Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
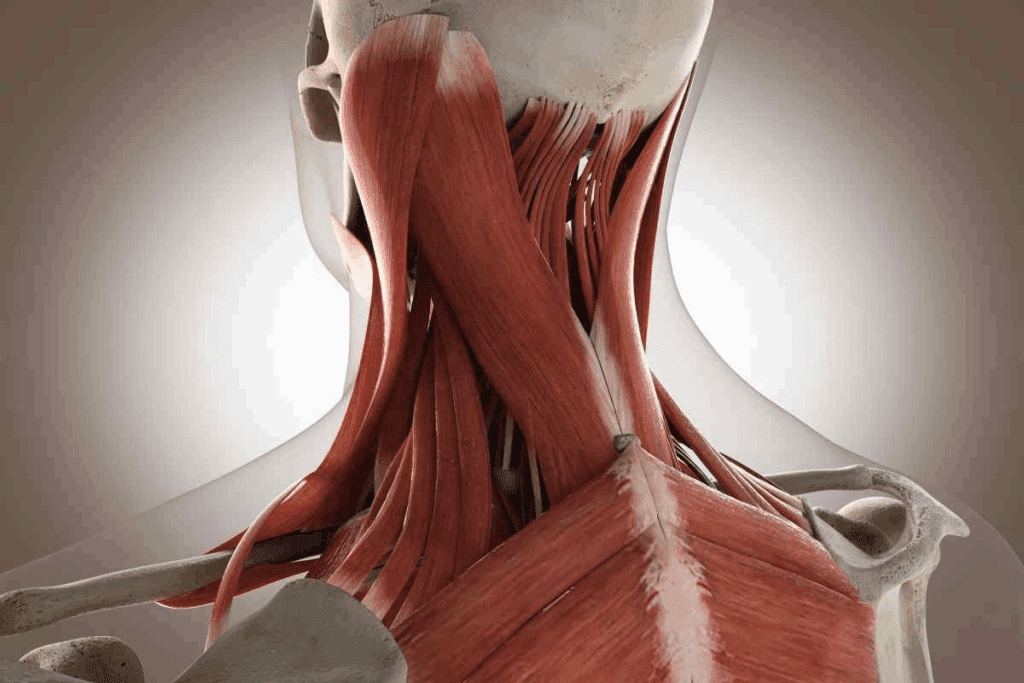
The posterior cervical lymph nodes are key to the neck’s immune system. They are found along the back of the neck. They stretch from the mastoid bone to the clavicle.
The cervical lymph nodes posterior to the neck are bean-shaped. They filter fluid to catch harmful substances or cells. This helps the immune system find and fight off problems.
Knowing exactly where these nodes are is important. It helps doctors find issues during exams. It also helps them decide the best treatments.
The lymphatic system in the neck has a special classification system. This system helps doctors diagnose and treat diseases. It’s key to understanding the lymph nodes and their role in fighting off infections.
The lymphatic system is a vital part of our immune system. In the neck, it includes lymph nodes and vessels. Cervical lymph nodes are spread out in the neck and help protect us from infections and diseases. They filter lymph fluid, catching pathogens and abnormal cells, and help move immune cells.
The cervical lymph node system divides nodes into six levels. This helps doctors diagnose, stage, and treat head and neck cancers. This system is used by healthcare professionals everywhere. Each level is based on the lymph nodes’ location in the neck.
Levels I to VI are named based on specific neck landmarks. Knowing these levels is key for tracking disease spread and treatment planning. This system makes it easier to describe lymph nodes’ locations and their role in diseases.
We’ll dive into these levels and their importance soon. The six-level system is a cornerstone in head and neck surgery and oncology.

The posterior cervical lymph nodes are found in a specific spot. This spot is key for understanding their role in health. These nodes are part of the posterior cervical chain. This chain helps drain lymph from the head and neck.
The posterior cervical lymph nodes sit behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle and in front of the trapezius muscle. Knowing where they are helps doctors during exams.
The posterior cervical lymph nodes stretch from the mastoid process to the clavicle. This range is important for understanding how they drain and for checking them during exams.
Doctors use palpable landmarks to find the posterior cervical lymph nodes. These nodes can be felt when there’s an infection or cancer.
