Nephrology : Expert Kidney Care, Diagnosis and Treatment
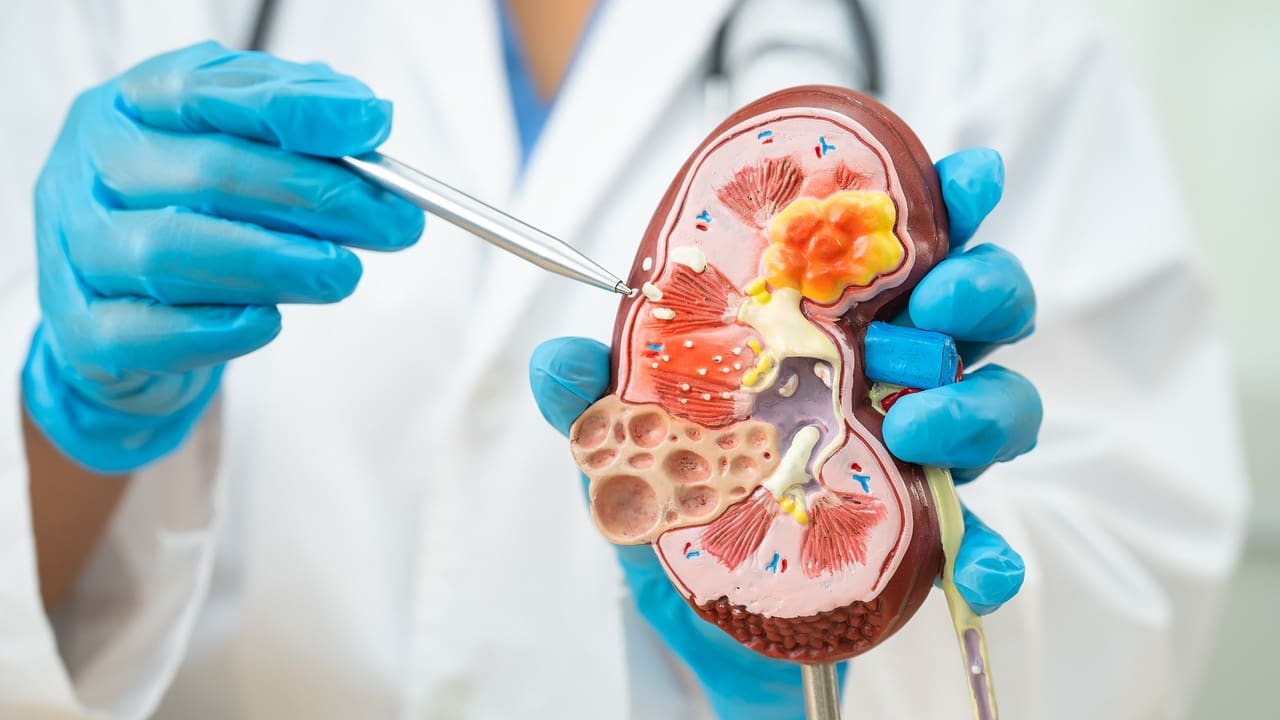
Nephrology Clinic is the branch of medicine that focuses on your kidneys. These organs filter waste, balance fluids and electrolytes, help control blood pressure, keep bones healthy, and support red blood cell production. Simply put, nephrology means kidney care. Terms like “renal function,” “eGFR,” or “protein in the urine” all relate to how nephrology works to protect and improve kidney health.
At a nephrology clinic, you can get answers about symptoms like swelling in your legs or around your eyes, changes in urination, foamy urine, tiredness, or ongoing high blood pressure. Getting checked early can catch problems before they get worse, so treatment can help slow or prevent complications.
The first step in nephrology clinic care is confirming how well your kidneys work. Your care team reviews your history, checks your blood pressure, and orders blood and urine tests. Key tests include creatinine (used to estimate the glomerular filtration rate, or eGFR), a urine albumin to creatinine ratio (to detect kidney damage), and electrolytes like sodium and potassium.
