A resting heart rate between 60-100 beats per minute is seen as normal for adults. Yet, research shows that a lower resting heart rate links to better heart health.
Keeping a healthy resting heart rate is key for good health. Studies on radial artery pulse waveforms and CAC severity in ESRD patients shed light on non-invasive heart risk checks. They stress the need to watch your average resting heart rate.
Knowing your resting heart rate range is a big step in checking your heart health. We’ll dive into how this simple measure can reveal a lot about your health.
Key Takeaways
- A normal resting heart rate ranges from 60-100 beats per minute.
- Lower resting heart rates are often associated with better cardiovascular health.
- Monitoring your resting heart rate can provide insights into your overall well-being.
- Understanding your resting heart rate range is key for checking heart health.
- A healthy lifestyle can help keep your resting heart rate normal.
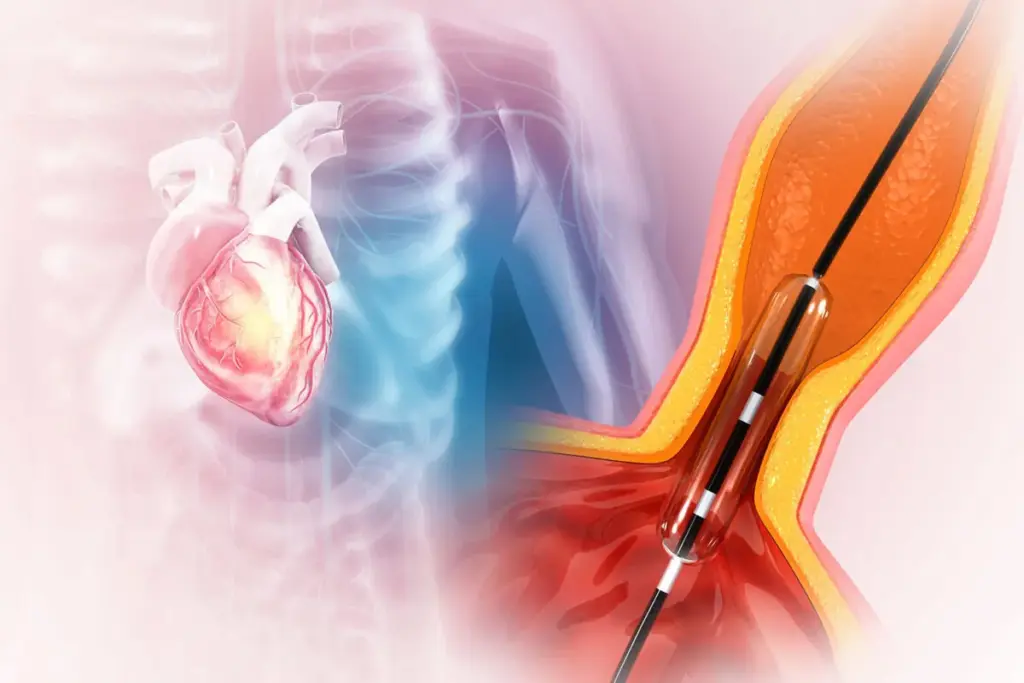
Defining Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) in Cardiovascular Health
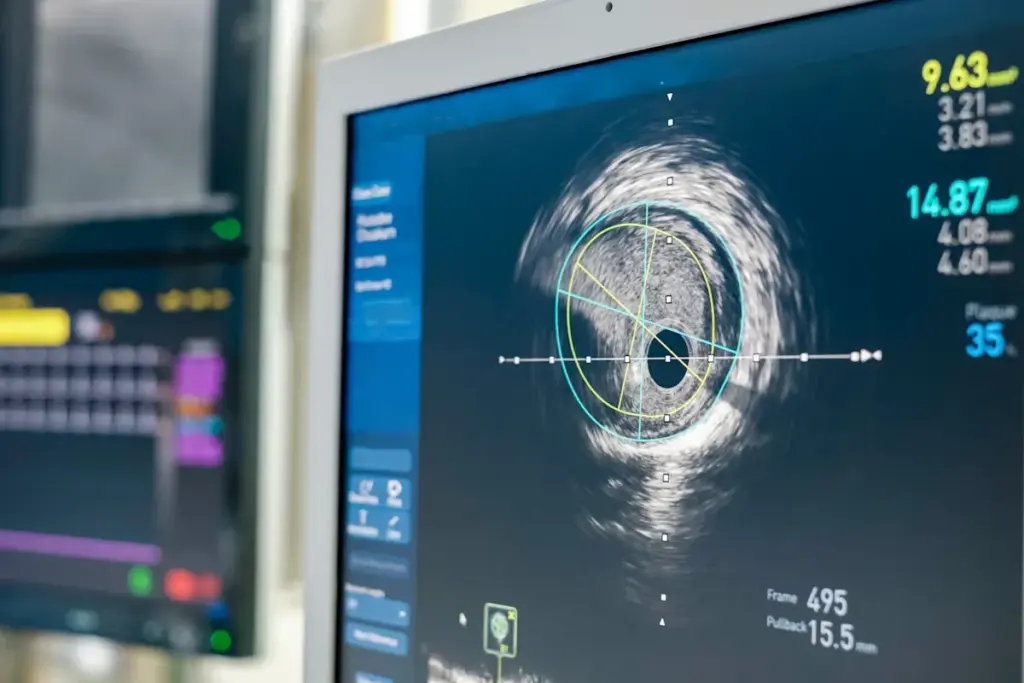
Knowing about Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) is key for heart health. FFR helps find out how bad coronary artery disease is. It shows how a blockage affects blood flow to the heart.
The Technical Definition of FFR
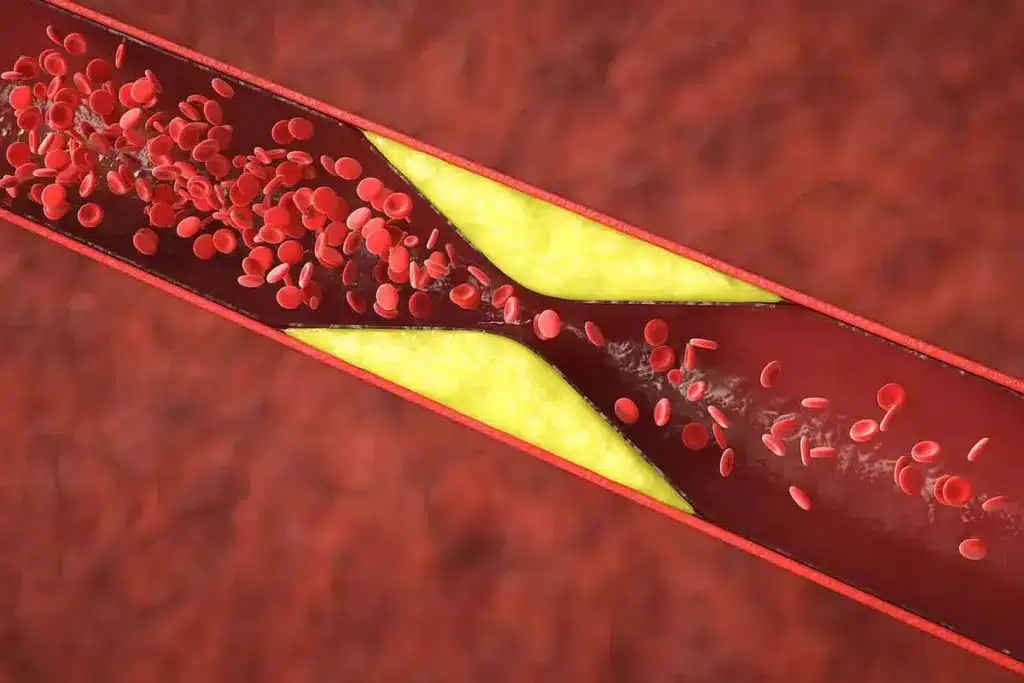
FFR is the blood flow ratio in a coronary artery, with and without a blockage. It’s found during a coronary angiography. An FFR of 0.8 or less means a blockage is likely to cause heart problems.
How FFR Relates to Heart Function
FFR checks if the heart gets enough blood. A low FFR means a blockage is cutting off blood to the heart. This could lead to heart pain or ischemia. Knowing this helps doctors decide the best treatment.
