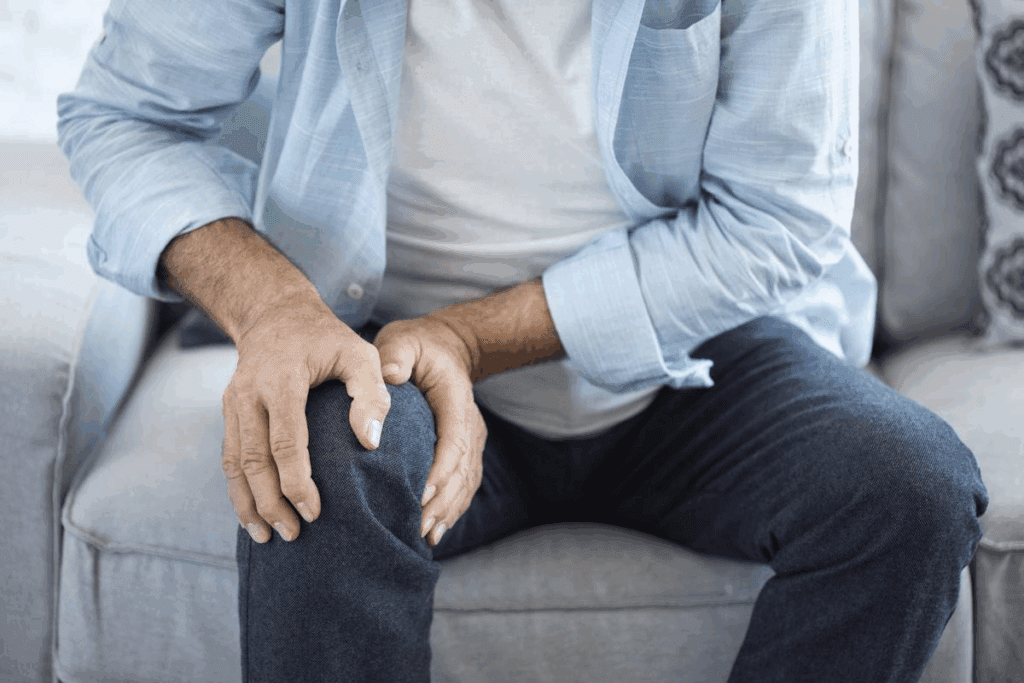
Osteoarthritis affects millions of Americans, causing a lot of pain and disability. Theexperts says getting an accurate osteoarthritis diagnosis is key to a good treatment plan. Discover how to test for osteoarthritis with accurate methods for early and reliable osteoarthritis diagnosis.
To diagnose osteoarthritis, doctors look at your medical history, do a physical exam, and might run some tests. They check your symptoms, do a physical exam, and might use imaging tests to see if you have osteoarthritis.
Knowing how to diagnose osteoarthritis is very important. If you’re feeling symptoms, getting diagnosed quickly can really improve your life.
Key Takeaways
- Accurate diagnosis is key for effective treatment.
- Diagnosis includes looking at your medical history, doing a physical exam, and running tests.
- Getting diagnosed quickly can greatly improve your life.
- A doctor will check your symptoms and do a physical exam.
- They might use imaging tests to confirm osteoarthritis.
Understanding Osteoarthritis: The Basics
Learning about osteoarthritis is key to catching it early and managing it well. This condition affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and making it hard to move.
What Is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is a disease where the cartilage in joints wears down. Cartilage is the soft tissue that cushions the joints. When it breaks down, bones rub against each other, causing pain and swelling. Osteoarthritis symptoms can differ, but often include joint pain, stiffness, and trouble moving.
Common Locations for Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis can happen in any joint, but it often hits the knees, hips, and spine. It also affects the hands, mainly the fingers. This can make everyday activities hard and lower your quality of life.
Risk Factors for Developing Osteoarthritis
There are several risk factors for osteoarthritis. These include getting older, being overweight, having past joint injuries, and genetics. Knowing these risk factors helps you take steps to prevent it and get help early if you start to feel symptoms.