When needed, a kidney ultrasound helps assess size, structure, and any signs of obstruction or cysts. Because kidney disease often advances silently, routine checks are essential for people with diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, or a family history of kidney problems. With consistent nephrology care, many patients stabilize their kidney function, improve blood pressure control, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Nephrology Clinic vs Urology: What’s the Difference and Which Specialist Do I Need?
Knowing the difference between nephrology clinic and urology helps you find the right specialist for your needs. Nephrology clinic deals with medical (non surgical) kidney problems like chronic kidney disease, acute kidney injury, glomerulonephritis, electrolyte and acid base issues, and hard to control high blood pressure.
Urology is a surgical field that treats problems in the urinary tract, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, prostate, and urethra. Urologists handle things like kidney stones that need procedures, urinary blockages, incontinence, and cancers of the urinary system.
If your primary concerns are abnormal kidney tests (elevated creatinine, reduced eGFR), protein or blood in the urine, hard-to control high blood pressure, swelling, or complications of diabetes affecting the kidneys, a nephrology clinic appointment is the right place to start.
If you have severe side or back pain from suspected stones, difficulty urinating, prostate symptoms, or need procedures to remove stones or relieve blockages, urology is often the better first step. Many patients benefit from coordinated care: for example, nephrology clinic optimizes kidney function and blood pressure while urology treats a stone or obstruction that is contributing to kidney stress.
Nephrology Clinic and Hypertension: How Kidney Doctors Help Control High Blood Pressure
The kidneys are key to controlling blood pressure by managing fluids and hormones like renin and angiotensin. High blood pressure can harm the kidneys over time, and when kidney function drops, blood pressure can rise even more. This cycle needs careful, coordinated care. Nephrology clinic and hypertension management work together to protect both your kidneys and your heart.

During your nephrology clinic visit, the team looks at your blood pressure readings from home and the clinic, reviews your medications, diet, and sleep habits. They also check for other causes of high blood pressure, such as narrowed kidney arteries or hormone problems, and keep an eye on electrolytes that medicines can affect.
Treatment usually includes lifestyle changes like eating less salt, keeping a healthy weight, being as active as you can, drinking less alcohol, and getting better sleep, along with medications that protect your kidneys.
Your nephrologist will also watch for side effects, such as high potassium or changes in kidney function, and adjust your plan as needed. This team approach helps lower your risk of heart disease, stroke, and needing dialysis.
Pediatric Nephrology Clinic: Kidney Care for Children and Families
Pediatric nephrology clinic provides specialized kidney care for infants, children, and adolescents. Children can experience unique kidney issues, including urinary tract infections with reflux, congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract, nephrotic syndrome, blood or protein in the urine, and childhood hypertension. Early recognition and gentle evaluation are essential because timely treatment can prevent long term kidney damage.

A pediatric nephrology appointment is family centered and age appropriate. Your child may have blood and urine tests, blood pressure measured with a pediatric cuff, and an ultrasound if needed. Treatment plans often include strategies to prevent infections, nutrition guidance for growth, and carefully selected medications.
Families also receive practical support for home monitoring, hydration, and when to seek urgent care. The goal is to protect kidney function while supporting normal growth, development, and day to day activities.
Nephrology Clinic Patients: Common Symptoms, Conditions, and When to See a Specialist
Many nephrology clinic patients first notice subtle changes: swelling in the ankles or around the eyes, fatigue, muscle cramps, foamy urine, blood in the urine, or more frequent nighttime urination. Others are referred after routine labs show reduced eGFR or increased creatinine.
You are at higher risk if you have diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, obesity, a family history of kidney disease, frequent use of certain pain relievers (like NSAIDs), or autoimmune conditions.
Common conditions seen in a nephrology clinic include:
- Chronic kidney disease (stages 1–5), often due to diabetes or hypertension
- Acute kidney injury (sudden decline in kidney function, sometimes related to illness, dehydration, medications, or procedures)
- Glomerulonephritis and nephrotic syndrome (immune related kidney diseases)
- Polycystic kidney disease and other inherited disorders
- Kidney stone risk evaluation and prevention
- Electrolyte and acid base disorders (for example, high potassium, low sodium, or metabolic acidosis)
- Resistant hypertension and edema (fluid retention)
If you notice warning signs, especially ongoing high blood pressure, swelling, or unusual lab results, seeing a nephrology specialist early can help slow down the disease and keep you feeling your best.
