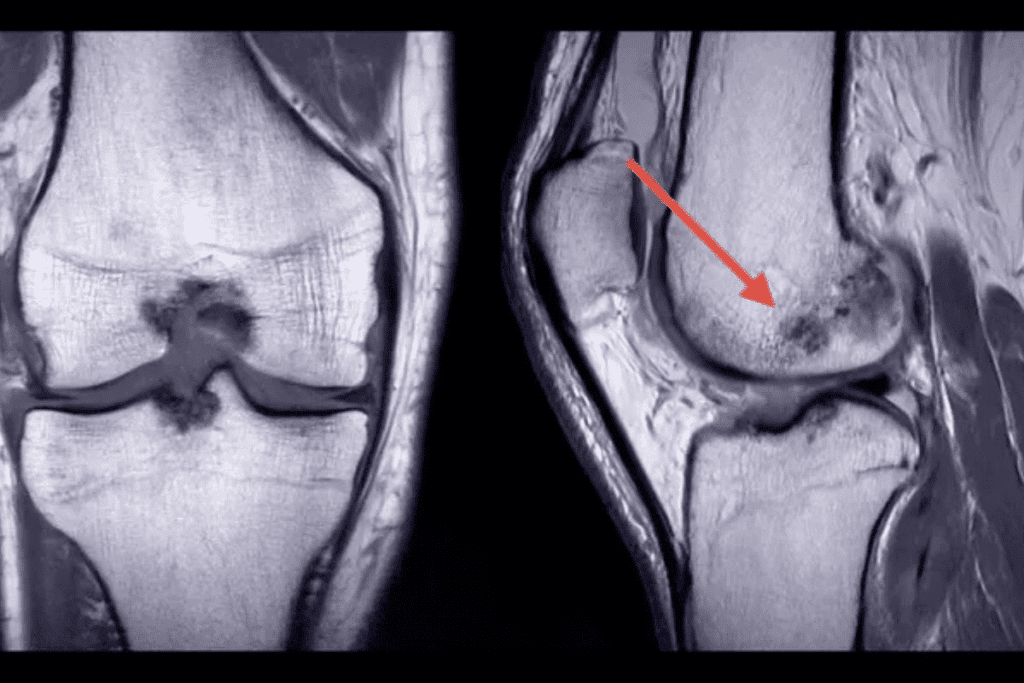
MRI is the best way to find stress fractures. This shows how important MRI bone imaging is for spotting fractures.
Doctors use imaging tech to find bone injuries. MRI’s ability to spot fractures is key. This article will look into MRI’s role in finding fractures and what it means for patients.
Key Takeaways
- MRI is highly effective in detecting stress fractures.
- The technology provides detailed images of bone structures.
- Understanding MRI capabilities can improve diagnosis accuracy.
- MRI bone imaging plays a critical role in medical diagnosis.
- Patients can benefit from knowing how MRI technology works.
The Science Behind MRI Bone Imaging
It’s important to understand MRI bone imaging to see how it finds fractures. MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to show the body’s inside. This helps doctors see what’s going on inside.
Basic Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI scans work by using a strong magnetic field. This field makes hydrogen atoms in the body line up. Then, radiofrequency pulses disturb these atoms, causing them to send out signals.
These signals are caught and turned into detailed images. The process needs a few things:
- A strong magnetic field to align hydrogen atoms
- Radiofrequency coils to emit and receive signals
- A computer system to make images from the signals
How MRI Visualizes Bone Tissue
MRI shows bone tissue by catching signals from hydrogen atoms in bone marrow and soft tissues. Bone marrow, full of fat and hydrogen, sends out a strong signal. This helps doctors check if bones are healthy.
The clear images MRI makes let doctors see how bad bone injuries are. They can also spot any damage to soft tissues.
Can MRI Detect Fractures? Capabilities and Limitations
MRI is great for showing both bone and soft tissue details. It’s very useful for finding fractures that X-rays or CT scans can’t see.
Types of Fractures Visible on MRI
MRI is excellent for spotting stress fractures, hairline fractures, and occult fractures. Stress fractures are small cracks in bones, often in athletes. Hairline fractures are very thin and hard to find with regular imaging. Occult fractures are not seen on X-rays but are clear on MRI.
