Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Nearly 2 million PET scans are done every year in the United States. They are key in finding and managing health issues. A PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scan is a diagnostic tool that shows how active the body’s cells are. It helps doctors spot problems.
A positive PET scan result means there might be a health issue. This could be cancer, neurological problems, or heart disease. Knowing what a positive result means and the side effects of the scan is important for patients.
PET scans are mostly safe, but they can cause side effects. These can be mild, like a reaction to the tracer, or serious, like an allergic reaction. Knowing about these helps patients get ready and handle any issues that come up.
Key Takeaways
- A positive PET scan result can indicate serious health conditions.
- PET scans are used to diagnose and manage various diseases.
- Understanding the side effects is key for patient care.
- PET scans are generally safe but can have side effects.
- Being informed helps patients prepare for the scan and its outcomes.
Understanding PET Scans: Definition and Purpose
PET scans are a key tool in medicine. They help doctors see how the body works and find diseases. It’s important to know what PET scans are, how they work, and their uses in healthcare.
What is a PET scan?
A PET scan, or Positron Emission Tomography scan, shows how your body’s tissues and organs work. It uses a special drug that lights up the body’s activity. This drug is absorbed by the body and shows up on the PET scanner, giving detailed images.
This defines PET scan as a tool that looks at how the body works, not just its structure.
How PET scans work
Getting a PET scan starts with a special drug being injected into you. This drug goes to areas that are very active, like cancer cells. The PET scanner picks up the signals from this drug.
A computer then makes images of where the drug is. This shows where the body’s activity is high. The PET imaging wiki explains more about how this works.
Common uses for PET scans
PET scans are used in many ways, like finding and tracking cancer. They also help with brain and heart problems. By showing how active the body’s tissues are, PET scans help doctors make better plans for treatment.
So, what do PET scans reveal? They show how well the body’s tissues and organs are working. This is key for doctors to make good decisions.
The PET Scan Procedure: What to Expect
Knowing what to expect from a PET scan can make a big difference. A PET scan checks how your body works, like how it uses energy and blood flow. It’s a detailed tool for doctors to look at your body’s functions.
Before the Scan: Preparation Guidelines
Getting ready for a PET scan is important. You might need to not eat for 4-6 hours before. This can change based on your health and the scan’s needs.
Avoid hard exercise and caffeine before the scan. This helps get better results. Wear comfy clothes without metal on the day of the scan. You’ll get a special injection with a tiny bit of radioactive material right before.
During the Scan: Step-by-Step Process
The PET scan itself is simple. After the injection, wait 30-60 minutes for the tracer to spread. Stay calm and don’t move much during this time.
Then, you’ll lie down in the PET scanner. The scan takes 30 to 60 minutes, depending on what’s being checked. The scanner uses the tracer’s radiation to make detailed pictures of your body.
After the Scan: Immediate Recovery
After the scan, you can usually go back to your normal day unless told not to. Drink lots of water to help get rid of the tracer. You might feel a bit tired or have minor side effects, but these usually go away quickly.
It’s key to follow any instructions from your healthcare team after the scan. Knowing what to expect can help you feel less anxious and make the process easier.
Interpreting PET Scan Results: Positive vs. Negative
When a PET scan shows positive or negative results, it’s a big deal. It helps doctors make important decisions. Knowing what the scan says is key to figuring out if a disease is there, getting worse, or getting better.
What makes a PET scan “positive”
A PET scan is “positive” if it finds areas that are more active than usual. This usually means there might be a disease, like cancer. Cancer cells use more energy than normal cells, so they show up on the scan.
Increased uptake of the radiotracer in certain spots is a sign of a positive scan. For example, if a cancer scan shows activity in lymph nodes or organs, it could mean there’s a tumor.
Areas of increased metabolic activity
When a PET scan shows “hot spots,” it means there’s more activity in those areas. This is where the radiotracer builds up, showing possible problems.
