A Positron Emission Tomography or PET scan is a high-tech medical test. It shows how the body’s cells work.
When you get a PET scan, you get a special dye. Then, you lie in a tunnel-like machine. This machine picks up the dye’s signals to make clear pictures.
This tool is key for seeing how the body works and finding health issues. The PET scan helps doctors understand the body’s metabolic activities. It’s a big help in medical diagnosis.
Key Takeaways
- PET scan is a diagnostic imaging test.
- It involves injecting a radioactive tracer.
- The PET scan machine is typically tunnel-shaped.
- It’s used to visualize metabolic processes.
- Positron Emission Tomography is another term for PET scan.
PET Scan Meaning: Understanding the Basics
Medical diagnostics have changed a lot with PET scans. Positron Emission Tomography, or PET, is a key tool in medical imaging. It lets doctors see how the body’s cells work.
Definition of Positron Emission Tomography
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a test that shows how your body’s tissues and organs work. It uses a special drug that lights up on the scan. This drug is injected into you, and the PET scan picks up its signals.
This creates images that tell a lot about your body’s activity.
The PET scan process has a few main steps:
- The patient gets a special drug that lights up, called Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG).
- This drug goes to areas of the body that are very active, like growing cancer cells.
- The PET scanner picks up the signals from the drug, making detailed images of the body’s activity.
How PET Scans Work in the Body
PET scans find out how active the body is by using a special drug. This drug is a sugar molecule with a radioactive atom. Cancer cells and other active tissues use more sugar than normal cells, so the drug lights them up on the scan.
Here’s how PET scans work in simple terms:
- Tracer Uptake: The body takes in the drug, which goes to tissues and organs.
- Emission of Signals: As the drug breaks down, it sends out signals that the PET scanner catches.
- Image Creation: These signals make detailed pictures of how active the body’s tissues are.
Knowing how PET scans work helps patients understand their health better. They can see what their diagnosis means and what treatment options they have. PET scans give doctors the info they need to care for patients well.
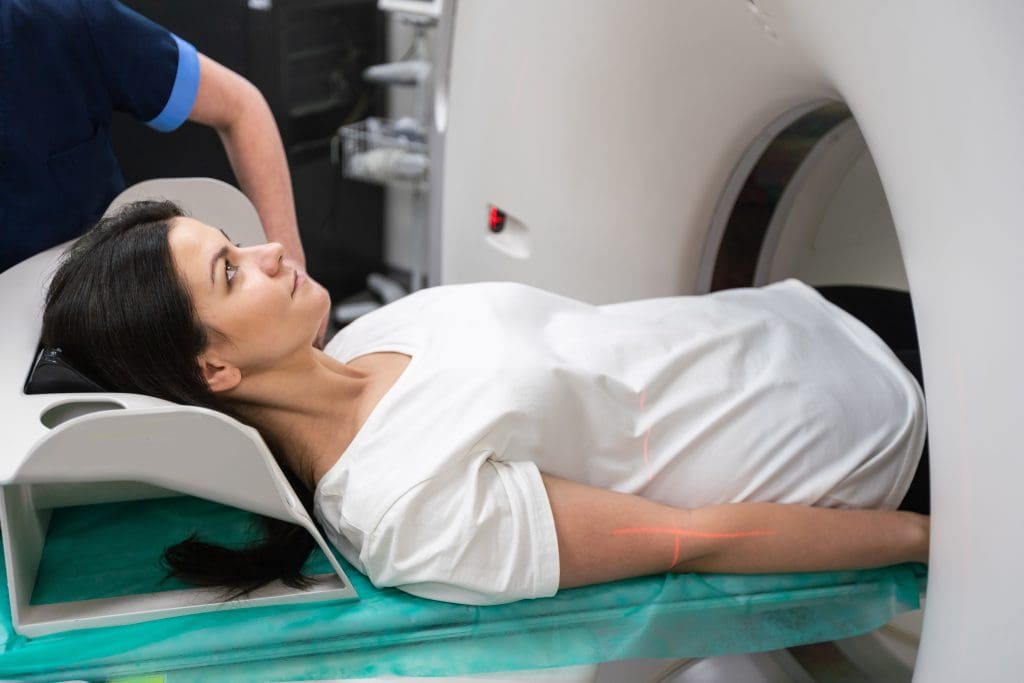
The PET Scan Machine: Design and Tunnel Configuration
A PET scan machine looks like a big tunnel. It has the tech needed for positron emission tomography. Knowing about its design and parts can ease worries and get patients ready for the scan.
