Jaw tumors are a big health worry worldwide. They are the 16th most common cancer globally. Early detection is key, as it boosts survival chances by 84%, says the Oral Cancer Foundation. At Liv Hospital, we focus on caring for your mouth and face fully. View 7 jaw tumor pictures to help visually identify the signs and features of a suspicious growth on the jawbone.
Knowing what jaw tumors look like is important for catching them early. With detailed pictures, patients and doctors can spot signs and get help. Our guide helps those dealing with jaw tumors understand and get the care they need.
Key Takeaways
- Early detection of jaw tumors significantly improves survival rates.
- Jaw tumors can develop silently without noticeable symptoms in early stages.
- Visual identification through professional imaging is vital for timely diagnosis.
- Liv Hospital offers full care for mouth and face issues.
- Knowing what jaw tumors look like helps in getting the right care.
Understanding Jaw Tumors: An Overview
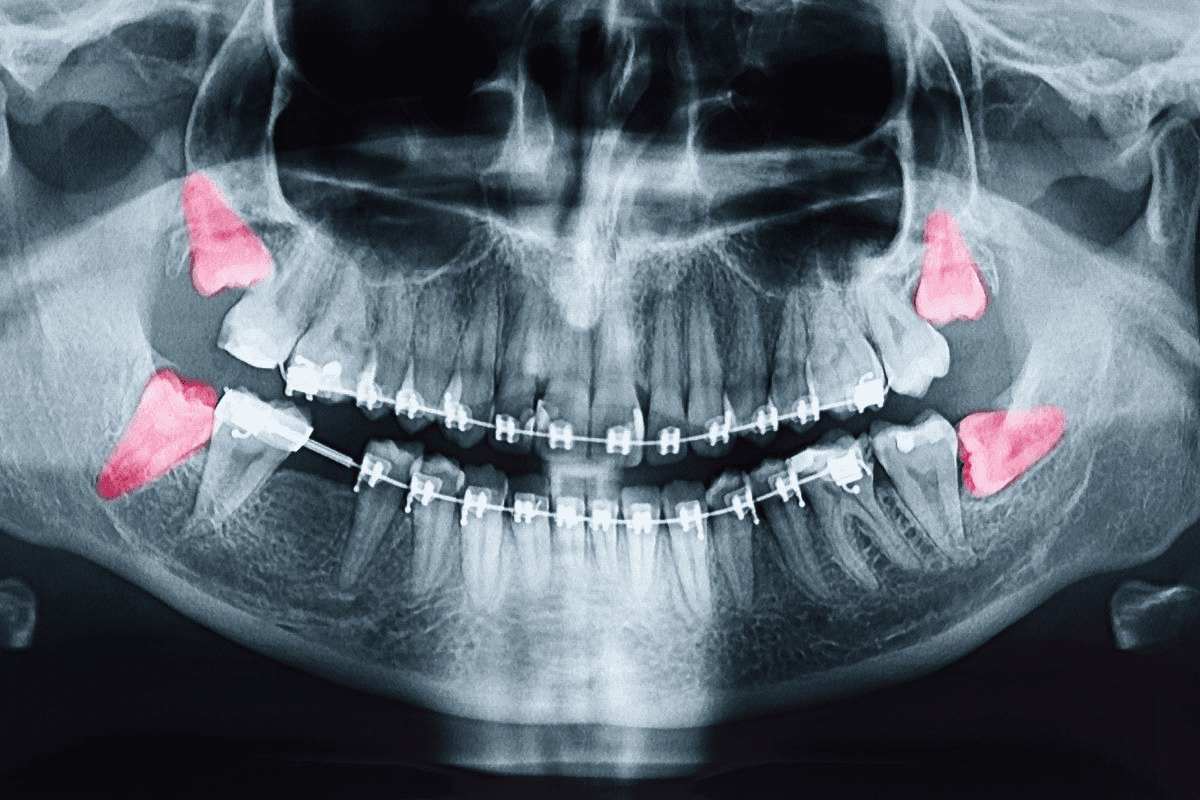
Jaw tumors are abnormal growths in the jawbone. Knowing about them is key for treatment. These growths can be benign or malignant, affecting patients differently.
