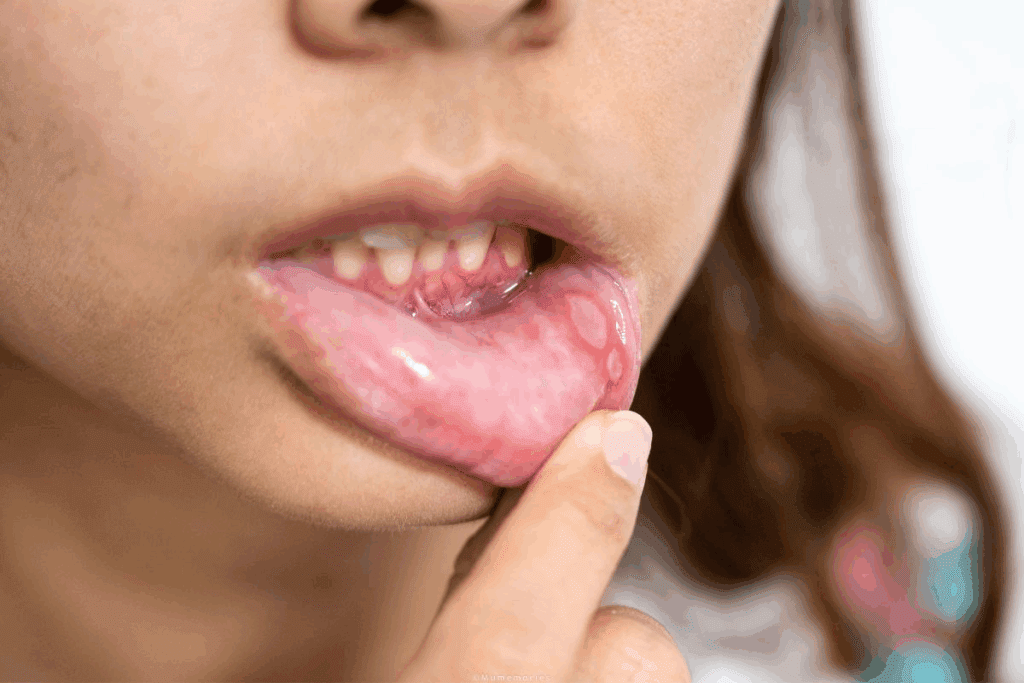
Lip cancer is a serious form of oral cancer that starts in squamous cells. It’s important to spot its signs early for effective treatment. This helps in providing timely medical care.
Lip cancer usually starts on the lower lip. Here, abnormal cells grow uncontrollably. It’s key to know the difference between harmless sores and serious tumors.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on catching lip cancer early. We offer patient-centered care for any suspicious lip lesions.
Guide to identifying the signs of lip cancer and information regarding the likelihood of Lip cancer cure.
Key Takeaways
- Early detection of lip cancer is key for effective treatment.
- Spotting the signs and symptoms of lip cancer can save lives.
- Lip cancer often starts on the lower lip with abnormal cell growth.
- It’s important to tell harmless sores from serious tumors.
- Liv Hospital uses advanced tests for suspicious lip lesions.
