Kidney disease is a big problem in the United States. Over 37 million adults have some form of kidney disease, says the National Kidney Foundation.
Early detection is key to managing and treating kidney disease. The renal ultrasound has become a popular tool for this.
A kidney ultrasound uses sound waves to make images of the kidneys. Doctors use it to find and track kidney problems.
But can it spot kidney failure? The answer depends on what it can and can’t do.
Key Takeaways
- Ultrasound technology is important for finding kidney issues.
- Early detection is vital for kidney disease management.
- Renal ultrasound is a safe way to diagnose.
- Knowing what ultrasound can do is important.
- Kidney disease affects millions of adults in the United States.
Understanding Kidney Ultrasound Technology
Ultrasound imaging is key in finding kidney diseases. It lets doctors see the kidneys and nearby areas without surgery.
How Ultrasound Imaging Works
Ultrasound uses sound waves to make pictures of inside organs. For kidneys, it checks their size, shape, and where they are.
A transducer sends and gets sound waves. These waves turn into images on a screen. Key parts of ultrasound imaging are:
- Transducer: The device that sends and receives sound waves.
- Sound waves: High-frequency waves that go through the body.
- Image processing: The tech that makes sound waves into pictures.
Advancements in Renal Ultrasound Technology
New tech has made renal ultrasound better. Doppler ultrasound checks blood flow to the kidneys. This helps find blood problems.
Also, contrast-enhanced ultrasound makes kidney pictures clearer. These updates make renal ultrasound great for finding and tracking kidney diseases.
What Does a Kidney Ultrasound Show?
Understanding what a kidney ultrasound shows is key to knowing your kidney health. This test uses sound waves to create images of your kidneys and nearby structures.
Normal Kidney Anatomy on Ultrasound
A normal ultrasound shows kidneys that are symmetrical and smooth. The outer layer, called the renal cortex, looks uniform. The renal sinus, with the renal pelvis and blood vessels, is also seen.
The size and brightness of the kidneys on the ultrasound are important. They show if your kidneys are healthy.
Common Abnormalities Detected
Kidney ultrasounds can spot many issues, like cysts, stones, and tumors. Cysts are fluid-filled and usually harmless. Kidney stones show up as bright spots with shadows.
Tumors, which can be benign or cancerous, look like solid masses or complex cysts. Other problems, like swelling and scarring, can also be found.
This test is vital for diagnosing and tracking kidney issues. It helps doctors make the right treatment plans.
Can Ultrasound Detect Kidney Failure?
Early detection of kidney failure is key to managing it well. Ultrasound is a big help in this area. It helps check if the kidneys are working right and spots problems early.
Direct Signs of Kidney Failure
Ultrasound can spot several signs of kidney failure. One key sign is a change in kidney size. Chronic kidney disease often results in shrunken kidneys, while acute kidney injury may show enlarged kidneys.
It also looks at the echogenicity of the kidneys, or how well they reflect sound. If the kidneys are too echoey, it could mean they’re not healthy.
Another sign is hydronephrosis, where the kidney swells because urine can’t drain. This could mean there’s an obstruction that can be fixed. Ultrasound is great at finding this, helping doctors figure out what’s wrong.
Indirect Indicators of Renal Dysfunction
Ultrasound also finds indirect signs of kidney problems. For example, it checks the resistive index (RI) of the renal arteries. A high RI might mean the kidneys are not getting enough blood, which is common in chronic kidney disease.
It can also spot vascular calcification or stenosis in the arteries. These can cause the kidneys to not work right because they’re not getting enough blood.
Ultrasound can also find cysts or tumors in the kidneys. While these aren’t direct signs of failure, they can lead to problems. It also helps decide if more tests or treatments are needed.
In short, ultrasound is a top tool for finding signs of kidney failure. It’s safe and shows what’s happening in real-time. This makes it very useful for doctors to help patients with kidney issues.
