Many people with lower back pain also face frequent urination. This link makes us wonder if spinal compression and bladder issues are connected.
Studies show that spinal compression can harm bladder function. It can lead to various urinary problems. This happens because the nerves controlling the bladder are affected by the compression.
This article dives into the link between spinal compression and bladder problems. We’ll look at the causes and ways to find relief for those dealing with back pain relief and urinary issues.
Key Takeaways
- Spinal compression can affect bladder function.
- Nerves controlling the bladder can be impacted by spinal compression.
- Lower back pain is often associated with urinary issues.
- Understanding the causes can lead to effective relief measures.
- Relief from back pain may also alleviate urinary problems.
The Connection Between Spine Health and Bladder Function
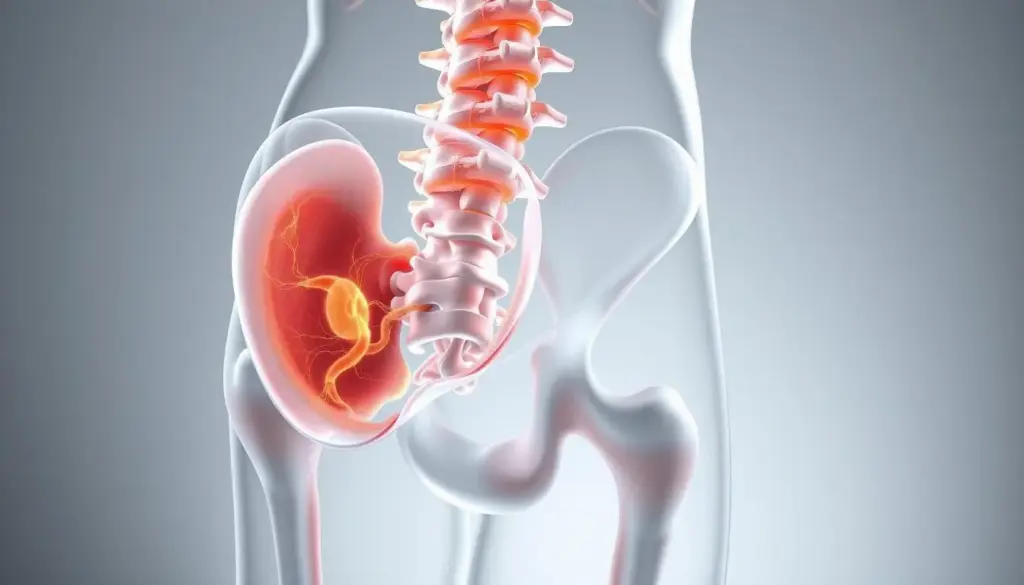
It’s key to know how the spine affects bladder function. This is important for dealing with lower back pain and frequent urination. The spine helps control our body’s functions, including how we use the bathroom, through the nervous system.
How the Nervous System Controls Urination
The nervous system manages when we pee. It sends and gets messages to and from the bladder. The nervous system is like a communication path. It lets the brain tell the bladder to pee or hold it.
The autonomic nervous system is a big part of this. It works without us thinking about it. It makes sure we pee at the right time.
The Role of the Spinal Cord in Bladder Control
The spinal cord is vital for bladder control. It connects the brain to the bladder, sending and getting messages. Damage to the spinal cord can mess with these messages, causing pee problems.
Tests like urinalysis (81000 Urinalysis nonauto w/scope) help find pee issues linked to spinal health. Knowing how the spinal cord affects the bladder shows why keeping the spine healthy is important.
Understanding Spinal Compression
Spinal compression is a key issue for health problems like lower back pain and more frequent urination. It happens when too much pressure is put on the spine. This can cause discomfort and other health issues.
Types of Spinal Compression
There are different types of spinal compression, based on where and why it happens. The main types are:
- Cervical spinal compression: This is in the neck area.
- Thoracic spinal compression: It affects the middle back.
- Lumbar spinal compression: This is in the lower back, often linked to lower back pain.
Common Causes of Spinal Compression
Many things can cause spinal compression. Some common causes are:
- Herniated discs: When the soft inner gel leaks out, it can press on nerves.
- Spinal stenosis: This is when the spinal canal gets narrower, putting pressure on the spinal cord.
- Degenerative disc disease: This is wear and tear on the spinal discs.