MRI can see bone marrow edema, which means it can find fractures early. This is before they show up on other scans.
Sensitivity and Specificity Rates
Research shows MRI is very good at finding fractures. It’s better than X-rays and CT scans, mainly for stress and occult fractures.
| Imaging Modality | Sensitivity for Fracture Detection | Specificity for Fracture Detection |
| MRI | High (often >90%) | High (often >90%) |
| X-ray | Moderate (varies, often | High (often >90%) |
| CT Scan | High (often >85%) | High (often >90%) |
When MRI Is the Preferred Method for Fracture Detection
MRI is often the first choice when fractures are suspected but not seen on X-rays. It’s also used for stress fractures and soft tissue injuries with fractures. Its detailed views of bone and soft tissue are very helpful.
In summary, MRI is a big help in finding fractures, even the hard ones. Its accuracy and ability to see soft tissue injuries make it key in orthopedic care.
Stress Fracture Detection Using MRI
MRI is a key tool for finding stress fractures. It gives detailed images that help doctors diagnose these injuries better. Stress fractures are small cracks in bones, often caused by overuse or repetitive stress. They are common in athletes and people who are very active.
Why Stress Fractures Are Difficult to Diagnose
Stress fractures are hard to diagnose because they may not show up on first X-rays. Symptoms can be vague. This makes it tough to spot these injuries, as they often happen in healthy, active people.
Key challenges in diagnosing stress fractures include:
- Nonspecific symptoms that can mimic other conditions
- Lack of clear evidence on initial imaging studies
- Variability in patient presentation and history
MRI Protocols for Stress Fracture Identification
MRI protocols are set up to spot stress fractures better. Specific sequences like STIR and fat-suppressed T2-weighted images are key. They show bone marrow edema, which is linked to stress fractures.
These MRI sequences help by:
- Showing bone marrow edema better
- Spotting fractures that other images miss
- Showing soft tissues around the fracture
Clinical Case Examples
Clinical examples show MRI’s role in finding stress fractures. For example, a young athlete with leg pain and normal X-rays got an MRI. It found a stress fracture in the tibia. This led to quick treatment and prevented more harm.
These examples highlight MRI’s role in diagnosing stress fractures. It’s vital, even more so for high-risk individuals or when other tests are unclear.
Hairline Fracture MRI: Detecting Subtle Bone Injuries
MRI is a key tool for finding hairline fractures. It’s very good at spotting these small bone cracks.
Characteristics of Hairline Fractures
Hairline fractures, or stress fractures, are tiny cracks in bones. They happen when bones are stressed too much. These fractures are hard to find because they’re so small.
Key characteristics of hairline fractures include:
- Small, hairline cracks in the bone
- Often caused by repetitive stress or force
- Can occur in various bones, mainly those that carry weight
MRISensitivity for Hairline Fracture Detection
MRI is very good at finding hairline fractures. It shows both bone and soft tissue well. This makes it a top choice for doctors.
The sensitivity of MRI for finding hairline fractures comes from its:
- High-resolution images of bone marrow and soft tissues
- Ability to spot early bone marrow edema changes
- Power to see the fracture line in different angles
“MRI is great for finding hairline fractures. It can see the fracture and any soft tissue injuries.”
Medical Imaging Expert
Common Locations for Hairline Fractures
Hairline fractures can happen in many bones. But they’re more common in some places.
Common sites for hairline fractures include:
- The lower leg (tibia and fibula)
- The foot (metatarsals)
- The hip (femoral neck)
Knowing where these fractures often happen helps doctors use MRI to find them early.
Occult Fracture Diagnosis: Finding Hidden Bone Injuries
Hidden bone injuries, known as occult fractures, are tricky to spot. They often need advanced tools for diagnosis. These fractures are hard to find because they are not obvious at first glance.
Definition and Challenges of Occult Fractures
Occult fractures are not seen on first X-rays. This is because they are subtle or imaging techniques are limited. Finding these fractures is hard, which can lead to wrong or late treatment.
