Learn how lifestyle choices, brain-healthy diets, and exercise routines can support ADHD prevention and improve focus.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.

Recovery in ADHD doesn’t mean the condition disappears; instead, it refers to reaching a stage where symptoms no longer dominate daily life. This can be seen in improved school performance, stronger social connections, and better self-esteem.
ADHD cannot be prevented entirely, as genetics play a major role, but some early influences, such as prenatal health, can help reduce risk. Secondary prevention focuses on stopping symptoms from worsening. Creating a brain-healthy environment through balanced nutrition, physical activity, consistent routines, and good sleep habits can lessen symptom severity and reduce the need for intensive interventions.
While no specific food causes ADHD, diet plays a crucial role in brain function. A brain starved of nutrients cannot focus. An ADHD diet should focus on stabilizing blood sugar and fueling neurotransmitters.

Exercise is often called “nature’s Ritalin.” Physical activity immediately raises the baseline levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, the same chemicals that ADHD medications target.

Children with ADHD function best when their day is predictable and clearly structured. Uncertainty or sudden changes can easily elevate stress levels, and stress directly affects the prefrontal cortex, the very part of the brain already challenged in ADHD, making focus and self-control even harder.
Visual schedules such as charts, checklists, and step-by-step routines for mornings and bedtime help by externalizing tasks, reducing the mental load on the child, and increasing independence. Maintaining proper sleep hygiene is equally important, as sleep deprivation can mimic or worsen ADHD symptoms. A firm “no screens” rule at least one hour before bedtime helps promote restful sleep. Additionally, simple mindfulness practices, like guided breathing or short grounding exercises, teach children to pause, reset, and manage impulsive behavior more effectively.

Parents can take steps to minimize the risk of developing ADHD or worsening existing behaviors.
If ADHD is left untreated or unmanaged, it can lead to a range of secondary complications, including low self-esteem, anxiety, academic struggles, and social difficulties. Prevention focuses on early identification and timely intervention to reduce these risks. Positive reinforcement is essential, as children with ADHD often hear “no” or “stop” far more than praise.
By consciously acknowledging and rewarding good behavior, parents and teachers can support self-confidence and prevent the development of oppositional behaviors. Social coaching is equally important, teaching children essential skills such as taking turns, joining games appropriately, and avoiding interruptions, which helps prevent social isolation, peer rejection, and long-term emotional difficulties.
ADHD is not a “set it and forget it” diagnosis. As the child grows, their brain, daily routines, and academic expectations continue to change, which makes ongoing monitoring essential for long-term success.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
You cannot change genetics, but you can manage environmental risks. The most effective ADHD prevention strategy during pregnancy is to avoid cigarette smoke, alcohol, and illicit drugs. Maintaining a healthy pregnancy weight and avoiding exposure to environmental toxins like lead and pesticides also supports healthy brain development.
A high-protein, low-sugar diet is best. Protein (eggs, meat, beans) helps synthesize neurotransmitters for focus. Avoiding simple sugars (candy, soda) prevents energy crashes that worsen mood and attention. Some families also see benefits from removing artificial food dyes.
Children with ADHD should aim for at least 60 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous exercise every day. Activities that combine physical exertion with mental focus, like martial arts or team sports, are particularly beneficial for building self-discipline and burning off excess energy.
Stress does not cause the neurological condition of ADHD, but it significantly worsens symptoms. A chaotic home environment or high academic pressure can make a child more scattered and impulsive. Reducing stress through routine and structure often leads to better behavior.
The most impactful change is establishing a consistent routine. Having a set time and quiet place for homework, using planners, and breaking tasks into small chunks help the child succeed. Limiting screen time during the school week also ensures their brain is rested and ready to learn.


Millions of people worldwide suffer from allergies. Over 25 million Americans experience allergic rhinitis, says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). We look
Asthma affects millions worldwide, and knowing what triggers symptoms is key. Did you know that asthma triggers can vary a lot from person to person?