Components of a Modern PET Scanner
Today’s PET scanners are advanced. They have several key parts that work together. These parts include:
- Detector Rings: These capture gamma rays from the tracer, turning them into electrical signals.
- Gantry: This is the main part that holds the detector rings. It lets the patient be placed exactly right in the scanner.
- Patient Table: A comfy, moving table that slides the patient through the gantry. It makes sure they’re in the right spot for the best images.
- Computer System: This is the brain of the scanner. It uses software and hardware to make detailed images from the data it gets.
The Tunnel Experience: What to Expect
The tunnel shape of the PET scan machine can worry some patients, mainly those with claustrophobia. But knowing what to expect can help ease these worries.
During the scan, the patient lies on the table, which moves into the gantry. The tunnel is about 70 cm wide. The scan takes 30 to 60 minutes, depending on what’s needed.
To help with claustrophobia, some places offer:
- Open PET scanners that give more room and less feeling trapped.
- Relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation to calm the patient.
- Mild sedation in some cases, to help the patient relax during the scan.
It’s key for patients to talk to their doctor before the scan. This way, they can figure out the best way to handle their fears.
PET Scan vs. Other Imaging Technologies
Choosing between PET scans, CT scans, and MRI depends on the condition and the info needed. Each has its own strengths for different uses.
PET Scan vs. CT Scan: Key Differences
PET scans and CT scans are both important tools. PET scans are great for seeing how tissues work, helping find cancer and check treatment. They’re also good for some brain issues.
CT scans give clear pictures of body parts. They help spot injuries, tumors, and blood vessel problems. But, they don’t show how tissues work.
| Feature | PET Scan | CT Scan |
| Primary Use | Metabolic activity assessment | Anatomical imaging |
| Typical Applications | Cancer diagnosis, neurological disorders | Injury assessment, tumor detection, vascular disease |
PET Scan vs. MRI: When Each Is Used
MRI gives detailed pictures of soft tissues. It’s safe and great for the brain, spinal cord, and joints. Unlike PET scans, MRI doesn’t use radiation.
PET scans are best for seeing how tissues work, like in cancer or treatment checks. MRI is better for soft tissue images. It’s used for things like multiple sclerosis or herniated discs.
Combined PET/CT Scans: Benefits of Fusion Imaging
Combined PET/CT scans are a big step forward. They mix functional and anatomical info in one go. This helps diagnose and stage diseases, like cancer, more accurately.
The combined PET/CT scan shows metabolic and anatomical details together. This helps find and treat problems better. It’s a big help in planning and checking treatments.
Preparing for Your PET Scan: Essential Guidelines
To get the best results from your PET scan, it’s important to follow some key steps. Getting ready properly is essential for a good scan.
Dietary Restrictions and Fasting Requirements
Before your PET scan, you might need to stick to a special diet. This could mean fasting for 4 to 6 hours before the scan. It’s important to avoid sugary foods and drinks because they can mess with the tracer.