Doctors must be very careful when diagnosing these fractures. This is true for patients with pain or swelling after an injury, even if X-rays look normal. Advanced imaging, like MRI, is key in spotting these hidden injuries.
MRI as the Gold Standard for Occult Fracture Detection
MRI is the top choice for finding occult fractures. It shows soft tissues well and can spot bone marrow edema. This helps find fractures early, even when they’re not seen on other scans.
MRI is great at finding bone marrow edema. This is a sign of a fracture, even before it’s clear on other scans.
High-Risk Anatomical Areas
Some areas, like the hip, wrist, and ankle, are more prone to occult fractures. Missing a fracture here can cause big problems. It might lead to the bone not healing right, or to long-term disability.
| Anatomical Region | Common Causes of Occult Fractures | Clinical Implications |
| Hip | Falls, osteoporosis | Risk of displacement, possible need for surgery |
| Wrist | Falls onto outstretched hand | Could lead to malunion, affects wrist function |
| Ankle | Twisting injuries, sports-related trauma | May cause chronic instability, affects mobility |
Knowing which areas are at risk and how MRI helps diagnose occult fractures is vital. It helps doctors give the right care and avoid complications.
Bone Marrow Edema: An Early Indicator of Fractures
MRI can spot bone marrow edema early, which is a sign of fractures. This condition happens when fluid builds up in the bone marrow. It’s often seen after injuries, like fractures.
Understanding Bone Marrow Edema Patterns
Bone marrow edema shows up as a bright spot on MRI, mainly on T2-weighted and STIR sequences. The edema can spread out or stay in one spot. This depends on how bad the injury is.
- Wide spread edema might mean a serious injury or stress reaction.
- Spot-like edema is linked to certain fractures or bone problems.
Relationship Between Edema and Fracture Presence
Bone marrow edema is a strong sign of a fracture. Research shows edema can show up before you can see a fracture on MRI or other scans.
- Edema might be the first sign of a fracture.
- How much edema there is can tell you how bad the fracture is.
Prognostic Value of Bone Marrow Edema
Looking at bone marrow edema helps guess how a fracture will do. If the edema goes away, it means the bone is healing well. But if it stays or gets worse, it could mean trouble.
- Edema going away usually means the bone is healing.
- Edema staying or getting worse might mean the bone isn’t healing right.
In short, bone marrow edema found by MRI is key in spotting fractures early. It helps doctors understand how bad the injury is and how it will heal. This is very important for treating fractures right away.
MRI vs. X-Ray: Comparative Analysis for Fracture Detection
Choosing between MRI and X-ray for fracture detection is key to accurate diagnosis. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses. Healthcare professionals need to understand these to make the best choices.
X-Ray Limitations in Fracture Diagnosis
X-rays are often the first choice for finding fractures because they’re easy to get and cheap. But, they have big drawbacks. They can’t spot all types of fractures, like those that aren’t displaced or involve soft tissue injuries.
“X-rays may miss fractures that are not immediately apparent, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment.”
The main issues with X-rays are:
- They struggle to find non-displaced or hairline fractures
- They can’t see soft tissue injuries linked to fractures
- They’re not good at finding fractures in tricky spots
When to Choose MRI Over X-Ray
MRI is better than X-ray for finding fractures, mainly because it’s more sensitive and shows soft tissues well. It’s best used when:
- There’s a strong belief a fracture exists, even if X-rays don’t show it
- Soft tissue injuries are suspected or need checking
- Fractures in hard-to-reach areas, like the spine or pelvis, are thought to be present
Medical experts say,
“MRI gives a full view of fracture size and soft tissue damage, which is key for planning treatment.”
Cost and Accessibility Considerations
MRI is better for finding fractures but costs more and is harder to get than X-ray. The price is because MRI tech is complex and needs special places. But, its better accuracy and less need for more tests can save money in the long run.
In summary, while X-rays are useful for starting, MRI is the top choice for fracture detection. It’s more accurate and shows soft tissue injuries well. The decision between MRI and X-ray should be based on what each patient needs.
