Otolaryngology meaning is broad ENT. Laryngology is voice only. Get best facts. Specialists are vital for treating dangerous cord issues.
When you have ear, nose, or throat problems, knowing the difference between otolaryngology and laryngology is key. Many patients are unsure about who to see.
Otolaryngology, or ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) medicine, deals with a wide range of issues. These include problems with the ear, nose, throat, and related areas. Laryngology, on the other hand, is a special area that focuses on the larynx (voice box) and throat.
It’s important for patients to know the difference. An otolaryngologist can handle many ENT issues. But a laryngologistgoes deeper into the larynx and throat problems.
Key Takeaways
- Otolaryngology is also known as ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) medicine.
- Laryngology is a subspecialty focusing on larynx and throat disorders.
- Otolaryngologists handle a broad range of ENT issues.
- Laryngologists specialize in the complexities of the larynx and throat.
- Understanding the difference is key for the right medical care.
Understanding Otolaryngology Meaning and Practice
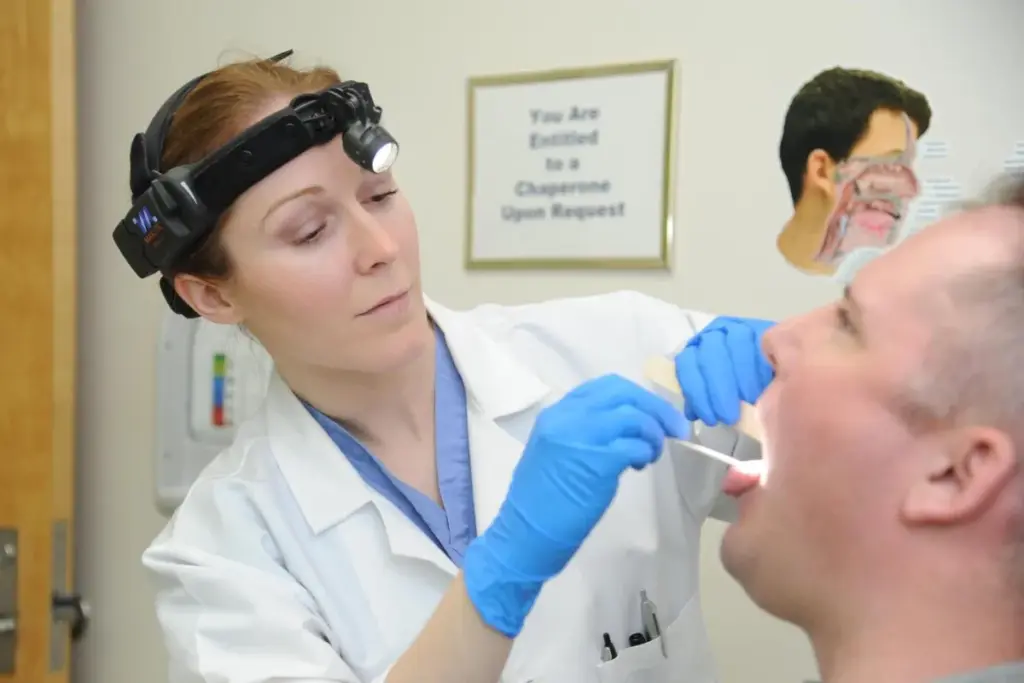
Otolaryngology is key to understanding ENT care and the role of otolaryngologists. It’s a medical field that deals with ear, nose, and throat issues. Otolaryngologists diagnose and treat head and neck disorders.
Definition and Etymology of Otolaryngology
The word “otolaryngology” comes from Greek words. “Otos” means ear, “rhinos” means nose, “larynx” means voice box, and “logos” means study. So, otolaryngology is the study of the ear, nose, and throat.
Otolaryngologists, or ENT doctors, are experts in ear, nose, throat, and head and neck issues. They use both medicine and surgery to treat many conditions. They are vital in healthcare.