Clinical Significance in Cardiology
FFR is important for deciding when to do heart procedures. Research shows FFR helps pick the right blockages to fix. Here’s what different FFR values mean:
|
FFR Value |
Clinical Implication |
|---|---|
|
> 0.8 |
Non-significant stenosis; medical therapy recommended |
|
≤ 0.8 |
Functionally significant stenosis; consider revascularization |
|
Highly significant stenosis; revascularization often necessary |
Cardiologists use FFR to make better choices for patients. This leads to better heart health results.
Normal Resting Heart Rate: Standards and Variations
Resting heart rate shows how well our heart is working. Doctors use it to check our heart health. We’ll look at what’s normal for adults, how heart rate changes with age, and any gender differences.
Standard Ranges for Healthy Adults
For adults, a normal resting heart rate is between 60 to 100 beats per minute (bpm). Doctors agree on this range after lots of research. A heart rate in this range usually means a healthy heart. But, a heart rate that’s way off could mean a health problem.
Age-Related Variations in Heart Rate
Heart rate changes a lot with age. Newborns have a heart rate of 100 to 160 bpm. Older people might have a slightly higher rate than younger ones. Our heart changes as we get older, affecting our heart rate. It’s key to understand these changes for accurate health checks.
Gender Differences in Baseline Measurements
Studies show men and women have different resting heart rates. Women usually have a slightly higher rate than men. This is due to differences in heart size and hormones. Knowing these differences helps doctors better assess heart health.
Understanding resting heart rate standards and variations helps us spot heart health issues early. This knowledge is vital for keeping our hearts healthy and our overall well-being.
Factors That Influence Your Resting Heart Rate
Resting heart rate is more than just a simple vital sign. It’s influenced by many factors that affect heart health. Knowing these factors can help people take steps to keep their heart healthy.
Physical Fitness and Athletic Conditioning
Physical fitness greatly affects resting heart rate. Athletes or those who exercise regularly often have a lower resting heart rate. Aerobic exercises, like running or cycling, can lower resting heart rate over time. This is because their heart gets stronger and pumps blood more efficiently.
A study on endurance athletes showed their resting heart rates were much lower than those who don’t exercise. This shows how training and conditioning improve heart health.
Medications and Substances That Affect Heart Rate
Some medications and substances can change resting heart rate. For example, beta-blockers, used for high blood pressure and heart conditions, can lower heart rate. On the other hand, caffeine and nicotine can make heart rate go up. It’s important to know how these can affect heart rate.
- Beta-blockers: Lower heart rate
- Caffeine: Can increase heart rate
- Nicotine: Increases heart rate
- Certain antidepressants: May affect heart rate variability
Environmental and Psychological Factors
Environmental and psychological factors also play a big role in resting heart rate. Stress, for example, can raise heart rate due to stress hormones like adrenaline. Extreme temperatures can also affect heart rate, with hot conditions leading to a faster heart rate to cool down the body.
Managing stress through meditation or deep breathing can help. Being aware of your environment and avoiding extreme conditions can also help keep your heart rate healthy.
Understanding and managing factors that affect resting heart rate can improve heart health. Regular checks and lifestyle or treatment adjustments, with a healthcare provider’s guidance, can lead to a healthier heart.
The Connection Between FFR and Normal Resting Heart Rate
FFR and resting heart rate are closely linked. They both affect how well the heart works and overall heart health. Knowing about this connection is key for spotting and treating heart diseases.
How Resting Heart Rate Affects Coronary Blood Flow
A normal resting heart rate is between 60 to 100 beats per minute. This range is best for coronary blood flow. It makes sure the heart muscle gets enough oxygen and nutrients.
Key factors that influence coronary blood flow include:
- Myocardial demand
- Coronary artery resistance
- Aortic pressure
An abnormal heart rate can harm coronary blood flow. This might cause heart problems or ischemia.
FFR Measurements in Relation to Heart Rate
FFR tests are done during cardiac catheterization. A pressure wire checks the pressure drop across a coronary lesion. The link between FFR and heart rate is complex. It depends on the pressure drop and microvascular resistance.
Studies have shown that:
- High or low heart rates can change FFR measurements. They increase demand and alter microvascular resistance.
- FFR values can be affected by heart rate. This might lead to wrong interpretations if not seen in the patient’s heart rate context.
Clinical Implications of the Relationship
Knowing how FFR and resting heart rate interact is very important. It helps doctors make better choices for treating coronary artery disease. This includes deciding if a revascularization procedure is needed.