Nephrology Dialysis and Transplantation
When kidney function declines severely, nephrology dialysis and transplantation become important options. Dialysis replaces some kidney functions by removing fluid and waste from the body, while transplantation offers the most complete kidney replacement for eligible patients. Your nephrology team will explain timing and choices based on your health, home situation, and preferences.
Hemodialysis: Blood is filtered through a machine to remove waste and extra fluid. Most patients start with in center treatments three times per week, each lasting several hours. Some choose home hemodialysis after training. Access to the bloodstream is via an arteriovenous fistula, graft, or catheter.
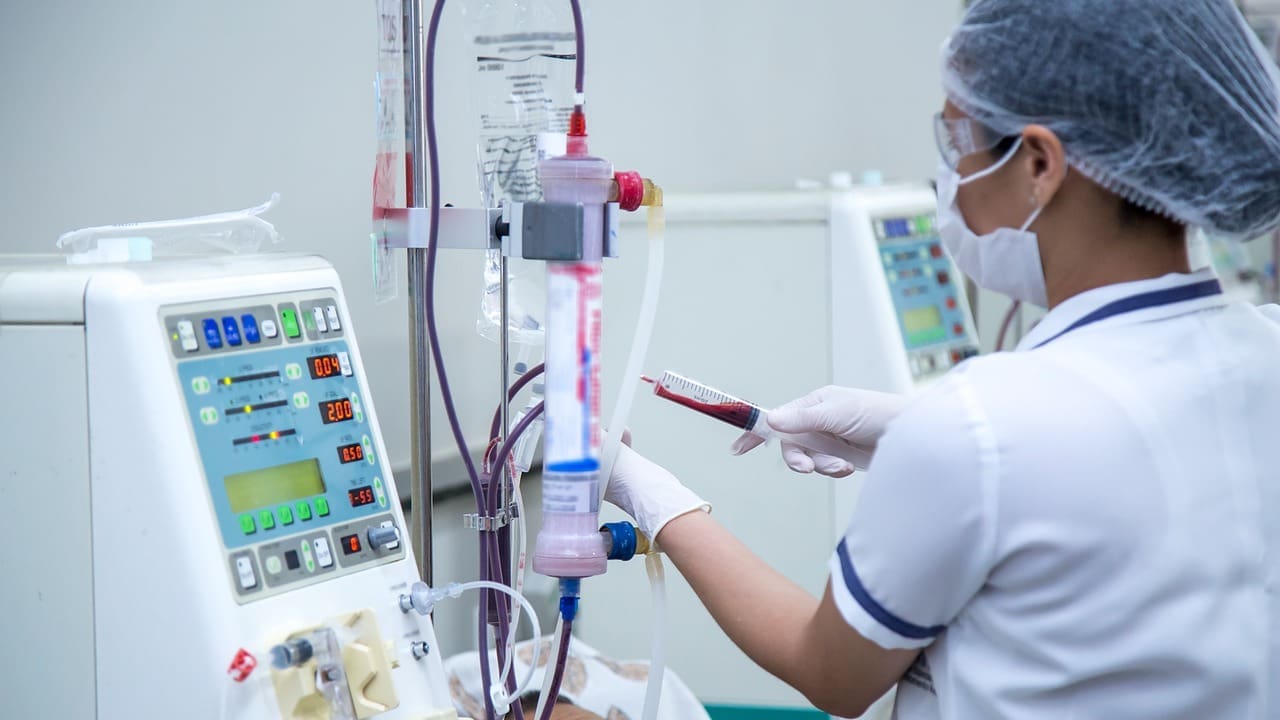
Peritoneal dialysis uses a soft catheter placed in your abdomen. Special dialysis fluid goes in and out to remove waste and extra fluid. This type of dialysis is done at home, either with manual exchanges during the day or with a machine at night. It offers flexibility for your work and family life.
