Learn to recognise early warning signs of common dental issues like gum bleeding, swelling, bad breath, and tooth sensitivity to ensure prompt professional care.
Dental health problems, such as gum disease and tooth decay, are caused by the buildup of bacteria and plaque. While many diseases start without pain, noticing early warning signs is crucial for effective and early treatment. This section describes the common symptoms, progression of disease, and the factors that increase your risk of developing severe, long-term dental issues, such as losing the bone that supports your teeth.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Many oral problems start quietly, but the mouth often gives early warning signs when something is wrong. Symptoms like toothache, sensitivity, bleeding gums, swelling, bad breath, mouth sores, and loose teeth can signal issues ranging from minor irritation to serious infection or gum disease. Knowing what these dental symptoms might mean and when to seek care helps you protect your teeth, gums, and overall health.
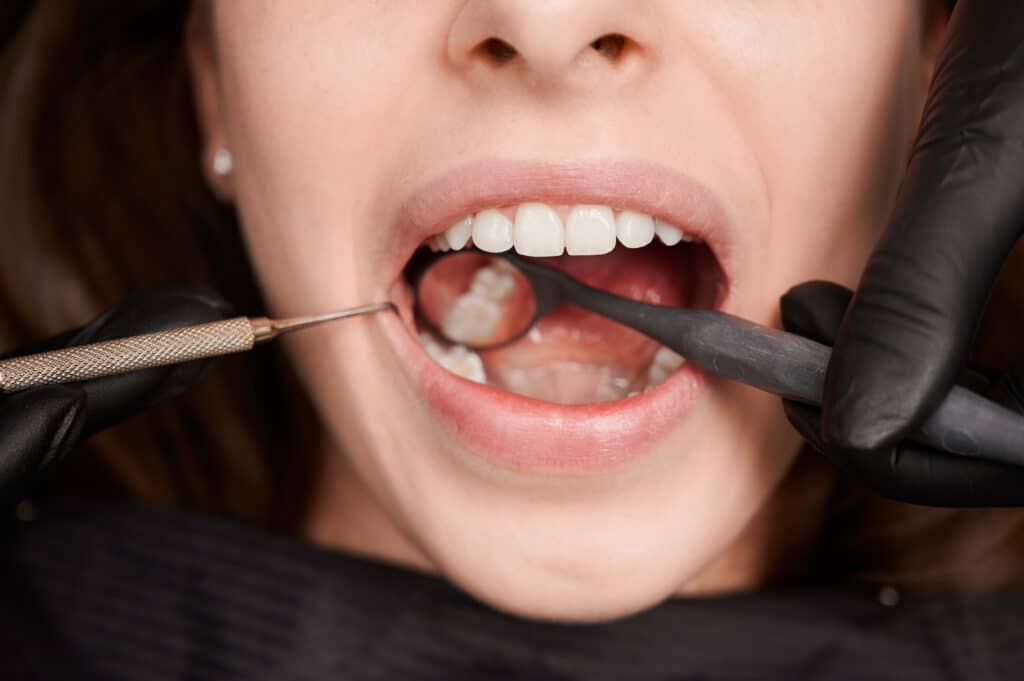
Tooth pain can range from mild discomfort to sharp, throbbing pain that keeps you awake or makes it hard to eat. Short, sharp sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods may come from exposed dentin, receding gums, early decay, or worn enamel, while lingering or spontaneous pain often suggests deeper decay, a cracked tooth, or an infected nerve.
Delaying care can allow infection to spread, increasing the risk of serious complications and the need for more extensive treatment.
Gums that bleed when you brush or floss, look red and swollen, or feel tender are common signs of gum disease. Early gum disease (gingivitis) is often painless and reversible with professional cleaning and better oral hygiene, but if left untreated it can progress to periodontitis, leading to gum recession, bone loss, loose teeth, and even tooth loss.