Definition and Prevalence of Jaw Tumors
Oral cancer, which includes jaw tumors, is when cells grow out of control. In 2022, about 389,846 new cases were reported worldwide. This shows how common it is.
Jaw tumors can start in bone, cartilage, or epithelial cells. Their common occurrence highlights the need for awareness and early detection.
Global Impact of Oral and Jaw Cancer
Oral and jaw cancer have a big impact globally. They put a lot of pressure on healthcare systems. The rate of oral cancer varies by region, influenced by tobacco use, alcohol, and viruses.
“The burden of oral cancer is expected to increase in the coming years, stressing the need for better prevention and early detection.”
World Health Organization
Looking at the global impact shows we need to work together to tackle this issue.
Region | Incidence Rate | Mortality Rate |
Asia | High | Moderate |
Europe | Moderate | Low |
North America | Moderate | Low |
Why Early Visual Recognition Matters
Spotting jaw tumors early is vital for treatment. Seeing swelling, ulcers, or color changes in the mouth can lead to early medical care.
Early detection can lead to better survival rates and less suffering. So, knowing the visual signs of jaw tumors is important for both doctors and the public.
- Regular self-examination can catch problems early.
- Dentists are key in finding jaw tumors during check-ups.
- Public awareness campaigns can teach people about jaw tumor signs and symptoms.
Types of Jaw Tumors and Their Characteristics
It’s important to know about jaw tumors to catch them early and treat them well. Jaw tumors vary in type and severity. Knowing these differences helps doctors choose the right treatment.
Benign vs. Malignant Jaw Tumors
Jaw tumors can be either benign or malignant. Benign tumors are not cancerous and usually don’t spread. But, they can grow big and cause problems. Malignant tumors, or cancerous ones, can spread and invade nearby tissues.
Knowing if a tumor is benign or malignant is key for treatment. Malignant tumors, like squamous cell carcinoma, need stronger treatments.
Common Types of Jaw Cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma is the main type of oral cancer, including jaw cancers. Other types include:
- Odontogenic tumors, which start from tooth-forming tissues
- Ameloblastoma, a rare, non-cancerous tumor in the jaw
- Odontogenic keratocysts, cysts that can form in the jaw
These tumors differ in how serious they are and what treatment they need.
Common Locations of Jaw Tumors
Jaw tumors can happen in the mandible (lower jaw) or maxilla (upper jaw). Where a tumor is can affect its symptoms and treatment. For example, tumors in the mandible can mess with jaw alignment and how teeth fit together.
Most mouth cancers, including jaw cancers, are linked to tobacco use, alcohol, or both. Knowing these risks helps prevent and catch cancers early.
Risk Factors and Causes of Jaw Tumors
Knowing the risk factors for jaw tumors is key to catching them early. These tumors, like many cancers, are shaped by genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
Studies have found several risk factors for jaw tumors. These can be split into lifestyle choices and other factors.
Lifestyle Risk Factors
Lifestyle choices greatly affect jaw tumor risk. Key factors include:
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or chewing tobacco is the biggest risk for oral cancer, which can hit the jaw.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Drinking too much alcohol raises the risk of oral and jaw cancers.
- Betel Nut Chewing: This habit, common in some cultures, boosts the risk of oral and jaw tumors.
- Excess Body Weight: Being overweight or obese links to a higher risk of jaw and other cancers.
Other Contributing Factors
Other factors also play a part in jaw tumor risk. These include:
- Genetic Predisposition: People with a family history of cancer might be at higher risk.
- Viral Infections: Viruses like human papillomavirus (HPV) raise the risk of oral cancers.
- Radiation Exposure: Head and neck radiation increases jaw tumor risk.