Understanding Lip Cancer
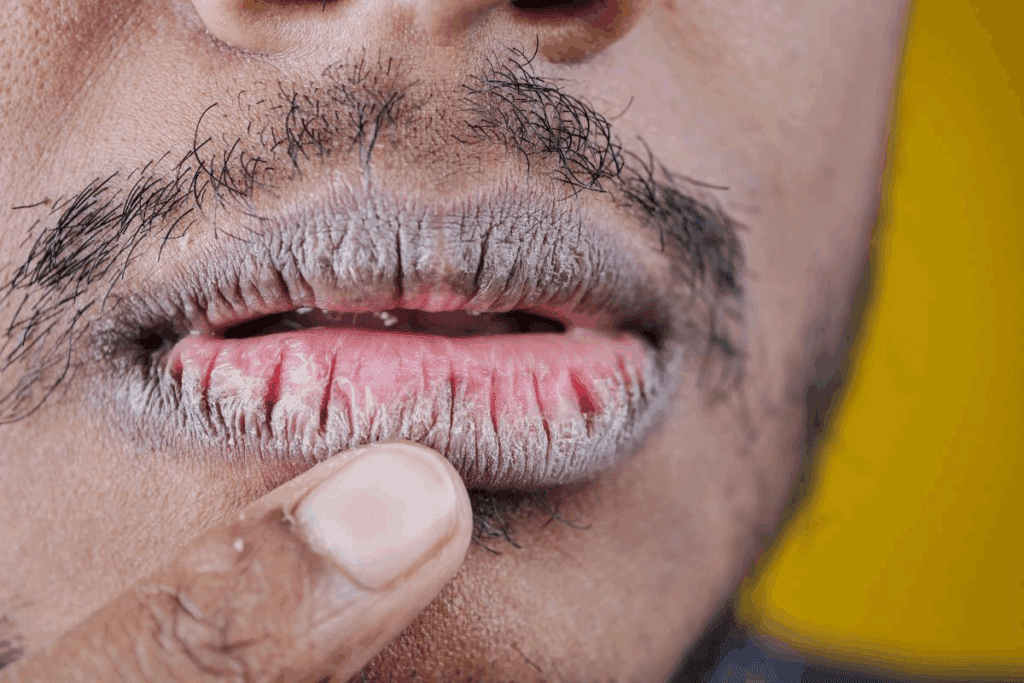
It’s important to know about lip cancer to catch it early and treat it well. Lip cancer is a type of oral cancer that happens on the lips. Knowing about it helps us spot who’s at risk and how to prevent it.
What is Lip Cancer?
Lip cancer is a tumor that grows on the lips. It often shows up on the lower lip but can also be on the upper lip or at the mouth’s corner. Lip cancer is a subtype of oral cancer, which includes cancers of the mouth and oral cavity.
Lip cancer is divided into two types: lower lip cancer and upper lip cancer. The lower lip gets more sun, making it more likely to get cancer.
Incidence and Statistics
Lip cancer is a big part of oral cancers. About 0.1 percent of people will get lip cancer in their lifetime. Those diagnosed with oral cancer, including lip cancer, are usually 63 years old on average.
| Age Group | Incidence Rate |
|---|---|
| Under 45 | Low |
| 45-63 | Moderate |
| Above 63 | High |
Common Risk Factors
Many things can increase your chance of getting lip cancer. Tobacco use is a big risk because it has carcinogens that can cause cancer. Drinking a lot of alcohol is also risky because it can irritate the mouth and raise cancer risk.
Being out in the sun without protection is another big risk, mainly for lip cancer. Spending too much time in the sun can lead to lip cancer, mostly on the lower lip.
Knowing these risks helps us take steps to lower our chance of getting lip cancer.
Early Warning Signs of Lip Cancer
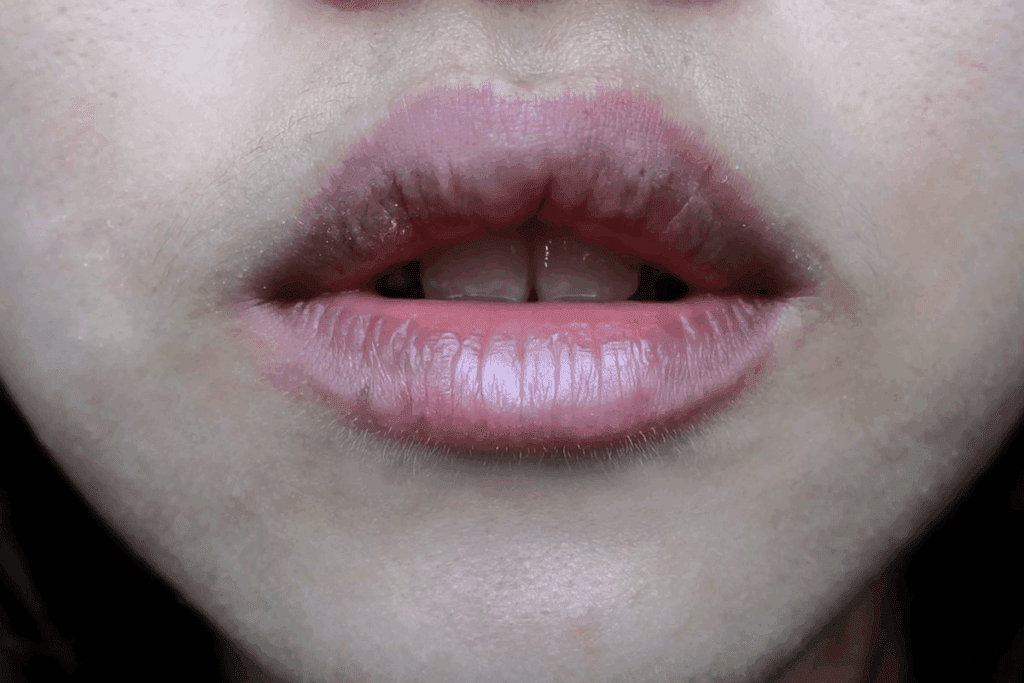
Understanding the early signs of lip cancer is key to managing it well. Lip cancer is easier to treat if caught early. We will look at the important signs that may show lip cancer is present.