Acute vs. Chronic Kidney Failure: Ultrasound Differences
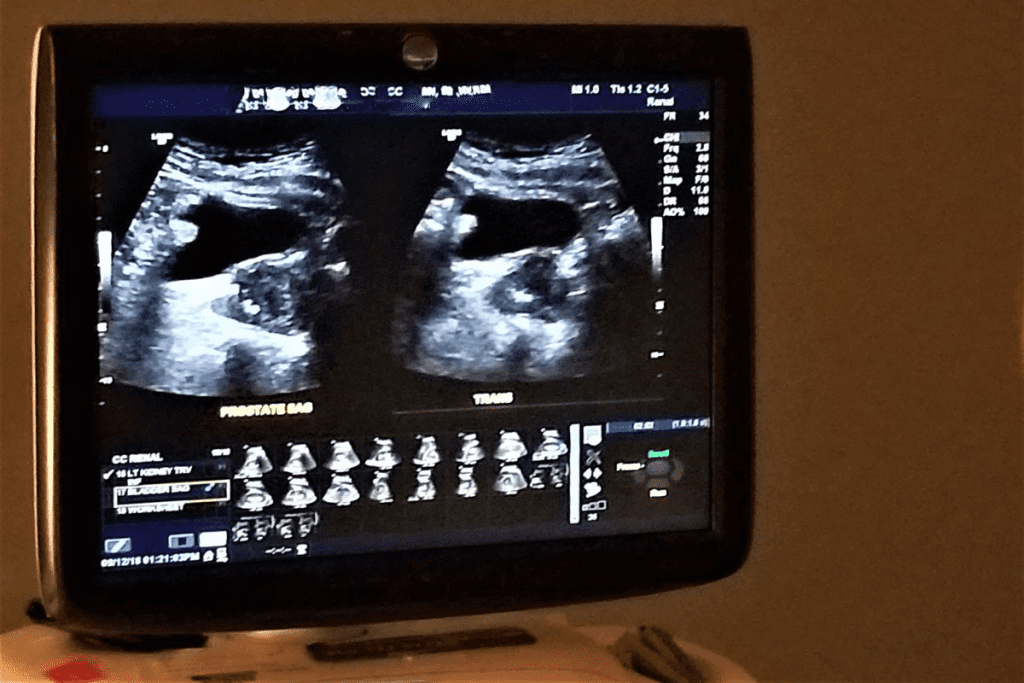
Ultrasound technology has become key in telling acute kidney injury from chronic renal failure. It shows how the kidneys work and look, helping doctors tell these two apart.
Ultrasound Findings in Acute Kidney Injury
Ultrasound shows clear signs of acute kidney injury (AKI). The kidneys might look normal or slightly bigger and have preserved corticomedullary differentiation. They can also appear more echoey, but this isn’t always a sure sign.
Doppler ultrasound helps by checking blood flow in the kidneys. This flow can change in AKI. The resistive index (RI) from Doppler ultrasound is also important. A high RI can mean the kidneys are not working right and could have AKI.
Ultrasound Patterns in Chronic Renal Failure
Chronic renal failure shows different signs on ultrasound. The kidneys are smaller and more echoey than in AKI. They lose corticomedullary differentiation and their shape can be irregular. These signs show long-term damage and scarring.
Ultrasound can also spot problems like cysts or stones in chronic kidney disease. Looking at kidney size, texture, and any extra features helps doctors diagnose and keep track of chronic renal failure.
Identifying Causes of Kidney Failure Through Ultrasound
Finding the cause of kidney failure is key to treating it. Ultrasound imaging is a major tool for this. It lets doctors see the kidneys and spot problems that might be causing kidney issues.
Obstructive Causes
Obstructive kidney failure happens when something blocks the urinary tract. This stops urine from flowing right. Ultrasound can spot these blockages by showing enlarged parts of the kidney. Common causes include kidney stones, tumors, and blood clots.
The ultrasound image helps guide further tests or treatments to clear the blockage.
Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammation in the kidneys can also lead to failure. Ultrasound can show signs of inflammation, like a kidney that looks more dense or swollen. Conditions like pyelonephritis or interstitial nephritis can be spotted through ultrasound, helping doctors diagnose and treat them.
Vascular Problems
Vascular issues, like narrowed renal arteries or blood clots in the renal veins, can harm kidney function. Ultrasound, with Doppler imaging, checks blood flow to the kidneys. Renal artery stenosis, for example, shows up as abnormal Doppler waveforms, pointing to possible kidney failure causes.
Ultrasound helps doctors find these causes. Then, they can create treatment plans to fix the underlying problems leading to kidney failure.