Clinical considerations include:
- Looking at how heart rate affects FFR measurements
- Thinking about the patient’s resting heart rate when looking at FFR values
- Using cardiac MRI to check heart function and blood flow without surgery
How to Properly Measure Your Resting Heart Rate
Learning to measure your resting heart rate can give you insights into your heart health. It’s important to measure it right to keep track of your heart’s condition.
Manual Pulse Checking Techniques
One easy way to find your resting heart rate is by feeling your pulse. You can do this at your wrist or neck. Count the beats for 15 seconds and then multiply by four to get your heart rate in beats per minute (bpm).
For the most accurate results, take your pulse at the same time every day. Morning is best, right after waking up. Using a stopwatch or phone timer can help you keep track of time.
Tips for Manual Pulse Checking:
- Use your index and middle fingers to feel the pulse.
- Avoid using your thumb as it has its own pulse.
- Count the beats for 15 seconds and then multiply by four.
- Take your pulse at the same time daily for consistency.
Using Digital Monitors and Wearables
Digital devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers make tracking your heart rate easy. They offer continuous monitoring. When picking a device, choose one that’s clinically validated and fits your needs.
|
Device Type |
Features |
Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
|
Smartwatches |
Continuous monitoring, user-friendly interface |
High |
|
Fitness Trackers |
Heart rate monitoring, activity tracking |
High |
|
Chest Straps |
Highly accurate heart rate monitoring during exercise |
Very High |
Optimal Timing and Frequency for Measurements
The best time to check your resting heart rate is in the morning, right after waking up. It’s also best before any exercise. Being consistent is key, so measure at the same time every day.
“Consistency in measuring resting heart rate is key for reliable data. It helps monitor changes in heart health over time.” – Dr. Heart, Cardiologist
For most people, checking your resting heart rate once a day is enough. But athletes or those with heart conditions might need to do it more often.
Interpreting Heart Rate Measurements and FFR Values
Heart rate measurements and FFR values give insights into your heart’s health. Knowing these metrics is key to checking your heart health and making smart care choices.
Understanding Normal vs. Abnormal FFR Readings
FFR values show how blocked your coronary arteries are. A normal FFR is above 0.80, meaning your arteries are mostly open. But, if it’s below 0.80, it means you have a big blockage that might need treatment.
Normal FFR Values: Above 0.80
Abnormal FFR Values: Below 0.80
Remember, FFR values must be seen with your symptoms and other tests too.
What High Resting Heart Rate Might Indicate
A high resting heart rate can mean stress, anxiety, or heart problems. For adults, a normal heart rate is between 60 to 100 beats per minute.
Potential causes of high resting heart rate include:
- Stress or anxiety
- Dehydration
- Certain medications
- Underlying heart conditions
If your heart rate is always over 100 bpm, see a doctor to find out why.
Clinical Significance of Low Heart Rate
A low heart rate, or bradycardia, can be good for athletes. But, for non-athletes, it might mean health issues.
Potential causes of low resting heart rate include:
- Athletic conditioning
- Certain medications
- Hypothyroidism
- Heart block
If your heart rate is under 60 bpm, you should see a doctor to check for health problems.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
If you’re worried about your heart rate or FFR values, talk to a doctor. They can give advice based on your health and history.
“Understanding your heart health is a journey, and having the right information is the first step towards making informed decisions about your care.” – A healthcare professional
Knowing your heart rate and FFR values helps you keep your heart healthy. Always talk to a doctor for advice tailored to you.
Cardiac MRI: Advanced Imaging for Heart Rate Assessment
Healthcare experts now use cardiac MRI to check heart rate and function with great detail. This advanced tool gives clear images of the heart’s structure and how it works.
What is Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Cardiac MRI is a safe way to see the heart without harm. It uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images. This method doesn’t use harmful radiation, making it safe for many patients.
Key benefits of cardiac MRI include:
- High-resolution images of cardiac anatomy
- Assessment of cardiac function and blood flow
- Evaluation of myocardial viability and scarring
How Heart MRIs Evaluate Cardiac Function
Cardiac MRI looks at how well the heart works by checking things like ventricular volumes and ejection fraction. This helps doctors diagnose and treat heart problems.
During a cardiac MRI, we can:
- Assess the heart’s pumping efficiency
- Evaluate blood flow through the coronary arteries
- Identify areas of myocardial damage or scarring
What a Cardiac MRI Can Reveal About Heart Rate
A cardiac MRI shows how heart rate impacts the heart’s function. Doctors can see how heart rate affects heart health by looking at MRI images and data.