CT Scan Comparison: When to Use CT vs. MRI for Fractures
CT scans and MRI are both used for fracture imaging. They have different uses and benefits. The choice depends on the fracture type, patient condition, and what’s needed for diagnosis.
Strengths of CT in Fracture Imaging
CT scans are great for seeing bone structures. They’re often chosen for fractures in hard-to-reach areas like the spine, pelvis, and face. CT scans show bone details well, helping to check if a fracture has moved or broken into pieces.
- High-resolution images of bone structures
- Rapid scanning time, beneficial for emergency situations
- Excellent for detecting calcifications and bone fragments
Situations Where MRI Outperforms CT
While CT scans are good for bones, MRI is better for soft tissue injuries like ligament and tendon damage. MRI also spots stress and hidden fractures better than CT scans.
- MRI is preferred for assessing soft tissue damage
- More sensitive for detecting stress and occult fractures
- Provides detailed images of marrow changes and edema
Radiation Concerns and Safety Profiles
CT scans use radiation, which is a worry, mainly for young patients or when scans are needed again. On the other hand, MRI doesn’t use radiation, making it safer for some patients.
“The choice between CT and MRI should consider the patient’s age, the need for repeated imaging, and the specific diagnostic question being addressed.”
— Expert in Diagnostic Imaging
In summary, both CT scans and MRI are important for fracture imaging. Knowing their strengths and weaknesses helps pick the best imaging for each patient.
Soft Tissue Evaluation in Fracture Assessment
Fracture assessment isn’t just about the bone; evaluating soft tissue injuries is equally important for complete care. When a fracture happens, the soft tissues around it, like ligaments, tendons, and muscles, get hurt too. Knowing how bad these injuries are is key to making a good treatment plan.
Associated Soft Tissue Injuries in Fracture Cases
Soft tissue injuries are common in fracture cases and can greatly affect patient outcomes. These injuries may include:
- Ligament sprains or tears
- Tendon ruptures or strains
- Muscle contusions or tears
- Nerve damage
Checking these injuries is vital for knowing the full damage and for making treatment choices.
How MRI Evaluates Ligament and Tendon Damage
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is great for checking soft tissue injuries because it’s very sensitive and specific. MRI can:
- Directly see ligaments and tendons
- Find tears, sprains, and other injuries
- See how bad the soft tissue damage is
By showing detailed images of both bone and soft tissue, MRI helps doctors understand the injury fully.
Impact on Treatment Planning
The info from soft tissue evaluation greatly affects treatment planning. For example:
- Seeing ligament or tendon damage might mean surgery is needed
- Knowing about muscle injury helps set up rehab plans
- Finding nerve damage might change treatment plans
By adding soft tissue evaluation to fracture assessment, doctors can give better, more focused care.
Early Fracture Detection: The Role of Advanced MRI Techniques
MRI is key in spotting fractures early. New MRI methods help find fractures sooner. This is vital for good treatment and results.
High-Field Strength MRI Applications
High-field MRI shows bones and soft tissues better. High-field MRI catches small fractures that lower field machines miss. It’s great for finding stress fractures in athletes.
Specialized Sequences for Early Fracture Identification
Sequences like STIR and fat-suppressed T2-weighted images are top for spotting early fractures. They make MRI better at finding fractures early.
“The use of advanced MRI sequences has revolutionized the detection of early fractures, allowing for timely intervention and better patient outcomes.”
An Orthopedic Specialist
Clinical Impact of Early Detection
Spotting fractures early with MRI makes a big difference. Doctors can start treatment sooner. This cuts down on complications and speeds up recovery.
| Benefit | Description | Clinical Impact |
| Timely Intervention | Early detection allows for prompt treatment. | Reduces risk of complications. |
| Improved Recovery | Early treatment leads to faster healing. | Enhances patient outcomes. |
| Reduced Healthcare Costs | Early detection minimizes the need for prolonged care. | Lowers overall healthcare expenses. |
In conclusion, advanced MRI techniques are essential for early fracture detection. They offer big benefits for patient care and outcomes.
