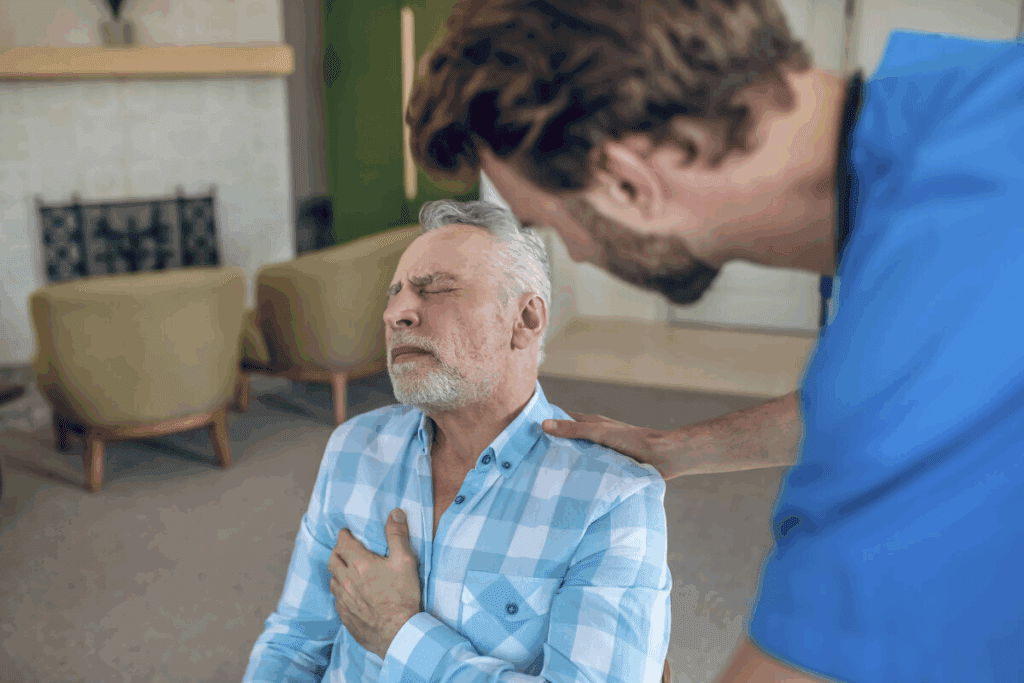
Knowing about left anterior descending artery (LAD) blockage is key for those at risk of heart attacks. This serious issue, called a “widowmaker,” affects a main artery that supplies blood to the heart. Learn left ascending artery blockage: 7 key facts, symptoms, and treatments.
At Liv Hospital, we understand the need for quick medical help for coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD happens when plaque builds up, narrowing arteries and reducing blood flow.
Learning about the heart’s blood vessels helps patients understand CAD risks. It also shows why getting medical help fast is so important if symptoms show up.
Key Takeaways
- Left anterior descending artery blockage is a critical form of coronary artery disease.
- CAD can lead to high-risk heart attacks if not treated promptly.
- Understanding coronary artery anatomy is vital for assessing CAD risks.
- Timely medical intervention is key for managing CAD and preventing complications.
- Liv Hospital provides top-notch expertise for CAD treatment.
Coronary Artery Anatomy and Function
Coronary artery anatomy is key to understanding heart function and managing diseases. The coronary arteries branch off from the aorta. They deliver oxygen and nutrients to the heart’s layers.
The Native Arteries of the Heart
The native arteries of the heart are present from birth. They include the left main coronary artery, the left anterior descending artery (LAD), and the right coronary artery (RCA). The native artery of the heart is vital for blood supply to the heart muscle.
The Left Main Coronary Artery and Its Branches
The left main coronary artery splits into the LAD and left circumflex arteries. Both are key for heart blood supply. The LAD is important for the heart’s anterior wall and the interventricular septum.
The left circumflex artery covers the lateral and posterior heart walls. Knowing the left main coronary artery branches is vital for disease diagnosis and treatment.
The Right Coronary Artery (RCA) and Its Role
The right coronary artery (RCA) mainly serves the heart’s right side. It includes the right atrium, right ventricle, and parts of the conduction system. In many, the RCA also supplies the posterior descending artery to the septum’s posterior third.
| Artery | Primary Supply Area | Clinical Significance |
| Left Main Coronary Artery | Anterior and lateral heart | Critical for cardiac function; blockage can be life-threatening |
| Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD) | Anterior wall and interventricular septum | Often referred to as the “widowmaker” due to high mortality in blockages |
| Right Coronary Artery (RCA) | Right atrium, right ventricle, and parts of the conduction system | Important for right heart function and parts of the heart’s electrical system |
Knowing the anatomy and function of these arteries is key for disease diagnosis and treatment. The coronary artery anatomy varies, but its basic structure and function are the same for everyone.
