As a parent, knowing about paediatric leukaemia is key for early action. Childhood leukemia is the top cancer in kids, making up almost a third of all cases. We’ll look at eight important facts about paediatric leukaemia in children — including its occurrence, signs, how it’s found, and treatment choices. At Liv Hospital, we help parents understand their child’s fight against paediatric leukaemia and support them through every stage of care.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the risks and symptoms of pediatric leukemia.
- The importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
- Overview of treatment options available.
- The role of Liv Hospital in treating childhood leukemia.
- Support available for families facing leukemia diagnosis.
What Parents Should Know About Blood Cancer in Children
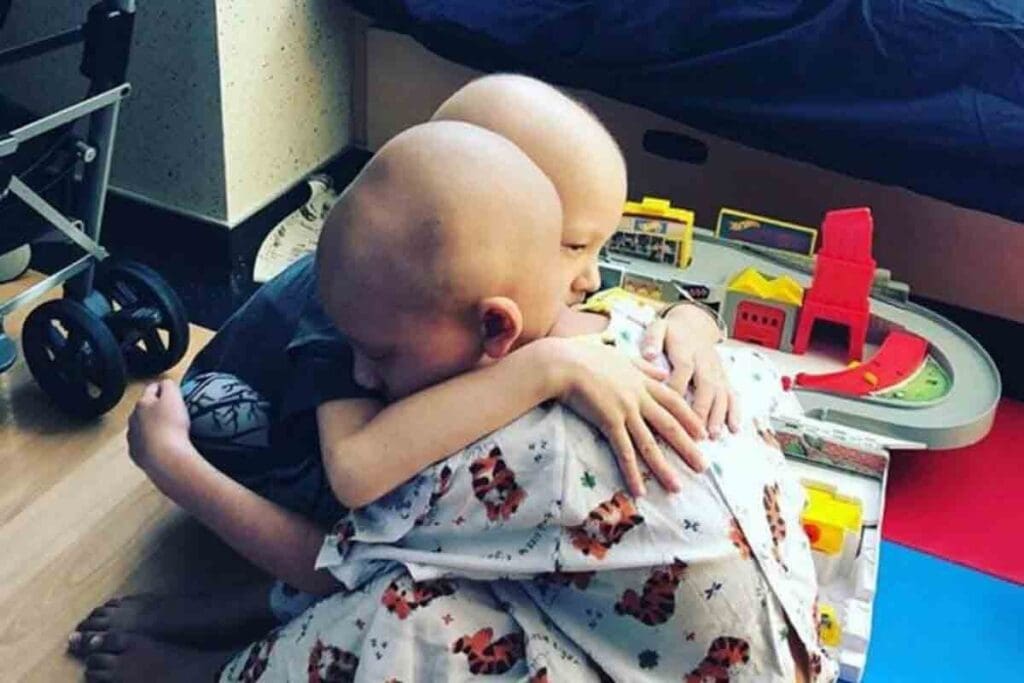
Parents are key in spotting early signs of leukemia in kids. This can greatly affect treatment success. Blood cancer, like leukemia, affects not just the child but the whole family.
The Impact of Childhood Cancer on Families
Childhood cancer, like leukemia, deeply affects families. It can be overwhelming, touching on emotions, money, and social life. Knowing about leukemia in kids is the first step to handling this tough journey.
Leukemia in kids is a big issue worldwide. In 2021, about 2.9 per 100,000 kids got leukemia. This means nearly 59,000 kids worldwide got leukemia that year. These numbers show why we need to be aware and catch it early.
Why Understanding Leukemia Matters for Parents
Parents need to understand leukemia to spot symptoms early. Symptoms of childhood ALL include not enough red blood cells and platelets, and too many white blood cells that don’t work right. Common signs are fever, easy bruising or bleeding, and feeling very tired.
| Symptom | Description | Action |
| Fever | High temperature, often without an obvious infection | Consult a doctor if persistent or high |
| Easy Bruising or Bleeding | Unexplained bruises or bleeding gums | Seek medical attention if unusual or frequent |
| Fatigue | Unusual tiredness or lack of energy | Discuss with a healthcare provider if persistent |
By knowing about leukemia, parents can help a lot in their child’s treatment. Spotting it early and understanding leukemia can lead to better results. It also helps families get the support they need during this hard time.