Kidney Ultrasound: Procedure and Experience
Understanding the kidney ultrasound procedure can ease anxiety and make the experience smoother. This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of the kidneys. It helps doctors diagnose and monitor kidney conditions.
Preparation Requirements
Preparation for a kidney ultrasound is simple. Patients are usually told to:
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing that allows easy access to the abdomen.
- Avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the procedure, though this can vary.
- Reveal any relevant medical history, including allergies or sensitivities, to the ultrasound technician.
Arriving a few minutes early to complete paperwork is also recommended.
What Happens During the Examination
During the procedure, the patient lies on an examination table. A clear gel is applied to the abdomen for sound wave transmission. The ultrasound technician uses a transducer to capture images of the kidneys from different angles.
Patients might be asked to hold their breath or change positions. This helps the technician get the necessary images.
After the Procedure
After the ultrasound, the gel is wiped off, and patients can go back to their normal activities right away. The images are reviewed by a radiologist. Then, the results are shared with the patient’s healthcare provider.
Results may be available immediately, or they might be sent to the doctor for further analysis. The patient will discuss the results during a follow-up appointment.
Ultrasound Appearance of Normal vs. Damaged Kidneys
Ultrasound imaging is key in telling normal from damaged kidneys. It’s a non-invasive way to check kidney health. Healthcare pros use it to look at kidney structure and spot any issues.
Characteristics of Healthy Kidneys
A normal kidney ultrasound shows a kidney with a smooth shape and even texture. It also has a clear difference between the cortex and medulla. Healthy kidneys are usually 9-12 cm long and look like a bean.
The renal cortex is isoechoic or slightly hyperechoic compared to the liver. The renal sinus, with its fat and blood vessels, is hyperechoic. Knowing these details helps spot any kidney issues.
| Characteristic | Normal Kidney Ultrasound Findings |
| Size | 9-12 cm in length |
| Contour | Smooth |
| Echotexture | Homogeneous |
| Corticomedullary Differentiation | Distinct |
Abnormal Kidney Ultrasound Findings
Damaged kidneys show different signs on ultrasound, like size and texture changes. Abnormalities can mean kidney diseases or injuries, like chronic kidney disease or blockages.
Common signs include more echoes, loss of texture difference, and irregular shapes. Sometimes, ultrasound finds cysts, stones, or tumors. Advanced imaging techniques might be needed to check these findings.
| Abnormal Finding | Possible Indication |
| Increased Echogenicity | Chronic kidney disease |
| Loss of Corticomedullary Differentiation | Acute or chronic kidney damage |
| Irregular Contour | Scarring or chronic disease |
Detecting Kidney Stones with Ultrasound
Ultrasound technology is key in finding kidney stones. It’s a safe and effective way to diagnose them.
Accuracy Rates for Stone Detection
Ultrasound can accurately spot kidney stones, mostly the bigger ones. Its success rate varies from 70% to over 90%. This depends on the stone’s size and the operator’s skill.
Several factors affect ultrasound’s accuracy in finding kidney stones:
- Stone size: Bigger stones are easier to spot.
- Stone location: Stones in some spots, like the mid-ureter, are harder to find.
- Operator expertise: The person doing the ultrasound greatly impacts the results.
Limitations Compared to CT Scans
Ultrasound is useful for finding kidney stones but has its limits. CT scans are better at diagnosing them because they’re more accurate.
Ultrasound’s drawbacks compared to CT scans are:
- Lower sensitivity for small stones: Ultrasound might miss tiny stones that CT scans can see.
- Difficulty in detecting stones in certain locations: Some stone locations are harder to find with ultrasound.
In summary, ultrasound has its own set of challenges in finding kidney stones. Yet, it’s a valuable tool, mainly for those who can’t have CT scans or need frequent checks. The choice between ultrasound and CT scans depends on the patient and the situation.
Polycystic Kidney Disease on Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging is key in diagnosing and managing polycystic kidney disease (PKD). This genetic disorder causes many cysts to grow in the kidneys. If not treated, it can lead to kidney failure.
Diagnostic Criteria and Appearance
To diagnose PKD on ultrasound, doctors look for many cysts in the kidneys. The diagnostic criteria for PKD include the number and size of cysts and the patient’s age. Finding many cysts in both kidneys usually means PKD.
