What is Pediatric Cardiology?
Pediatric Cardiology: Understanding Heart Care for Children Pediatric cardiology focuses on diagnosing, treating, and caring for heart conditions in infants, children, and adolescents. If you’re a parent seeking trustworthy information about children’s heart health, understanding the basics of pediatric cardiology can help you make confident decisions. Common concerns include heart murmurs, congenital heart defects, chest pain, palpitations, fainting episodes, and shortness of breath during activity. Pediatric cardiologists use child focused tests and treatments to ensure safe, effective care tailored to growing bodies.
Key diagnostic tests:
• ECG (electrocardiogram): Measures electrical activity to detect rhythm problems, conduction issues, or signs of heart muscle strain.
• Echocardiogram (cardiac ultrasound): Visualizes the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow to identify structural abnormalities.

• Holter monitor and event recorder: Portable devices that track heart rhythm for one or two days or longer to help find the cause of occasional palpitations or fainting.
• Exercise stress test: Assesses heart response to physical activity, helpful for chest pain or exercise intolerance.
• Pulse oximetry and blood pressure checks: Quick screenings that provide vital information about oxygenation and circulation.

Common treatments and care plans:
- Observation and lifestyle guidance: Many innocent heart murmurs simply require monitoring.
- Medications: For rhythm control, blood pressure management, or heart function support when necessary.
- Interventional procedures: Minimally invasive catheter based treatments for certain defects (see the section below).
- Surgery referral: For complex congenital conditions when surgical repair is indicated.
- Follow up care: Regular evaluations to track growth, activity tolerance, and heart function over time.
- Pediatric Interventional Cardiology: Minimally Invasive Options Pediatric interventional cardiology uses catheter based techniques to diagnose and treat heart conditions without open surgery. Through a small puncture (often in the groin), a thin catheter is advanced into the heart using imaging guidance.
Common minimally invasive procedures include:
- Closure of certain holes (such as atrial septal defects or patent ductus arteriosus) with device implants.
- Balloon dilation (valvuloplasty) to open narrowed heart valves.
- Stent placement to support narrowed vessels.
- Diagnostic cardiac catheterization to measure pressures and oxygen levels, guiding tailored treatment plans.
Benefits:
- Smaller incisions and faster recovery times
- Minimal scarring
- Reduced hospital stays
- Less pain and quicker return to normal activity
Pediatric Cardiology Specialists: When to See a Pediatric Heart Doctor ?