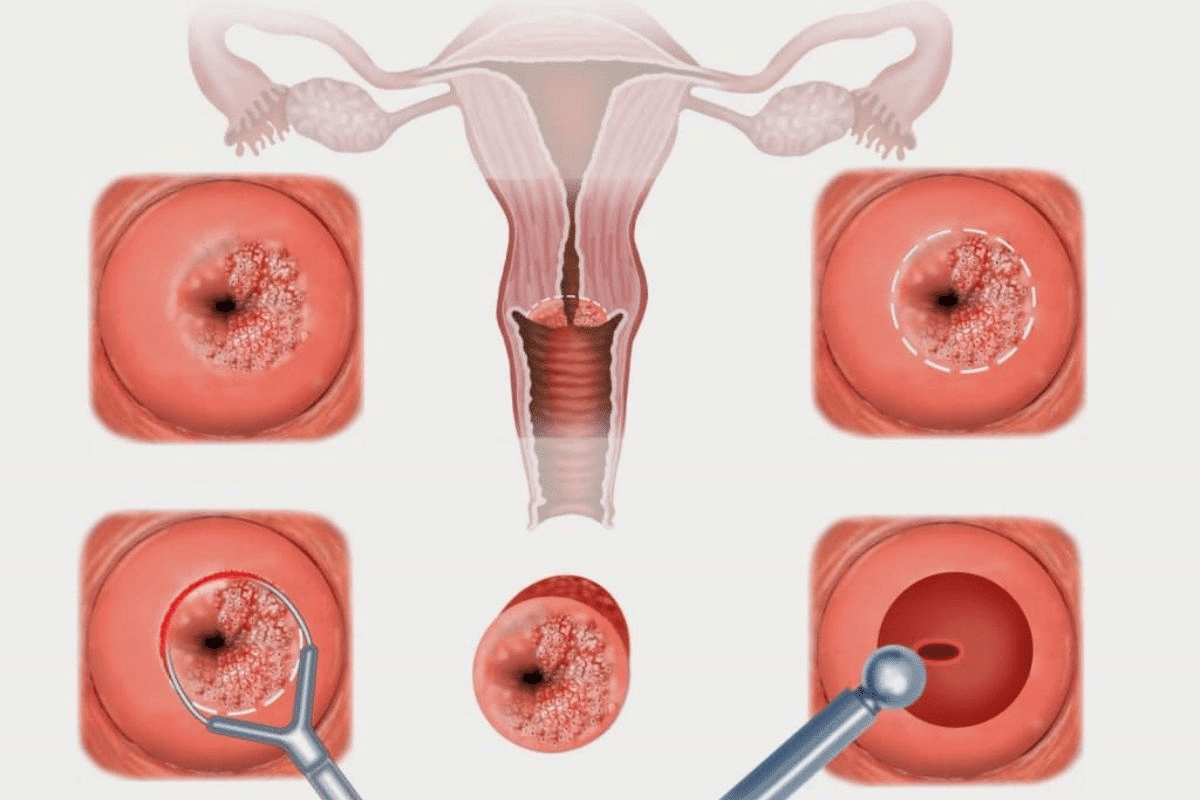
The 7 5 3 rule tonsillectomy guide defines need. specific surgery criteria. Learn the infection frequency that qualifies a child for surgery. Recurrent throat infections
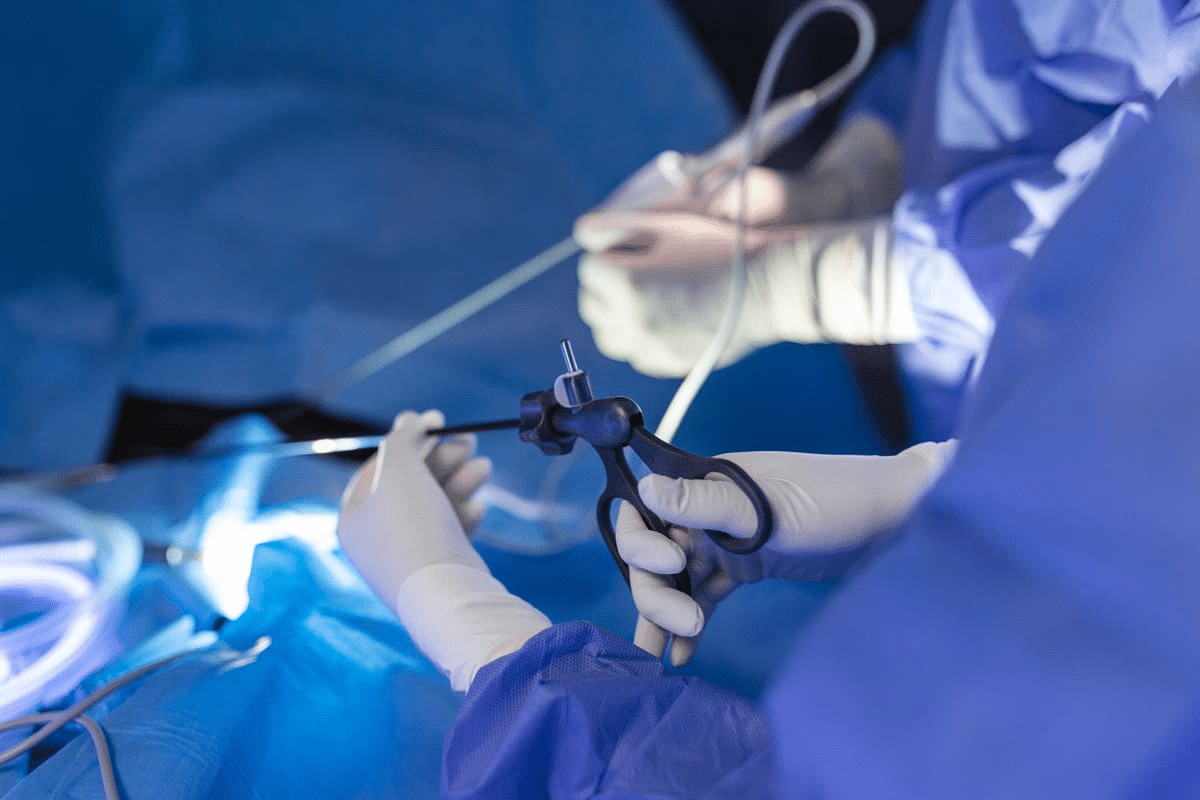