- Spondylolisthesis: A condition where one vertebra slips over another.
The link between these causes and spinal compression can be complex. For example, spinal stenosis and herniated discs often go together. Stenosis can make disc herniation more likely.
|
Cause |
Description |
Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
|
Herniated Discs |
Soft inner gel leaks out, compressing nerves. |
Lower back pain, numbness, tingling. |
|
Spinal Stenosis |
Narrowing of the spinal canal. |
Pain, weakness, numbness in legs. |
|
Degenerative Disc Disease |
Wear and tear on spinal discs. |
Chronic back pain, stiffness. |
Risk Factors for Developing Spinal Compression
Some things can make you more likely to get spinal compression. These include:
- Age: As you get older, wear and tear can lead to conditions like spinal stenosis.
- Obesity: Being overweight puts extra strain on the spine.
- Genetics: Your family history can affect your risk of spinal conditions.
- Occupational hazards: Jobs that involve heavy lifting or bending can increase your risk.
Knowing these risk factors can help prevent or manage spinal compression. By tackling these factors, you can lower your chance of getting related conditions.
Lower Back Pain and Increased Urination: The Connection
Spinal compression can greatly affect bladder function, causing urinary symptoms. When the spine is compressed, it can harm the nerves that control the bladder. This can lead to various urinary issues.
How Spinal Compression Affects Urinary Function
Spinal compression can mess with the nerves that control the bladder. This can cause urinary urgency, needing to urinate suddenly and strongly. It can also lead to urinary incontinence, where urine leaks out without control.
The nerves that manage the bladder are part of our complex nervous system. When these nerves get compressed or damaged, it can cause many urinary problems. These include frequent urination and leaking urine.
Common Urinary Symptoms Associated with Spinal Issues
People with lower back pain and leaking urine or other urinary symptoms might have spinal problems. Common urinary symptoms linked to spinal issues include:
- Urinary urgency
- Frequent urination
- Urinary incontinence
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
These symptoms can really affect someone’s quality of life. It’s very important to see a doctor if these symptoms keep happening or get worse.
Spinal Stenosis and Its Impact on Bladder Control
Spinal stenosis is when the spinal canal gets narrower. This can press on nerves that help us urinate. It often causes lower back pain and can lead to urinary problems.
What Is Spinal Stenosis?
Spinal stenosis happens when the spinal canal shrinks. This puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. It can be caused by aging, herniated discs, or injuries.
The nerves getting compressed can cause pain, numbness, and bladder issues. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe.
How Stenosis Affects Nerves Controlling the Bladder
The nerves that control the bladder can be affected by spinal stenosis. When these nerves are compressed, it can cause urinary problems. These include needing to urinate more often, feeling a sudden urge to go, and in severe cases, losing bladder control.
Spinal stenosis can greatly affect bladder control, impacting daily life. It’s important to understand how spinal stenosis and urinary symptoms are connected for proper treatment.
|
Symptom |
Description |
Relation to Spinal Stenosis |
|---|---|---|
|
Increased Urination Frequency |
Frequent need to urinate |
Nerve compression affecting bladder control |
|
Urgency |
Sudden, intense need to urinate |
Disruption of normal nerve signals to the bladder |
|
Incontinence |
Involuntary leakage of urine |
Severe nerve compression impacting bladder muscles |
Effective lower back pain treatment often involves addressing the underlying cause of spinal stenosis. This can include physical therapy, medications to manage pain and inflammation, and in some cases, surgical intervention to relieve pressure on the nerves.
By understanding the impact of spinal stenosis on bladder control, individuals can seek appropriate medical care. This can help manage symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Herniated Discs and Urinary Dysfunction
When a disc herniates, it can cause many problems, including bladder issues. Herniated discs happen when the soft center of the disc leaks out. This can press on nearby nerves.
This pressure can mess with the nerves that help us go to the bathroom. How bad the bladder problems are depends on where and how big the herniation is.
How Disc Herniation Affects Bladder Function
Disc herniation can mess with bladder function by pressing on or irritating the nerves that control it. These nerves start in the lower back, making herniations there more serious.
Nerve compression can cause symptoms like needing to pee a lot, feeling like you have to pee right away, and sometimes not being able to pee at all. How bad the nerve damage is affects how bad these symptoms are.
L4-L5 Herniation and Bladder Problems
Herniations at the L4-L5 level are a big deal for bladder problems. This area is key for controlling lower limb functions and bladder control.