The table below lists main risk factors and their risks:
Risk Factor | Description | Associated Risk |
Tobacco Use | Smoking or chewing tobacco | High |
Excessive Alcohol Consumption | Drinking alcohol in excess | Moderate to High |
Betel Nut Chewing | Chewing betel nuts | High |
Excess Body Weight | Being overweight or obese | Moderate |
Genetic Predisposition | Family history of cancer | Variable |
Understanding these risk factors helps people lower their jaw tumor risk. Early detection and prevention are key to managing jaw tumors well.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
It’s important to spot the early signs of jaw tumors to get medical help quickly. Jaw cancer often doesn’t show symptoms in its early stages.
Physical Changes in the Jaw
A swelling or lump in the jaw area is a key sign of a jaw bone tumor. This swelling might start without pain but can become uncomfortable later. Facial bone cancer can also change the shape of your face, making it look uneven.
A chin tumor might look like a hard, painless lump or swelling. Watch for any jaw changes and see a doctor if you notice anything odd.
Pain and Discomfort Patterns
The pain from jaw tumors can be different for everyone. Some feel a dull ache, while others have sharp pains. The pain might stay the same or get worse over time.
Numbness or tingling in the mouth, like in the lower lip or chin, could mean a jaw tumor is pressing on nerves. If you keep feeling numbness or tingling, you should get medical help right away.
Changes in Oral Function
Jaw tumors can make it hard to chew, swallow, or speak. If your teeth feel loose, it could be a sign of a jaw problem, like a tumor.
Some people notice their bite or how their teeth fit together has changed. This could mean a tumor is affecting the jawbone.
Why Symptoms May Go Unnoticed
The signs of jaw tumors can be subtle and may take time to show up. Sores or ulcers in the mouth, red or white patches, and bleeding can be signs of oral cancer linked to jaw tumors.
People often think these symptoms are from something less serious, which can delay getting a diagnosis. Regular dental visits and knowing these symptoms can help catch problems early.
Jaw Tumor Pictures: Visual Guide to Identification
Jaw tumor pictures are helpful for doctors and patients to spot jaw cancer signs. They show how jaw tumors look, which is important for catching them early and treating them well.
Picture 1: Early Stage Squamous Cell Carcinoma
At first, squamous cell carcinoma might look like a small, painless spot or sore on the jaw or nearby. These spots can be red or white and might bleed. Spotting these signs early can help get treatment sooner.
Picture 2: Advanced Mandibular Tumor
Big mandibular tumors can make the jaw swell and change shape. They can hurt, make eating hard, and mess up tooth alignment. In serious cases, they might also cause numbness or tingling in the lower lip or chin.
Picture 3: Ameloblastoma of the Lower Jaw
Ameloblastoma is a non-cancerous tumor in the lower jaw. It can make the jawbone swell and grow, causing the face to look uneven. Even though it’s not cancer, it can grow and might need surgery.
Picture 4: Odontogenic Keratocyst
Odontogenic keratocysts are jaw cysts linked to tooth roots. They might not cause symptoms but can make the jaw bigger and could lead to breaks if not treated. Finding them early with X-rays is very important.
Looking at these jaw tumor pictures helps people know what to look for in jaw cancer or tumors. Finding them early is the best way to manage and treat these issues.
How to Visually Distinguish Different Jaw Tumors
Looking closely at jaw tumors is key to figuring out what they are. Knowing how they look helps doctors make better diagnoses and treatment plans.
Color and Texture Variations
Jaw tumors come in different colors and textures. This gives clues about their type. For example, leukoplakia looks like white patches, and erythroplakia is red.
Benign tumors usually look the same all over. On the other hand, ameloblastoma is a well-defined, multicystic lesion in the mandible.
Size and Growth Patterns
The size and how fast a tumor grows can tell a lot. Benign tumors grow slowly and might make the jawbone bigger. Malignant tumors grow faster and can damage the bone around them.
An odontogenic keratocyst can get big before you notice it. It might make the jaw bigger and could even cause a pathological fracture.
Tumor Type | Typical Size | Growth Pattern |
Ameloblastoma | Variable, often large | Slow, expansive |
Odontogenic Keratocyst | Variable, can be large | Slow, potentially aggressive |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Variable, often ulcerated | Rapid, invasive |
Location-Specific Characteristics
Where a tumor is in the jawbone can also give clues. For example, ameloblastomas often show up in the mandible, near the molars.