Persistent Sores That Don’t Heal
A common sign of lip cancer is sores that don’t heal in two weeks. These sores might not hurt and can bleed sometimes. If a sore on your lip lasts, see a doctor right away.
Early lip cancer often looks like a sore that won’t go away. It might be white or red, or a lump that doesn’t heal in two weeks. Watch for sores and get medical help if they don’t heal.
Unusual Lumps or Thickening
Another symptom of lip cancer is lumps or thickening on the lip. These can be painless and don’t always bleed. But, they might mean cancer is growing. Any new or growing lump needs a doctor’s check.
Unusual lumps on the lip could mean cancer. It’s important to notice any changes in the lip’s look or feel.
Changes in Lip Color and Texture
Changes in lip color and texture can hint at skin cancer on lips. Look for white or red patches, or scaly or crusted areas. Any lasting change in lip color or texture needs a doctor’s look.
Cancer white spots on lips, or leukoplakia, might lead to cancer. Not all white spots are cancer, but lasting ones should be checked. Also, any unusual texture change, like thickening or scales, needs a doctor’s visit.
Identifying Cancer White Spots on Lips
It’s important to spot cancerous white spots on lips early. This can save lives. We want to help you know how to find these dangerous spots.
Characteristics of Cancerous White Lesions
Cancerous white spots on lips can look different. They often don’t go away with usual treatments. They might also cause bleeding or pain.
These spots can be flat or raised and feel rough. They might look like harmless conditions. So, it’s key to see a doctor for a correct diagnosis.
Leukoplakia vs. Cancerous Spots
Leukoplakia is a white patch that can’t be rubbed off. It’s a sign that might turn into cancer. But not all leukoplakia becomes cancer.
Leukoplakia can turn into cancer, but cancer spots are already bad. Knowing the difference is important for treatment.
Timeline for Concern: The Two-Week Rule
See a doctor if a white spot on your lip lasts over two weeks. The two-week rule is a guide. It means if a spot doesn’t go away in two weeks, get it checked.
Spotting these spots early can lead to better treatment. So, watch your lip health and see a doctor if you notice anything odd.
Recognizing Lip Cancer by Location
Lip cancer can appear in different spots on or around the lips. Each spot has its own signs. Knowing where lip cancer is helps doctors diagnose and treat it better. We’ll look at the differences in lip cancer by location, like the lower lip, upper lip, and inside the lip.
Lower Lip Cancer: Most Common Type
Lower lip cancer is the most common type. It’s because the lower lip gets more sun. Sun exposure is a big risk factor. We need to watch for changes here.
Key characteristics of lower lip cancer include:
- Lesions or sores that do not heal
- Unusual thickening or lumps
- Changes in lip color or texture
Upper Lip Cancer: Distinctive Features
Upper lip cancer is less common but has its own signs. It shares some symptoms with lower lip cancer but has different risk factors.
Notable aspects of upper lip cancer include:
- More likely to be associated with other health conditions
- May have a different demographic profile
- Requires a thorough examination for diagnosis
Inner Lip Cancer: Hidden Dangers
Cancer inside the lip is tricky to spot early. It’s hidden inside, making it hard to see.