For some scans, like those of the heart or cancer, you might be told to eat a low-carb, high-fat diet. But your doctor or the PET scan center will give you the exact instructions you need.
| Dietary Requirement | Guideline |
| Fasting Period | 4 to 6 hours before the scan |
| Foods to Avoid | Sugary foods and drinks |
| Recommended Diet | Low-carbohydrate, high-fat for certain scans |
Medications to Avoid Before a PET Scan
Some medicines can mess with your PET scan results. Tell your doctor about all the medicines you’re taking. This includes:
- Diabetic medications
- Certain antidepressants
- Stimulants and some over-the-counter medicines
Your doctor will tell you if you should keep taking your medicines, change them, or stop them before the scan.
What to Wear and Items to Leave at Home
On the day of your PET scan, wear comfy, loose clothes. Don’t wear anything with metal, like jewelry or zippers, because it can get in the way. Also, leave things you don’t need at home, like:
- Purses or wallets
- Electronic devices
- Metal objects
By following these tips, you can help make sure your PET scan goes well and gives accurate results.
The PET Scan Procedure: Step by Step Experience
Learning about the PET scan procedure can make you feel less anxious. It’s a detailed process that starts with checking in and ends with the actual scan.
Registration and Initial Preparation
First, you need to register. When you arrive, you’ll check in and give your ID and medical records. Showing up on time is important to avoid delays.
Getting ready is important for a good PET scan. You might need to wear a hospital gown and remove any metal items or jewelry.
The FDG Injection Process and Uptake Period
Next, you’ll get an injection of Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). This radioactive tracer shows where your body is most active. The injection goes into a vein in your arm.
After the injection, you’ll wait for the FDG to spread through your body. This can take 30 minutes to an hour. You’ll rest in a quiet area to help the tracer spread evenly.
“The use of FDG in PET scans has revolutionized the field of oncology, allowing for precise monitoring of tumor activity and treatment response.”
Positioning and Actual Scanning Experience
When the waiting time is over, you’ll get on the PET scan table. The table slides into the PET scanner, a big, doughnut-shaped machine.
Getting in the right position is key for good images. You’ll need to lie very quietly and might be asked to hold your breath sometimes.
| Step | Description | Duration |
| Registration | Check-in and preparation | 15 minutes |
| FDG Injection | Administration of radioactive tracer | 5 minutes |
| Uptake Period | Resting after FDG injection | 30-60 minutes |
| Scanning | Actual PET scan procedure | 15-30 minutes |
The PET scan process is detailed and requires careful preparation. Knowing what to expect can help you feel more ready.
How Long Does a PET Scan Take? Timeline Breakdown
A PET scan’s time varies based on the scan type and patient needs. Knowing the scan’s phases helps patients prepare and understand what to expect.
Duration of Different Phases of the Procedure
The whole PET scan takes about 2 to 3 hours. But the actual scan time is much shorter. The process has several phases:
- Preparation and Registration: 30 minutes to 1 hour
- FDG Injection and Uptake Period: 1 to 2 hours
- Scanning: 15 to 60 minutes
The first phase is getting ready, changing clothes, and getting instructions. Then, you get an FDG injection. This is followed by a period where your body absorbs the tracer. The scan time depends on the body area and scan type.
Factors That May Extend Your Scan Time
Several things can make your PET scan longer:
- Type of Scan: Different scans, like whole-body or focused scans, take different times.
- Patient Condition: Some medical conditions or trouble staying calm can add time.
- Need for Additional Imaging: Sometimes, extra images are needed, making the scan longer.
Talking to your healthcare provider about any concerns before the scan is key. This helps the process go smoothly.
Managing Claustrophobia During a PET Scan
Claustrophobia can make PET scans uncomfortable. But, knowing the alternatives and coping methods can help a lot. For those with claustrophobia, the idea of a PET scan is scary because of the scanner’s closed space.
Open PET Scan Options for Claustrophobic Patients
Open PET scan machines are a good solution for claustrophobic patients. They are different from traditional PET scanners, which are closed tunnels. Open PET scan machines offer more space, making patients feel less trapped.
Not all places have open PET scan machines. But, patients can ask about them when they schedule their scan. Some places might have them or know where to find them.