The importance of these hot spots depends on the scan’s purpose and the patient’s history. For cancer, hot spots might mean tumors or spread. In brain scans, they could show inflammation or diseases like Alzheimer’s.
The significance of “hot spots”
“Hot spots” on a PET scan mean there’s more activity than usual. This is important for finding and understanding diseases, like cancer.
It’s important to understand the meaning of hot spots. Doctors look at the scan, symptoms, medical history, and other tests together. This helps them make the right diagnosis and treatment plan.
What Happens When a PET Scan is Positive
A positive PET scan means more tests and talks with experts. It shows where the body is working too hard, like with cancer.
Common Next Steps After a Positive Result
Getting a positive PET scan leads to more tests and talks with doctors. They want to know why and how much the body is affected.
- Additional Imaging Tests: More scans like MRI or CT might be needed for more details.
- Biopsy: If cancer is thought of, a biopsy gets tissue for tests.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests look for signs of certain health issues.
Additional Testing That May Be Required
More tests depend on the PET scan’s findings and the patient’s health. If cancer is suspected, tests will check for it and how far it has spread.
| Test Type | Purpose | Clinical Utility |
| MRI or CT Scan | Detailed anatomical imaging | Assesses the extent and spread of disease |
| Biopsy | Tissue sampling for pathology | Confirms cancer diagnosis and type |
| Blood Tests | Identifying biomarkers or indicators | Helps in monitoring disease progression or response to treatment |
Consultation with Specialists
After a positive PET scan, talking to specialists is key. They figure out the best next steps. This could be with oncologists, neurologists, or cardiologists.
Specialist consultation means discussing the PET scan and other findings. They create a treatment plan just for you. This team effort makes sure you get the best care.
PET Scan Side Effects: Common Reactions and Management
It’s important for patients to know about PET scan side effects. PET scans help doctors diagnose diseases. But, it’s key to know about the possible reactions to the radiotracer used.
Immediate Side Effects After Injection
Right after the radiotracer injection, some people might feel:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Nausea, which is usually mild
- Headache
- Allergic reactions to the radiotracer, though these are rare
Post-Procedure Reactions
Most people can go back to their usual activities after the scan. But, some might feel:
- Fatigue or feeling tired
- Soreness at the injection site
- In some cases, patients might experience a metallic taste
Managing and Minimizing Side Effects
To deal with side effects, patients can:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Avoid strenuous activities for the rest of the day
- Tell their healthcare provider about any severe or lasting side effects
The table below shows common side effects and how to handle them:
| Side Effect | Management Strategy |
| Nausea | Stay hydrated, eat small meals |
| Dizziness | Rest, avoid sudden movements |
| Allergic reactions | Inform healthcare provider immediately |
Knowing about PET scan side effects and how to manage them helps patients prepare. It makes the procedure and its aftermath easier to handle.
Radiation Exposure: How Long Are You Radioactive After a PET Scan?
Knowing how long you’re radioactive after a PET scan is key for safety. PET scans use tiny amounts of radioactive tracers. They help diagnose and treat diseases like cancer and neurological disorders.
Radiotracer Half-Life
The tracers in PET scans decay fast, losing radioactivity quickly. For example, Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) has a half-life of about 110 minutes. This means half of the radioactive material decays in 110 minutes.
This quick decay helps keep radiation exposure low. But, it’s important for patients to follow safety tips after the scan to protect others.
Safety Precautions After the Scan
To lower radiation exposure to others, patients should take certain steps. These include:
- Drinking lots of fluids to flush out the tracer
- Avoiding close contact with pregnant women, kids, and others sensitive to radiation
- Practicing good hygiene, like washing hands well after using the restroom
Comparing Radiation Exposure to Other Procedures
To understand PET scan radiation better, compare it to other imaging tests. The table below shows the effective doses from different procedures.
| Procedure | Effective Dose (mSv) |
| PET Scan (FDG) | 4-7 |
| CT Scan (Abdomen) | 8-14 |
| X-ray (Chest) | 0.1 |
The table shows PET scans have doses similar to or sometimes less than CT scans. But, the dose can change based on the procedure, tracer amount, and patient factors.