Historical Development of ENT Medicine
Otolaryngology started as a medical field in the late 19th century. It has grown with new technology and understanding of ENT disorders. Now, it includes many subspecialties like pediatric otolaryngology and otology.
Key milestones in otolaryngology include:
- The founding of ENT medicine societies
- Advances in diagnostic tools like endoscopy and imaging
- New surgical techniques, including minimally invasive ones
The Comprehensives Scope of an Otolaryngologist
Otolaryngologists handle many conditions, from common to complex. They diagnose and treat ear, nose, and throat issues. They also perform head and neck surgery.
- They diagnose and treat ear infections, hearing loss, and balance problems
- They manage nasal and sinus conditions like sinusitis and nasal polyps
- They treat throat disorders, including tonsillitis and vocal cord issues
- They perform head and neck surgery for cancer and other conditions
Understanding otolaryngology helps patients see the importance of otolaryngologists in their health.
Laryngology: The Science of Voice and Throat
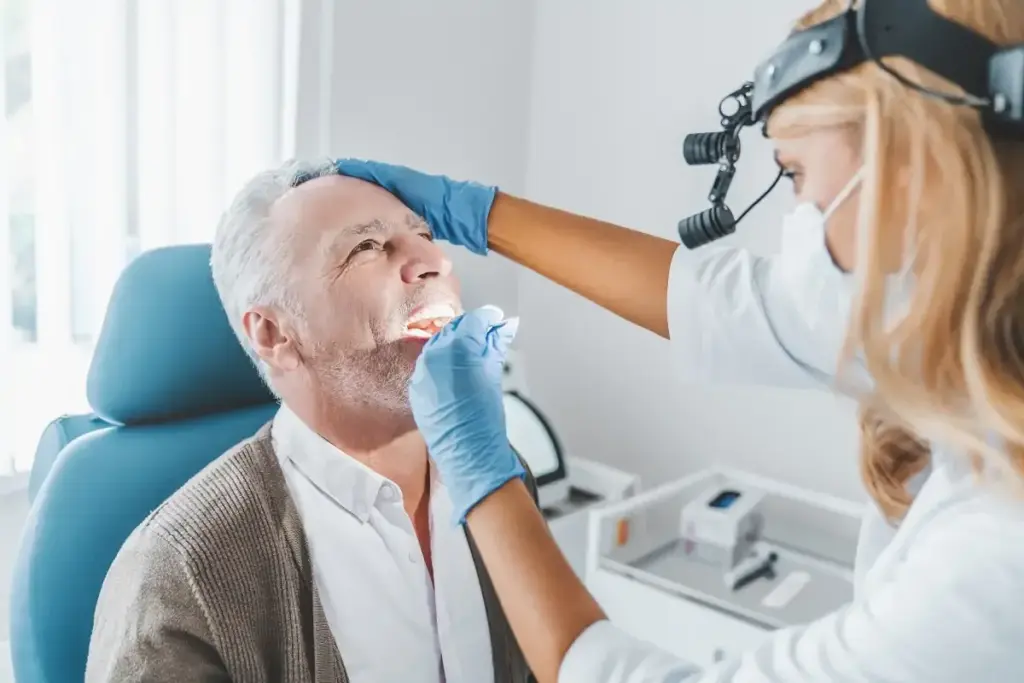
Laryngology is a part of otolaryngology that deals with voice and throat problems. It requires a deep understanding of the larynx and its functions. This field is key in helping patients with voice and throat issues, improving their life quality and communication skills.
Defining Laryngology as a Subspecialty
Laryngology is the study, diagnosis, and treatment of larynx and throat disorders. It’s a specialized area within otolaryngology that needs extra training. This training helps manage complex voice and throat problems.
This field covers many conditions, from simple vocal cord lesions to complex airway issues. Laryngologists handle both medical and surgical treatments. They often work with other specialists to give complete care.