Nearly 1.5 million laparoscopic procedures are done every year in the United States. Many of these involve students who must return to school after their
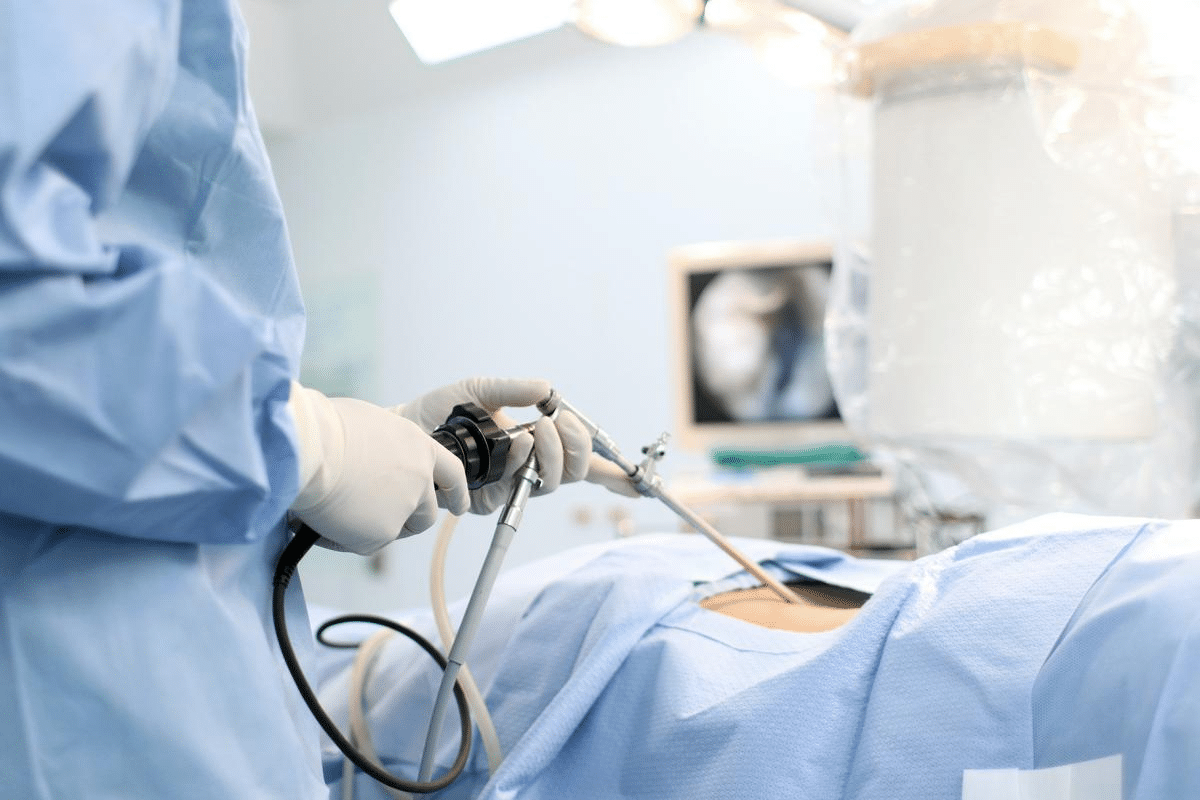
Nearly 1 in 100 patients who have diagnostic laparoscopy might face some complications. This shows why it’s important to know about the risks involved.The diagnostic