Nonunion Fracture MRI: Assessing Healing Complications
MRI is now a key tool for checking on nonunion fractures. It gives detailed views of how the bone is healing.
MRI Features of Nonunion Fractures
Nonunion fractures don’t heal, leading to ongoing pain and disability. MRI spots specific signs of nonunion, like:
- Persistent bone marrow edema
- Lack of bridging callus formation
- Presence of fibrous tissue at the fracture site
MRI’s ability to see these signs helps doctors accurately diagnose nonunion fractures and understand their severity.
Distinguishing Between Delayed Union and Nonunion
It’s important to tell delayed union apart from nonunion, as treatments differ. MRI helps by:
- Checking bone marrow edema extent
- Looking at callus formation quality
- Examining the fracture gap and tissue
Delayed union means healing is slower, but not stopped. Nonunion means healing has stopped completely. MRI helps doctors make this call.
Treatment Planning Based on MRI Findings
MRI findings are key for planning treatment for nonunion fractures. The treatment plan might include surgery, like bone grafting or using orthobiologics, based on what MRI shows.
| MRI Finding | Treatment Implication |
| Presence of fibrous tissue | May require surgical debridement |
| Lack of callus formation | May necessitate bone grafting |
| Persistent bone marrow edema | May indicate need for orthobiologic treatment |
Fracture Healing Monitoring with MRI
Monitoring fracture healing is key, and MRI gives us detailed views. It’s a top tool in orthopedics for tracking fracture recovery.
Timeline of Normal Fracture Healing on MRI
MRI shows the healing stages of fractures clearly. It starts with inflammation, then soft callus, hard callus, bony union, and remodeling.
Normal Fracture Healing Stages on MRI:
- Inflammation (0-4 days): Edema and hemorrhage are visible.
- Soft Callus Formation (4-14 days): Soft tissue callus appears.
- Hard Callus Formation (14-28 days): Calcification begins.
- Bony Union (28 days+): Gradual bony bridging occurs.
- Remodeling (months to years): Continued strengthening of the bone.
Detecting Complications During Healing Process
MRI spots problems like nonunion, infection, or hardware failure early. This lets doctors act fast.
| Complication | MRI Findings |
| Nonunion | Failure of bony bridging, persistent gap |
| Infection | Soft tissue swelling, abscess formation, bone destruction |
| Hardware Failure | Breakage or loosening of orthopedic hardware |
Follow-up Protocols and Recommendations
Follow-up MRI plans change based on the fracture. Early scans are done, with more as needed based on how it’s healing.
Recommended Follow-up Protocol:
- Initial scan within 1-2 weeks post-injury.
- Follow-up scans at 4-6 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months as necessary.
- Adjust protocol based on clinical findings and healing progress.
Orthopedic MRI Use in Clinical Practice
Orthopedic MRI use is growing in clinics. It gives unmatched accuracy for managing fractures. MRI’s ability to see both bones and soft tissues makes it key in orthopedic care.
Common Orthopedic Indications for MRI
MRI is often used for diagnosing orthopedic issues. This includes fractures, ligament sprains, and tendon injuries. Its detailed images of soft tissues are great for complex joint injuries.
| Condition | Diagnostic Accuracy with MRI | Clinical Utility |
| Fractures | High | Essential for detecting occult fractures and assessing fracture healing |
| Ligament Sprains | High | Critical for evaluating ligament integrity and planning rehabilitation |
| Tendon Injuries | High | Helps in assessing tendon damage and guiding treatment decisions |
Workflow Integration in Fracture Management
MRI has made diagnosing and managing fractures easier. It shows detailed images of fractures and soft tissue injuries. This helps in making accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Patient Selection Criteria
Choosing the right patients for MRI is important. It depends on the clinical reason, symptom severity, and treatment planning impact. MRI is best for patients with suspected hidden fractures or complex injuries needing detailed checks.
In summary, MRI has greatly improved orthopedic diagnosis, mainly in fracture management. Knowing when to use MRI, how it fits into workflows, and who to test helps doctors use it best in care.
Patient Experience During Fracture-Related MRI Scans
Getting an MRI for a fracture can seem scary, but being ready helps a lot. People worry a lot about the test, even more so after an injury.