Historical Evolution of Voice Medicine
The study of voice disorders has a long history. From ancient times to now, our understanding and treatment of voice and throat issues have grown a lot. New technology has greatly improved laryngology.
Early treatments were based on experience and observation. The invention of laryngoscopy in the 19th century was a big step. It allowed for direct larynx and vocal cord viewing, leading to better diagnoses and treatments.
The Focused Expertise of Laryngologists
Laryngologists have special knowledge and skills for voice and throat disorders. They can handle both medical and surgical treatments, including advanced phonosurgery.
They are skilled in managing complex cases, like those of singers and actors. Laryngologists work with speech-language pathologists and other professionals. They tailor care to each patient’s needs.
|
Condition |
Description |
Typical Treatment |
|---|---|---|
|
Vocal Cord Nodules |
Benign growths on the vocal cords, often due to vocal abuse |
Voice therapy, potentially surgery |
|
Laryngitis |
Inflammation of the larynx, can be acute or chronic |
Conservative management (rest, hydration), antibiotics if bacterial |
|
Vocal Cord Paralysis |
Paralysis of one or both vocal cords, affecting voice and sometimes breathing |
Varies; may include voice therapy, injection laryngoplasty, or surgery |
Anatomy of the Ear, Nose, Throat, and Voice Box
Learning about the ear, nose, throat, and voice box is key to understanding otolaryngology. These areas work together to help us hear, speak, and stay healthy. They are vital for our senses and communication.
Ear Structure and Function
The ear is a complex organ that helps us hear and balance. It has three parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. Sound goes from the outer ear to the inner ear, where it becomes signals for our brain.
The inner ear also helps us stay balanced. It has the vestibular system.
Key components of the ear include:
- The pinna (outer ear)
- The ear canal
- The eardrum (tympanic membrane)
- The ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes)
- The cochlea and vestibular system
Nasal and Sinus Anatomy
The nasal cavity and sinuses are important for breathing. They filter, warm, and humidify the air. The nasal cavity has mucous membranes to catch dust and bacteria.
The paranasal sinuses produce mucus to keep the nasal passages moist. This helps keep them clean.
The structure of the nasal and sinus area includes:
- The nasal septum, which divides the nasal cavity into two nostrils
- The turbinates, which are long, thin bones that project into the nasal cavity
- The paranasal sinuses, including the frontal, maxillary, ethmoid, and sphenoid sinuses
The Larynx (Voice Box): Medical Structure and Function
The larynx, or voice box, is at the top of the trachea. It’s important for speaking and protects the airway when we swallow. The vocal cords vibrate to make sound when we speak or sing.
The main components of the larynx include:
- The thyroid cartilage, which forms the Adam’s apple
- The vocal cords
- The epiglottis, a flap that separates the trachea from the esophagus during swallowing
Knowing how these areas work is key for diagnosing and treating problems. Otolaryngologists, or ear nose throat specialists, deal with many issues. This includes hearing loss, sinus infections, throat problems, and voice issues.
Key Differences Between Otolaryngology and Laryngology
Exploring ear, nose, and throat (ENT) medicine, we find two important fields: otolaryngology and laryngology. Both are vital for treating head and neck issues. Yet, they specialize in different areas.
Scope of Practice Comparison
Otolaryngology deals with a wide range of ear, nose, throat, and related issues. An otolaryngologist can handle ear infections, hearing loss, and head and neck surgeries. Laryngology, on the other hand, focuses on the larynx (voice box) and throat problems, like voice and swallowing issues.
Otolaryngologists handle many conditions, from ear problems to throat and neck issues. Laryngologists, being otolaryngologists too, specialize in voice, swallowing, and airway disorders.
Generalist vs. Subspecialist Approach
Otolaryngologists are generalists in ENT, treating a wide range of conditions. They are often the first doctors for ENT issues. Laryngologists, as subspecialists, focus on voice and throat disorders. Their expertise is critical for complex voice and swallowing problems.