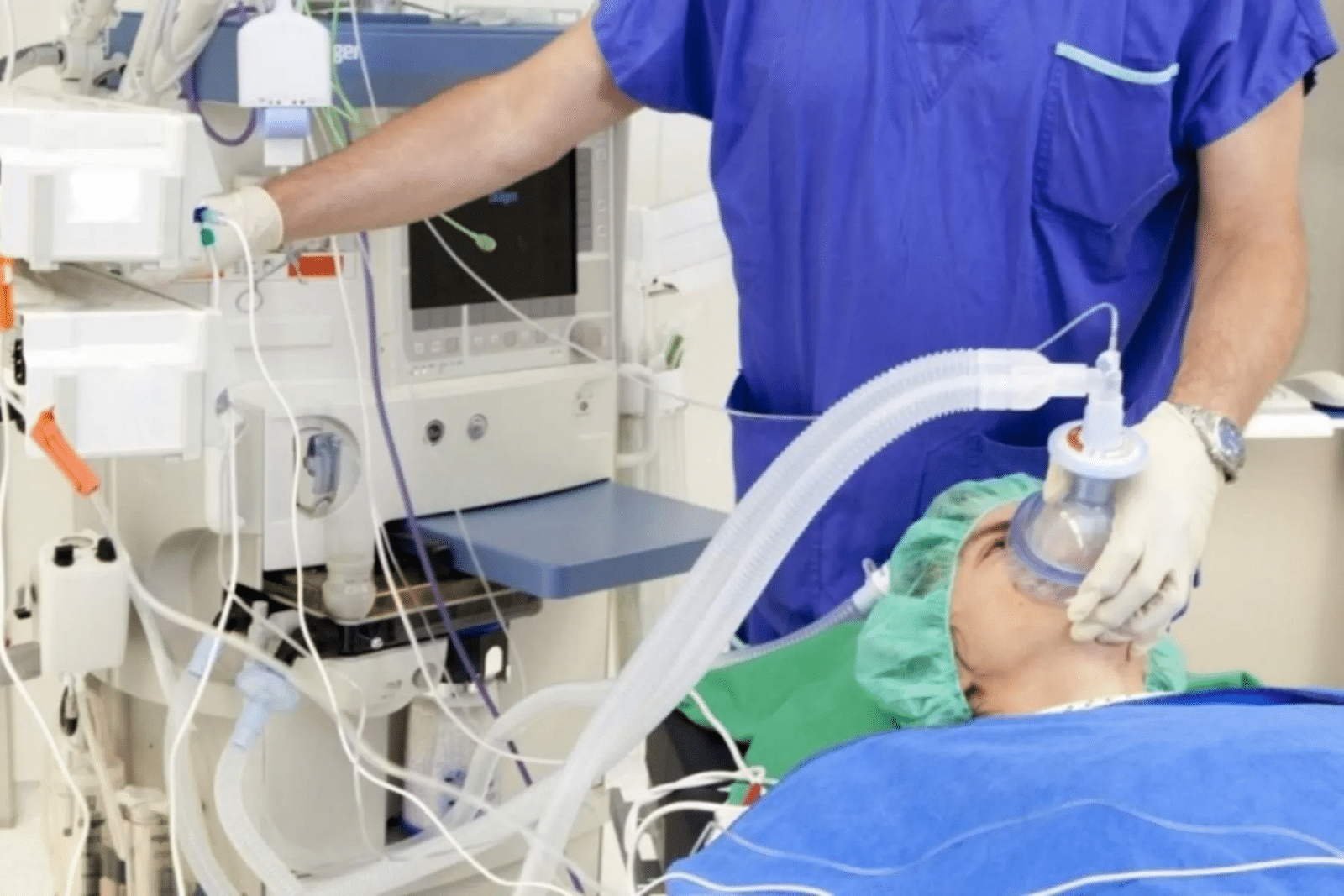
Did you know that advances in medical technology have made anesthesia safer? Recent studies show a big drop in anesthesia-related deaths. Now, we can better

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)