Preparation for an MRI Scan
Being prepared is key for a good MRI scan. Tell your doctor about any metal implants or pacemakers. Also, take off metal items like jewelry and clothes with metal parts.
Wear comfy, loose clothes to feel better during the test. A radiologist says it’s important to follow the instructions given by your doctor or the MRI place. This means arriving early and being ready to talk about your health history.
Managing Pain and Discomfort During Imaging
It’s important to handle pain and discomfort during an MRI, more so with fractures. The machine is loud, and the space can make some people feel trapped. Many places offer earplugs or headphones to help with the noise.
Some MRI machines are also designed to feel less cramped. If you’re in a lot of pain, tell the MRI tech. They might be able to adjust your position or offer support to make you more comfortable.
Understanding MRI Results and Next Steps
After the MRI, a radiologist will look at the images and write a report. This report will show how bad the fracture is and if there are any soft tissue injuries. Knowing this is key to figuring out what to do next.
Talk to your doctor about the MRI results to understand what they mean for your treatment. This could include more tests, physical therapy, medicine, or surgery, depending on the fracture.
In short, while an MRI for a fracture is tough, being ready and knowing what to expect helps a lot. By managing pain and understanding the results, patients can better handle their diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion: The Value of MRI in Fracture Diagnosis and Management
MRI has become a key tool in diagnosing and managing fractures. It gives detailed views of bone and soft tissue injuries. This technology can spot fractures that X-rays or CT scans miss, like stress or hairline fractures.
MRI can see bone marrow edema, a sign of fracture, early on. This helps doctors act fast. It also looks at soft tissue injuries, giving a full picture of the problem. This helps plan better treatment and improves patient results.
As medical tech gets better, MRI’s role in fracture care will grow. It will help us find and treat fractures better. With MRI, doctors can make more accurate diagnoses and tailor treatments. This will lead to better care for patients.
FAQ
What is the primary advantage of using MRI for fracture detection?
MRI gives a detailed look at both bone and soft tissue. It can spot fractures that X-rays or CT scans miss. It also finds soft tissue injuries.
Can MRI detect stress fractures that are not visible on X-ray?
Yes, MRI is great at finding stress fractures early. It spots bone marrow edema and small bone changes that X-rays can’t see.
How does MRI compare to CT scans for fracture imaging?
MRI and CT scans are good for different things. MRI is better for soft tissue and bone marrow edema. CT scans are better for detailed bone views and complex fractures.
What are occult fractures, and how can MRI help diagnose them?
Occult fractures are hidden injuries not seen on X-rays. MRI finds these by showing bone marrow edema and small bone changes. It’s the best way to find these fractures.
Can MRI be used to monitor fracture healing?
Yes, MRI tracks how fractures heal. It spots problems like nonunion or delayed healing. This helps doctors plan treatment.
How does bone marrow edema relate to fracture presence?
Bone marrow edema is an early sign of a fracture. It shows the body’s injury response, like inflammation and bleeding. MRI finds this edema early, helping detect fractures quickly.
What are the limitations of X-ray in fracture diagnosis, and when is MRI preferred?
X-rays miss some fractures, like subtle or occult ones. MRI is better when there’s a strong fracture suspicion despite a negative X-ray. It’s also used for soft tissue checks.
How does MRI evaluate soft tissue injuries associated with fractures?
MRI checks for ligament and tendon damage, and other soft tissue injuries. It gives a full injury picture, helping plan treatment.
What are the benefits of early fracture detection using advanced MRI techniques?
Early MRI fracture detection helps patients by starting treatment quickly. This reduces complications and speeds recovery.
Can MRI be used to assess nonunion fractures, and what features are indicative of nonunion?
Yes, MRI checks nonunion fractures. Signs like a persistent fracture line, no callus, and ongoing edema mean nonunion. This guides treatment.
References
- Sheen, J. R., & Krummel, T. M. (2023). Fracture Healing Overview. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551678/


