Kidney transplantation: A healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor is surgically placed, allowing your body to filter waste more naturally. After recovery, many patients experience greater energy and fewer dietary restrictions. Your nephrology clinic coordinates evaluation and referral to a transplant center, and provides long term care to keep the transplanted kidney healthy.
Not everyone needs dialysis or a transplant right away. Many people can keep their condition stable with the right medications, better blood pressure and blood sugar control, and changes in nutrition. Talking about your options early, before any emergencies happen, helps you and your family feel more prepared and confident.
What to Expect at a Nephrology Appointment: Tests, Imaging, and Follow Up
A typical nephrology appointment includes:
- History and symptom review: swelling, shortness of breath, changes in urination, cramps, sleep quality, and home blood pressure readings
- Medication review: prescription and over the counter drugs (including NSAIDs and supplements) to identify kidney related risks and interactions
- Physical exam: blood pressure measurements, assessment of fluid status, heart and lung exam, and checks for signs of anemia or bone mineral issues
- Lab tests: creatinine and eGFR, urine albumin to creatinine ratio, electrolytes (sodium, potassium, bicarbonate), calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, and hemoglobin as needed
- Imaging: kidney ultrasound when indicated to evaluate size, structure, stones, cysts, or obstruction
You will get a clear plan that may cover blood pressure goals, advice on how much salt to eat, tips for staying hydrated, diabetes management, and ways to avoid stressing your kidneys, such as what to do with certain medicines if you are dehydrated.
How often you need follow up visits depends on your stage of kidney disease and how stable your condition is. Some people come in every few months, while others need more frequent checks if their lab results are changing.
Chronic Kidney Disease Stages and Treatment: A Patient’s Guide from a Nephrology Clinic
Chronic kidney disease is categorized by eGFR (a measure of how well your kidneys filter) and albuminuria (protein leakage in the urine). Staging guides treatment and helps predict risk:
In the early stages, eGFR may be normal, but urine albumin is present. Focus is on blood pressure control, diabetes management, lifestyle changes, and kidney protective medications as directed by your clinician.
- Moderate stages: Your team intensifies blood pressure and glucose control, addresses cholesterol, treats anemia or mineral and bone disorders when present, and closely monitors potassium and bicarbonate levels.
- Advanced stages: Planning for kidney replacement therapy if needed (dialysis or transplant), vaccination updates, access planning (for example, creating a dialysis fistula ahead of time), and education for you and your caregivers.
Across all stages, prevention is powerful:
- Blood pressure: Use a validated home monitor, follow targets set by your nephrology team, and share logs at visits.
Diabetes: Maintain individualized glucose goals and ask about strategies that protect kidney function through nutrition and medications as advised by your clinician. - Nutrition: Aim for appropriate sodium limits, and tailor protein, potassium, and phosphorus based on your labs. A nutrition plan can reduce swelling and support blood pressure control.
- Medications: Take medicines as prescribed, avoid unnecessary NSAIDs, and review supplements with your clinician to prevent interactions.
- Heart health: Quit smoking, stay as active as you can, and manage your cholesterol. Your heart and kidneys are closely connected, so caring for one helps the other.
- Infection prevention: Kidney disease can increase infection risk, so ask about recommended vaccinations and hygiene steps.
With proactive nephrology care, many patients maintain stable kidney function and a good quality of life for years.

What Does a Nephrology Doctor Do? Roles, Tests, and Ongoing Care
A nephrology doctor evaluates kidney related symptoms and test results, creates a personalized treatment plan, and follows you over time to keep your kidneys as healthy as possible.
That plan often includes:
- Setting safe blood pressure goals and selecting medications that protect the kidneys
- Monitoring labs such as eGFR, urine albumin, electrolytes, and hemoglobin at intervals matched to your risk
- Preventing complications like high potassium, fluid overload, bone mineral disorders, and anemia
- Helping you manage day to day choices—hydration, sodium intake, pain reliever use and giving clear sick day guidance
- Coordinating care with other specialists when needed, especially for stone procedures, heart health, or diabetes management
- Educating you and your family so you feel confident about your health decisions
If advanced treatments are needed, your nephrologist will guide you through dialysis options and transplant referral, at a pace that respects your preferences and life plans.