In conclusion, cardiac MRI is a key tool for understanding the heart. It helps doctors see how heart rate affects the heart. This knowledge helps in creating better treatment plans for heart health.
Preparing for a Cardiac MRI Procedure
To get the most out of your cardiac MRI, it’s essential to follow specific guidelines and understand the safety considerations involved. A cardiac MRI is a sophisticated diagnostic tool that provides detailed images of the heart’s structure and function.
Pre-Procedure Guidelines and Restrictions
Before undergoing a cardiac MRI, there are several steps you should take to prepare:
- Inform your doctor about any metal implants, pacemakers, or other medical devices you have, as these can be contraindications for an MRI.
- Remove all metal objects, including jewelry, glasses, and clothing with metal parts, before the procedure.
- Disclose any claustrophobia; your healthcare provider may suggest ways to help you feel more comfortable during the enclosed MRI procedure.
- Follow any dietary instructions provided by your healthcare provider, though fasting is usually not required for a cardiac MRI.
What to Expect During the Test
During the cardiac MRI procedure, you will be asked to lie on a movable table that slides into the MRI machine. Here’s what you can expect:
- Comfort measures will be taken to ensure you are comfortable during the procedure, including the provision of earplugs or headphones to reduce noise.
- Contrast dye may be used in some cases to enhance the images; your healthcare provider will inform you if this is necessary.
- Monitoring will be performed throughout the procedure to ensure your safety and the quality of the images.
- The procedure typically lasts between 30 to 90 minutes, depending on the complexity of the scan.
Safety Considerations and Contraindications
While cardiac MRI is generally a safe procedure, there are certain safety considerations and contraindications to be aware of:
- Magnetic field interactions can occur with certain metal implants or devices, so it’s vital to inform your healthcare provider about any such devices.
- Contrast dye allergy is rare but can occur; your healthcare provider will assess the risk and take necessary precautions.
- Claustrophobia can be a challenge; discussing your concerns with your healthcare provider beforehand can help mitigate this.
By understanding these aspects of the cardiac MRI procedure, you can better prepare yourself for a successful and stress-free diagnostic experience.
Types of Cardiac MRI Procedures for Heart Rate Evaluation
Cardiac MRI procedures help understand heart health. They assess cardiac function and heart rate. This aids in diagnosing and managing heart diseases.
Standard Cardiac MRI Protocols
Standard cardiac MRI protocols evaluate the heart’s structure and function. They take images in different planes. This assesses cardiac anatomy, function, and blood flow.
“Cardiac MRI has become an indispensable tool in cardiology, providing unparalleled insights into heart health,” a leading cardiologist notes.
These protocols include cine imaging for ventricular function, tagging for myocardial deformation, and phase-contrast imaging for blood flow. These images give a detailed picture of cardiac health.
Stress Cardiac MRI Testing
Stress cardiac MRI tests the heart’s function under stress. This stress is usually from exercise or medication. It’s key for spotting ischemia or reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
Images are taken at rest and during stress. This comparison helps diagnose coronary artery disease and assess future cardiac risks.
Contrast vs. Non-Contrast Studies
Cardiac MRI can be done with or without contrast agents. Contrast-enhanced MRI uses a gadolinium-based agent to highlight heart areas like scar tissue or inflammation.
Non-contrast studies use tissue differences to create images. While contrast agents offer more info, non-contrast studies are better for patients with kidney issues or allergy risks.
The choice between contrast and non-contrast MRI depends on the clinical question and patient condition. Both are valuable in assessing heart health.
How Cardiologists Use FFR and MRI Together
FFR and MRI are changing cardiology, giving a detailed look at the heart and blood flow. They help us understand heart health better. This leads to better diagnoses and treatments.
Complementary Diagnostic Approaches
FFR and MRI work together, each giving unique insights. FFR checks the pressure in coronary arteries, while MRI shows the heart’s structure and function. This combo lets us see both the heart’s function and its anatomy.
Non-Invasive FFR Estimation Through MRI
Using FFR and MRI together means we can estimate FFR without invasive tests. MRI’s advanced tech can do this, making it safer and more comfortable for patients.
Clinical Decision-Making Based on Combined Data
FFR and MRI data help doctors make better choices. They look at both the heart’s function and structure. This helps decide the best treatment for each patient.