Fact 1: Pediatric Leukemia Is the Most Common Type of Childhood Cancer

Leukemia is the top cancer in kids, worrying many parents. It’s a big deal, making up almost a third of all childhood cancers. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the main type, found in about 75 percent of cases.
Representing Nearly One-Third of All Childhood Cancers
Leukemia is a big health problem for kids all over the world. It’s important for parents and caregivers to know that leukemia is not just one disease. It’s a group of cancers affecting the blood and bone marrow. This high rate of leukemia in kids shows we need to spread awareness and catch it early.
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): 75% of Cases
ALL is the leading type of leukemia in kids, making up 75 percent of cases. It happens when too many stem cells turn into lymphoblasts that don’t grow into B or T lymphocytes. These leukemia cells can’t fight off infections well, making kids more likely to get sick.
Other Types of Childhood Leukemia
While ALL is the most common, other types like acute myeloid leukemia (AML) also affect kids. Knowing about the different types of leukemia is key for the right treatment. Each type needs its own approach.
Getting a leukemia diagnosis can be tough for families. But, thanks to medical progress, kids’ chances of beating leukemia are better than ever. It’s vital for parents to know the signs and symptoms to get help quickly.
Fact 2: Global Incidence Rates and Recent Statistics
Recent data on childhood leukemia shows its global impact. Knowing how often it happens helps us plan better for health care and resources.
2.9 Cases per 100,000 Children Worldwide
Every year, about 2.9 out of 100,000 kids get leukemia. This means a lot of new cases happen all over the world.
Global Incidence Rate: 2.9 per 100,000 children
Nearly 59,000 New Cases Reported in 2021
In 2021, almost 59,000 kids got leukemia. This shows we need to keep working on treatments and research.
Annual New Cases: Approximately 59,000
Tracking Changes in Incidence Over Time
By watching how often leukemia happens, we learn more. This helps us find out what causes it and how to stop it.
| Year | Global Incidence Rate (per 100,000) | New Cases Reported |
| 2015 | 2.8 | 55,000 |
| 2020 | 2.85 | 57,500 |
| 2021 | 2.9 | 59,000 |
We don’t always know why leukemia starts, but some things can make it more likely. Looking at the numbers helps us understand how big a problem it is.
Fact 3: Recognizing the Warning Signs of Leukemia in Kids
It’s vital to spot leukemia signs in kids early. This helps in getting the right treatment fast. Leukemia symptoms can look like other common childhood illnesses. So, knowing the specific signs of leukemia is key for parents.
Physical Symptoms That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Children with leukemia might show:
- persistent fever
- easy bruising or bleeding
- pale skin
- bone or joint pain
- painless lumps in the neck, underarm, stomach, or groin
These signs come from abnormal white blood cells. They can cause anemia, infections, and bleeding problems. A study onMedical News Today talks about these symptoms.
Behavioral and Energy Changes
Leukemia can also affect a child’s mood and energy. Look out for:
- weakness or fatigue
- loss of appetite
- irritability
These changes might seem small but are important signs.
Differentiating from Common Childhood Illnesses
It’s hard to tell leukemia symptoms from other childhood illnesses. But, if symptoms keep coming back or seem unusual, it could be leukemia. For example, a fever that won’t go away with usual treatments might be a sign.
Knowing these signs and talking to doctors can help parents catch leukemia early. This is key for effective treatment.
Fact 4: The Diagnosis Process for Childhood Leukemia
Learning about the diagnosis process for childhood leukemia can make parents feel more confident. It involves important tests to find the right treatment.
Initial Screening and Blood Tests
The first step is usually blood tests and screening. A complete blood count (CBC) is often the first test. It shows the levels of different blood cells. If the results are off, it might mean leukemia.
Blood tests are key in finding leukemia. They look for abnormal white blood cell counts. Sometimes, leukemia cells can be found in the blood itself.
Bone Marrow Biopsy and Other Diagnostic Procedures
If blood tests show leukemia, a bone marrow aspiration and biopsy follows. This involves taking a bone marrow sample from the hipbone. The sample is then checked for leukemia cells.
Other tests might include a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) to check the cerebrospinal fluid. Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans are also used. They help see if leukemia has spread.