Which Diseases Does Nephrology Treat
Nephrologists specialize in diseases related to the kidneys and affecting the kidneys.
These diseases can be quite diverse:
Kidney Failure: This is a condition in which the kidneys cannot perform their normal functions. Kidney failure can be acute or chronic. Nephrologists assess kidney function and provide management to patients with kidney failure.
Kidney Stones: These are solid particles that form in the kidneys. These stones can cause obstructions and pain in the urinary tract. Nephrologists diagnose kidney stones and recommend treatment methods.
Kidney Infections: Infections that affect the kidneys include conditions such as pyelonephritis. Nephrologists determine the cause of infections and provide appropriate antibiotic treatment.
Kidney Inflammation: Conditions of inflammation of the kidneys, such as glomerulonephritis, are in the study areas of nephrology. These conditions are usually associated with immune system problems or infections.
Diseases of the Renal Arteries: Conditions such as stenosis or blockage of the renal arteries can affect the blood flow to the kidneys. Nephrologists play a role in the diagnosis and management of renal artery diseases.
Kidney Damage Due to Hypertension: High blood pressure can damage the kidneys over time. Nephrologists assess and manage kidney damage due to hypertension.
Diabetic Nephropathy: Diabetes can cause kidney damage. Nephrologists monitor diabetic nephropathy and offer treatment options.
Electrolyte Balance Disorders: The kidneys regulate the fluid and electrolyte balance in the body. Nephrologists diagnose and treat electrolyte balance disorders.
Liv Hospital Nephrology Clinic
Problems such as hypertension, nephritis, chronic kidney disease, acute kidney failure, bleeding in the urine, protein loss in the urine and cystic kidney diseases are successfully monitored and treated using high-tech devices at the Liv Hospital Nephrology Clinic.
Specialists and experienced physicians
All important procedures and treatments in nephrology practice are performed at Liv Hospital Nephrology Clinic.
There are opportunities to create solutions to all kinds of problems of patients who have had a kidney transplant or are receiving continuous dialysis treatment.
In addition, temporary hemodialysis services are provided for chronic dialysis patients or patients requiring emergency dialysis for a period of 24 hours. Patients who need chronic dialysis and organ transplant are referred to the relevant centers after all kinds of preparations have been made.
Hemodialysis machines have the latest technology and patient specific treatment is arranged. The catheters required for hemodialysis are inserted by specialist doctors in intensive care.
For more information about our academic and training initiatives, visit Liv Hospital Academy.
Frequently Asked Questions for Nephrology Clinic
What is nephrology, dialysis, and transplantation?
Dialysis (hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis) replaces some kidney function when the kidneys are failing. Transplantation places a healthy donor kidney to restore function. Nephrology teams counsel patients on timing, options, and ongoing care.
What is nephrology and hypertension care?
It’s integrated management of high blood pressure with kidney protection—using lifestyle changes, medications, and monitoring to reduce kidney damage and cardiovascular risks.
What does nephrology specialize in?
Nephrology specializes in chronic kidney disease, acute kidney injury, hypertension related to kidney disease, glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, kidney stone risk reduction, electrolyte and acid base disorders, and guidance on dialysis and transplantation.
Are nephrology and urology the same?
No. Nephrology manages medical kidney conditions; urology performs surgical treatments for the urinary system. They often collaborate to provide comprehensive care.
How should I prepare for a nephrology appointment?
Bring a list of medications and supplements, recent lab results if available, home blood pressure readings, and notes about symptoms (swelling, urine changes). Hydrate as advised and be prepared to provide a urine sample.
What happens at a nephrology appointment?
Expect a review of symptoms and medications, a physical exam (including blood pressure and fluid status), blood and urine tests to assess kidney function and electrolytes, and sometimes a kidney ultrasound. You’ll receive a personalized plan and follow up schedule.