PET Scan Risks: Long-term Considerations
It’s important to know the long-term effects of PET scans. They help diagnose and manage health issues but also expose you to radiation. This can lead to long-term health problems.
Cumulative Radiation Exposure
PET scans involve radiation that can build up in your body over time. Cumulative radiation exposure is a big concern. It may raise your risk of health issues caused by radiation.
A PET scan’s radiation dose is measured in millisieverts (mSv). A typical scan has 5-10 mSv. This is more than the average yearly background radiation of 3 mSv. So, having many PET scans can greatly increase your total radiation dose.
Cancer Risk Assessment
There’s also a risk of cancer from PET scans. Radiation can damage DNA, which might lead to cancer. The risk depends on how much radiation you get from PET scans.
While the cancer risk from one PET scan is low, it adds up with more scans. The BEIR VII report helps estimate this risk. It’s a detailed study on radiation’s effects.
| Radiation Dose (mSv) | Estimated Cancer Risk |
| 10 mSv | 1 in 1,000 |
| 50 mSv | 1 in 200 |
| 100 mSv | 1 in 100 |
Risk-Benefit Analysis
When thinking about PET scans, weighing the risks and benefits is key. The benefits of diagnosing serious conditions often outweigh the risks. But, this depends on the patient’s situation and other options.