Left Ascending Artery Blockage: The “Widowmaker” Explained

The left ascending artery blockage, also called the “widowmaker,” is a serious condition that needs quick medical help. It happens in the left anterior descending (LAD) artery. This artery is key for blood flow to the heart.
We’ll look at the dangers of LAD blockages, how they happen, and the risk factors. Knowing these helps us see why managing risks and getting medical help fast is so important.
What Makes LAD Blockage So Dangerous
LAD blockages are very dangerous because they can harm a lot of the heart muscle. The LAD artery feeds a big part of the heart. A blockage can cause a big heart attack.
The severity of an LAD blockage is due to several factors:
- The LAD artery’s large territory of supply
- The risk of big damage to the heart muscle
- The chance of serious complications, like arrhythmias and heart failure
How Blockages Develop in the LAD
Blockages in the LAD artery usually come from atherosclerosis. This is when plaque builds up in the artery walls. It starts with lipids and inflammatory cells.
As the plaque grows, it narrows the artery and cuts down blood flow. If the plaque breaks, it can cause a blood clot. This clot can block the artery completely.
Risk Factors for LAD Blockage
Many things can increase the risk of LAD blockages. These include:
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Smoking | Increases the risk of plaque formation and speeds up atherosclerosis |
| Hypertension | High blood pressure can damage the artery walls, making them more likely to block |
| Hypercholesterolemia | High cholesterol levels can help plaque build up |
| Diabetes Mellitus | Diabetes can make atherosclerosis worse and increase the risk of heart disease |
Knowing these risk factors is key to preventing LAD blockages. By controlling these factors, people can lower their risk of heart disease and heart attacks.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): The Underlying Condition
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a major cause of heart problems. It’s linked to atherosclerosis. Knowing about CAD is key for good health care.
CAD affects the heart’s blood supply. It happens when the arteries get damaged. This damage is often due to atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up, narrowing the arteries.
How CAD Is Characterized by Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the main cause of CAD. It’s when fats, inflammatory cells, and fibrous elements build up in arteries. This buildup forms plaques that can be stable or unstable.
The American Heart Association says, “Atherosclerosis involves many cell types.” This shows why managing CAD needs a detailed approach.
Progression of Coronary Artery Disease
CAD can lead to serious heart issues. These include stable or unstable angina, heart attacks, and sudden death. Many factors, like high blood pressure and smoking, affect how CAD progresses.
- Hypertension
- Hyperlipidemia
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Smoking
Differences Between Stable and Unstable CAD
Stable CAD has predictable angina, triggered by exertion and relieved by rest. Unstable CAD, on the other hand, has unpredictable chest pain, often at rest. This is a more serious condition with a higher risk of heart attack.
It’s important to know the difference between stable and unstable CAD. This helps doctors make better treatment plans. As guidelines say, “Early treatment of CAD can greatly lower the risk of heart problems.”
Warning Signs and Symptoms of Left Ascending Artery Blockage
It’s important to know the warning signs of Left Ascending Artery (LAD) blockage. This condition, also known as the “widowmaker,” can cause serious heart damage if not treated quickly.
Classic Symptoms of LAD Blockage
The main symptoms of LAD blockage include chest pain or discomfort, known as angina. This pain can spread to the arm, neck, or jaw. Other symptoms include shortness of breath, feeling tired, and irregular heartbeats.
These symptoms happen because the blockage limits blood flow to a big part of the heart. This can lead to ischemia or infarction.
In some cases, people might show atypical symptoms. These can include nausea, dizziness, or pain in the upper abdomen. It’s important to recognize these signs, as they can mean a serious problem.
Atypical Presentation in Different Populations
Atypical symptoms of LAD blockage can be seen in different groups. Women, older adults, and people with diabetes might not show the usual symptoms. Women might have less severe chest pain, while older adults could seem confused or weak.
Healthcare providers need to know these differences. This helps them make the right diagnosis and start treatment fast.
Distinguishing LAD Blockage from RCA Blockage Symptoms
It’s key to tell LAD blockage symptoms from those of RCA blockage. Both can cause chest pain, but the symptoms can vary. LAD blockage often leads to more severe symptoms, like big problems with the left ventricle.
RCA blockage might cause nausea and vomiting. Knowing these differences helps doctors diagnose and treat coronary artery blockages better.