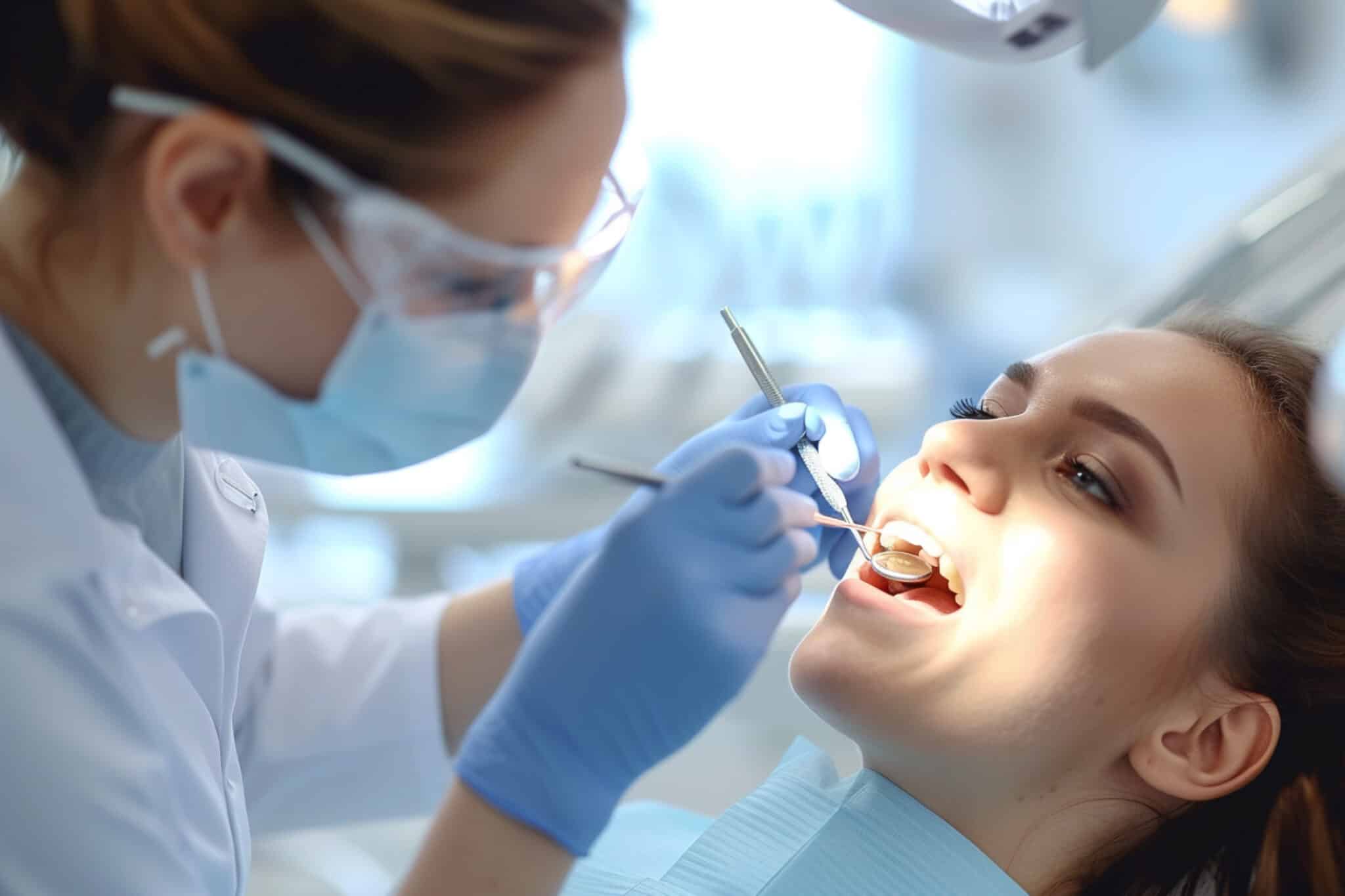
Bleeding gums can also be influenced by systemic conditions such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, so they should not be ignored. A dental check-up can determine whether you have gum disease and what level of treatment you need.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
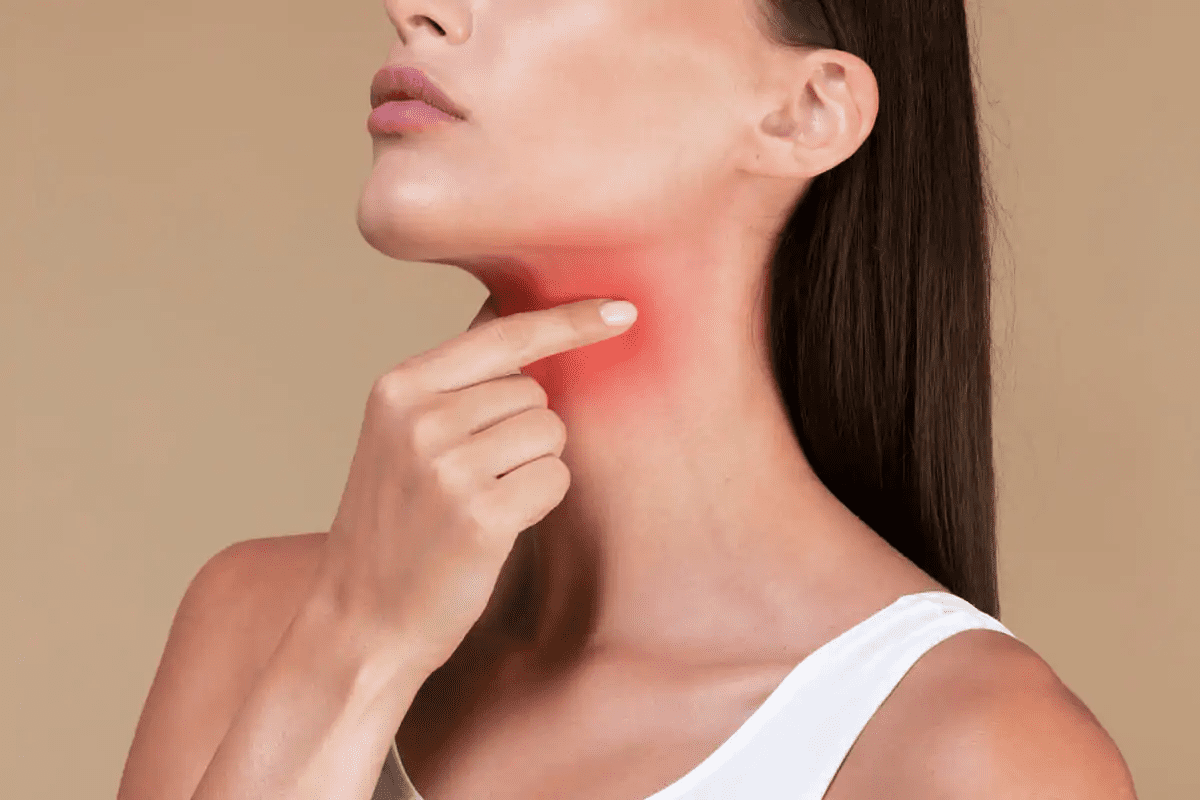
Occasional morning breath is normal, but bad breath that persists despite brushing, flossing, tongue cleaning, and mouthwash can signal an underlying problem. Common dental causes include gum disease, trapped food and plaque, dry mouth, cavities, poorly fitting dentures, or infections.
Persistent halitosis can sometimes reflect medical issues, such as sinus infections, reflux, liver or kidney problems, or uncontrolled diabetes, so your dentist may coordinate with your doctor if needed.
