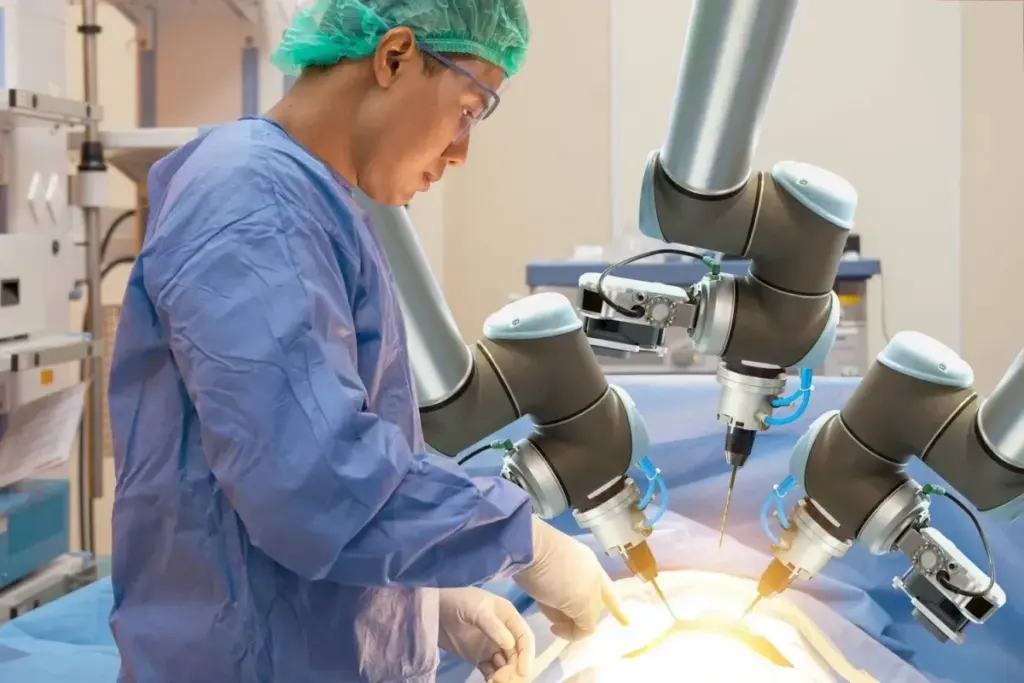
Did you know that medical robotics has changed healthcare? It makes complex procedures more accurate than ever.
The LIBERTY Endovascular Robotic System by Microbot Medical shows precision robotics in action. It allows for precise control during endovascular procedures.
We’re seeing a big change in healthcare. Robotics is key to better patient care.
Key Takeaways
- The LIBERTY Endovascular Robotic System shows the value of precision in robotics.
- Precision robotics is changing medical procedures. It makes complex tasks more accurate.
- Medical robotics is making healthcare better. It’s changing the way we treat patients.
- Robotic precision is important in many medical areas, like endovascular procedures.
- Precision robotics will keep growing in medicine.
The Fundamentals of Precision in Robotics
In robotics, precision is key, not just nice to have. It’s essential for robots to work well. Let’s explore what precision means and why it matters.
Definition and Importance in Modern Robotics
Precision in robotics means a robot can do tasks exactly right. Robotic precision is vital today. It affects how well and reliably robots work. This is true in many fields, like making things, helping in healthcare, or in service robots.
We say precision is how well a robot can do the same thing over and over again. It’s about being consistent. But precision is different from accuracy, which is about how close a robot gets to its goal.
Accuracy vs. Precision: Understanding the Distinction
It’s important to know the difference between accuracy and precision. Accuracy is about how close a robot’s actions are to what it’s supposed to do. Precision is about how consistent it is in doing that.