Knowing this can help doctors figure out what kind of tumor it is and how to treat it.
Visual Differences Between Benign and Malignant Tumors
Telling benign from malignant jaw tumors is important for treatment. Benign tumors have clear edges and look the same all over. Malignant tumors have irregular edges and might have ulceration or necrosis.
Symptoms like loose teeth, numbness or tingling in the mouth, and big changes in the jaw’s shape or function might mean there’s a tumor. It could be benign or malignant.
Diagnostic Approaches for Jaw Tumors
Getting a correct jaw tumor diagnosis is key for good treatment. We use many tools and methods to find and understand jaw tumors. These include clinical exams, advanced imaging, and precise biopsies.
Clinical Examination Techniques
First, we do a detailed clinical exam to find jaw tumors. We look at your medical history and do a physical check. We check for any jaw swelling or lesions.
Key aspects of clinical examination include feeling the jaw for tenderness or hardness. We also check the mouth for any lesions or abnormalities. And we look at lymph nodes for any enlargement.
Imaging Methods
Imaging is very important for jaw tumor diagnosis. It gives us detailed info about the tumor’s size, location, and how far it has spread. We use:
- X-rays: Good for the first look, showing bone involvement.
- CT scans: Give detailed images of the tumor and its surroundings.
- MRI scans: Show soft tissue details, helping with tumor spread assessment.
- PET scans: Help find tumor activity, useful for cancer detection.
Biopsy Procedures and Histopathology
A biopsy is the main way to diagnose jaw tumors. We remove tissue for detailed examination. We choose the biopsy method based on the tumor’s type and location.
Histopathological analysis is key for tumor type, grade, and behavior. Our pathologists study the biopsy to find cell abnormalities and make a diagnosis. This helps us plan treatment.
By using clinical exams, imaging, and biopsies, we can accurately diagnose jaw tumors. This leads to effective treatment plans.
Treatment Options for Jaw Tumors
Treating jaw tumors depends on the tumor’s type and stage. Options include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a mix of these.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is a common treatment for jaw tumors. The goal is to remove the tumor and keep the jaw working well.
The surgery needed depends on the tumor’s size and where it is. Small tumors might need a simple cut. But bigger tumors might need a more serious surgery, like segmental mandibulectomy, where part of the jawbone is removed.
Radiation Therapy Approaches
Radiation therapy is used for tumors that respond well to it or when surgery isn’t possible. There are two main types: external beam radiation therapy and brachytherapy.
External beam radiation therapy sends radiation from outside the body to the tumor. Brachytherapy places radioactive material inside or near the tumor.
Chemotherapy Protocols
Chemotherapy is often used with other treatments, mainly for cancerous jaw tumors. The drugs chosen depend on the tumor and the patient’s health.
Chemotherapy can be given before surgery to shrink the tumor or after to kill any cancer cells left. Sometimes, it’s the main treatment when surgery isn’t an option.
Emerging Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapy is a newer method that attacks specific molecules in cancer cells. It’s more effective and has fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
For jaw tumors, researchers are studying targeted therapies in clinical trials. These include drugs that target genetic mutations or pathways important for tumor growth.
The following table summarizes the main treatment options for jaw tumors:
Treatment Option | Description | Typical Use |
Surgery | Removal of the tumor | Primary treatment for many jaw tumors |
Radiation Therapy | Use of radiation to kill tumor cells | Tumors sensitive to radiation, or when surgery isn’t possible |
Chemotherapy | Use of drugs to kill cancer cells | Malignant tumors, often in combination with other treatments |
Targeted Therapy | Drugs targeting specific cancer cell mechanisms | Emerging treatment, often in clinical trials |
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s important to know when to see a doctor for jaw tumors. Symptoms like mouth sores or trouble swallowing mean you should go right away. We’ll show you the urgent signs, help you find the right specialist, and give tips for your doctor’s visit.