Diagnostic Approaches for Coronary Artery Blockages
Healthcare professionals use many ways to find coronary artery blockages. They start with a patient’s medical history and non-invasive tests. Then, they use coronary angiography for a detailed look.
Initial Evaluation and Medical History
The first step is a detailed check-up and looking at the patient’s medical history. We look for things like high blood pressure, diabetes, and family heart disease history. This helps us know who might be at risk and what tests to do next.
Important parts of the first check-up include:
- Looking at the patient’s medical history for risk factors and symptoms
- A physical exam to find signs of heart disease
- Basic blood tests, like blood counts and lipid profiles
Non-Invasive Testing Methods
Non-invasive tests are key in finding coronary artery blockages. They check the heart’s work and spot blockages without surgery.
Some common tests are:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): It records the heart’s electrical signals to find problems
- Stress Test: It checks how the heart works when stressed, usually through exercise or medicine
- Imaging Tests: Like echocardiography, cardiac MRI, or CT scans, which show the heart and blood vessels in detail
These tests are great for first checks and keeping an eye on heart disease.
Coronary Angiography: The Gold Standard
Coronary angiography is the top choice for finding coronary artery blockages. It’s a procedure where dye is put into the arteries to see blockages on an X-ray.
This test shows exactly where and how bad the blockages are. It helps doctors decide on treatments like angioplasty or CABG.
Even though it’s a more invasive test, coronary angiography is very important for diagnosing and treating heart disease.
Emergency Management of Acute LAD Blockage
Handling an acute LAD blockage quickly is key to saving lives and reducing heart damage. A blockage in the Left Ascending Artery can cause a severe heart attack, known as a “widowmaker.” It’s vital for healthcare teams and patients to know how to manage this emergency.
First Response and Initial Treatment
When an acute LAD blockage happens, it’s important to act fast. Recognize the symptoms like severe chest pain and call for help right away. Quick action is essential for better results.
At the scene, medical staff will give aspirin and other drugs to help. They’ll also do an electrocardiogram (ECG) to check the heart and see how bad the blockage is.
Time-Critical Interventions
Quick actions are critical in treating acute LAD blockage. The main goal is to get blood flowing to the heart muscle fast. There are two main steps:
- Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): This non-surgical method opens blocked arteries. It’s the best choice when it can be done quickly.
- Thrombolysis: If PCI isn’t possible fast, thrombolysis might be used. It breaks up the clot but is riskier and used when PCI can’t be done quickly.
Hospital Emergency Protocols
Hospital emergency plans are vital for managing acute LAD blockage. When a patient arrives, a team of experts works together to help right away. This team includes cardiologists and emergency doctors.
The hospital’s plan usually includes:
- Quick diagnosis with ECG and other tools.
- Getting the cardiac catheterization lab ready for PCI.
- Starting antiplatelet and anticoagulation therapy.
- Watching for complications and giving support.
By sticking to these plans, hospitals can greatly improve patient outcomes for acute LAD blockage.
Treatment Options for Left Ascending Artery Blockage
There are many ways to treat LAD blockage. Doctors use medication, interventional procedures, and surgery. The best treatment depends on how bad the blockage is, the patient’s health, and their medical history.
Medication Therapy Approaches
Medicine is key in treating LAD blockage. Anti-platelet agents like aspirin and clopidogrel stop platelets from clumping. Beta-blockers help by making the heart work less hard. Statins lower cholesterol and help prevent plaque from growing.
Doctors also use ACE inhibitors or ARBs to control blood pressure. Nitrates help with chest pain. The goal is to ease symptoms, slow disease growth, and improve life quality.
Interventional Procedures
For serious blockages, interventional procedures are often needed. Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) with stenting is common. It uses a catheter and stent to open the artery.
Rotational atherectomy is used to remove plaque. It uses a high-speed device to grind away blockages, improving blood flow.
Surgical Interventions
For complex cases, Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is considered. CABG uses a graft to bypass the blockage. This improves blood flow and reduces symptoms.
Choosing between PCI and CABG depends on several factors. A team of cardiologists and surgeons decides the best course of action for each patient.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After LAD Treatment
The journey to recovery after LAD treatment is complex. It includes immediate care, structured rehab, and long-term monitoring. Understanding these steps is key to a successful recovery.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Right after treatment, care is critical to avoid complications. Patients are watched closely in a recovery room for hours. Monitoring vital signs and the access site is standard.
A study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found most complications happen soon after.
“Early detection and management of these complications are critical to improving outcomes.”