Doctors must talk to patients about these risks and benefits. This way, patients can make better choices about their health.
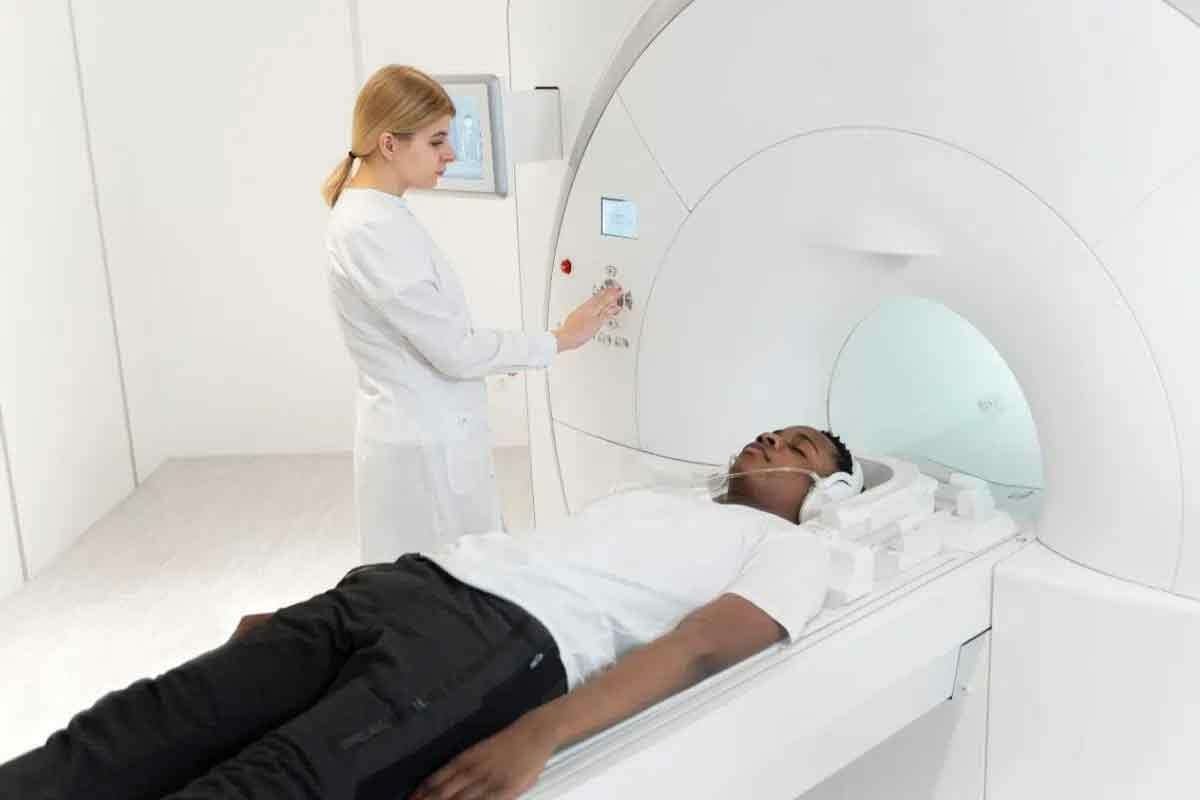
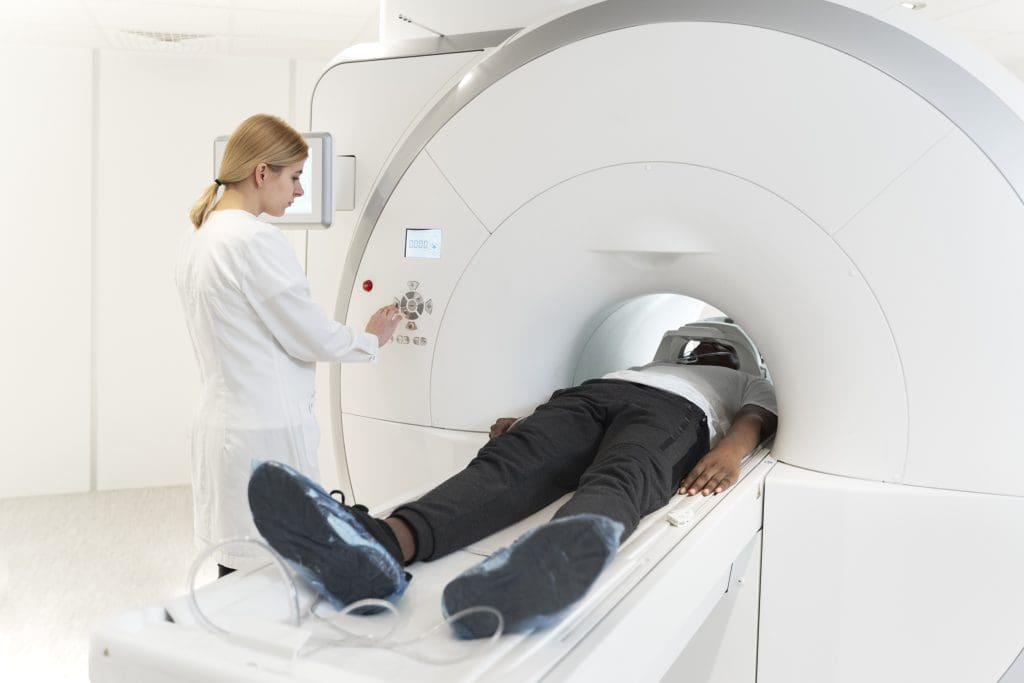
What Does a PET Scan Machine Look Like?
Many people are not familiar with the PET scan machine. But knowing what it looks like can make things easier. It’s a complex device that takes detailed pictures of how the body works.
Physical Appearance and Components
A PET scan machine looks like a big, round or doughnut-shaped thing. It has a hole in the middle where you lie down. You move into the hole on a table, and the scanner takes pictures of your body.
The scanner is wrapped in a big ring called a gantry. Inside the gantry, detectors catch the gamma rays from a special tracer. All this information goes to a computer that makes the images.
Open vs. Closed Designs
PET scan machines can be either open or closed. Closed ones have a full ring around you for clear images. Open ones are more open, which is good for people who get scared in tight spaces.
Open scanners might not be as detailed as closed ones. But, they’re better for people who get anxious in tight places. The choice depends on what you need and what the doctors think is best.