Urgent Warning Signs
Some symptoms need quick medical help. These include:
- Persistent mouth sores or ulcers that don’t heal
- Unexplained swelling or lumps in the jaw or mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Numbness or pain in the jaw or face
- Loose teeth or a change in the fit of dentures
If you notice any of these, see a doctor fast. Early action can greatly improve treatment for jaw tumors.
Finding the Right Specialist
For jaw tumor concerns, you might need to see different specialists. These include:
- Oral and maxillofacial surgeons
- Otolaryngologists (ENT specialists)
- Oncologists (cancer specialists)
- Dentists with experience in oral pathology
Your primary care doctor can direct you to the right specialist. It’s key to find someone experienced in jaw tumors.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
Make a list of questions for your doctor’s visit. Ask about:
- What are the possible causes of my symptoms?
- What diagnostic tests will be needed to determine the cause?
- What are the treatment options if a jaw tumor is diagnosed?
- What are the possible risks and benefits of each treatment option?
- Are there any clinical trials or new treatments available?
Preparing for Your Appointment
To get the most from your visit, prepare by:
- Writing down your symptoms and when they started
- Listing any medications you’re currently taking
- Bringing any relevant medical records or test results
- Preparing a list of questions to ask your doctor
- Having a friend or family member accompany you for support
Being ready can help you understand your diagnosis and treatment options better.
Conclusion: The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection is key to better treatment outcomes for jaw tumors. The 5-year survival rate for oral cancer found early is much higher than for late-stage diagnoses. This shows how vital it is to be aware of oral and jaw tumors to get timely medical help.
Knowing the signs and symptoms of jaw tumors is essential. We’ve discussed these in our visual guide and talked about risk factors. It’s important to watch your oral health closely and see a doctor if you notice anything odd. Early jaw cancer detection is critical for effective treatment and better patient results.
Being informed and proactive can lower your risk of advanced jaw cancer. Regular health check-ups and talks with doctors are important. They help catch jaw tumors early and manage them properly.
FAQ
What are the common signs and symptoms of jaw tumors?
Signs include swelling or lumps in the jaw and pain or numbness in the jaw or face. You might also have trouble chewing or swallowing. Look out for loose teeth, bleeding gums, or bad breath that won’t go away.
How can I identify jaw tumors through pictures?
Pictures can show abnormal growths, swelling, or jawbone changes. We look at the tumor’s color, texture, size, and where it is. This helps us tell if it’s benign or malignant.
What are the risk factors for developing jaw tumors?
Risk factors include tobacco use, too much alcohol, HPV infection, and certain genetic conditions. Most cases happen in people over 40.
What are the different types of jaw tumors?
There are benign and malignant types. Benign ones are ameloblastoma, odontogenic keratocyst, and osteoma. Malignant types include squamous cell carcinoma, osteosarcoma, and mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
How are jaw tumors diagnosed?
We use clinical exams, X-rays, CT scans, or MRI, and biopsies. These tools help us find out what kind and how big the tumor is.
What are the treatment options for jaw tumors?
Treatment depends on the tumor’s type, size, and location. Options include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and new targeted therapies. Our goal is to remove the tumor and improve your life.
Can jaw tumors be prevented?
Not all jaw tumors can be prevented, but we can lower the risk. Avoid tobacco, drink less alcohol, keep good oral hygiene, and get HPV vaccines.
What are the early warning signs of jaw cancer?
Watch for persistent jaw pain or numbness, swelling or redness in the mouth, and trouble swallowing or chewing. Also, look out for voice changes or bad breath that lasts.
How can I prepare for a doctor’s appointment for jaw tumor evaluation?
Make a list of your symptoms, medical history, and questions for the doctor. Bring any imaging studies or medical records you have.
What questions should I ask my doctor about jaw tumors?
Ask about the diagnosis, treatment options, and what to expect. Also, ask about the risks and benefits of treatments and recovery.
What is the importance of early detection and treatment of jaw tumors?
Early detection and treatment lead to better outcomes and fewer complications. Treating jaw tumors early can save function and improve your life.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). 7 Jaw Tumor Pictures Visual Guide to Identify. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4245411/

































