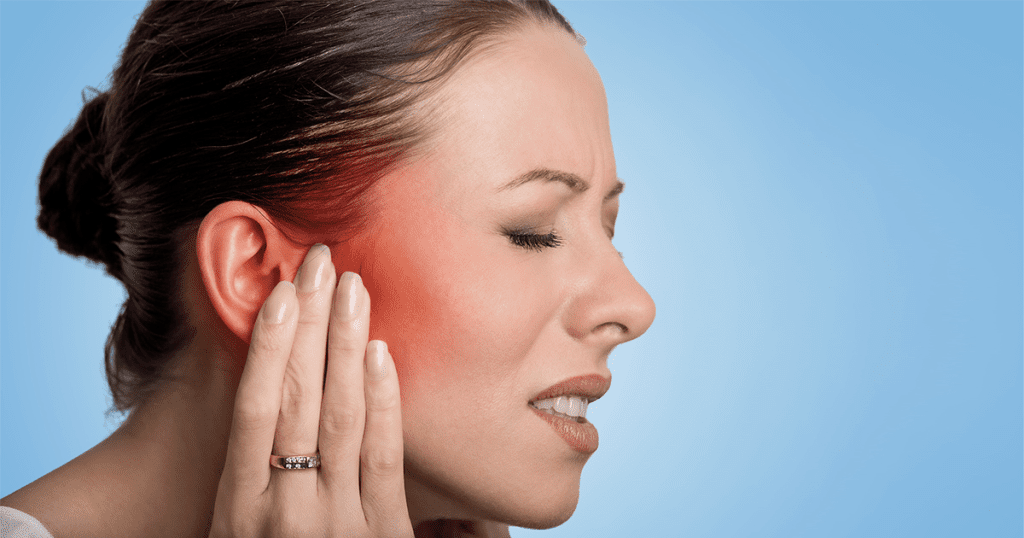
An ear infection can cause more than just discomfort. It can lead to jaw pain and serious complications. The ear and jaw are close, making it easy for an infection to spread.
A Mount Nittany Health Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) provider, says, “Outer ear infections, such as otitis externa, often cause pain that spreads to the jaw area.” This shows why it’s key to understand the link between ear infections and jaw pain.
It’s important to know the signs of an ear infection, like otitis externa symptoms. If you have jaw pain with an ear infection, getting medical help is a must.
Key Takeaways
- Ear infections can cause jaw pain due to anatomical proximity.
- Outer ear infections, like otitis externa, can radiate pain to the jaw area.
- Understanding the connection between ear infections and jaw pain is key.
- Knowing the symptoms of ear infections is vital for timely medical care.
- Coordinated medical care is needed to treat ear infections and jaw pain.
The Anatomical Connection Between Ear and Jaw
The ear and jaw are connected through nerves and bones. The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) links the jaw to the skull. It’s near the ear, which helps explain how infections can spread between them.
Shared Nerve Pathways
The trigeminal nerve runs to both the TMJ and the ear. This nerve connection is why TMJ problems can cause ear pain. And ear issues can also lead to jaw pain.
This nerve’s role in both areas shows how closely they’re linked. When an infection happens, the TMJ’s closeness to the ear and shared nerves can spread it. This can cause jaw hurts and ear pain.
Proximity of Structures
The TMJ is right next to the ear canal and the middle ear. This close location means infections in the ear can easily reach the TMJ. And vice versa, because of their direct connection.
Developmental Relationship Between TMJ and Middle Ear
In the womb, the TMJ and middle ear grow together. This early connection explains why infections in one can affect the other. It shows how closely these areas are linked.
Knowing how the ear and jaw are connected is key to treating their problems. Their shared nerves and close location mean we must look at both areas when dealing with ear and jaw pain.
Types of Outer Ear Infections That Can Spread to the Jaw
Outer ear infections can be more than just a nuisance; they can sometimes lead to complications involving the jaw. The outer ear is prone to various infections. Understanding these conditions is key to recognizing their spread to other areas, like the jaw.
Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear)
Otitis externa, commonly known as swimmer’s ear, is an infection of the outer ear canal. It’s often caused by water remaining in the ear canal, creating a moist environment that fosters bacterial or fungal growth. While typically not serious, otitis externa can cause significant discomfort. In some cases, the infection can spread to surrounding tissues, including those in the jaw.
Symptoms of otitis externa include itching, redness, and discomfort in the ear canal. It also causes pain when pulling on the outer ear. If the infection spreads, it can lead to jaw pain, making chewing or opening the mouth wide uncomfortable.