The PKD appearance on ultrasound is:
- Many cysts of different sizes in both kidneys
- Large kidneys because of many cysts
- Cysts can be simple or complex, with debris or calcifications inside
Monitoring Disease Progression
Ultrasound is not just for diagnosing PKD but also for monitoring PKD progression. Regular ultrasounds track changes in cyst size and number. They also check kidney function.
Ultrasound’s benefits for monitoring PKD include:
- It’s non-invasive and safe for repeated use
- No radiation, making it good for long-term monitoring
- It shows changes in cyst size and number over time
By monitoring PKD with ultrasound, doctors can adjust treatment plans. This helps slow disease progression and manage symptoms.
Medical Renal Disease Ultrasound Findings
Ultrasound imaging is key in diagnosing medical renal diseases. These diseases affect the kidneys in many ways, including glomerular and tubulointerstitial diseases. It helps by showing the kidney’s structure and any issues.
Glomerular Diseases
Glomerular diseases harm the kidneys’ filtering units. Ultrasound can spot changes in kidney size and how it looks. Increased echogenicity often means kidney damage or disease.
Ultrasound is vital in diagnosing glomerular diseases. It helps find who needs more tests or treatment.
Tubulointerstitial Diseases
Tubulointerstitial diseases affect the kidneys’ tubules and tissue. Ultrasound can find signs like kidney enlargement or increased echogenicity. These findings help in planning further tests and treatment.
Knowing what ultrasound shows in medical renal diseases is key. It helps doctors plan the best treatment for patients with kidney issues.
Interpreting Kidney Ultrasound Results
A kidney ultrasound gives important info about your kidney health. But, it needs expert eyes to understand. It’s key for spotting kidney problems, from shape issues to signs of failure.
Understanding Your Ultrasound Report
Your kidney ultrasound report might use terms you don’t get. It talks about your kidneys’ size, shape, and where they are. It also points out any oddities. Look for these important parts:
- Kidney size and how bright they appear
- Cysts or growths
- Signs of blockage or swelling
- How thick the outer layer is
Your doctor will look at these details with your health and past in mind. Talking about your results with your doctor is key to understanding them.
When Further Testing Is Needed
At times, a kidney ultrasound might not give a clear answer. Or, it might show things that need more looking into. In these cases, more tests might be suggested, like:
| Test | Purpose |
| CT Scan | Detailed look at kidney shape and nearby areas |
| MRI | Checks how well your kidneys work and their shape |
| Kidney Biopsy | Looks at kidney tissue directly for disease |
Knowing when more tests are needed helps you understand your health journey better. Your doctor will help you through this. They’ll suggest the best next steps based on your ultrasound findings.
Comparing Ultrasound to Other Kidney Diagnostic Methods
Several methods are used to diagnose kidney diseases. Ultrasound is one of them. But how does it stack up against CT scans, MRI, and lab tests?
Ultrasound vs. CT Scan
CT scans give clearer images of the kidneys than ultrasound. But, they use radiation and contrast agents that can harm the kidneys. Ultrasound, on the other hand, is safe and doesn’t use radiation.
Key differences:
- CT scans offer higher resolution images
- Ultrasound is safer and more cost-effective
- CT scans involve radiation and potentially harmful contrast
Ultrasound vs. MRI
MRI gives detailed kidney images without radiation. It’s great for checking blood vessels and some kidney issues. But, MRI is pricier and not as common as ultrasound. Some people might feel claustrophobic or have metal implants that make MRI risky.
Notable advantages of MRI include:
- High-resolution imaging without radiation
- Excellent for vascular and certain lesion assessments
Ultrasound vs. Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests like serum creatinine and urine analysis are key for kidney function. They’re vital for diagnosing and tracking kidney disease. But, they don’t show kidney images. Ultrasound, by contrast, gives visual info on kidney structure and issues. Together, ultrasound and lab tests offer a full picture of kidney health.
When Is a Kidney Ultrasound Recommended?
A kidney ultrasound is a key tool for doctors to check on kidney health. It helps find any problems early. Doctors suggest a kidney ultrasound in many cases to check health and plan treatment.