Important signs of inner lip cancer include:
- Unexplained pain or discomfort inside the lip
- Unusual bleeding or ulceration
- Changes in the texture or color inside the lip
Physical Symptoms That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
It’s key to spot the signs of lip cancer early. This can lead to better treatment and outcomes. Knowing these symptoms is the first step.
Pain, Numbness, and Tingling Sensations
Lip cancer can make your lip feel painful, numb, or tingle. This happens when the tumor presses on nerves and tissues. If your lip hurts or feels odd, see a doctor right away.
Bleeding and Ulceration
Bleeding or ulcers on your lip are serious signs. Cancer can make your lip bleed or form sores that won’t heal. Seeing a doctor quickly is important.
Scaly Appearance and Surface Irregularities
Lip cancer can also change how your lip looks. It might look scaly or have bumps. Watching for these changes can help catch cancer early.
Difficulty Speaking, Eating, or Swallowing
In later stages, lip cancer can make it hard to talk, eat, or swallow. This happens when the tumor gets big. If you’re having trouble, get help fast.
| Symptom | Description | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Pain, Numbness, Tingling | Unusual sensations on the lip | Tumor affecting nerves |
| Bleeding, Ulceration | Bleeding or ulcers on the lip | Advanced cancer, needs immediate evaluation |
| Scaly Appearance | Changes in lip texture or appearance | Possible cancerous growth |
| Difficulty Speaking, Eating, Swallowing | Interference with daily functions | Advanced tumor growth |
Differentiating Lip Cancer from Benign Conditions
It’s important to tell the difference between lip cancer and other lip issues. Many people get lip sores or lesions that worry them. But not all of these are cancer. Knowing the difference helps you get the right medical care.
Lip Cancer vs. Cold Sores
Cold sores, or fever blisters, come from the herpes simplex virus. They show up as small blisters on the lip and can hurt. Unlike lip cancer, cold sores usually go away in a few weeks. But, if a sore doesn’t heal, see a doctor.
Cold sore characteristics:
- Typically appear as clusters of small blisters
- Can be painful
- Usually heal within a few weeks
- Caused by the herpes simplex virus
Lip Cancer vs. Canker Sores
Canker sores are small, shallow ulcers on the inside of the lips or cheeks. They’re not contagious and can be caused by stress, injury, or certain foods. They can hurt, but usually go away in a few weeks. If a sore lasts or is big, see a healthcare professional.
Canker sore characteristics:
- Small, shallow ulcers
- Develop on the inside of the lips or cheeks
- Not contagious
- Usually resolve within a few weeks
Lip Cancer vs. Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions can make your lip swell, turn red, or get sores. These can be from food, cosmetics, or the environment. Unlike lip cancer, these usually go away when the allergen is removed or treated with antihistamines. But, if lip symptoms don’t go away or are severe, get medical help.
Lip Cancer vs. Traumatic Injuries
Lip injuries, like cuts or bites, can look like lip cancer. They can swell, hurt, or cause sores that take time to heal. If a lip injury doesn’t heal or looks infected, see a doctor to check for lip cancer.
Key differences to watch for:
- Persistence: Lip cancer tends to persist or grow over time.
- Appearance: Lip cancer can appear as a new growth, sore, or change in lip texture or color.
- Symptoms: Lip cancer may cause pain, numbness, or tingling sensations.
Knowing these differences helps you know when to see a doctor for lip symptoms. If you’re not sure about your lip symptoms or if they don’t go away, always check with a healthcare professional. They can give you the right diagnosis and treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to see a doctor is key for catching lip cancer early. Being aware of warning signs can save lives.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Evaluation
Don’t ignore certain lip symptoms. Look out for persistent sores that don’t heal, unusual lumps or thickening, and changes in lip color and texture. If you see these, see a doctor right away.
Other signs that need quick attention are pain, numbness, or tingling sensations on your lip, bleeding or ulceration, and a scaly appearance or surface irregularities. These could mean lip cancer and need a doctor’s check.
The Diagnostic Process
The first step in diagnosing lip cancer is a physical examination of your lip and mouth. Your doctor will look for any signs of cancer, like lesions or growths.