Patient Populations and Case Types
Otolaryngologists see a broad range of patients, from kids with ear infections to adults with head and neck cancers. Laryngologists focus more on voice disorders, like those affecting singers or voice-dependent professionals. They also manage swallowing and airway issues.
In summary, otolaryngologists and laryngologists are both essential in ENT care. Their expertise and approaches differ. Knowing these differences helps ensure patients get the right care for their needs.
Educational Pathways and Training Requirements
Becoming an otolaryngologist requires a lot of hard work and dedication. You need to understand the ear, nose, throat, and related areas well. This means you need a strong educational base.
Becoming an Otolaryngologist: Education and Certification
To start, you need a bachelor’s degree in a science field. Then, you go to medical school for four years to get an MD or DO. After that, you do a five-year residency in otolaryngology-head and neck surgery.
This residency gives you hands-on experience in treating ENT issues. After finishing your residency, you must get certified by the American Board of Otolaryngology (ABO). You pass a tough exam to show your skills and knowledge.
Key steps in becoming an otolaryngologist:
- Completion of a bachelor’s degree
- Four years of medical school
- Five-year residency in otolaryngology-head and neck surgery
- Certification by the American Board of Otolaryngology
Additional Training for Laryngology Specialization
If you want to specialize in laryngology, you need more training. This includes fellowship programs that focus on voice and swallowing disorders. You must understand the larynx and its functions well.
Fellowship programs in laryngology offer advanced training. You learn about vocal cord disorders, professional voice care, and airway management. These programs help you develop the skills to treat complex laryngeal conditions.
“Specialized training in laryngology is essential for providing high-quality care to patients with voice and swallowing disorders.” – Dr. [Last Name], Laryngologist
Continuing Education and Professional Development
It’s important for otolaryngologists and laryngologists to keep learning. They should attend conferences, workshops, and online courses. This helps them stay up-to-date with new technologies and treatments.
They also need to keep up with the latest research and guidelines in ENT medicine. Joining organizations like the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS) helps. It offers resources, networking, and continuing education.
Benefits of continuing education:
- Staying updated with the latest medical advancements
- Enhancing patient care through new techniques and technologies
- Networking with other professionals in the field
By always learning and growing, otolaryngologists and laryngologists can give the best care to their patients.
Common Conditions Treated by Otolaryngologists
Otolaryngologists, or ear, nose, and throat (ENT) doctors, are key in diagnosing and treating many conditions. They deal with ear, nose, throat, and related issues. Their skills help patients with a wide range of problems.
Ear Disorders: From Infections to Hearing Loss
Ear problems are common for otolaryngologists to treat. These include:
- Ear infections (otitis media)
- Hearing loss (conductive, sensorineural, and mixed)
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Balance disorders (vertigo, dizziness)
ENT specialists use advanced tools to find the cause of these issues. They then create treatment plans. This can include medicine, surgery, or hearing aids.
Nasal and Sinus Conditions
Nasal and sinus problems can really affect someone’s life. Otolaryngologists treat many issues, such as:
- Chronic sinusitis
- Nasal polyps
- Deviated septum
- Allergic rhinitis
Treatment can be medical, like nasal sprays and antibiotics. Or it might need surgery, like balloon sinuplasty or FESS.
General Throat and Neck Pathologies
Otolaryngologists also handle throat and neck issues. These include:
- Tonsillitis and adenoiditis
- Thyroid disorders (nodules, goiter, cancer)
- Neck masses and cysts
- Swallowing disorders (dysphagia)
These problems might need both medicine and surgery. For example, thyroid nodules might get a biopsy. Severe tonsillitis might need a tonsillectomy.
In summary, otolaryngologists are essential in treating many ear, nose, throat, and neck issues. Their training helps them offer the best care for patients with various ENT problems.
Laryngology: Voice Disorders and Treatment Approaches
Laryngology has made big strides in treating voice and swallowing problems. Laryngologists focus on diagnosing and treating voice issues and throat problems. We’ll look at the voice disorders they handle.
