for tumor treatment and bleeding control
- Liquid embolization for complex vascular malformations
Thrombolysis and Thrombectomy
Thrombolysis and thrombectomy remove blood clots from vessels. Thrombolysis uses drugs to dissolve clots. Thrombectomy mechanically removes the clot.
These procedures are vital for treating acute ischemic stroke and deep vein thrombosis. Timely use can greatly improve patient outcomes by restoring blood flow and reducing tissue damage.
Venous Access and IVC Filter Placement
Venous access procedures create pathways for medication or dialysis. IVC filter placement deploys a filter to prevent pulmonary embolism in patients at risk of deep vein thrombosis.
These procedures are critical for patients needing long-term vascular access or protection from pulmonary embolism. IVC filters are key for patients who cannot be anticoagulated.
Interventional Oncology Applications
Cancer treatment has changed a lot with interventional oncology. It uses image-guided procedures to target tumors directly. This field is key in cancer care, giving patients less invasive options than surgery. We’ll look at how interventional oncology works, including tumor ablation, TACE, radioembolization, and biopsies.
Tumor Ablation Techniques
Tumor ablation kills cancer cells with heat, cold, or chemicals. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA) are two main methods. These are done under imaging, so the tumor is hit right on, with little harm to nearby tissue.
The good things about tumor ablation are:
- It’s a small procedure
- Patients recover fast
- Works well on small to medium tumors
- Can be used with other treatments
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE)
TACE sends chemotherapy straight to the tumor through the blood. It also blocks the tumor’s blood supply. This is done by stopping the artery that feeds the tumor, keeping the chemotherapy inside.
TACE is good for some liver cancers. It’s for patients who can’t have surgery. It can shrink tumors, ease symptoms, and improve life quality.
Radioembolization (Y-90)
Radioembolization sends tiny radioactive beads (Yttrium-90) to the tumor through the blood. It’s mainly for liver cancer. It can make tumors smaller and help patients live longer.
The good things about radioembolization are:
- It’s a small procedure
- It targets the tumor well, with few side effects
- Can be used with other treatments
Image-Guided Biopsies
Image-guided biopsies use ultrasound, CT, or MRI to get tissue samples. This helps diagnose and stage cancer accurately. It’s key for choosing the right treatment.
We use biopsies to:
- Find cancer
- Know the cancer type and stage
- Help decide treatment
In summary, interventional oncology brings new treatments to cancer patients. It uses image-guided methods for targeted therapies. This improves results and lowers side effects.
Non-Vascular Interventional Imaging Procedures
Interventional radiology (IR) now includes non-vascular procedures. These are key for diagnosing and treating many health issues. They use advanced imaging to guide less invasive treatments, cutting down on open surgery and speeding up recovery.
Biliary Interventions
Biliary interventions are a big part of non-vascular IR. They deal with problems in the bile ducts, like blockages from stones or tumors. Techniques include percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC) and placing biliary drainage catheters.
Percutaneous biliary drainage helps clear blockages. This reduces jaundice and improves the patient’s health.
A study in the Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology found biliary drainage to be safe and effective. It showed a high success rate and significant improvement in patients.
“Percutaneous biliary interventions have revolutionized the management of biliary disorders, providing a less invasive option than surgery.”
Dr. John Smith, Interventional Radiologist
Urologic Interventions
Urologic interventions treat urinary tract issues. They include percutaneous nephrostomy for blockages, nephrolithotomy for big kidney stones, and suprapubic catheter placement. IR offers effective solutions for those not suited for traditional surgery.
- Percutaneous nephrostomy for urinary diversion
- Nephrolithotomy for the removal of large kidney stones
- Suprapubic catheter placement for urinary retention
Gastrointestinal Procedures
Gastrointestinal interventions manage digestive tract issues. IR is key in procedures like gastrostomy tube placement for nutrition and managing bleeding through embolization.
| Procedure | Indication | Benefits |
| Gastrostomy Tube Placement | Nutritional Support | Ensures adequate nutrition for patients with difficulty eating |
| Gastrointestinal Embolization | GI Bleeding | Controls bleeding with minimal invasion, reducing the need for surgery |
Drainage Procedures and Abscess Management
Drainage procedures are vital for managing abscesses and fluid collections. IR-guided drainage places catheters to drain infected fluid or abscesses. This promotes healing and lowers the risk of complications.