- Your child has persistent chest pain, especially with exercise
- There are episodes of fainting (syncope), dizziness, or unexplained fatigue
- You notice a rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- Your pediatrician hears a heart murmur or suspects a structural abnormality
- There’s cyanosis (bluish discoloration), poor feeding in infants, or failure to thrive
- A screening indicates elevated blood pressure or abnormal oxygen saturation
- There is a family history of congenital heart disease or significant arrhythmia
- Appointments generally include a detailed history and physical exam, along with tests such as an ECG and echocardiogram. Most visits are reassuring, but when an issue is identified, pediatric cardiologists create personalized plans that take into account age, growth, and activity goals.
Pediatric Cardiology Care: From Newborns to Teens Heart care changes as children grow:
Preschool and school age: Monitoring for murmurs, exercise tolerance, and any symptoms such as shortness of breath or fatigue with play. Guidance on safe sports participation is common.
Teens and adolescents: Evaluation of chest pain, palpitations, and exercise-induced symptoms. Counseling on healthy habits, hydration, and recognizing warning signs becomes a key part of care.
Pediatric Cardiology and Congenital Heart Disease: A Parent’s Guide
Congenital heart disease (CHD) includes structural differences present at birth, from small holes that may close on their own to complex defects requiring intervention. Pediatric cardiologists classify and manage CHD with individualized plans.
What parents can expect:
• Early detection: Newborn screening and prenatal ultrasounds can identify many conditions.
• Diagnostic clarity: Echocardiograms describe the anatomy and function of the heart; cardiac catheterization may provide additional detail when needed.
• Tailored treatment: Options range from monitoring and medication to catheter based procedures and surgery for more complex cases.
• Long term follow up: As children grow, cardiology teams monitor heart function, rhythm, and exercise capacity, adjusting care as needed.
• Activity guidance: Most children with CHD can safely participate in many activities; your cardiology team will advise on any restrictions.
Ongoing Pediatric Cardiology Care:
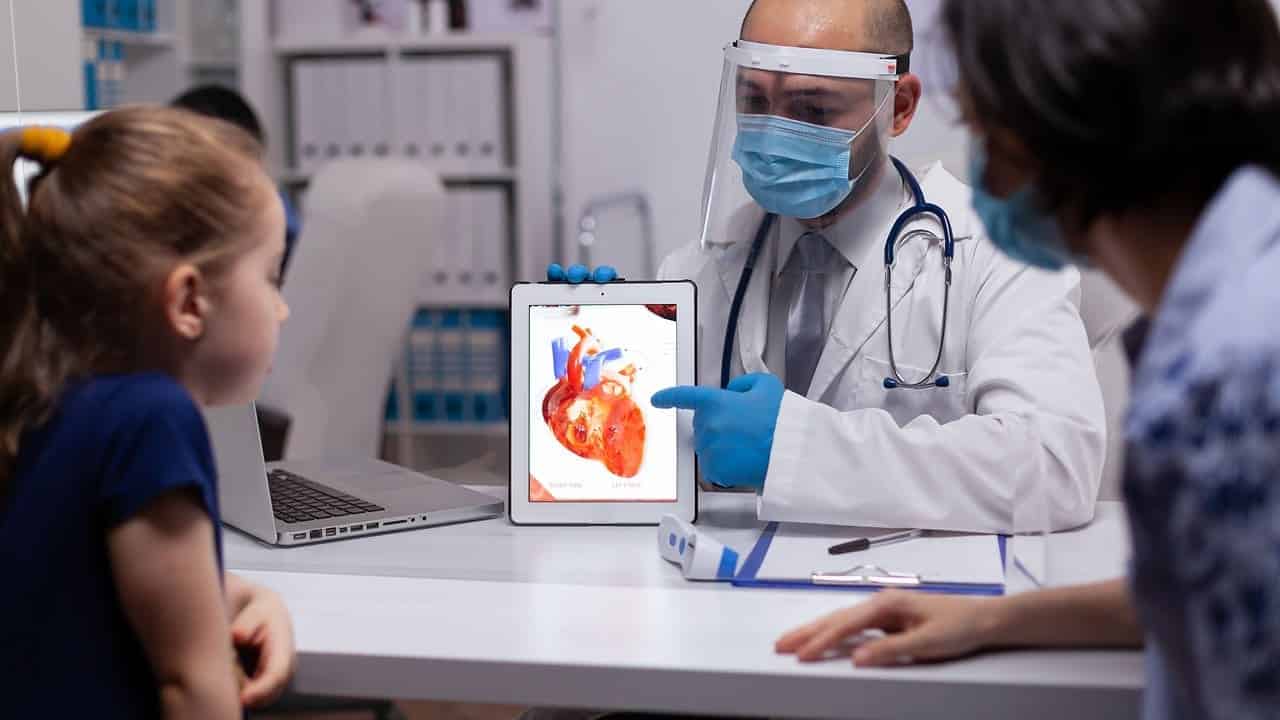
- Growth and development checks ensure the heart keeps pace with body changes.
- Periodic ECGs or echocardiograms monitor rhythm and structure.
If your child has an implanted device or has undergone an interventional procedure, specialized follow up confirms proper function.
Diagnosis with Echocardiography (ECHO) at Liv Hospital
Fetal ECHO
Who should undergo Fetal ECHO?
- Parents with congenital heart disease
- Children of mothers with diabetes or connective tissue disorders
- Previous pregnancy involving a baby born with congenital heart disease
- Detection of abnormalities in the baby’s digestive system, kidneys, brain, or other organs
- Low or excessive amniotic fluid during pregnancy
- Irregular fetal heartbeats
- Multiple pregnancies
- Risk factors like high blood pressure
In such cases, fetal ECHO is necessary.
Congenital Heart Surgeries
Equipped with state of the art technology, Liv Hospital Pediatric Cardiology Clinic offers modern approaches to treating heart diseases in babies and children aged 0-18 with a team of experienced doctors and specialists from various disciplines. While performing anesthesia and heart surgeries on children weighing under 10 kilograms may not be possible in many clinics, congenital heart surgeries are successfully performed at Liv Hospital Pediatric Cardiology Clinic. The experienced pediatric cardiologists, pediatric anesthesia specialists, and the surgical and intensive care teams aim for exceptional success.
Watch for Cyanosis in Babies!
For more information about our academic and training initiatives, visit Liv Hospital Academy
Frequently Asked Questions for Pediatric Cardiology
Where can I find information on pediatric cardiology for parents?
Reliable sources include your clinic’s patient education materials, your pediatric cardiologist’s guidance, and reputable health organizations’ websites. Look for clear, child focused explanations of tests (ECG, echocardiogram), procedures (catheter based treatments), and symptom checklists to support informed decisions at home.
What is new in pediatric cardiology care for families?
Advances include improved imaging, refined catheter based techniques for closing heart defects and relieving valve narrowing, better ambulatory monitoring for intermittent palpitations, and family centered care models. These developments aim to enhance safety, comfort, and recovery while reducing hospital stays.
Why is pediatric cardiology follow up important?
Children grow and change rapidly. Follow up ensures the heart’s structure and function are appropriate for age and activity, monitors rhythm, adjusts medications if needed, and confirms that any devices or catheter based repairs are working well. Regular check ins support safe exercise and long term health.
What symptoms can pediatric cardiology help with?
Pediatric cardiology commonly evaluates chest pain, palpitations, fainting (syncope), shortness of breath, exercise intolerance, heart murmurs, poor feeding, and sweating in infants, as well as cyanosis. Many causes are benign, but timely assessment ensures safe daily activities and participation in sports.
How is an echocardiogram different from an ECG for children?
An ECG records the heart’s electrical activity to detect rhythm and conduction issues. An echocardiogram is an ultrasound that shows the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow, helping identify structural problems. Both are commonly used together for a complete evaluation and are safe and painless for children.
What is pediatric interventional cardiology?
Pediatric interventional cardiology uses minimally invasive catheter based procedures to diagnose and treat heart conditions without open surgery. Through a small access site, cardiologists can close certain heart holes, open narrowed valves (balloon valvuloplasty), place stents in narrowed vessels, and measure pressures and oxygen levels. Benefits include shorter recovery and less discomfort.
When should I consult pediatric cardiology?
If your child experiences chest pain (especially during exercise), fainting or dizziness, rapid or irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, bluish discoloration (cyanosis), poor feeding or growth in infants, high blood pressure, abnormal oxygen levels, or a heart murmur detected by your pediatrician, seek evaluation by a pediatric cardiologist. A family history of significant heart rhythm problems or congenital heart disease is also a reason to consult a doctor.