Vocal Cord Pathologies
Vocal cord problems like nodules, polyps, and cysts can harm your voice. These often come from too much strain or misuse of the voice. If not treated, they can cause long-term voice issues. Laryngologists use new ways to find these problems and plan treatments, like voice therapy or surgery.
- Vocal cord nodules: benign growths that develop due to repeated strain on the vocal cords.
- Vocal cord polyps: soft, non-cancerous growths that can result from vocal abuse.
- Vocal cord cysts: fluid-filled sacs that can occur on the vocal cords.
Swallowing Disorders (Dysphagia)
Swallowing problems, or dysphagia, can be signs of many issues, like neurological problems or physical abnormalities. Laryngologists work with other doctors to find and treat dysphagia. They use swallowing studies to check how well you swallow.
- Assessment of swallowing function through clinical evaluation and instrumental assessment.
- Development of personalized treatment plans, which may include dietary modifications and swallowing therapy.
- Collaboration with other specialists to address underlying causes of dysphagia.
Airway Management and Breathing Issues
Managing the airway is key in laryngology, for breathing problems like laryngeal stenosis or tracheal blockage. Laryngologists are experts in both surgery and non-surgery to fix airway issues. They make sure patients get the right care to keep their airway safe and working well.
|
Condition |
Symptoms |
Treatment Approaches |
|---|---|---|
|
Vocal Cord Nodules |
Hoarseness, vocal fatigue |
Voice therapy, surgical removal |
|
Dysphagia |
Difficulty swallowing, aspiration |
Swallowing therapy, dietary modifications |
|
Laryngeal Stenosis |
Breathing difficulties, stridor |
Surgical intervention, airway stenting |
Diagnostic Methods and Technologies
Getting a correct diagnosis is key to treating ear, nose, and throat problems. We use many methods and technologies to check and manage these issues.
General ENT Examination Techniques
First, we do a detailed ENT check-up. We use several ways to look at the ear, nose, and throat. These include:
- Otoscopy to see the ear canal and eardrum
- Nasopharyngoscopy to look at the nasal passages and throat
- Laryngoscopy to check the larynx and vocal cords
These checks give us important info about the patient’s health. They help us decide what tests to do next.
Advanced Imaging in Otolaryngology
Advanced imaging is very important for finding and understanding complex ENT problems. We use:
- CT scans to see detailed images of the ear, sinuses, and more
- MRI to find soft tissue issues like tumors or swelling
- DCE-MRI and DWI to help diagnose and manage head and neck cancers
These tools help us accurately find and understand different conditions. They guide our treatment plans and help improve patient results.
Specialized Voice and Swallowing Assessments
For voice or swallowing problems, we do special tests. These include:
- Videostroboscopy to check how the vocal cords work
- Swallowing studies to look at swallowing issues
- Voice assessments to measure and find voice problems
These tests help us find the cause of voice and swallowing issues. This way, we can create specific treatment plans.
Surgical Procedures: Comparing Approaches
Surgery is key in treating patients with otolaryngologists and laryngologists. They use different methods to fix problems. These methods range from simple operations to complex rebuilds.
Common Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgeries
Otolaryngologists do many surgeries for head and neck issues. Some common ones are:
- Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy
- Myringotomy with tube insertion
- Septoplasty and turbinoplasty
- Thyroid surgery
- Neck dissections for cancer treatment
These surgeries need a deep knowledge of the head and neck’s complex anatomy. Thanks to new techniques and tech, patient results have greatly improved.
Specialized Laryngological Procedures
Laryngologists focus on surgeries for the larynx and vocal cords. Some specific procedures are:
- Vocal cord microsurgery
- Laryngeal framework surgery
- Injection laryngoplasty
- Laser surgery for vocal cord lesions
These surgeries need exact techniques and a deep understanding of voice and laryngeal anatomy. Laryngologists often team up with speech-language pathologists to help patients the most.