Managing Claustrophobia During the Scan
If you’re scared of tight spaces, the PET scan machine might worry you. But, there are ways to feel better.
- Communication: Tell the doctors about your fear. They can help and support you.
- Relaxation Techniques: Try deep breathing or meditation to relax.
- Open PET Scanners: Choose an open scanner if you can. It feels less tight.
- Accompaniment: Having someone you trust with you can make you feel safer.
Knowing about the PET scan machine can help you feel more ready. It can make the whole experience less scary and more comfortable.
How Long Does a PET Scan Last? Time Expectations
Many patients wonder how long a PET scan takes. Knowing the process can make it less scary. A PET scan’s time includes preparation, scanning, and recovery.
Preparation Time
Preparation for a PET scan varies but usually involves a few steps. Patients arrive early to fill out paperwork and get ready. The radiotracer injection is key, and waiting after it can be 30 minutes to an hour.
During this wait, patients rest quietly. This helps the radiotracer spread evenly in the body. It’s important for clear images.
Actual Scanning Duration
The actual scan takes 30 to 60 minutes. Patients lie on a table in a large machine. The PET scanner captures metabolic activity during this time.
The scan’s length depends on its specific needs and technology.
Total Appointment Length
The total time for a PET scan visit is 2 to 4 hours. This includes check-in, preparation, the scan, and post-scan talks with doctors.
- Check-in and preparation: 30 minutes to 1 hour
- Radiotracer uptake period: 30 minutes to 1 hour
- Scanning time: 30 to 60 minutes
- Post-scan activities: 15 to 30 minutes
Knowing these times helps patients plan their day. It also reduces anxiety about the PET scan.
Why Would a Doctor Recommend a PET Scan?
A PET scan is a key tool for doctors. It shows how body tissues work. This helps in finding and treating many health issues.
Cancer Diagnosis and Staging
Doctors often suggest PET scans for cancer diagnosis and staging. They help find cancer cells and see how far they’ve spread. This info is key for treatment plans.
PET scans are great for finding cancer because cancer cells use more energy. This makes them show up clearly on scans.
Neurological Conditions
PET scans are also used for neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. They check brain activity. This helps find these conditions early and track how they change.
For brain disorders, PET scans give important details. They help doctors understand what’s going on in the brain.
Cardiac Evaluations
For heart disease, doctors might suggest PET scans to check cardiac function. They look at heart tissue to see if it’s working right. This helps decide if treatments like stents are needed.
PET scans are key for heart disease. They help plan the best treatments.
In short, doctors use PET scans for many important health checks. These include finding and treating cancer, checking the brain, and looking at the heart. The info from PET scans is very helpful for making treatment plans and improving health outcomes.
PET Scan Results Explained: Reading the Images
Understanding PET scan images means knowing about SUV values and color coding. These scans show how active the body’s cells are. Getting these images right is key for finding and treating diseases.
Understanding SUV Values
The Standardized Uptake Value (SUV) is a crucial metric in PET scans that indicates the level of radiotracer uptake in the body’s tissues. It shows how much of the radiotracer is taken up by the body. This helps doctors see which parts are most active.
- SUV Calculation: SUV is figured out by comparing the activity in certain areas to the dose given and the patient’s weight.
- Interpretation: Higher SUV values mean more activity, which can point to tumors or inflammation.
Color Coding in PET Images
PET images use a color scale to show how much radiotracer is taken up. Knowing this color scale is important for understanding the scans.
- Color Scale: The scale goes from blue (low uptake) to red (high uptake), with different shades in between.
- Significance: High uptake areas (red or yellow) might show tumors or other active areas.
Comparing “Glow” Intensity
The “glow” in PET images shows how bright or active different areas are. Looking at these differences can give important clues.
- Baseline Comparison: First scans are used as a starting point for future comparisons. This helps track changes in activity over time.
- Monitoring Progress: Changes in “glow” can show how well treatment is working. A decrease usually means the treatment is effective.