Knowing exactly where the posterior lymph nodes are in the neck is vital for doctors. It helps them do accurate exams and diagnose problems. By understanding their location, doctors can better handle issues with these nodes.
The posterior triangle is a key area in the neck. It helps us understand where the posterior cervical lymph nodes are and what they do. We’ll look at what makes up this area and its importance.
The posterior triangle is shaped by the sternocleidomastoid muscle in front, the trapezius muscle in back, and the clavicle below. These lines show where the posterior cervical lymph nodes are. The sternocleidomastoid muscle is a key landmark for finding the front edge of the triangle.
The posterior triangle holds important structures. It includes the level V lymph nodes, which are part of the cervical lymph node chain. These nodes help drain lymph from the neck and nearby areas. The triangle also has the spinal accessory nerve and the transverse cervical vessels, which are vital for both study and medical practice.
Knowing what’s inside the posterior triangle is key to understanding the role of the posterior cervical lymph nodes. The level V lymph nodes, found in this area, play a big part in health and disease. Their location is important for doctors to find during exams.
The Level V classification is key in the cervical lymph node system. It focuses on the posterior triangle group. This system helps us understand the neck’s anatomy and diagnose and treat various conditions.
We will explore Level V classification in detail. We’ll look at its definition and the parts it has in the cervical node system. Knowing this is important for doctors to manage neck conditions well.
Level V in the cervical node system is about lymph nodes in the neck’s posterior triangle. This area is important because of its unique location and role in draining the head and neck. The posterior triangle is shaped by the sternocleidomastoid, trapezius muscles, and the clavicle.
The lymph nodes in Level V help drain the scalp, neck, and shoulders. Knowing the posterior triangle’s boundaries is key to finding these lymph nodes.
Level V is split into two parts: Level VA and Level VB. This split is based on the lymph nodes’ position relative to the cricoid cartilage. Level VA nodes are above the cricoid cartilage, and Level VB nodes are below it.
Knowing these parts is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment of neck lymph node issues.
The superior posterior triangle in the neck is home to Level VA nodes. These nodes are key for lymphatic drainage. They are part of the cervical lymph node system, which helps track disease spread in the head and neck.
Level VA nodes sit above the cricoid cartilage’s bottom edge. Knowing this is key for finding these nodes during exams. Spotting them accurately is vital for diagnosis and treatment.
“The cervical lymph node system’s levels help standardize cancer descriptions,” say doctors. This standard is important for clear communication among healthcare teams.
The spinal accessory nerve runs through the posterior triangle. Level VA nodes are near it. This close relationship affects surgery and diagnosis. It’s important to avoid nerve damage during procedures.
Level VA nodes drain lymph from the head and neck, like the nasopharynx and scalp. Their drainage is complex, with many lymphatic vessels involved. Knowing these patterns helps find cancer sources in the head and neck.
Drainage from Level VA nodes goes to other cervical nodes, then to the thoracic duct or right lymphatic duct. This info is key for understanding disease spread.
In summary, Level VA nodes in the superior posterior triangle are vital for head and neck lymphatic drainage. Their location, relation to the spinal accessory nerve, and drainage patterns are critical in clinical practice.
The inferior posterior triangle has Level VB nodes, key for lymphatic drainage. These nodes are found below the cricoid cartilage and near the transverse cervical vessels.
Level VB nodes are between the cricoid cartilage’s bottom and the clavicle. Their location is key to understanding their role in neck lymphatic drainage.
These nodes are near the transverse cervical vessels, which feed the neck. Their closeness to these vessels is important for surgeries and tests.
Level VB nodes link to the supraclavicular lymph nodes. This network drains lymph from the neck and nearby. It’s vital for disease tracking and treatment planning.
The main points about Level VB nodes are:
Knowing about Level VB nodes is key for medical assessments and treatment plans. Their spot, near important vessels, and link to other nodes make them vital in the neck’s lymph system.
Superficial and deep posterior cervical lymph nodes have different locations and roles. Knowing these differences helps doctors diagnose and treat better.
The superficial nodes are near the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the external jugular vein. They are easy to feel during a check-up. The deep nodes, though, are deeper, near the spinal accessory nerve and the internal jugular vein.
Key differences in location:
Superficial nodes drain the skin and superficial tissues of the neck. Deep nodes, by contrast, drain deeper structures like the pharynx, larynx, and thyroid gland.