For example, a patient with a borderline FFR and MRI signs of ischemia might need surgery. But a patient with a clear negative FFR and normal MRI might just need medicine. This approach makes sure treatments fit each patient’s needs.
As cardiology advances, FFR and MRI will be key in diagnosing heart issues. They offer a precise and less invasive way to check the heart.
Lifestyle Modifications to Improve Your Resting Heart Rate
Making smart lifestyle choices is key to a better resting heart rate and heart health. By making a few changes, you can greatly improve your heart’s health.
Evidence-Based Exercise Recommendations
Regular exercise is essential for a healthy resting heart rate. Aerobic exercises like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming are great. You should do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity each week.
Adding strength training to your routine is also good. It boosts your heart health by increasing muscle and metabolism. Try to do two or more strength training sessions a week.
Dietary Considerations for Heart Health
Eating a balanced diet is important for a healthy heart rate. Eat whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods are full of nutrients and antioxidants that are good for your heart.
Try to eat less of processed and high-sodium foods. They can harm your heart rate and overall heart health. Drinking plenty of water is also key.
Stress Management and Sleep Optimization
Good stress management is important for a lower resting heart rate. Try meditation, deep breathing, or yoga. Chronic stress can raise your heart rate, so it’s important to manage it well.
Getting enough sleep is also critical for heart health. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night. It helps regulate your heart rate and supports your overall well-being. A consistent sleep schedule and a relaxing bedtime routine can help improve your sleep.
Athletes and Heart Rate: Special Considerations
Heart rate in athletes is unique due to their body’s changes. Their heart rates differ from others because of their training and health.
Typical FFR and Heart Rate Ranges in Athletes
Athletes usually have lower resting heart rates. This is because their hearts work better. Normal heart rates for adults are 60 to 100 beats per minute. But athletes often have rates between 40 and 60 bpm.
FFR measurements in athletes are usually normal. This shows their coronary blood flow is healthy.
Training Effects on Cardiovascular Function
Training changes athletes’ hearts a lot. It makes their hearts pump more efficiently. This means they can deliver oxygen and nutrients better to their muscles.
Training also changes how the heart rate is controlled. Athletes’ hearts beat slower because of this. This is good for their resting heart rate.
Monitoring Heart Rate for Optimal Performance
Tracking heart rate helps athletes perform better. It shows how well they’re doing, recovering, and staying healthy.
It helps spot signs of overtraining early. This lets athletes adjust their training. It also helps tailor workouts to the right intensity.
Athletes should get help from doctors to set up heart rate monitoring. This plan should match their training goals and needs.
Technology for Tracking Heart Rate and Estimating FFR
Today, we have many tools to track heart rate and estimate FFR. These tools help improve patient care and make diagnoses more accurate. They have changed how we handle heart health.
Consumer Wearable Devices and Their Accuracy
Smartwatches and fitness trackers are popular for tracking heart rate. They use photoplethysmography (PPG) to measure heart rate. This makes it easy to monitor heart rate all the time.
But, their accuracy can change. This is true during hard workouts or for people with heart problems. It’s important to pick devices that are proven to be accurate.
Smartphone Applications for Heart Monitoring
Smartphone apps are also used for heart rate tracking. They work with wearable devices or the phone’s camera and flash. These apps give quick feedback and can spot irregular heartbeats.
But, their accuracy can also vary. They shouldn’t be the only way to diagnose heart issues. Yet, they’re good for initial checks and to remind people to see a doctor.
Medical-Grade Monitoring Systems
Medical-grade systems are for doctors’ offices and hospitals. They give very accurate heart rate and vital sign readings. These systems are used for patient care and during surgeries.
For FFR, advanced imaging and models are used in these systems. They help doctors make better treatment plans. These tools are key for guiding care.
Here’s a comparison of different technologies used for heart rate monitoring and FFR estimation:
|
Technology |
Accuracy |
Clinical Use |
|---|---|---|
|
Consumer Wearable Devices |
Variable |
Limited |
|
Smartphone Applications |
Variable |
Preliminary Screening |
|
Medical-Grade Monitoring Systems |
High |
Diagnostic and Treatment Guidance |
In conclusion, there are many technologies for heart rate and FFR tracking. Each has its own good points and downsides. Knowing about these technologies helps both doctors and patients make better choices for heart health.
