The 256 Slice Computed Tomography (CT) scanner represents a significant evolution in X-ray imaging technology, designed to capture comprehensive images of the human body with exceptional speed and coverage. While standard CT scanners capture images in 64 or 128 “slices” (cross-sections) per rotation, a 256 Slice system captures 256 simultaneous anatomical layers in a single rotation of the gantry. This exponential increase in data acquisition capability transforms the scanner from a static anatomical camera into a dynamic volumetric device.
The primary problem this technology solves is the limitation of time and motion. In cardiac imaging, for instance, the heart is constantly beating. Older scanners required multiple rotations to image the entire heart, leading to “motion artifacts” blurriness caused by the heartbeat which could render the images undiagnostic. The 256 Slice CT covers a much wider area (typically 8 to 16 centimeters) in one rapid pass. This capability effectively “freezes” motion, allowing physicians to image entire organs, such as the heart or brain, in a fraction of a second. It is the definitive tool for diagnosing life-threatening conditions like coronary artery disease, pulmonary embolisms, and acute stroke where every second of scanning time counts.
How the Computed Tomography (256 Slice) Works?
Computed Tomography operates on the principle of rotating X-ray beams. The 256 Slice system refines this process through advanced detector architecture and high-speed rotation mechanics.
The Gantry and X-ray Source
The patient lies on a motorized table that slides into the large, donut-shaped ring known as the “gantry.” Inside this ring, invisible to the patient, is an X-ray tube that rotates at extreme speeds often completing a full circle in just 0.28 seconds.
- X-ray Emission: The tube emits a fan-shaped beam of X-rays as it spins around the patient.
- Attenuation: As these X-rays pass through the body, they are absorbed (attenuated) differently by different tissues. Dense bone absorbs a lot of radiation (appearing white), while air in the lungs absorbs very little (appearing black).
The Multi-Detector Row System
The defining feature of this technology is the detector array located opposite the X-ray tube.
- 256 Unique Channels: Instead of a single row of sensors, this scanner utilizes a wide detector panel consisting of 256 distinct rows of microscopic sensors.
- Volumetric Capture: Because the detector panel is physically wider, it can capture a larger volume of tissue in a single rotation. For example, it can capture the entire heart in one heartbeat or the entire brain during a single rotation, without the table needing to move back and forth (step-and-shoot).
Image Reconstruction
The detectors convert the X-rays into digital signals, which are sent to a powerful computer. The computer uses complex algorithms to reconstruct these millions of data points into detailed, 2D cross-sectional images (slices) and 3D volumetric models. The “slice” thickness is often sub-millimeter (e.g., 0.625 mm), allowing for incredibly fine detail.
Clinical Advantages and Patient Benefits
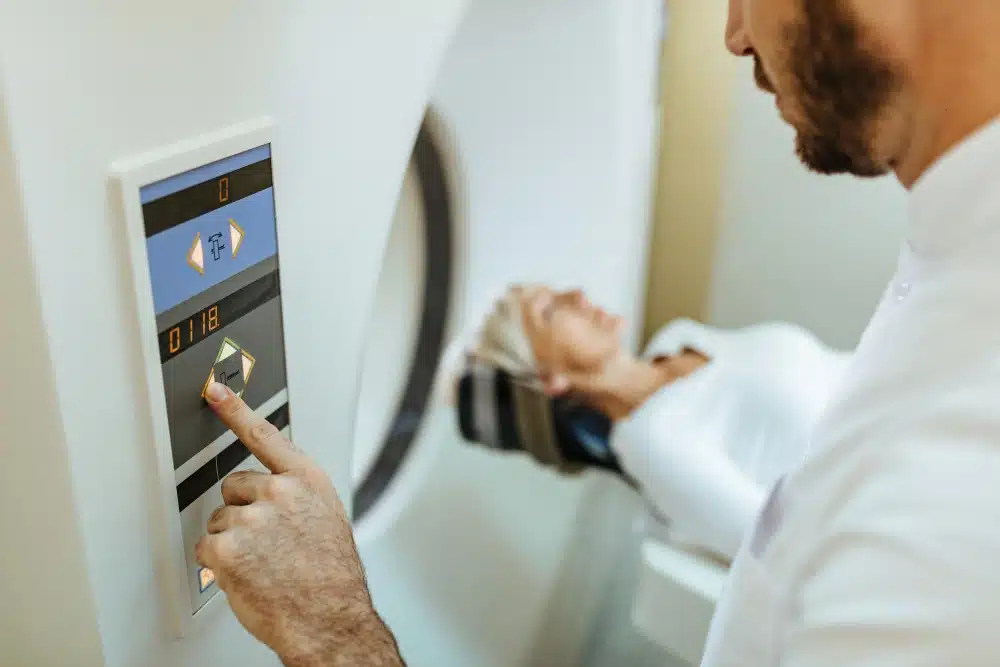

Transitioning to 256 Slice CT technology offers quantifiable clinical benefits, particularly for patients with complex cardiovascular conditions or those requiring emergency assessment.