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Age | The risk of developing osteoarthritis increases with age due to wear and tear on the joints. |
| Obesity | Excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis. |
| Previous Injuries | Joint injuries, such as fractures or ligament sprains, can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis. |
Recognizing the Warning Signs
It’s important to spot the early signs of osteoarthritis to get help quickly. This condition breaks down cartilage and bone in joints. If not treated early, it can really hurt your quality of life.
Early Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Joint pain and stiffness are early signs of osteoarthritis. These symptoms might seem like just normal wear and tear at first. But as the condition gets worse, the pain can last longer and make everyday tasks hard.
Advanced Symptoms That Require Medical Attention
When osteoarthritis gets worse, symptoms get more severe. You might feel significant pain, swelling, and have trouble moving. At this point, you should see a doctor to stop things from getting worse and to find ways to treat it.
Symptom Patterns in Different Joints
The symptoms can change based on which joint is affected. For example, knee problems might hurt when you walk or climb stairs. On the other hand, hand issues can make it hard to hold things.
| Joint Affected | Common Symptoms |
| Knee | Pain during walking, climbing stairs, or squatting |
| Hand | Difficulty gripping objects, pain in fingers |
| Hip | Pain in groin or thigh, limited mobility |
Knowing how symptoms vary can help doctors diagnose and treat osteoarthritis better.
Osteoarthritis Diagnosis: The Complete Process
When osteoarthritis is suspected, healthcare providers follow a structured diagnostic process. This process is key to confirming the diagnosis and ruling out other conditions. It’s also important for creating an effective treatment plan.
Initial Consultation with Healthcare Providers
The journey starts with an initial consultation. Here, patients talk about their symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle with their healthcare provider. This information helps understand the possible causes of joint pain and stiffness.
The Diagnostic Journey: What to Expect
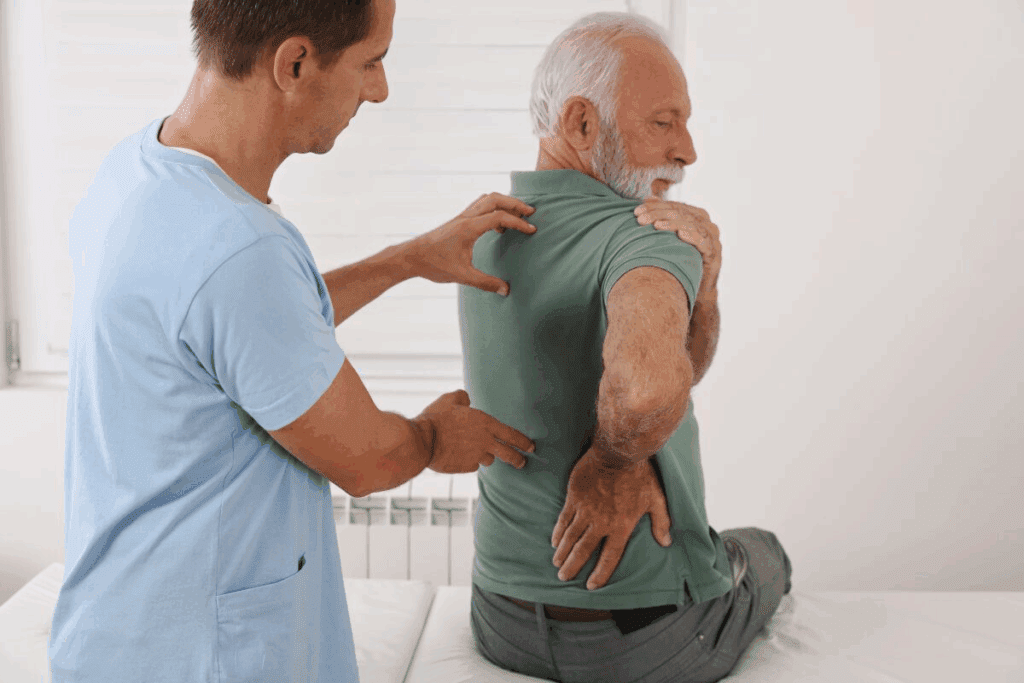
During the diagnostic journey, patients undergo a comprehensive physical examination. This checks joint mobility and looks for any abnormalities. Healthcare providers might also order imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to see the extent of joint damage.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s important to seek medical attention if you have persistent joint pain or stiffness. This is true if it affects your daily activities. Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve life quality for those with osteoarthritis.