Minimally Invasive Techniques in Both Fields
Both otolaryngology and laryngology have made big strides with new, less invasive surgeries. These methods often mean:
- Smaller or no cuts
- Less damage to tissue
- Shorter recovery times
- Less pain after surgery
Techniques like endoscopic sinus surgery and transoral robotic surgery (TORS) have changed the game. They let for more detailed and safer surgeries.
As tech keeps getting better, we’ll see even better results for patients. We’ll also see more use of less invasive methods in otolaryngology and laryngology.
When to See an Otolaryngologist vs. a Laryngologist
Knowing when to see an otolaryngologist versus a laryngologist is key for the right care. Both handle ear, nose, and throat problems but focus differently.
Symptoms That Warrant an ENT Doctor Visit
See an otolaryngologist for symptoms like ear pain, hearing loss, or a sore throat. They can handle everything from colds to thyroid disorders.
Some symptoms that need an ENT doctor include:
- Persistent ear pain or discharge
- Hearing loss or tinnitus
- Nasal obstruction or difficulty breathing
- Recurring sinus infections
- A lump or swelling in the neck
When to Seek a Voice Specialist
For voice problems like hoarseness, see a laryngologist. They focus on the larynx and can treat voice issues.
Symptoms needing a voice specialist include:
- Chronic hoarseness or voice changes
- Vocal fatigue or strain
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Breathing difficulties related to the larynx or upper airway
The Referral Process Between Specialties
Your primary care doctor will first assess your symptoms. They’ll then refer you to an otolaryngologist or laryngologist based on your condition.
If an otolaryngologist finds a larynx or voice issue, they’ll refer you to a laryngologist. A laryngologist might refer you to an otolaryngologist or another specialist if needed.
|
Condition |
Specialist |
Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
|
General ENT issues (ear pain, sinus infections) |
Otolaryngologist |
Ear pain, nasal congestion, sore throat |
|
Voice disorders (hoarseness, vocal strain) |
Laryngologist |
Hoarseness, vocal fatigue, difficulty swallowing |
Understanding the differences between otolaryngologists and laryngologists helps you get the right care. Whether it’s a general ENT issue or a voice disorder, these specialists aim for the best outcome.
Patient Experience: What to Expect During Consultations
Knowing what to expect during a consultation can make a big difference. It helps patients feel more at ease with otolaryngologists and laryngologists. Being informed helps them prepare better, making the visit more productive and less stressful.
Initial Evaluation with an Otolaryngologist
At the start, an otolaryngologist will check your ear, nose, and throat health. They’ll ask about your symptoms, past health issues, and any medicines you’re taking. This is the first step in understanding your health.
Next, they’ll do a physical check. This might include looking at your ears, nose, and throat with special tools. They might also order tests like hearing checks or imaging studies, depending on your condition.
|
Evaluation Component |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Medical History |
A thorough review of the patient’s medical background and current symptoms. |
|
Physical Examination |
A visual and manual examination of the ears, nose, and throat. |
|
Diagnostic Tests |
Additional tests such as hearing assessments or imaging studies as needed. |
Specialized Assessment by a Laryngologist
A laryngologist specializes in the larynx (voice box) and voice issues. They focus on voice problems, swallowing disorders, or airway issues. Their assessment is designed to address these specific concerns.
Their evaluation might include a detailed look at the larynx with a scope. They might also do voice tests to check the quality and characteristics of your voice.
Follow-up Care and Management
After the initial check or specialized assessment, follow-up care is key. Otolaryngologists and laryngologists work with patients to create a treatment plan. This might include medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery.
Follow-up visits are set to track progress and adjust the plan if needed. They also address any concerns or questions patients have. Good follow-up care ensures patients get the support they need throughout their treatment.
Understanding what to expect during consultations can make patients feel more comfortable and prepared. This leads to a better experience overall.
The Interdisciplinary Nature of Ear, Nose, and Throat Medicine
Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) medicine needs a team effort. It’s complex, so many healthcare experts work together. This team approach helps patients get the care they need.