An L4-L5 herniation can press on the nerves that control the bladder. This can cause symptoms like:
- Frequent urination
- Urgency
- Difficulty initiating urination
- Urinary retention
Because the L4-L5 disc is close to the bladder nerves, even a small herniation can have big effects on bladder function.
It’s important to understand how herniated discs and bladder problems are connected. If you have back pain and bladder issues, you should see a doctor. They can check for spinal problems that might be causing these symptoms.
Sciatica and Its Relationship to Urinary Symptoms
It’s important to know how sciatica and urinary problems are connected. Sciatica causes pain that spreads along the sciatic nerve. This pain can also affect bladder control and how we urinate.
Can Sciatica Cause Frequent Urination?
Yes, sciatica can lead to frequent urination. The sciatic nerve runs from the lower back to the legs. When this nerve gets irritated or compressed, it can mess with the pelvic area. This might cause problems with urination.
- Irritation of the sciatic nerve can disrupt normal nerve signaling.
- This disruption can affect bladder control.
- Patients may experience an increase in urinary frequency.
Distinguishing Sciatica-Related Urinary Issues from Other Causes
It’s key to tell apart urinary problems caused by sciatica from other issues. Urinary symptoms can come from many places. This includes infections, diabetes, and other neurological problems.
- Identify the primary cause of sciatica (e.g., herniated disc, spinal stenosis).
- Assess the severity of urinary symptoms.
- Consider other possible causes of urinary problems.
Knowing the root of both sciatica and urinary symptoms helps doctors create better treatment plans. These plans tackle both problems at once.
Cauda Equina Syndrome: A Medical Emergency
Cauda Equina Syndrome is a serious medical issue that needs quick action. It happens when nerves in the lower back get compressed. This causes severe pain, numbness, and problems with urination.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The signs of Cauda Equina Syndrome vary but often include intense back pain and numbness in the legs. People may also have trouble with urination. In some cases, they might lose control of their bladder or bowel.
Key symptoms to watch for:
- Severe lower back pain
- Numbness or tingling in the legs
- Difficulty urinating or loss of bladder control
- Loss of bowel control
Why Immediate Medical Attention Is Crucial
Getting medical help right away is key for those with Cauda Equina Syndrome symptoms. Waiting too long can cause permanent nerve damage. This can lead to long-term problems with bladder and bowel control.
Timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with Cauda Equina Syndrome.
|
Symptom |
Potential Consequence if Untreated |
|---|---|
|
Severe lower back pain |
Permanent nerve damage |
|
Urinary dysfunction |
Long-term bladder control issues |
|
Loss of bowel control |
Chronic bowel dysfunction |
Diagnosing Spinal Issues That Affect Bladder Function
Identifying spinal problems that affect the bladder is key. It needs a detailed approach. This includes many medical fields and tools.
Physical Examination
The first step is a thorough physical check-up. Doctors look at muscle strength, reflexes, and feeling in the legs. They search for signs of spinal or bladder problems.
They also ask about your medical history. This helps spot risk factors and symptoms linked to spinal issues and bladder control.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are vital for finding spinal problems. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is great for seeing the spinal cord and nerves. It can spot issues like spinal stenosis or tumors that affect bladder control.
Computed Tomography (CT) scans and X-rays are also used. They help find bone problems or fractures that might be causing spinal compression.
Urodynamic Testing
Urodynamic tests check how the bladder and urethra work. They measure pressure and flow to see if there are problems. This helps find out how spinal issues affect the bladder.
These tests give insights into how spinal conditions impact bladder function. They help doctors make better treatment plans for both the spinal issue and urinary symptoms.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Spinal-Related Bladder Issues
Managing spinal-related bladder issues often involves a multi-faceted approach. This includes non-surgical treatments that can significantly improve quality of life. These treatments aim to alleviate symptoms, improve bladder function, and enhance overall well-being without the need for surgical intervention.
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy plays a key role in managing spinal-related bladder issues. It involves exercises and techniques designed to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine. It also improves flexibility and reduces pressure on the nerves controlling bladder function.
A physical therapist can create a personalized exercise program. This program may include pelvic floor exercises, stretches, and strengthening exercises for the back and abdominal muscles. These exercises can help improve bladder control and reduce symptoms associated with spinal compression.