Understanding the diagnostic process helps patients navigate their healthcare journey. It also helps them make informed decisions about their care.
Physical Examination Techniques
Physical exams are key in spotting osteoarthritis. They help doctors check joints and tissues. This confirms if someone has the condition.
Joint Mobility Assessment
Checking how well joints move is critical. Doctors look for any pain or stiffness when moving. This shows how much damage there is.
Special Tests for Knee Osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis gets special tests. These check if the knee is stable and working right. Tests look at ligaments and meniscus health.
Hip Arthritis Examination Methods
Checking the hip involves looking at its movement and pain. Doctors also check for any deformities. Tests check if the hip is stable and working well.
Evaluating Hand and Foot Osteoarthritis
Hand and foot osteoarthritis exams focus on deformities, pain, and stiffness. Doctors do specific tests to check the joints and tissues.
Using these techniques, doctors can accurately diagnose osteoarthritis. Then, they can create a treatment plan.
Imaging Tests for Osteoarthritis
Healthcare experts use different imaging tests to diagnose osteoarthritis. These tests show how joints are doing. They help figure out how much damage there is and what treatment to use.
X-Ray Findings in Osteoarthritis
X-rays help see joint damage in osteoarthritis. They show joint space narrowing, bone spurs, and other signs. X-rays are great for checking how bad osteoarthritis is and if it’s getting worse.
MRI Evaluation for Joint Damage
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) gives a closer look at joints than X-rays. It checks for bone and soft tissue damage. MRI is key for catching osteoarthritis early, when it’s easier to treat.
CT Scans and Their Role
Computed Tomography (CT) scans show detailed images of joints. They help spot bone damage and other changes. CT scans are not as common for osteoarthritis but are useful for complex cases.
Ultrasound in Osteoarthritis Assessment
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create joint images. It’s good for finding soft tissue damage and early osteoarthritis signs. It also helps with injections and treatments.
In summary, many imaging tests are vital for osteoarthritis diagnosis and care. Knowing what each test does helps doctors make better diagnoses and treatment plans.
Laboratory Tests and Their Limitations
Imaging tests are key, but lab tests also play a big role in diagnosing osteoarthritis. They help rule out other joint pain causes and check the joint’s health.
Can Blood Tests Detect Osteoarthritis?
Blood tests can’t confirm osteoarthritis but help rule out other joint pain causes like rheumatoid arthritis. They check for inflammation markers like CRP and ESR.
Joint Fluid Analysis
Joint fluid analysis takes fluid from the joint to check for inflammation or infection. It helps tell osteoarthritis apart from other arthritis types.
Biomarkers for Osteoarthritis
Biomarkers are being studied to spot osteoarthritis early and track its progress. They are molecules in blood, urine, or joint fluid that show joint damage.
| Laboratory Test | Purpose | Limitations |
| Blood Tests | Rule out other causes of joint pain | Not definitive for osteoarthritis |
| Joint Fluid Analysis | Differentiate osteoarthritis from other arthritis types | Invasive, not always necessary |
| Biomarkers | Potential for early diagnosis and monitoring | Stil under research, not widely available |
Differential Diagnosis: Osteoarthritis vs. Other Conditions
Differential diagnosis is key in spotting osteoarthritis among other joint issues. It’s vital to correctly identify osteoarthritis to avoid confusing it with similar diseases.
Rheumatoid Arthritis vs. Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) are different. OA is about joint wear and tear, while RA is an autoimmune disease causing inflammation. RA has systemic symptoms like fatigue and fever, and its joint involvement is symmetrical.