Structured Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
Cardiac rehab is vital after LAD treatment. These programs include exercise, heart-healthy education, and stress counseling. They help patients manage their condition well.
| Component | Description | Benefits |
| Exercise Training | Supervised exercise sessions tailored to the patient’s condition | Improves cardiovascular health, increases stamina |
| Education | Information on diet, lifestyle changes, and medication management | Empowers patients to manage their condition |
| Counseling | Stress reduction and psychological support | Enhances mental well-being, reduces anxiety |
Long-term Monitoring and Follow-up
Long-term monitoring and follow-up are key. Regular check-ups help track progress and adjust treatment. Following medication and lifestyle advice is also important for long-term health.
The American Heart Association says managing coronary artery disease needs a long-term plan. This includes ongoing monitoring, lifestyle changes, and medical therapy.
Understanding the importance of immediate care, rehab, and long-term monitoring helps patients recover better. It improves their long-term outcomes after LAD treatment.
Preventing Coronary Artery Blockages
To stop coronary artery blockages, we need a plan that includes lifestyle changes and managing risk factors. Knowing and using these steps can greatly lower the chance of getting coronary artery disease.
Lifestyle Modifications for Heart Health
Living a heart-healthy lifestyle is key to avoiding coronary artery blockages. This means eating less saturated fats and more fruits, veggies, and whole grains.
It’s also important to be active, like walking fast, cycling, or swimming, for 150 minutes a week. And, quitting smoking is a must for smokers, as smoking greatly increases the risk of heart disease.
Managing Risk Factors and Comorbidities
It’s vital to manage risks like hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes to prevent blockages. Work with your doctor to keep these conditions in check with meds, lifestyle changes, or both.
Preventive Medications and Their Role
Preventive meds are key in lowering the risk of blockages. Statins help lower cholesterol, and antiplatelet agents stop blood clots.
Conclusion
Knowing about left ascending artery blockage is key for those at risk of heart attacks. Coronary artery disease is a major cause of death globally. It needs a full approach to manage it.
Patients can protect their heart by recognizing symptoms and looking into treatment options. Managing coronary artery disease involves prevention, treatment, and ongoing care.
We talked about the need to understand coronary artery anatomy and the dangers of left ascending artery blockage. We also looked at different treatment options. Taking care of your heart can lower the risk of heart problems.Prevention and management strategies, like changing your lifestyle and taking medicines, are vital for heart health. Working with healthcare providers helps create a plan to manage coronary artery disease. This can lead to better health outcomes.
FAQ
What is the left main coronary artery, and what are its branches?
The left main coronary artery is key. It quickly splits into the left anterior descending (LAD) and left circumflex arteries. These arteries are vital for the heart’s blood supply.
What is the “widowmaker” in medical terms?
The “widowmaker” is a blockage in the LAD artery. It’s called this because it’s very dangerous. It can lead to a high death rate because of its importance in heart blood supply.
What is coronary artery disease (CAD), and how is it characterized?
CAD is a condition where plaque builds up in the coronary arteries. This buildup narrows or blocks the arteries.
What are the symptoms of LAD blockage, and how do they differ from RCA blockage symptoms?
LAD blockage symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and other heart distress signs. These symptoms can be more severe than those of RCA blockage. They also carry a higher risk of complications.
What is the role of the right coronary artery (RCA) in heart health?
The RCA is vital for the heart. It supplies blood to the right ventricle and sometimes parts of the left ventricle.
How is coronary artery blockage diagnosed?
Diagnosis starts with a thorough check-up and medical history. It also includes non-invasive tests and coronary angiography. Angiography is the top method for finding blockages.
What are the treatment options for LAD blockage?
Treatments include medicines, angioplasty, and stenting. Sometimes, surgery like CABG is needed. The choice depends on the blockage’s severity and the patient’s needs.
What is the importance of cardiac rehabilitation after LAD treatment?
Cardiac rehab is key for recovery. It includes exercise, education, and support. It helps patients get back to health and lowers the risk of future heart problems.
How can coronary artery blockages be prevented?
Prevention involves healthy lifestyle choices. It includes managing risk factors and using preventive medicines. These steps help avoid coronary artery disease.
What is the significance of the OM (obtuse marginal) branches in cardiac health?
The OM branches are important in the heart’s blood flow. They come from the left circumflex artery. They help supply blood to the left ventricle’s lateral wall.
What does RCA stand for in medical terms?
RCA stands for right coronary artery. It’s a vital artery that supplies blood to the heart.
What are the risk factors for developing CAD?
Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, and family history of CAD. Lifestyle and genetic factors also play a role in atherosclerosis development.
References:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). 7 Key Facts About Left Ascending Artery Blockage. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482375/