Medications for Pain and Bladder Control
Medications can be an effective component of non-surgical treatment plans for spinal-related bladder issues. Pain relief medications can help manage discomfort associated with spinal compression. Medications targeting bladder control can help alleviate symptoms such as urgency and frequency.
Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Pain relievers (e.g., NSAIDs, muscle relaxants)
- Anticholinergics for overactive bladder
- Beta-3 adrenergic agonists for overactive bladder
|
Medication Type |
Primary Use |
Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Pain Relievers |
Manage pain associated with spinal compression |
NSAIDs, muscle relaxants |
|
Anticholinergics |
Treat overactive bladder symptoms |
Oxybutynin, tolterodine |
|
Beta-3 Adrenergic Agonists |
Treat overactive bladder symptoms |
Mirabegron |
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact the management of spinal-related bladder issues. Simple adjustments can help alleviate symptoms and improve bladder control.
Some effective lifestyle modifications include:
- Dietary changes (e.g., reducing caffeine and spicy foods)
- Fluid management (e.g., timed voiding)
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the spine
- Quitting smoking to improve overall spinal health
By incorporating these non-surgical treatments into their care plan, individuals with spinal-related bladder issues can experience significant improvements in their symptoms and quality of life.
Surgical Interventions for Spinal Compression
When other treatments don’t work, surgery might be needed for spinal compression. This condition can cause a lot of pain and affect how you live. Surgery aims to take pressure off the spinal cord or nerves, easing symptoms.
When Surgery Is Necessary
Surgery is usually considered when:
- Other treatments haven’t helped enough
- There’s a big drop in nerve function
- Pain is too much to handle daily
- There’s nerve damage or cauda equina syndrome
Talking to a healthcare provider about risks and benefits is key to decide if surgery is right.
Types of Surgical Procedures
There are several surgeries for spinal compression, including:
- Laminectomy: Taking out part or all of the vertebrae (lamina) to ease pressure
- Discectomy: Removing a herniated disc that’s pressing on nerves
- Spinal Fusion: Joining two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine
- Microdiscectomy: A less invasive version of discectomy
The right surgery depends on the cause and where the compression is, plus the patient’s health.
Recovery and Expectations
Recovery from spinal compression surgery varies. It depends on the surgery and the person. Generally, patients can expect:
- A hospital stay from a few days to a week
- Weeks to months of recovery at home
- Physical therapy to get strength and mobility back
- Slow improvement in symptoms over time
Following post-operative instructions and going to follow-up appointments are important for a good recovery.
Bowel and Bladder Problems After Back Surgery
Back surgery can sometimes cause bowel and bladder issues. This is a big worry for those having surgery, as it can really affect their life quality.
Common Post-Surgical Complications
Some people face bowel and bladder problems after back surgery. This can happen because of nerve damage or swelling during the surgery. Symptoms include trouble peeing, losing bladder control, or constipation.
Nerve damage is a main reason for these problems. The nerves that control bladder and bowel are near where the surgery is done. Knowing about these risks helps set realistic expectations and aids in recovery.
|
Complication |
Description |
Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
|
Urinary Retention |
Inability to empty the bladder |
Catheterization, pelvic floor exercises |
|
Urinary Incontinence |
Loss of bladder control |
Behavioral therapy, medication |
|
Constipation |
Difficulty in bowel movements |
Dietary changes, laxatives |
Managing Post-Surgical Bladder Dysfunction
Handling bladder issues after back surgery needs a few steps. This includes physical therapy to strengthen pelvic muscles, medication for symptoms, and lifestyle changes for better bladder health.
Patients should stick to a post-operative care plan made just for them. This might include regular check-ups with their doctor to keep an eye on how they’re doing and fix any problems fast.
By knowing about possible problems and working with doctors, patients can handle bowel and bladder issues after back surgery. This helps them recover better and enjoy a better life.
Managing Both Lower Back Pain and Urinary Symptoms
Lower back pain and urinary symptoms need a special approach. It’s important to understand how they are connected. This helps in managing both issues effectively.
Integrated Treatment Approaches
For both lower back pain and urinary symptoms, a team effort is key. This includes:
- Multidisciplinary care teams: Working together with doctors, physical therapists, and pain specialists.
- Comprehensive treatment plans: Plans that cover both spinal health and bladder issues, using different treatments.