Think of it like target shooting. Accuracy is hitting the bullseye. Precision is hitting the same spot every time, even if it’s not the bullseye.
|
Characteristics |
Accuracy |
Precision |
|---|---|---|
|
Definition |
Closeness to true value |
Consistency of results |
|
Importance |
Critical for achieving desired outcomes |
Essential for reliability and repeatability |
Repeatability as a Core Performance Metric
Repeatability is a key measure in robotics. It shows how well a robot can do the same thing again and again. A robot with high repeatability can do its tasks reliably and consistently.
Manufacturers test robots to see how consistent they are. They use this info to make the robots better. This helps improve the robot’s precision.
Precision Robotics: Technologies and Applications
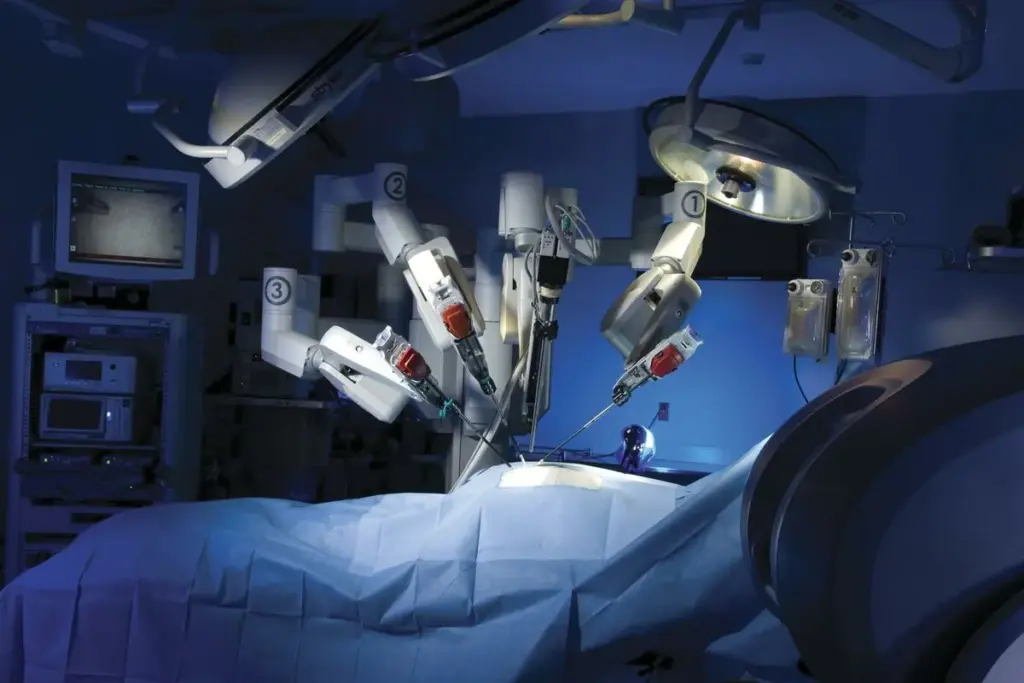
The use of precision robotics technologies is changing many industries. It makes tasks more accurate and efficient. Robotics are key in achieving high precision in these areas.
Core Technologies Enabling High Precision
Several key technologies are making robotics more precise. Advanced sensor systems like vision and optical sensors give robots real-time feedback. This lets them adjust their actions.
The LIBERTY® Endovascular Robotic System is a great example. It shows how advanced tech can lead to precise medical robotics.
High-precision actuators and advanced control algorithms are also important. They help robots do complex tasks with great accuracy. Adding machine learning and AI boosts their abilities even more.
Industry-Specific Applications
Precision robotics is used in many fields, like manufacturing, healthcare, and aerospace. In manufacturing, it helps with assembly, welding, and checking products. This improves quality and makes production faster.
In healthcare, it’s changing surgery. Robots help surgeons do complex operations with more accuracy and less invasion. This leads to better patient results and shorter recovery times.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Precision Implementation
Getting precision robotics can cost a lot. But the benefits are often worth it. A cost-benefit analysis helps see the return on investment. It looks at better product quality, faster production, and lower labor costs.