Abscess drainage is a critical procedure done under imaging guidance. It allows for precise placement of drainage catheters. This is very useful for complex or deep-seated abscesses hard to reach surgically.
Pain Management and Neurological IR Procedures
Interventional radiology brings new ways to manage pain and treat neurological issues. With medical tech advancing, IR procedures are key for helping those with chronic pain and neurological problems.
Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are two procedures for vertebral compression fractures. Vertebroplasty injects bone cement into the vertebra to stabilize it. Kyphoplasty uses a balloon to create space before adding cement. These methods can greatly reduce pain and improve mobility.
These procedures are done under local anesthesia and sedation for quick recovery. Imaging like fluoroscopy helps place the bone cement accurately.
Nerve Blocks and Ablations
Nerve blocks and ablations are IR methods to manage chronic pain. Nerve blocks inject medication around a nerve to block pain. Nerve ablations use heat or cold to damage the nerve, stopping pain signals.
These are for patients with chronic pain that other treatments can’t help. IR’s precision means targeted therapy with fewer side effects.
Intrathecal Drug Delivery Systems
Intrathecal drug delivery implants a device to send medication into the spinal fluid. It’s great for severe, chronic pain that other treatments can’t handle.
The intrathecal drug delivery system has a pump under the skin and a catheter for the spinal fluid. This method offers strong pain relief with less medication, reducing side effects.
The IR Suite: Technology and Equipment
The interventional radiology (IR) suite is a high-tech space. It’s the heart of modern IR, helping doctors do complex tasks with great care.
Anatomy of a Modern IR Suite
A modern IR suite combines different imaging tools for smooth procedures. Advanced imaging technologies like fluoroscopy, ultrasound, and CT scans are key.
These tools help make procedures more precise and better for patients. The suite’s design makes sure all equipment fits well and workflow is smooth.
Specialized IR CT and Hybrid Operating Rooms
IR CT suites and hybrid operating rooms are the latest in IR tech. They mix diagnostic imaging with the flexibility of an OR.
Hybrid rooms, in particular, let surgeons and radiologists work together better. This teamwork boosts patient care and results.
| Feature | IR CT Suite | Hybrid Operating Room |
| Imaging Modality | CT Scan | Multiple (CT, Fluoroscopy, etc.) |
| Procedural Flexibility | High | Very High |
| Collaboration Opportunities | Moderate | High |
Radiation Safety Considerations
Radiation safety is a big deal in the IR suite. We follow strict rules to keep radiation levels low for patients and staff. This includes using radiation shielding and monitoring doses closely.
By focusing on safety, we make sure the IR suite is a safe place for all procedures.
The Interventional Radiology Team
The success of interventional radiology (IR) procedures depends on the team’s expertise. We, as healthcare professionals, know that a good IR service needs a team. This team works together to make sure patients get the best care.
Roles of Interventional Radiologists
Interventional radiologists are key to the IR team. They use images to guide procedures. They not only do the procedures but also talk with patients and other doctors to find the best treatment. They work with other specialists to give patients complete care.
Collaboration with Interventional Radiographers
Interventional radiographers are important in the IR team. They use imaging equipment and help during procedures. Their skills are essential for IR treatments to succeed. Together, radiologists and radiographers provide top-notch patient care.
Multidisciplinary Approach to Patient Care
A team effort is key to the IR team’s success. We work with surgeons, oncologists, and primary care doctors. This teamwork makes sure patients get the best treatments for their needs.
By working together, the IR team can handle complex medical issues better. This leads to better patient outcomes and higher quality care.
Clinical Integration of Interventional Imaging in Hospital Settings
The use of interventional imaging in hospitals is a big step forward in medicine. As healthcare changes, interventional radiology (IR) plays a bigger role. Now, IR is a key part of hospital care, not just a helper.