Techniques and Medications for Scan Anxiety
For those getting a traditional PET scan, there are ways to handle anxiety. Deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation can help. Also, talking to your doctor about your claustrophobia can lead to anti-anxiety medicationsbefore the scan.
Some places let you have someone with you during the scan. This can offer support and help with anxiety. Virtual reality (VR) is also being tested to distract and reduce claustrophobia during scans.
By knowing what’s available and working with your doctor, patients with claustrophobia can have easier and less stressful PET scans.
Radiation Exposure and Safety Concerns
PET scans use small amounts of radioactive tracers for medical imaging. This raises concerns about radiation exposure and safety. It’s important to know how much radiation is involved to keep patients safe.
How Much Radiation Is in a PET Scan
The radiation from a PET scan varies. It depends on the procedure and the tracer used. Generally, it’s similar to a CT scan of the chest or abdomen, with a dose of 4 to 7 millisieverts (mSv).
Several factors affect radiation exposure:
- The type and amount of radioactive tracer used
- The specific PET scan protocol followed by the imaging facility
- Patient factors, such as body size and the condition being diagnosed
How Long Are You Radioactive After a PET Scan
How long you stay radioactive after a PET scan depends on the tracer’s half-life. For most tracers, like Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), it’s about 110 minutes. This means the radioactivity halves every 110 minutes.
To reduce radiation exposure to others, patients are advised to:
- Avoid close contact with pregnant women and children for a few hours after the scan
- Drink plenty of fluids to help flush out the radioactive tracer
- Urinate frequently
Safety Protocols During and After the Procedure
There are safety measures to reduce radiation exposure. These include using the least amount of tracer needed and following strict protocols. The PET scanner is also kept in good working order.
| Safety Measure | Description | Benefit |
| Use of Minimal Tracer Dose | Administering the smallest effective dose of radioactive tracer | Reduces radiation exposure to the patient |
| Strict Imaging Protocols | Following established guidelines for PET scan procedures | Ensures high-quality images while minimizing radiation |
| Scanner Maintenance | Regular calibration and maintenance of PET scanners | Ensures accurate and safe operation of the scanner |
Understanding radiation exposure and following safety protocols helps. Patients and healthcare providers can work together to reduce risks from PET scans.
What Does a PET Scan Show PET Scan Results? Interpreting Results
PET scan results give doctors important insights into how our bodies work. They help find and treat diseases. The results are analyzed by looking at the images and data from the scan.
Understanding PET Scan Images and SUV Values
PET scan images show how active our body’s cells are. SUV (Standardized Uptake Value) measures this activity. High SUV values mean our cells are working hard, which can be a sign of disease, like cancer.
How Long It Takes to Get PET Scan Results
How fast you get your PET scan results depends on a few things. It usually takes a few days to a week. Sometimes, you might get early results, but the full report comes after a radiologist checks it carefully.
What Different Uptake Patterns May Indicate
Each pattern in PET scan images means something different. High activity in some areas might show cancer. Low activity could mean less activity in those areas. These patterns help doctors diagnose and plan treatment.
Reading these patterns is a job for experts, like radiologists. They look at SUV values, where the tracer goes, and other info to make a correct diagnosis.
Side Effects and After-Care Following a PET Scan
PET scans are safe, but they can cause side effects. Knowing these and how to care for yourself after is key for a quick recovery.
Common Side Effects and Their Management
Some people might feel side effects from a PET scan. These can include:
- Discomfort or pain at the injection site
- Allergic reactions to the tracer
- Claustrophobia or anxiety during the scan
Dealing with these side effects is usually easy. For example, a warm compress can help with injection site pain. Telling your doctor about any allergies before the scan is important to avoid allergic reactions.
Post-Scan Precautions and Recovery
After your PET scan, there are steps to take for a smooth recovery:
| Precaution | Benefit |
| Drink plenty of water | Helps flush out the radioactive tracer |
| Avoid close contact with pregnant women and young children | Minimizes exposure to residual radiation |
| Resume normal activities as advised by your doctor | Ensures a safe return to daily routines |
Most people can go back to their usual activities right after the scan. But, always listen to what your doctor says.