- Medications: Using medicines for pain and bladder problems, like pain relievers and bladder medications.
Self-Management Strategies
Self-care is also important for managing these symptoms. This includes:
- Lifestyle modifications: Keeping a healthy weight, exercising, and improving posture.
- Pelvic floor exercises: Doing Kegels to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
- Bladder training: Using techniques like timed voiding and double voiding to manage bladder issues.
Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies
These symptoms can also affect your mind and mood. To cope, consider:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): Therapy to handle chronic pain and mental health issues.
- Support groups: Joining groups to meet others facing similar challenges.
- Stress management techniques: Using meditation, deep breathing, and yoga to reduce stress and improve well-being.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Knowing the signs of spinal compression and its impact on the bladder is key. It helps in getting medical help on time. Spinal problems can lead to serious issues if not treated quickly.
Red Flag Symptoms
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor fast. These include:
- Severe lower back pain that doesn’t get better with rest
- Sudden loss of bladder control or trouble starting to pee
- Numbness or tingling in the legs or groin area
- Weakness in the legs or trouble walking
If you have any of these signs, get medical help right away. It’s important to avoid lasting harm.
Emergency Situations
Spinal compression can cause serious problems like Cauda Equina Syndrome. You need to act fast if you see these symptoms:
- Severe pain
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Numbness in the saddle area
If you or someone you know has these symptoms, call for emergency care. Quick action is vital for better results.
Conclusion
It’s important to understand how spinal compression affects bladder problems. This is key for those with lower back pain and urinary issues. We’ve looked at how spinal health impacts bladder function and the nervous system’s role in urination.
Spinal compression can lead to urinary symptoms. Recognizing these signs, like lower back pain and more frequent urination, is critical. Seeking medical help is essential.
Conditions like spinal stenosis and herniated discs can harm bladder control. Timely diagnosis and treatment are vital. This helps manage symptoms effectively.
Addressing lower back pain and urinary issues requires a thorough approach. This includes non-surgical treatments and surgery when needed. Being aware of urgent symptoms is also important to avoid serious complications.
FAQ
Can lower back pain cause urinary frequency?
Yes, lower back pain can lead to more trips to the bathroom. This is because the nerves that control the bladder can be affected by spinal compression.
What is the connection between spinal stenosis and bladder control?
Spinal stenosis can press on nerves that help you urinate. This can cause problems with bladder control, like incontinence or needing to go more often.
Can a herniated disc cause urinary dysfunction?
Yes, a herniated disc, like the one at L4-L5, can press on nerves that control the bladder. This might lead to urinary problems.
Is sciatica related to urinary symptoms?
Sciatica can cause urinary symptoms, like needing to go more often. This is because the nerves that control the bladder can be compressed.
What is cauda equina syndrome, and how does it affect urination?
Cauda equina syndrome is a serious condition where nerves in the lower spine are compressed. It can cause severe urinary symptoms, like not being able to urinate or leaking.
How is spinal compression diagnosed when it affects bladder function?
Doctors use physical exams, MRI or CT scans, and urodynamic tests to find spinal compression affecting the bladder. These tests help check how well the bladder works.
What are the non-surgical treatments for spinal-related bladder issues?
Non-surgical treatments include physical therapy, pain and bladder control medications, and lifestyle changes. These help manage symptoms and improve life quality.
When is surgery necessary for spinal compression?
Surgery is needed for severe symptoms, like a lot of pain, nerve problems, or serious bladder issues. It’s also needed if other treatments don’t work.
Can back surgery cause bowel and bladder problems?
Yes, back surgery can sometimes cause bowel and bladder issues. But, these problems can usually be managed with the right medical care and strategies.
How can I manage both lower back pain and urinary symptoms?
To manage both, use a treatment plan that includes self-care and coping with the emotional side of these conditions. This helps improve both symptoms.
What are the red flag symptoms that require immediate medical attention?
Red flag symptoms include sudden severe pain, numbness or weakness in the legs, and loss of bladder or bowel control. These signs need immediate medical help.
Can spinal compression cause incontinence?
Yes, spinal compression can cause incontinence. This is because it presses on nerves that control the bladder, leading to loss of bladder control.
How does spinal health impact bladder function?
Spinal health is key to bladder function. The spinal cord and nerves control urination. Any compression or damage can lead to urinary issues.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4467746/