Malignant Otitis Externa
Malignant otitis externa is a more severe and potentially life-threatening infection of the outer ear. It predominantly affects individuals with diabetes or those who are immunocompromised. This aggressive infection can spread to the bones of the jaw and face, leading to severe complications. Malignant otitis externa requires prompt medical attention to prevent serious outcomes.
The symptoms of malignant otitis externa include severe ear pain, discharge, and swelling around the ear. If the infection spreads to the jaw, it can cause pain and difficulty when chewing. It also causes swelling in the face.
Middle Ear Infections (Otitis Media)
Otitis media, or middle ear infection, occurs when fluid builds up in the middle ear. This creates an environment conducive to bacterial or viral growth. While otitis media is more commonly associated with children, it can also affect adults. In some cases, the infection can spread to nearby structures, including the jaw.
Symptoms of otitis media include ear pain, fever, and hearing loss. If the infection spreads to the jaw, it can cause pain or discomfort. This is often felt when chewing or swallowing.
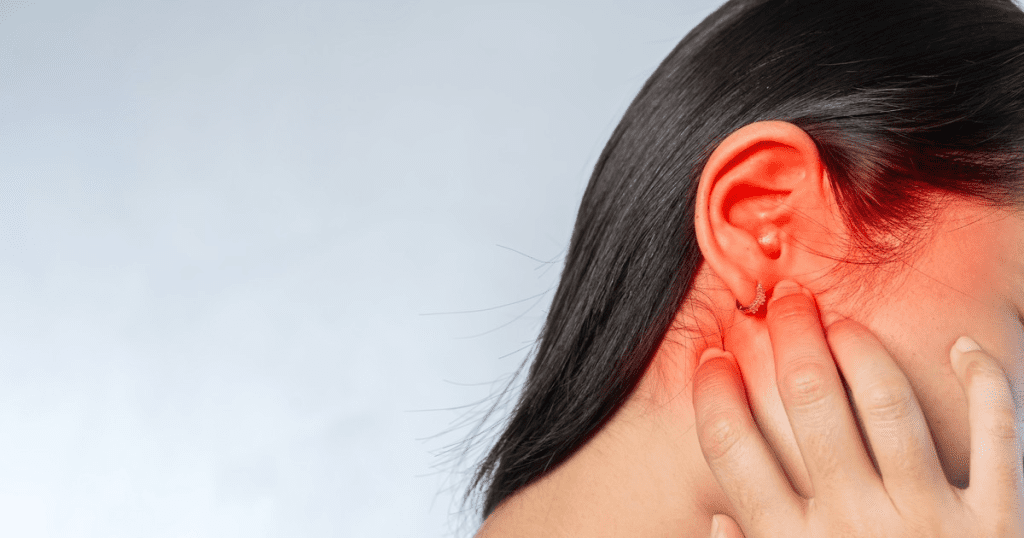

In conclusion, various types of outer ear infections, including otitis externa and malignant otitis externa, as well as middle ear infections like otitis media, have the ability to spread to the jaw. This can cause pain and other complications. Understanding these conditions is key to recognizing their symptoms and seeking appropriate medical care.
How Infections Spread From the Ear to Jaw Tissues
Ear infections can cause jaw pain because of how close the ear and jaw are. Infections can move from the ear to the jaw through different ways.
Inflammatory Process Progression
An infection in the ear can start an inflammatory process. This leads to swelling and pain in the area, which can spread to the jaw. The body’s fight against infection releases chemicals that cause more inflammation.
This inflammation can affect the TMJ. As the infection gets worse, it can cause ear pain that radiates to the jaw. This pain gets worse when you chew or open your mouth wide.
Formation of Abscesses
In severe cases, an infection can create abscesses around the ear. An abscess is a pocket of pus that causes a lot of pain and swelling. If an abscess forms near the TMJ, it can make jaw pain and mouth opening hard.
Infection Pathways to the Temporomandibular Joint
The TMJ is near the ear, and infections can reach it through different ways. The ear and TMJ are close, and they share nerve pathways. This is why ear infections can cause jaw pain.
Understanding how infections move is key to treating them. Quick medical help is needed to avoid lasting damage to the jaw and surrounding areas.
Recognizing Symptoms When an Outer Ear Infection Affects the Jaw
It’s important to know the signs of an outer ear infection that spreads to the jaw. This can happen in different ways, so being aware is key. Knowing the symptoms helps get the right treatment quickly.
Ear Pain That Radiates to the Jaw
Ear pain that radiates to the jaw is a common symptom. This pain can be sharp or dull. It often means the infection is moving beyond the ear. For more info, check out Mount Nittany Health.
Difficulty Opening the Mouth (Trismus)
Trismus, or trouble opening the mouth, can happen if the infection reaches the jaw. This makes simple tasks like eating and talking hard.