Understanding Your Child’s Diagnosis
Getting a leukemia diagnosis can be tough for parents. It’s important to know the type of leukemia, its stage, and your child’s overall health. This helps in making treatment decisions.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Measures levels of different blood cells |
| Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy | Examines bone marrow for leukemia cells |
| Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap) | Checks for leukemia cells in cerebrospinal fluid |
| Imaging Tests (X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans) | Assesses if leukemia has spread to other parts of the body |
Knowing about the diagnosis and tests can help parents feel more in control. It prepares them for the treatment journey ahead.
Fact 5: Treatment Approaches for Pediatric Leukemia
Treatment for pediatric leukemia has seen big improvements, giving hope to families. We now better understand leukemia, leading to better treatments.
Standard Treatment Protocols
For pediatric leukemia, treatment often combines different therapies. Chemotherapy is key, aiming to kill cancer cells. We also use risk stratification to tailor treatment to each child’s risk level.
The treatment plan has several phases. The first phase, induction, aims to reduce leukemia cells. Consolidation therapy then targets any remaining cells. Maintenance therapy helps keep the cancer from coming back.
Stem Cell Transplantation
Stem cell transplantation is a major treatment for some kids with leukemia. It replaces bad bone marrow with healthy cells, either from the patient or a donor.
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation is common for kids. It offers a chance for a cure by fighting leukemia. We match donors carefully to avoid complications.
Emerging Therapies and Clinical Trials
New treatments and trials are changing how we treat pediatric leukemia. Immunotherapy is showing great promise. CAR-T cell therapy, a type of immunotherapy, is very effective against certain types of leukemia.
We’re also looking into targeted therapies that only harm cancer cells. Clinical trials help us see if these new treatments are safe and work well. They give kids with leukemia access to new, possibly better treatments.
We’re working hard to make treatments better and safer for kids with leukemia. Our goal is to increase survival rates and improve their quality of life.
Fact 6: Survival Rates Have Improved to Over 85% in Developed Countries
The way we treat pediatric leukemia has changed a lot. Now, over 85% of kids in developed countries survive. This big jump is thanks to lots of research, new treatments, and a better understanding of the disease.
Historical Perspective on Treatment Outcomes
Long ago, leukemia was almost always fatal. But now, thanks to modern medicine and targeted treatments, kids have a much better chance. We now focus on long-term survival and improving their quality of life.
Back in the 1960s, the five-year survival rate for kids with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) was under 10%. But today, thanks to better chemotherapy, radiation, and bone marrow transplants, it’s over 90% in some studies.
Current Five-Year Survival Statistics
Today, over 85% of kids with leukemia survive for five years in developed countries. This shows how far we’ve come in medical research and treatment. The survival rates differ based on the type of leukemia, with ALL having a higher rate than Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML).
| Type of Leukemia | Five-Year Survival Rate |
| Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) | 85-90% |
| Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) | 60-70% |
Factors That Influence Prognosis
Many things can affect how well a child with leukemia will do. These include their age, the number of white blood cells at diagnosis, genetic issues, and how well they respond to treatment.
- Age: Kids between 1 and 9 tend to do better.
- White Blood Cell Count: A lower count at diagnosis means a better chance.
- Genetic Factors: Some genetic issues are better than others.
- Response to Treatment: Quick response to treatment is key.
Knowing these factors helps doctors create the best treatment plans for each child. This can lead to even better survival rates and outcomes.
Fact 7: Infant Leukemia Presents Unique Challenges
Leukemia in infants is a serious issue that needs special care. It is found in babies under one year. The treatment and outlook for these young patients differ from older kids.
Higher Risk Factors for Babies Under One Year
Babies under one with leukemia face higher risk factors. Their immune systems are not fully developed. The disease is also very aggressive in this age group.
Research shows that some genetic mutations in infants may lead to leukemia. These mutations could be present from birth. It’s important to watch for signs like unusual bruising, fever, and lethargy. This ensures quick medical help.
Specialized Treatment Approaches for Infants
Treatment for infant leukemia is tailored to the specific needs of the baby. This includes their age, health, and the leukemia’s characteristics. Chemotherapy is the main treatment, requiring intensive care and close monitoring.
In some cases, stem cell transplantation might be considered. A team of specialists works together to create the best treatment plan. This ensures the best possible outcome for the infant.