“One-Beat” Cardiac Imaging
The most dramatic advantage is in cardiac care. Standard CT scanners often require the patient to have a slow, stable heart rate (often requiring beta-blocker medication) to get a clear image.
- Freezing the Heart: The 256 Slice scanner is so fast that it can image the entire heart within a single diastole (the resting phase of the heartbeat). This eliminates motion blur even in patients with high or irregular heart rates (arrhythmia), who were previously ineligible for CT angiography.
- Reduced Contrast Volume: Because the scan is faster, the amount of iodine-based contrast dye injected into the patient can be significantly reduced. This is a major safety benefit for patients with compromised kidney function.
Whole-Organ Perfusion
Unlike older scanners that build an image slice-by-slice over time, this system covers whole organs instantly.
- Stroke Assessment: In acute stroke cases, the scanner can visualize not just the blockage, but the blood flow (perfusion) across the entire brain simultaneously. This “4D” imaging (3D volume + time) helps doctors differentiate between dead tissue and “at-risk” tissue that can still be saved.
Reduced Breath-Hold Times
For chest and abdominal scans, patients must hold their breath to prevent lung motion blur. On older machines, this could last 10-15 seconds, which is difficult for elderly or respiratory patients. The 256 Slice CT can scan the entire chest in less than 5 seconds, making the breath-hold effortless for most patients and reducing the need for repeated scans due to breathing errors.
Targeted Medical Fields and Applications
The 256 Slice CT is a versatile workhorse utilized across critical hospital departments, from the ER to specialized oncology units.
Cardiology (Coronary CT Angiography)
- Non-Invasive Angiogram: It serves as a non-invasive alternative to traditional catheter catheterization. It can rule out significant coronary artery disease with 99% accuracy.
- Triple Rule-Out: In emergency settings for chest pain, a single scan can simultaneously check for three killers: aortic dissection (tear in the aorta), pulmonary embolism (clot in the lung), and coronary artery blockage.
Neurology
- Acute Stroke Protocol: It provides immediate, comprehensive imaging of the brain’s vasculature (CTA) and tissue perfusion (CTP) to guide decisions on clot-busting drugs or mechanical thrombectomy.
Oncology
- Tumor Staging: The high resolution allows for the precise measurement of tumors and the detection of micro-metastases in the liver or lungs.
- Treatment Response: Its ability to measure blood volume within a tumor helps oncologists determine if a chemotherapy drug is effectively “starving” the tumor of its blood supply before the tumor actually shrinks in size.
Pediatric Imaging
- No Sedation Required: Because the scan is virtually instantaneous, infants and young children can often be scanned without the need for heavy sedation or general anesthesia, which carries its own risks.
What to Expect: The Patient Experience
A CT scan is a fast, non-invasive process. The 256 Slice system further streamlines the workflow, often making the preparation longer than the scan itself.
Preparation
- Contrast Injection: For most vascular studies, an IV line is placed in the arm. A contrast dye (iodine) is injected to make blood vessels stand out bright white on the images. Patients may feel a “warm flush” sensation spreading through the body or a metallic taste in the mouth for a few seconds.
- Positioning: The patient lies on the scanner table. The technologist positions the body part to be scanned in the center of the gantry ring using laser alignment lights.
The Scan
- Speed: The actual scanning time when the radiation is on is measured in seconds. For a heart scan, it may be less than one second. For a full-body trauma scan, it may be 5 to 10 seconds.
- Sensations: The machine is quiet and open. The gantry is a short ring, not a long tunnel, so claustrophobia is rarely an issue compared to MRI. The table moves swiftly and smoothly through the opening.
- Instructions: The machine or technologist will give automated voice commands like “Breathe in, hold your breath.”
Post-Scan
The IV is removed, and the patient can leave immediately. The contrast dye is filtered out by the kidneys and excreted in urine over the next 24 hours. Drinking plenty of water is recommended to speed up this process.
Safety and Precision Standards
While CT scans use ionizing radiation, the 256 Slice technology incorporates advanced engineering specifically to minimize dose exposure while maximizing diagnostic yield.
Adaptive Iterative Reconstruction (AIDR)
This is a sophisticated software algorithm that allows the scanner to produce crystal-clear images using significantly less radiation. It “denoises” the image mathematically, meaning the X-ray power can be turned down by up to 80% compared to older generation filtered back-projection techniques, without resulting in grainy images.
Organ-Based Dose Modulation
The scanner features “Active Collimation.” It shapes the X-ray beam to fit the exact anatomy of the patient, ensuring that radiation is strictly limited to the target organ.
- Eye and Thyroid Shielding: The system can automatically reduce the X-ray intensity when the tube passes over sensitive organs like the lens of the eye or the thyroid gland, protecting these tissues from unnecessary exposure.
ECG Gating
In cardiac scanning, the X-ray tube is synchronized with the patient’s ECG (heart rhythm). The beam is only turned on during the exact millisecond when the heart is resting and the image is being taken. During the other phases of the heartbeat, the X-ray is turned off or drastically reduced. This “pulsed” technique ensures the patient is not exposed to radiation during the parts of the cardiac cycle that aren’t being imaged.