If your doctor thinks you might have lip cancer, they might suggest a biopsy. A biopsy takes a small tissue sample from the area. It’s then checked for cancer cells under a microscope.
What to Expect During a Lip Examination
During a lip exam, your doctor will visually inspect your lip and may feel for abnormalities. They’ll also ask about your health history and symptoms.
Be honest with your doctor during the exam. Tell them about any changes you’ve noticed, no matter how small. This helps them make an accurate diagnosis.
Lip Cancer Cure: Treatment Options and Outlook
Early detection is key to a successful lip cancer treatment. If caught early, lip cancer is very treatable. The outlook is usually good.
Benefits of Early Detection
Finding lip cancer early is vital. It lets us act fast, stopping it from spreading. Early detection means we can pick the best treatment. This can lower risks and boost survival chances.
- Improved Survival Rates: Finding cancer early means better survival chances.
- Less Invasive Treatments: Early cancer might need less invasive treatments.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Early treatment lowers risks of serious problems.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for lip cancer depends on the stage, location, and patient’s health. Common treatments include:
- Surgery: Removing the tumor is often the main treatment.
- Radiation Therapy: This uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be used alone or with other treatments.
Recovery and survival rates for lip cancer patients depend on several factors. These include the stage at diagnosis and treatment success. Early diagnosis usually means a better outlook.
Survival rates show the percentage of patients who live with a certain cancer for a certain time. For lip cancer, early diagnosis leads to higher 5-year survival rates.
Follow-up Care and Monitoring
After treatment, follow-up care is critical. It helps watch for any signs of cancer coming back and deals with treatment side effects. Regular doctor visits are key to catching any problems early.
- Regular Check-ups: Frequent doctor visits to monitor recovery.
- Self-Examination: Patients should check themselves regularly for unusual changes.
- Supportive Care: Care to manage symptoms and side effects.
Conclusion
We’ve talked about how to spot lip cancer, its signs, and why early detection matters. Lip cancer is treatable if caught early. Knowing its signs is key to getting help fast.
Spotting warning signs like sores, lumps, and color changes in the lips is important. It helps with better treatment options. Knowing about upper lip cancer and inner lip cancer is also vital, as they can be hard to spot.
Understanding cancerous white spots and knowing the difference from harmless conditions is important. This way, people can get medical help quickly. Early detection is key to better treatment and fewer complications.
We stress the need to watch your lip health and see a doctor if something seems off. This proactive step can greatly improve your chances of beating lip cancer.
FAQ
What are the common signs and symptoms of lip cancer?
Signs include persistent sores and unusual lumps. You might also notice changes in lip color and texture. Pain, numbness, bleeding, and a scaly appearance are other symptoms.
How can I differentiate between lip cancer and benign conditions like cold sores or canker sores?
Lip cancer doesn’t heal and persists. Cold sores and canker sores usually go away in weeks. If a sore or lump doesn’t heal, see a doctor.
What are the characteristics of cancerous white spots on the lips?
Cancerous spots are persistent and may be white or red. They can be painful or bleed. It’s important to tell them apart from benign conditions like leukoplakia.
What is the significance of the two-week rule in diagnosing lip cancer?
If a sore lasts over two weeks, get it checked. It could be lip cancer.
How is lip cancer diagnosed?
Doctors use physical exams, biopsies, and imaging tests. They look for abnormalities in the lip and surrounding areas.
What are the treatment options available for lip cancer?
Treatments include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. The choice depends on the cancer’s stage, location, and your health.
What are the benefits of early detection in lip cancer?
Early detection improves treatment outcomes and survival rates. It means less invasive treatments and fewer complications.
Can lip cancer be cured?
Yes, lip cancer can be cured if caught early. The cure rate depends on the cancer’s stage, treatment, and your health.
How can I reduce my risk of developing lip cancer?
Avoid tobacco, excessive sun, and poor oral hygiene. Regular health check-ups help catch it early.
What is the difference between lower lip, upper lip, and inner lip cancer?
Lower lip cancer is common and linked to sun. Upper lip cancer is rarer. Inner lip cancer is harder to spot and may have a different outcome.
References
National Health Service (NHS). Lip Cancer: Early Identification of Signs and Symptoms. Retrieved from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/lip-cancer/symptoms/