Collaboration with Speech-Language Pathologists
Speech-language pathologists (SLPs) are key in treating voice and swallowing issues. They work with us to create treatment plans for each patient. For example, they help improve voice quality in cases of vocal cord paralysis.
A study in the Journal of Voice showed voice therapy helps patients with voice disorders. It greatly improves their vocal function.
“Voice therapy can be an effective treatment for patients with voice disorders, improving their quality of life.”
— Dr. Katherine Verdolini, Journal of Voice
Partnerships with Neurology and Pulmonology
Neurologists and pulmonologists are vital for patients with ENT issues linked to the brain or lungs. For instance, sleep apnea patients need pulmonologists to manage their condition. Neurologists help diagnose and treat conditions like vocal cord paralysis.
|
Specialty |
Role in ENT Care |
Example Conditions |
|---|---|---|
|
Neurology |
Diagnosing and treating neurological disorders affecting ENT |
Vocal cord paralysis, tinnitus |
|
Pulmonology |
Managing respiratory conditions related to ENT |
Sleep apnea, chronic cough |
The Role of Allied Health Professionals
Allied health professionals, like audiologists and nurse practitioners, are essential. They offer important services like hearing tests and patient education. We count on them for a complete care plan.
Audiologists are key in diagnosing and treating hearing loss. They do hearing tests and suggest treatments.
In conclusion, ENT medicine is all about teamwork. By working together, we ensure our patients get the best care possible.
Conclusion
It’s important to know the difference between otolaryngology and laryngology for those with ear, nose, throat, and voice problems. Otolaryngology covers a wide range of treatments, from simple to complex surgeries. An ENT specialist can handle everything from colds to major surgeries.
Laryngology is a part of otolaryngology that deals with voice issues. Knowing what otolaryngology meaning and laryngology offer helps patients make better health choices. It’s key to know when to see an ENT specialist or a laryngologist for different health issues.
We aim to help patients make informed decisions about their health. By choosing the right specialist, they get treatments that fit their needs. This can greatly improve their life quality.
FAQ
What is the difference between an otolaryngologist and a laryngologist?
An otolaryngologist treats many ear, nose, throat, and related issues. A laryngologist focuses on the larynx (voice box) and throat problems.
What does ENT stand for in medical terms?
ENT stands for Ear, Nose, and Throat. It’s also known as otolaryngology.
What kind of conditions do otolaryngologists treat?
Otolaryngologists handle many issues. These include ear infections, hearing loss, and nasal and sinus problems. They also treat throat and neck issues.
What is laryngology, and what conditions do laryngologists treat?
Laryngology is a part of otolaryngology that deals with the larynx and throat. Laryngologists treat voice problems, swallowing issues, and breathing problems.
How do I know whether to see an otolaryngologist or a laryngologist?
See an otolaryngologist for general ENT issues. For voice or throat problems, see a laryngologist. Your doctor can help decide.
What can I expect during my initial consultation with an otolaryngologist or laryngologist?
Expect a thorough check-up and a detailed medical history. They might do tests to find out what’s wrong. Then, they’ll create a treatment plan for you.
What diagnostic methods and technologies are used in otolaryngology and laryngology?
They use general exams, MRI and CT scans, and special tests for voice and swallowing issues.
Are surgical procedures common in otolaryngology and laryngology?
Yes, they do many surgeries. These include common and specialized procedures. They also use new, less invasive methods.
How do otolaryngologists and laryngologists collaborate with other healthcare professionals?
They work with speech-language pathologists, neurologists, and others. This team approach helps patients with complex conditions.
What is the educational pathway to becoming an otolaryngologist or laryngologist?
To be an otolaryngologist, you need medical school and a residency. For laryngology, there’s more specialized training. Both need ongoing education.
Reference
National Institutes of Health. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/how-are-hearing-voice-and-balance-disorders-treated https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/how-are-hearing-voice-and-balance-disorders-treated