Understanding side effects and following post-scan care helps ensure a safe recovery after a PET scan.
When and Why Doctors Order PET Scans
PET scans are key in medical diagnostics. But when are they used? Doctors order them for many reasons. It’s important for patients and doctors to know why.
Medical Conditions Requiring PET Imaging
PET scans are great for diagnosing and managing diseases. They’re used for cancer, neurological issues, and heart problems. In cancer care, they help see how far cancer has spread and if treatments are working.
Cancer Diagnosis and Management is a big use of PET scans. They show how far cancer has spread. This helps doctors plan treatments. For example, FDG-PET scans check how active tumors are, showing how aggressive they are.
PET scans also help with neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s and epilepsy. They check brain function and find abnormal areas.
Benefits and Limitations in Clinical Decision-Making
PET scans have many benefits. They can spot changes before they show up in other tests. They also check the whole body at once.
But, there are downsides. They expose patients to radiation, which is a big concern for kids and pregnant women. Also, they can be expensive and hard to find in some places.
Doctors need to know these points to decide when to use PET scans. This helps them make the best choices for their patients.
Conclusion
Knowing what a pet scan meaning is is key for those getting this test. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans show how the body works. They help find and track different health issues.
The pet scan procedure starts with a special dye being injected. This dye is then picked up by the pet scan machine. It makes detailed pictures of inside the body. Doctors use these pictures to see if there are diseases.
Reading pet scan results needs skill. The images can show if something is not right, like tumors. Doctors use this info to plan treatments and check how patients are doing.
In short, PET scans are very important in today’s medicine. They help doctors find and understand many health problems. By learning about PET scans, patients can understand their tests better.
FAQ
What is a PET scan?
A PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scan is a test that uses a special sugar molecule. It helps find cancer, neurological issues, and other diseases. It spots areas where the body’s activity is off.
Do you go through a tunnel for a PET scan?
Yes, you lie on a table that moves through a tunnel-like machine. The machine captures the sugar molecule’s radiation. This creates detailed images of your body’s inside.
How long does a PET scan take?
A PET scan usually takes 30-60 minutes. This includes getting ready, the sugar molecule injection, and scanning.
What are the side effects of a PET scan?
Side effects are usually mild. You might feel discomfort from the injection, anxiety, or claustrophobia. Rarely, you could have an allergic reaction to the sugar molecule.
How do I prepare for a PET scan?
To prepare, you might need to fast for hours before. Avoid certain meds and wear loose clothes. Your doctor will give you specific instructions.
Can I wear jewelry during a PET scan?
It’s best to remove jewelry and metal items. They can mess with the scan. You’ll be asked to take them off before starting.
How much radiation is in a PET scan?
A PET scan uses a small amount of radiation. It’s considered safe, but talk to your doctor if you’re worried.
How long are you radioactive after a PET scan?
The effects of the scan’s radiation last a few hours. Your doctor will tell you what precautions to take during this time.
What does a PET scan show?
A PET scan highlights abnormal activity in the body. It helps diagnose and monitor conditions like cancer, neurological disorders, and heart disease.
How long does it take to get PET scan results?
Results usually come within a few days to a week. Your doctor will explain what they mean to you.
Can claustrophobic patients undergo a PET scan?
Yes, people with claustrophobia can have a PET scan. Some places offer open machines or sedation. Talk to your doctor about your concerns.
What is the difference between a PET scan and a CT scan?
A PET scan looks at metabolic activity. A CT scan shows detailed internal structures. PET/CT scans combine both for a full view of the body.
Why do doctors order PET scans?
Doctors use PET scans to diagnose and monitor various conditions. They help guide treatment decisions by providing valuable information.