Gout and Pseudogout
Gout and pseudogout can look like osteoarthritis. Gout is caused by urate crystals in joints, leading to sudden pain. Pseudogout involves calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals, also causing sudden pain and swelling.
Other Inflammatory Joint Conditions
Conditions like psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis can also be mistaken for osteoarthritis. Psoriatic arthritis is linked to psoriasis and affects the spine and other joints. Ankylosing spondylitis mainly affects the spine, causing stiffness and vertebrae fusion.
In summary, accurately diagnosing osteoarthritis is critical. A detailed clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests are needed. This helps doctors provide the right treatment plan.
Diagnosing Osteoarthritis in Specific Joints
Diagnosing osteoarthritis in different joints needs a special approach. Each joint has its own features and functions. A tailored strategy is key for accurate diagnosis.
Knee Osteoarthritis Diagnosis
To diagnose knee osteoarthritis, doctors use both clinical checks and imaging. They look at symptoms like pain and stiffness. They also check joint mobility and stability.
X-rays help see joint space narrowing and bone spurs. These signs are common in osteoarthritis.
Hip Osteoarthritis Assessment
Assessing hip osteoarthritis requires a detailed clinical exam and imaging. Doctors look for pain in the groin or buttock and limited mobility. X-rays and sometimes MRIs confirm the diagnosis by showing joint changes.
Hand and Finger Joint Evaluation
Checking for osteoarthritis in hands and fingers focuses on symptoms like pain and stiffness. Clinical examination may find Heberden’s and Bouchard’s nodes. X-rays confirm the diagnosis by showing joint changes.
Foot and Ankle Osteoarthritis Testing
Diagnosing osteoarthritis in the foot and ankle looks at symptoms like pain and stiffness. Imaging studies, including X-rays, are key for confirming the diagnosis and assessing damage.
Spine Osteoarthritis Diagnosis
Diagnosing spine osteoarthritis combines clinical evaluation and imaging. Patients often have back pain and stiffness. X-rays and CT scans show degenerative changes in the spine.
Experts say understanding osteoarthritis in different joints is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Diagnosing osteoarthritis in specific joints is complex. It needs a detailed approach, combining clinical evaluation and imaging studies.
Diagnostic Criteria for Osteoarthritis
To diagnose osteoarthritis, doctors use diagnostic criteria like clinical and radiographic evaluations. This method gives a full picture of the condition.
Clinical Criteria
Doctors look at a patient’s medical history and do a physical exam. They check for joint pain, stiffness, and how well the joints move. These signs help figure out if someone has osteoarthritis.
Radiographic Grading Systems
Radiographic grading systems help measure how severe osteoarthritis is. They look at images of the joints. The Kellgren-Lawrence grade is one system that checks for joint space narrowing and bone growth.
Combined Approaches to Diagnosis
Using both clinical and radiographic methods makes diagnosis better. This way, doctors get a clearer picture of the condition. It helps them choose the right treatment.
Doctors can accurately diagnose osteoarthritis by combining these methods. This leads to better care for patients.
Self-Assessment: When to Suspect Osteoarthritis
Checking yourself for osteoarthritis is key to early detection and treatment. By keeping an eye on your joints, you can spot signs early. This helps you talk to doctors more effectively.
Home Tests and Observations
Simple tests at home can give you clues about your joints. Look for stiffness, pain, or trouble moving. Watching your joints every day can show you if something’s off.
Tracking Symptoms and Triggers
Keeping track of your symptoms and what makes them worse is important. Note when pain happens, how bad it is, and what makes it better or worse.
Using Pain Diaries
Keeping a pain diary is a smart way to track your symptoms. Write down when pain hits, what you were doing, and how bad it is. This helps you see patterns over time.
| Symptom | Description | Tracking Tip |
| Joint Pain | Pain or aching in the joints | Note the time of day and activities |
| Stiffness | Feeling of stiffness, specially after rest | Record duration and frequency |
| Limited Mobility | Reduced range of motion in the joints | Measure range of motion with a goniometer if possible |
Working with Healthcare Professionals
Managing osteoarthritis well needs a team of healthcare experts. Working together, they can make a big difference. This team effort can greatly improve life quality for those with osteoarthritis.