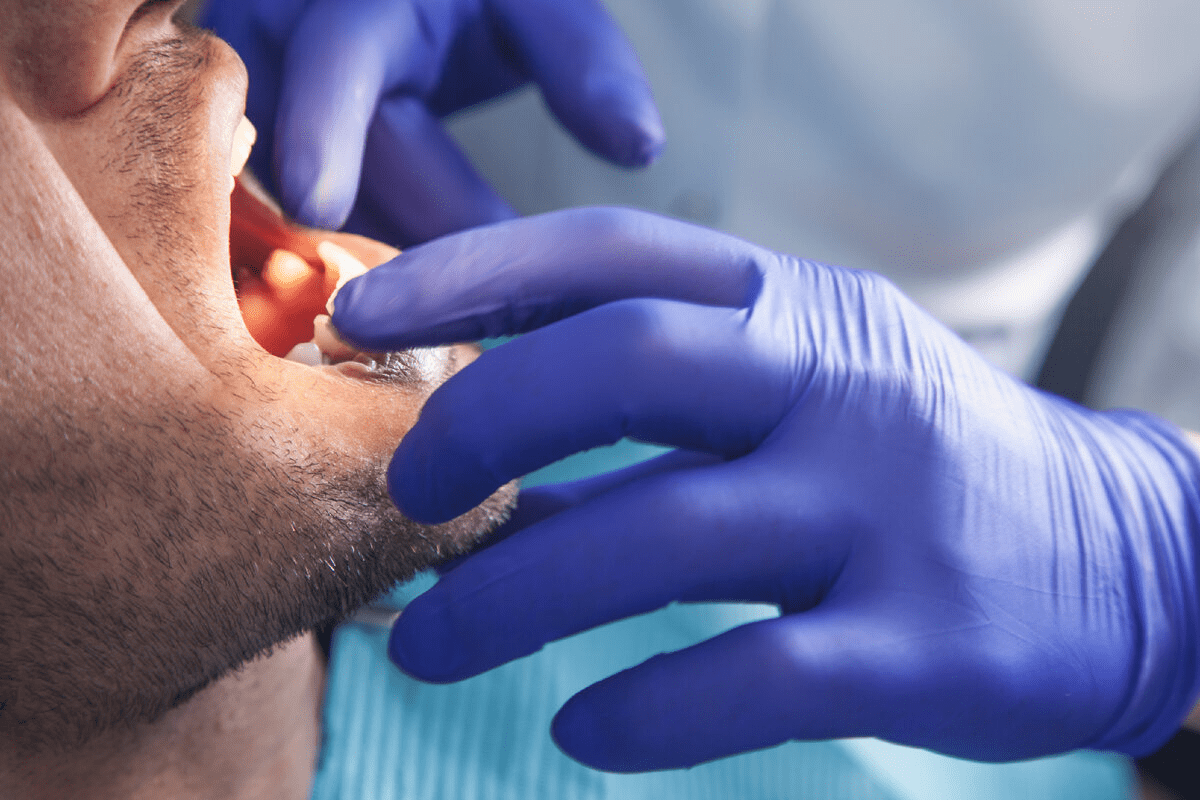
Swelling of the gums, face, or jaw; pus around a tooth; or painful lumps inside the mouth often indicate infection or other serious problems. Dental abscesses—pockets of pus due to advanced decay or gum disease—can cause severe pain, swelling, fever, and a bad taste, and sometimes lead to difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing.
These situations require prompt dental or medical care to drain infection, control pain, and prevent spread to other areas of the body.
Mouth ulcers, white or red patches, or lumps that do not heal can range from minor irritation to early signs of serious disease. Common benign causes include minor trauma (such as biting the cheek), aphthous ulcers, or irritation from sharp teeth or ill-fitting dentures, which usually heal within one to two weeks.
However, you should see a dentist or doctor promptly if you notice:
Some systemic diseases, autoimmune conditions, and oral cancers first appear as stubborn ulcers or unusual gingival changes, so persistent lesions require professional evaluation and sometimes biopsy.
Adult teeth should not feel loose. Teeth that start to move, create new gaps, or feel different when you bite together can indicate advanced gum disease, bone loss, trauma, or problems with the jaw joint or bite alignment.
Concerning signs include:
Early assessment allows more options to stabilize teeth, treat gum disease, and correct bite issues before tooth loss occurs.
Dry mouth (xerostomia) occurs when saliva production is reduced, making it easier for cavities, gum disease, and fungal infections to develop. It can be caused by medications, radiation therapy, autoimmune diseases such as Sjögren’s syndrome, poorly controlled diabetes, dehydration, or mouth breathing. Changes in taste, burning sensations, or difficulty chewing and swallowing can also accompany systemic illnesses.
You should mention to your dentist if you experience:
Your dentist can suggest saliva-support strategies, adjust oral care, and collaborate with your physician to investigate underlying causes.