Common Symptoms Leading to Ultrasound
Some symptoms might lead a doctor to suggest a kidney ultrasound. These include:
- Persistent pain in the flank or back
- Blood in the urine
- Frequent urinary tract infections
- Abnormal kidney function tests
Seeing these symptoms doesn’t always mean you have kidney disease. But, they do need looking into. A kidney ultrasound can find the cause and help decide the right treatment.
Risk Factors That Warrant Screening
Some people might need a kidney ultrasound even without symptoms. This is because of certain risk factors. These include:
- A family history of kidney disease
- Diabetes or high blood pressure
- Previous kidney problems or surgery
- Long-term use of certain medications that can affect the kidneys
Early detection through ultrasound can help manage kidney disease more effectively. If you’re at risk, talk to your doctor about the benefits of a kidney ultrasound.
Conclusion: The Value and Limitations of Ultrasound in Kidney Failure Detection
Ultrasound is key in spotting kidney failure. It’s a safe and effective way to check on kidney health. We’ve looked at what ultrasound can and can’t do for kidney health.
Ultrasound provides real-time images of the kidneys, which is very useful for diagnosis. It helps see if the kidneys are the right size and shape. It can also spot blockages, cysts, and tumors, which are important for finding the cause of kidney failure.
But, ultrasound isn’t perfect. It’s good at finding some problems but can’t tell everything about how well the kidneys work. Sometimes, more tests like blood work or other scans are needed.
To wrap it up, ultrasound is a big help in finding kidney failure. It’s a safe and quick way to check on kidney health. Knowing its strengths and weaknesses helps doctors make the best choices for their patients.
FAQ
What is a kidney ultrasound?
A kidney ultrasound is a test that uses sound waves to see the kidneys. It helps find problems in the kidneys.
Can ultrasound detect kidney failure?
Yes, it can spot signs of kidney failure. This includes changes in size and how the kidneys look.
How does ultrasound detect kidney stones?
Ultrasound finds kidney stones by looking for bright echoes and shadows. But, it’s not always perfect, depending on the stone’s size and where it is.
What does a renal ultrasound show?
A renal ultrasound shows the kidneys’ size, shape, and position. It also finds any problems like cysts or tumors.
Can ultrasound detect polycystic kidney disease?
Yes, it’s a key tool for finding polycystic kidney disease. It looks for many cysts in the kidneys.
What are the ultrasound findings in acute kidney injury?
Ultrasound might show bigger kidneys, different looks, and changes in the renal sinus. But, these signs can be unclear.
How is a kidney ultrasound performed?
To do a kidney ultrasound, a gel is applied to the skin. Then, a transducer sends and gets sound waves to show the kidneys.
Can ultrasound differentiate between acute and chronic kidney failure?
Yes, it can tell the difference. It looks at size, how the kidneys look, and other signs.
What are the limitations of ultrasound in detecting kidney stones?
Ultrasound might miss small stones or those in hard spots. CT scans are better for these cases.
How do I interpret my kidney ultrasound results?
Understanding your ultrasound report is key. It explains what was found. Knowing when more tests are needed is also important.
When is a kidney ultrasound recommended?
Get a kidney ultrasound for pain, blood in urine, or kidney disease signs. It’s also good for those at risk.
Can a sonogram detect kidney stones?
Yes, a sonogram can find kidney stones. But, it’s not always right. It’s often used with other tests.
What does a kidney ultrasound show in medical renal disease?
In medical renal disease, ultrasound might show size and look changes. It can hint at conditions like glomerulonephritis.
Can ultrasound detect kidney damage?
Yes, it can find kidney damage signs. This includes size, shape, and look changes, and certain problems.
How does ultrasound compare to CT scans for kidney imaging?
Ultrasound is safer because it’s non-invasive and doesn’t use harmful radiation. But, CT scans are better for finding small stones.
References
- Hosokawa, T., et al. (2022). Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound for detecting gastric or duodenal ulcers. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine, 41(7), 1557-1565.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/jum.15727
- Wu, L., et al. (2012). Sonographic diagnosis of peptic ulcer perforation. QJM: An International Journal of Medicine, 105(12), 1217-1224.



