Primary Care Physicians
Primary care physicians are usually the first doctors people see with osteoarthritis concerns. They do initial checks, send patients to specialists if needed, and manage overall care.
Rheumatologists
Rheumatologists focus on arthritis and other rheumatic diseases. They give detailed diagnoses and suggest advanced treatments for osteoarthritis.
Orthopedic Specialists
Orthopedic specialists are surgeons for musculoskeletal issues, like osteoarthritis. They suggest surgery when other treatments don’t work.
Physical Therapists
Physical therapists are key in keeping joints moving and strong. They create custom exercise plans to help with function and pain from osteoarthritis.
Conclusion: Moving Forward After Diagnosis
Getting an osteoarthritis diagnosis can change how you manage the condition. After finding out, you can work with your healthcare team. Together, you can make a plan that fits you and change your lifestyle to feel better.
It’s important to work together to manage osteoarthritis. You should talk to doctors, like primary care physicians and rheumatologists, and physical therapists. This way, you can make a plan that helps slow down the disease and makes life better.
After getting a diagnosis, you need to do a few things. You’ll need to get medical treatment, make lifestyle changes, and take care of yourself. By understanding your condition and being active in managing it, you can lessen pain, move better, and stay independent.
FAQ
What is osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is a disease that affects joints. It happens when cartilage breaks down. This leads to pain, stiffness, and less mobility.
How is osteoarthritis diagnosed?
Doctors use several methods to diagnose osteoarthritis. They look at your medical history and do a physical exam. They also use X-rays, MRI, and joint fluid analysis.
Can arthritis show up on an X-ray?
Yes, X-rays can show signs of osteoarthritis. They can reveal joint space narrowing and bone spurs.
Is there a blood test for arthritis?
There’s no blood test specific for osteoarthritis. But, blood tests can rule out other types of arthritis, like rheumatoid arthritis.
How can you test for arthritis?
Testing for arthritis involves several steps. Doctors do a physical exam, use imaging tests, and analyze joint fluid. They also look for biomarkers.
What are the symptoms of osteoarthritis in feet?
Symptoms in the feet include pain, stiffness, swelling, and less mobility. These are common in the toes and midfoot.
Can a blood test detect arthritis?
Blood tests can spot certain types of arthritis, like rheumatoid arthritis. But, they’re not used to diagnose osteoarthritis.
How do doctors check for arthritis?
Doctors use a few methods to check for arthritis. They look at your medical history, do a physical exam, and use imaging and lab tests.
What is the difference between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and damage. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease from wear and tear.
Will gout show up on an X-ray?
Gout might show up on an X-ray if there’s joint damage or tophi (urate deposits).
How can osteoarthritis be diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose osteoarthritis by looking at your medical history, doing a physical exam, and using imaging and lab tests.
What are the diagnostic criteria for osteoarthritis?
To diagnose osteoarthritis, doctors consider symptoms, physical exam findings, and imaging results. They use clinical criteria and radiographic grading systems.
Can osteoarthritis be detected by a bone density test?
Bone density tests aren’t used to diagnose osteoarthritis. But, they might check bone health in people with osteoarthritis.
What is the role of laboratory tests in diagnosing osteoarthritis?
Lab tests, like joint fluid analysis and biomarkers, help confirm osteoarthritis. They also rule out other conditions.
How do healthcare professionals diagnose osteoarthritis in specific joints?
Healthcare professionals use physical exams, imaging tests, and lab tests to diagnose osteoarthritis in joints like knees, hips, hands, and spine.
References
- Hunter, D. J., & McDougall, J. J. (2023). Osteoarthritis: Diagnosis and management. In StatPearls. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482326/



