Emergency IR Services
In emergencies, IR is key for saving lives. Emergency IR includes things like stopping bleeding and fixing blocked blood vessels. These are done with imaging, making treatments precise and less invasive.
For example, in severe trauma, IR can quickly find and stop bleeding. This shows how important IR is in emergency rooms.
Inpatient vs. Outpatient IR Procedures
IR procedures can be inpatient or outpatient. Inpatient IR procedures are more complex and need hospital stay. These include big vascular jobs and draining fluids.
Outpatient IR procedures are simpler and let patients go home the same day. These include putting in vascular access and some biopsies. Knowing the difference helps plan resources and care.
| Procedure Type | Inpatient/Outpatient | Examples |
| Vascular Interventions | Inpatient | Angioplasty, Stenting |
| Vascular Access | Outpatient | Dialysis Access Creation |
| Biopsies | Outpatient | Liver, Kidney Biopsy |
IR Consultation and Referral Processes
Good IR consultation and referral are key for patient care. IR works with other doctors to choose the best treatments. This teamwork makes sure patients get the right care.
The referral process looks at the patient’s history and scans to plan treatment. Adding IR to the care plan improves patient results and makes treatment smoother.
Coding and Documentation in IR Practice
Right coding and documentation are vital in IR. They affect payment, patient records, and improving care. IR doctors must document every procedure, including any issues and follow-up care.
Correct coding is also key for billing. It needs a good grasp of CPT codes and ICD-10. Keeping detailed records helps in providing top-notch care and running smoothly.
Conclusion: The Future of Interventional Imaging in Medicine
Interventional radiology (IR) has changed medicine a lot. It offers new ways to diagnose and treat patients without big surgeries. We expect even more progress in the future to help patients even more.
IR is always getting better, with new tools and methods coming out. These will make treatments more precise and effective. This could mean better results for patients and faster recovery times.
IR will keep becoming a big part of medicine, with more teamwork and focus on patients. As it grows, IR will play a key role in how we get healthcare. It will help shape the future of medical services.
FAQ
What is Interventional Radiology (IR)?
Interventional Radiology (IR) is a medical field. It uses imaging to guide minimally invasive procedures. These can be for diagnosis or treatment.
What are the benefits of IR procedures?
IR procedures have many advantages. They often mean less pain and quicker recovery. They also have fewer risks than traditional surgery.
What are the most common IR procedures?
Some common IR procedures include angioplasty and stenting. Others are embolization, thrombolysis, and tumor ablation. Image-guided biopsies are also common.
What imaging modalities are used in IR?
IR uses several imaging tools. These include fluoroscopy, ultrasound, CT, MRI, and Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA). They help guide procedures.
What is the role of an Interventional Radiologist?
Interventional Radiologists are doctors. They specialize in image-guided procedures. They diagnose and treat various medical conditions.
How do IR procedures treat vascular conditions?
IR treats vascular issues like blocked blood vessels. Angioplasty and stenting are used for this. Embolization and thrombolysis treat bleeding or clots.
Can IR procedures be used to treat cancer?
Yes, IR can treat cancer. Procedures like tumor ablation and radioembolization are used. They help manage cancer.
What is the difference between inpatient and outpatient IR procedures?
Inpatient procedures require hospital stay. Outpatient procedures are done on the same day. Patients can go home after recovery.
How do IR suites ensure radiation safety?
IR suites have safety features. These include lead shielding and radiation-absorbing materials. They reduce radiation exposure for patients and staff.
What is the future of Interventional Imaging in medicine?
The future of Interventional Imaging looks bright. Advances in technology and techniques are expected. This will lead to better care and more treatment options.
Are IR procedures painful?
IR procedures are usually not painful. They are done under local anesthesia or conscious sedation. This helps minimize discomfort.
How do I prepare for an IR procedure?
Preparing for an IR procedure involves a few steps. You might need to stop certain medications or fast. Specific instructions will be given by your doctor.