Support Resources for Families of Infants with Leukemia
Families with infant leukemia need a lot of support. This includes emotional, financial, and medical help. Support groups and counseling are key in helping families cope.
Also, access to specialized healthcare services and clinical trials is vital. It gives families more treatment options and hope. We are dedicated to providing top-notch healthcare and support for international patients.
Fact 8: Geographic and Socioeconomic Disparities in Outcomes
Geographic and socioeconomic factors greatly affect childhood leukemia outcomes worldwide. Even with better treatments, some kids in certain areas don’t get the care they need. This is because of differences in healthcare access and quality.
Developed vs. Low and Middle-Income Countries
In developed countries, kids with leukemia often do better than those in poorer areas. This is because of better healthcare, more advanced treatments, and higher living standards.
- Developed Countries: High survival rates thanks to top-notch healthcare and treatments.
- Low and Middle-Income Countries: Poorer outcomes due to less access to healthcare and resources.
Access to Care Challenges
In low- and middle-income countries, getting the care kids need is hard. This is because of:
- Not enough doctors and specialists.
- Bad healthcare facilities.
- Money problems that stop families from getting treatment.
To fix these issues, we need to improve healthcare, train more doctors, and help families pay for treatment.
Global Initiatives Addressing Treatment Disparities
Many global efforts aim to fix the treatment gaps for childhood leukemia. These include:
- Working together to share knowledge and resources.
- Training doctors in poorer countries.
- Getting more medicines and treatments to those who need them.
By joining forces, we can make sure all kids get the care they deserve. This way, every child, no matter where they live or their family’s income, can fight leukemia and win.
Conclusion: Navigating Your Child’s Journey with Knowledge and Hope
Dealing with a child’s leukemia journey needs a full approach. This includes medical care, emotional support, and access to good resources. Knowing the facts about pediatric leukemia helps parents support their child better and make informed care decisions.
Families facing childhood leukemia can find help through special organizations. These groups offer counseling, financial aid, and help with the healthcare system. Having access to these resources is key for families dealing with a leukemia diagnosis.
We urge families to look for these resources and stay updated on new leukemia treatments. With knowledge and hope, families can handle the tough parts of childhood cancer. Working with healthcare teams and support groups ensures a child gets the best care and support on their journey.
FAQ
What is pediatric leukemia?
Pediatric leukemia is a cancer that affects kids’ blood and bone marrow. It’s the most common childhood cancer. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is the most common type, making up about 75% of cases.
What are the symptoms of leukemia in children?
Symptoms include pale skin, fatigue, weight loss, and frequent infections. Kids might also act irritable or tired. Knowing these signs helps spot leukemia early.
How is pediatric leukemia diagnosed?
Diagnosing leukemia involves several steps. First, there’s an initial screening, then blood tests and a bone marrow biopsy. Understanding this process helps parents support their child.
What are the treatment options for pediatric leukemia?
Treatments include standard protocols, stem cell transplants, and new therapies. The right treatment depends on the leukemia type and the child’s health.
What is the prognosis for children with leukemia?
Survival rates for leukemia have greatly improved, over 85% in developed countries. The prognosis depends on the leukemia type, age, and treatment response.
How does infant leukemia differ from other types of pediatric leukemia?
Infant leukemia faces unique challenges due to the child’s age and developing body. It needs special treatments and care. Families often need extra support.
Are there disparities in leukemia outcomes globally?
Yes, there are disparities in care and outcomes worldwide. Developed countries have better access and outcomes. Global efforts aim to close these gaps.
What support is available for families dealing with pediatric leukemia?
Families can get help from healthcare providers and organizations focused on childhood cancer. It’s important to reach out for support during this challenging time.
What is the global incidence of pediatric leukemia?
Pediatric leukemia affects about 2.9 children per 100,000 worldwide. In 2021, nearly 59,000 new cases were reported. Understanding this helps with public health planning.
Can leukemia in children be cured?
Yes, many kids with leukemia can be cured thanks to better treatments. The five-year survival rates have significantly improved, giving families hope.
Reference
- National Cancer Institute. (2024). Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version. https://www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/hp/child-all-treatment-pdq



