Some dental symptoms require same-day or emergency care to prevent serious complications. In addition to severe toothache, urgent red flags include rapidly spreading swelling, difficulty breathing or swallowing, uncontrolled bleeding, major trauma to the teeth or jaw, and severe pain unrelieved by over-the-counter medication.
Seek emergency dental or medical help if you have:
Whenever you are unsure, it is safer to contact a dentist, who can advise whether you need urgent or routine care.

Bleeding is a sign of active inflammation or gingivitis; paradoxically, the more you floss correctly to remove the bacteria, the less they will bleed over time as the tissue heals.
Sudden sensitivity can be caused by gum recession, a new cavity, a cracked tooth, or even recent sinus pressure pushing on the upper tooth roots.
While 90% of bad breath originates from oral bacteria on the tongue or gums, persistent halitosis can also stem from sinus infections, gastric reflux, or tonsil stones.
Clicking occurs when the cartilage disc inside the jaw joint slips out of place and pops back in; it is common and usually requires treatment only if accompanied by pain or locking.
Yes, stress is a leading cause of teeth grinding and clenching, which can lead to fractured teeth, muscle pain, and temporomandibular joint disorders.

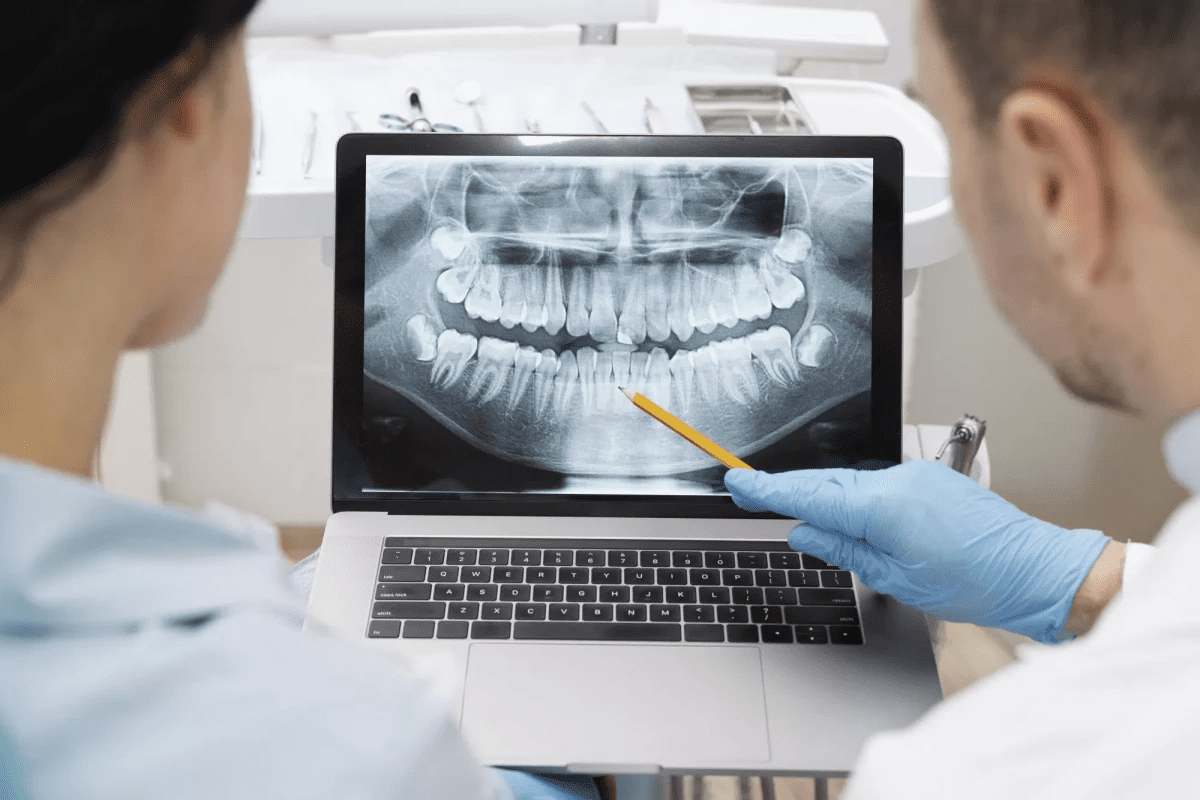
Maxillofacial radiology is a complex field that needs advanced training. It covers radiation physics, biology, and imaging techniques. New technologies like cone beam computed tomography
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a big reason for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC), a throat cancer type. Daniel Kwon, MD, a head and neck cancer
Many think oral sex is safe, but it’s not. Genital HPV can spread to the mouth and throat through oral contact. This can cause painful
Oral papillomas are growths in the mouth, often from low-risk HPV. They can show up as bumps on the tongue, lips, and gums. This can
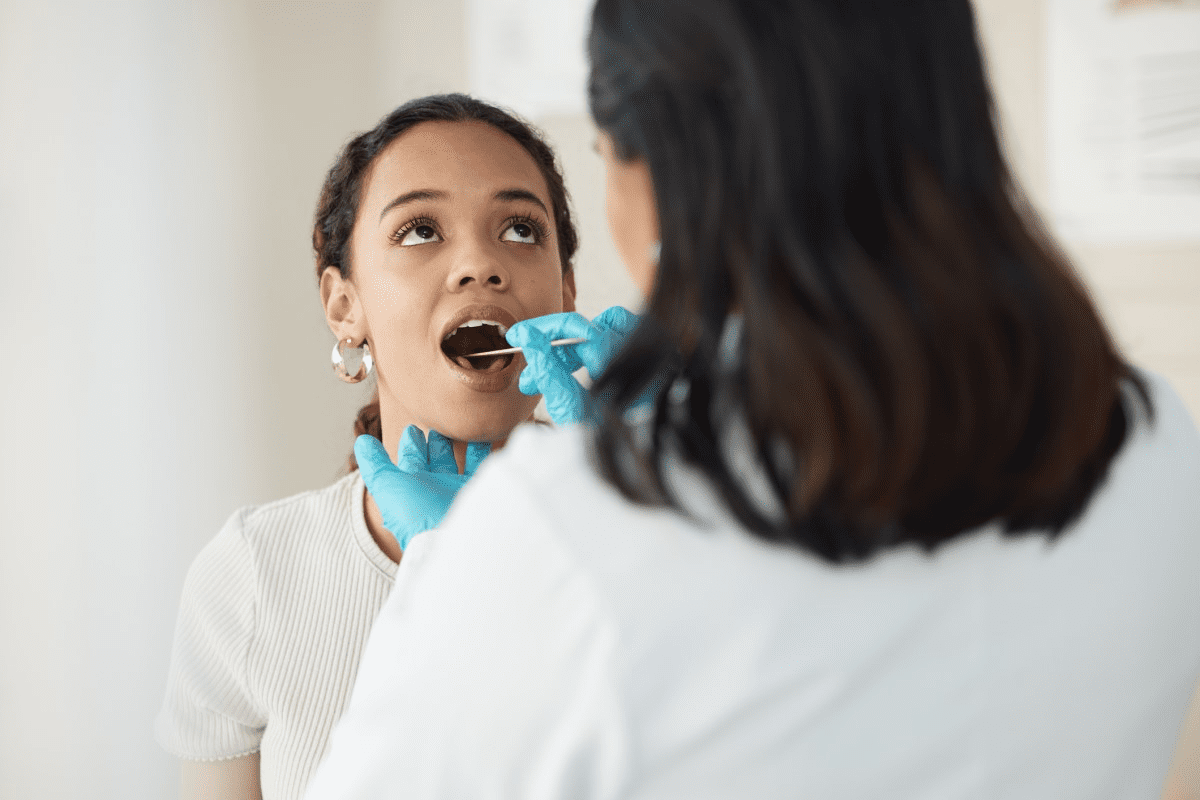

Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common virus that affects millions globally. The American Cancer Society says 43 million people in the United States have HPV.
Oral radiology is key in today’s dentistry. It helps us make accurate decisions. This technology ensures better patient care. The dental imaging market is growing fast.

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)