Common Heart Rate Disorders and Their Relationship to FFR
Heart rate disorders can greatly affect heart health. Knowing how Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) relates to these disorders is key. Conditions like tachycardia, bradycardia, and arrhythmias can make the heart less efficient.
Tachycardia: Causes, Symptoms, and FFR Impact
Tachycardia means the heart beats too fast. This can lower blood flow and increase oxygen demand. It can also affect FFR readings, leading to possible heart problems.
Stress, anxiety, and heart issues can cause tachycardia. Symptoms include heart palpitations, shortness of breath, and feeling dizzy. It’s important to manage tachycardia when checking FFR to get accurate results.
Bradycardia: When Slow Heart Rate Affects Coronary Flow
Bradycardia, or a slow heart rate, can also impact FFR. A slow heart rate might raise blood pressure, affecting blood flow. In some cases, it may need pacing to ensure blood circulates well.
Cardiologists must understand how bradycardia affects blood flow and heart function. This knowledge is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Arrhythmias and Their Effect on FFR Measurements
Arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats, can make FFR readings tricky. The irregular rhythm can change blood flow. Conditions like atrial fibrillation can greatly affect FFR, needing careful attention during tests.
It’s vital for cardiologists to understand how arrhythmias impact blood flow. This helps in making better decisions for patient care and treatment.
Conclusion: Maintaining Optimal Heart Rate and FFR for Cardiovascular Health
We’ve looked into how Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) and heart rate are linked. This connection is key to keeping our hearts healthy.
Keeping our heart rate in check is vital for good blood flow to the heart. FFR helps doctors see how bad coronary artery disease is. It helps decide the best treatment. Knowing how heart rate and FFR work together helps us stay healthy.
It’s important to take a full-body approach to heart health. This includes making lifestyle changes, checking in regularly, and using tests like cardiac MRI. Working with doctors helps us keep our heart rate and FFR in the best range. This lowers the chance of heart disease and boosts our overall health.
FAQ
What is a normal resting heart rate?
For adults, a normal resting heart rate is between 60 to 100 beats per minute. Athletes or very fit people might have a rate as low as 40 bpm.
How is Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) related to heart function?
FFR measures how severe a blockage in a coronary artery is. It checks the pressure difference across the blockage. This helps see if the blockage is seriously cutting off blood flow to the heart muscle.
Can I have a cardiac MRI with a pacemaker?
Having a pacemaker usually means you can’t have a cardiac MRI. But, some newer models might be safe for MRI under certain conditions. Always check with your doctor or cardiologist first.
How do I prepare for a cardiac MRI?
To prepare, remove any metal objects and tell your doctor about implants or conditions. You might need to fast or avoid certain medicines. Your healthcare team will give you specific instructions.
What factors can influence my resting heart rate?
Your resting heart rate can be affected by fitness, age, medicines, stress, and health conditions. Making lifestyle changes like exercising and managing stress can help improve it.
How often should I measure my resting heart rate?
Most people should check their resting heart rate once a week or month. But, if you have heart issues or are on certain medicines, your doctor might want you to check more often.
Can lifestyle changes improve my resting heart rate?
Yes, regular exercise, a healthy diet, managing stress, and enough sleep can lower your resting heart rate. These changes are good for your heart health.
What is the difference between a standard cardiac MRI and a stress cardiac MRI?
A standard cardiac MRI looks at the heart at rest. A stress cardiac MRI checks how the heart works under stress, usually from exercise or medicine.
Are consumer wearable devices accurate for tracking heart rate?
Many wearable devices can track heart rate fairly well. But, for precise medical use, medical-grade systems are usually more reliable.
How does FFR relate to coronary blood flow?
FFR measures how much a blockage in a coronary artery affects blood flow to the heart. A lower FFR means more blood flow is blocked.
Can arrhythmias affect FFR measurements?
Yes, arrhythmias can change FFR readings by affecting the heart’s rhythm and blood flow. The impact depends on the arrhythmia’s type and severity.
What are the clinical implications of the relationship between resting heart rate and FFR?
Knowing how resting heart rate and FFR are connected helps doctors better diagnose and treat heart diseases. It gives insights into the heart’s resting state and function.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6592896/



