Knowing about SUV values, color coding, and “glow” intensity helps doctors make better decisions. Accurate reading of PET scans is vital for good diagnosis and treatment.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Pros and Cons of PET Scans
It’s important to know the good and bad of PET scans. They are a key tool in medical tests, giving insights into how our bodies work.
Unique Benefits of PET Imaging
PET scans have many advantages. They show how active tissues are, which helps in finding cancer. This is a big plus in oncology.
They also help check if treatments are working. By comparing scans before and after treatment, doctors can see if it’s effective.
Limitations Compared to Other Imaging Methods
But, PET scans have some limitations. They cost more than CT or MRI scans. They also use some radiation, which worries some patients.
They don’t show detailed body structures like other scans do. While they highlight active areas, they don’t show the body’s layout well.
When PET Scans Are Most Valuable
PET scans are most valuable in specific areas. In cancer care, they help diagnose and track treatment. In brain diseases, they spot problems by showing brain activity.
In heart health, they check if heart tissue is working. This helps doctors choose the best treatment for heart issues.
Knowing the pros and cons of PET scans helps everyone make better choices. This is true for both patients and doctors.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About PET Scans
PET scans are a key tool in medicine. They help doctors understand many health issues, like cancer and heart problems. Knowing the good and bad sides of PET scans is important for your health care choices.
PET scans use a little radiation, but they are often very helpful. Knowing about possible side effects can make your experience better. This knowledge helps you prepare and feel more comfortable.
This article helps you understand PET scans better. From getting ready to understanding the results, being informed is key. Talking to your doctor about your worries can help you make the right choices for your health.
PET scans are a big part of today’s medicine. They help doctors find the best treatments for patients. Understanding the safety, risks, and benefits of PET scans is essential for good health care.
FAQ
What is a PET scan?
A PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scan is a medical test. It uses a small amount of radioactive material. This helps diagnose and monitor health conditions like cancer and heart disease.
What are the common side effects of a PET scan?
A PET scan can cause anxiety and claustrophobia. Some people may also have allergic reactions or redness at the injection site.
How long does a PET scan last?
A PET scan takes 30 minutes to an hour to scan. But, getting ready and recovering can take several hours.
What happens if a PET scan is positive?
A positive PET scan means there’s increased activity. This could be due to cancer, infection, or inflammation. More tests and specialist advice are needed to find out why.
How long are you radioactive after a PET scan?
The radiotracer in PET scans has a short half-life. This means the radiation exposure is safe. Precautions are taken to protect others.
What are the risks associated with PET scans?
PET scans carry risks like radiation exposure and cancer risk. But, they are often seen as valuable for diagnosis.
Can PET scans cause cancer?
While PET scans involve radiation, the risk of cancer from one scan is low. But, having many scans can increase this risk.
How do I prepare for a PET scan?
PET scan images are read by trained professionals. They look for areas of increased activity and use SUV values and color coding. Comparing “glow” intensity is also important.
What does a PET scan machine look like?
A PET scan machine is a large, cylindrical device. It has a tunnel or bore in the center. There are also open designs for those who are claustrophobic.
Why would a doctor recommend a PET scan?
Doctors recommend PET scans for many reasons. They help diagnose cancer, neurological conditions, and heart disease. They provide detailed information on metabolic activity.
How do I read and understand PET scan images?
PET scan images are read by trained professionals. They look for areas of increased activity and use SUV values and color coding. Comparing “glow” intensity is also important.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of PET scans?
PET scans are highly sensitive and specific. But, they involve radiation exposure and can be costly. They are most useful when used with other diagnostic tools.
Are PET scans safe?
PET scans are safe when done by trained professionals. But, there are risks and benefits to consider.
What is the difference between a PET scan and a CT scan?
A PET scan measures metabolic activity. A CT scan shows anatomical details. PET/CT scans combine both for a better understanding of the body.
Can I undergo a PET scan if I have claustrophobia?
Yes, open PET scan machines are available for claustrophobic patients. Relaxation techniques and sedation can also help during the scan.