Drainage patterns:
The depth of posterior cervical lymph nodes is very important. Swollen nodes can mean infection or other health problems. Superficial nodes are easy to feel, which helps doctors diagnose. Deep nodes, though not palpable, are key for diagnosing deeper issues.
Clinical considerations:
Swollen lymph nodes can signal many health issues, from infections to serious diseases like cancer. Knowing the difference between superficial and deep nodes helps doctors diagnose and treat these problems accurately.
To check posterior cervical lymph nodes, we need a detailed method. We’ll cover how to do a thorough check.
For a good check, we use a special touch method. We press our fingers on the neck to feel for nodes. The patient should sit comfortably with their neck a bit bent.
Step-by-Step Palpation:
Normal nodes are usually not felt or are tiny. But, if nodes are big, hurt, or stuck, it’s not normal.
| Characteristics | Normal Findings | Abnormal Findings |
| Size | Not palpable or very small | Enlarged |
| Tenderness | Not tender | Tender |
| Mobility | Mobile | Fixed to surrounding tissues |
It’s key to write down what we find during the check. We should note the size, where they are, if they hurt, and how they move. This helps us keep track of changes and decide what to do next.
Documentation Tips:
By sticking to these steps, we can make sure our check of the posterior cervical lymph nodes is complete and correct.
The posterior cervical lymph nodes can face many health issues, like infections and tumors. These problems can make the lymph nodes grow bigger, a condition called lymphadenopathy. Knowing what causes this growth is key to finding the right treatment.
Infections are a big reason for swollen posterior cervical lymph nodes. Bacterial infections like tuberculosis and cat-scratch disease can cause big swelling. Viral infections, such as mononucleosis and cytomegalovirus, also lead to swelling. It’s important to think about these infections when we see patients with swollen lymph nodes.
Both benign and malignant tumors can affect the posterior cervical lymph nodes. Lymphoma, a cancer of the lymphatic system, is a major concern. Also, tumors from other parts of the head and neck can spread to these lymph nodes. We must consider tumors when diagnosing swollen lymph nodes.
Diagnosing swollen posterior cervical lymph nodes requires a detailed approach. We start with a thorough medical history and physical exam. Sometimes, we need imaging like ultrasound or CT scans. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy or excisional biopsy might be needed for a clear diagnosis. Our approach depends on the patient’s symptoms and initial findings.
| Diagnostic Method | Description |
| Medical History | Detailed history to identify possible causes |
| Physical Examination | Examining the lymph nodes and other important findings |
| Imaging Studies | Using ultrasound, CT scans, or other methods to check the lymph nodes and nearby areas |
| Biopsy | Fine-needle aspiration or excisional biopsy to get tissue for lab tests |
We’ve looked into the anatomy and importance of posterior cervical lymph nodes. They play a big role in our immune system. The lymphatic system, with its organs and tissues, helps keep us healthy. Posterior cervical lymph nodes are key parts of this system.
Their location in the neck’s posterior triangle is important. Knowing where cervical lymph nodes are, like those in the posterior cervical area, helps doctors diagnose and treat diseases.
Understanding lymph node location and types helps doctors take better care of patients. As medical knowledge grows, so does the role of posterior cervical lymph nodes in patient care.
The posterior cervical lymph nodes are found along the neck’s back. They stretch from the mastoid bone to the clavicle.
They filter lymphatic fluid and help the immune system.
The neck’s lymph nodes are divided into six levels. This system helps us understand their role and function.
The posterior triangle is a key area. Knowing its boundaries helps us understand the posterior cervical lymph nodes’ location and function.
Level V includes lymph nodes in the posterior triangle. It’s split into Level VA and Level VB nodes.
Superficial and deep nodes differ in location and function. Their roles in the immune system vary.
Doctors use palpation to check these nodes. They report findings based on established standards.
Enlargement can be due to infections, tumors, or other diseases.
Diagnosing enlarged nodes involves identifying causes. Tests are used to find the root cause.
Knowing their anatomy is vital for healthcare professionals and those seeking medical info.
Level VA nodes are above the cricoid cartilage, near the spinal accessory nerve. Level VB nodes are below, connected to the supraclavicular nodes.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). Where Are the Posterior Cervical Lymph Nodes Located. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551521/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!