Pain While Chewing
Pain while chewing is another symptom. It’s linked to the TMJ or tissues around it. This pain can be a sign of infection in these areas.
Swelling in the Ear and Jaw Area
Swelling in the ear and jaw is a clear sign. It can be sore and might mean there’s an abscess or serious infection.
Spotting these symptoms early is vital to avoid worse problems. If you see these signs, get medical help right away.
Treatment Options for Ear Infections That Spread to the Jaw
Ear infections that spread to the jaw need quick and effective treatment. This is to prevent more problems. The treatment depends on the infection type, its severity, and the patient’s health.
Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotics are usually the first treatment for these infections. The right antibiotic is chosen based on the infection cause and severity. Starting antibiotics quickly can greatly help and lower the risk of more issues.
For mild to moderate infections, oral antibiotics are often given. But, for severe cases or high risk, intravenous antibiotics might be needed. It’s important to finish all antibiotics as directed to clear the infection fully.
Surgical Interventions
When infections cause abscesses, surgery might be needed. Surgery to drain abscesses can bring quick relief and stop the infection from spreading more.
Surgery is also an option for those not improving with antibiotics or with serious tissue damage. Surgery aims to remove infected tissue, drain abscesses, and fix function.
Pain Management Strategies
Managing pain is key in treating these infections. Pain medicines can reduce discomfort and improve life quality.
There are many pain management options. These include over-the-counter and prescription drugs, and alternative therapies. The right pain management depends on pain level and medical history.
Specialized Treatment for Malignant Otitis Externa
Malignant otitis externa is a serious and dangerous condition. It needs aggressive antibiotics and close monitoring to treat well.
“Malignant otitis externa demands a multidisciplinary approach to treatment, involving otolaryngologists, infectious disease specialists, and sometimes, surgeons.”
Expert Opinion
In severe cases, surgery to remove infected tissue might be needed. Quick and effective treatment is key for better outcomes in malignant otitis externa.
Conclusion
It’s important to know how ear infections and jaw pain are connected. This knowledge helps in managing and preventing serious issues.
Ear infections can move to the jaw, leading to pain and serious problems if not treated. This is why it’s key to act fast.
Getting a quick diagnosis and right treatment is vital. It stops the infection from spreading and relieves jaw pain.
Understanding the link between ear infections and jaw pain helps people get help early. This reduces the chance of serious problems and improves treatment results.
Preventing ear infections is also key. Good ear care and quick treatment of infections can help avoid jaw pain and other complications.
FAQ’s:
What are the symptoms of an outer ear infection that can spread to the jaw?
Symptoms include ear pain that spreads to the jaw. You might also have trouble opening your mouth or chewing. Swelling in the ear and jaw area is another sign.
Can an ear infection cause jaw pain?
Yes, an ear infection can cause jaw pain. This happens because the ear and jaw share nerve pathways. They are also close to each other.
What is otitis externa, and how does it relate to jaw pain?
Otitis externa, or swimmer’s ear, is an outer ear infection. It can cause pain that goes to the jaw. It’s often caused by bacteria or fungi.
What is malignant otitis externa, and who is at risk?
Malignant otitis externa is a severe outer ear infection. It can spread to the jaw and other tissues. People with diabetes are more at risk.
How do infections spread from the ear to jaw tissues?
Infections spread through inflammation and abscesses. They also go through pathways to the TMJ.
What are the treatment options for ear infections that spread to the jaw?
Treatment includes antibiotics and surgery. Pain management and special care for malignant otitis externa are also options.
Why is prompt diagnosis and treatment important for ear infections that spread to the jaw?
Quick diagnosis and treatment prevent complications. This includes abscesses and TMJ damage. It also improves outcomes.
Can a swollen ear canal be a sign of an ear infection that can spread to the jaw?
Yes, a swollen ear canal can mean an outer ear infection. This infection can spread to the jaw.
Is jaw pain a common symptom of an ear infection?
Yes, jaw pain is a symptom of an ear infection. This is true if the infection spreads to the surrounding tissues.
How does the trigeminal nerve contribute to referred pain between the ear and jaw?
The trigeminal nerve connects the TMJ and ear. This connection allows ear infections to cause jaw pain.
References
- Medina-Blasini, Y. (2023). Otitis Externa. In StatPearls. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved fromhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556055/
- Mardinger, O., et al. (2003). Temporomandibular joint involvement in malignant external otitis. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology, 96(4), 456-461. Retrieved fromhttps://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14561963/

