We need to compare these advantages to the initial and ongoing costs. This helps industries decide if precision robotics is right for them.
Sensors and Feedback Systems for Enhanced Precision
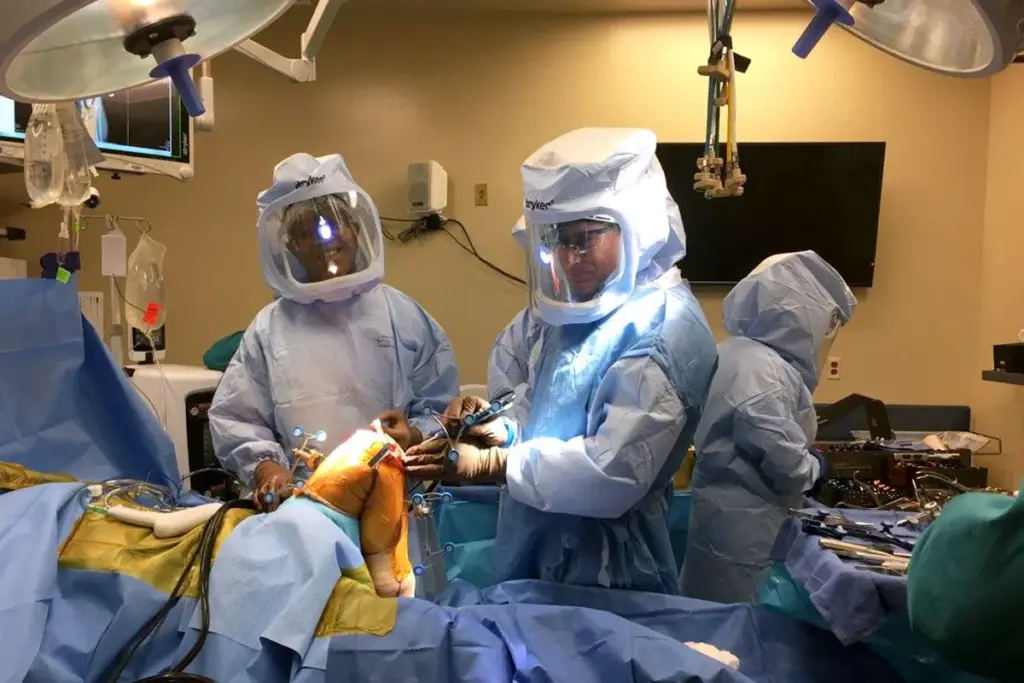
Advanced sensors and feedback systems are changing how robots work. They help robots see and interact with their world better. This is key for precise work in many areas.
Vision Systems and Optical Sensors
Vision systems and optical sensors let robots see their surroundings. They help robots do tasks like assembly and inspection more accurately. Advanced vision systems take clear pictures and give robots real-time feedback.
Optical sensors also help robots measure distances and find objects. They’re vital in places like chip factories and assembly lines where precision is a must.
Force and Torque Sensing
Force and torque sensing are key for robots that touch their environment. They help robots adjust their actions for better precision. This is very important in delicate tasks like robotic surgery.
Force sensors tell robots how much force they’re using. This helps them avoid damaging things or ensure things are put together right. Torque sensors measure rotational force, which is important for screwing or tightening.
Proprioceptive Feedback Mechanisms
Proprioceptive feedback helps robots know where they are and how they’re moving. Sensors that measure joint angles and speeds help robots move precisely. This is essential for tasks needing high accuracy, like in manufacturing.
Together, these feedback systems and advanced algorithms make robots do complex tasks well. Proprioceptive sensors are key for controlling robot movements accurately.
Calibration Techniques for High-Precision Robotics
In the world of high-precision robotics, calibration is key. It makes sure robots work accurately and reliably. This is vital in many industries and medical fields.
Factory Calibration Methods
Factory calibration happens in a controlled setting. It sets the standard for how well a robot works. The robot’s settings are adjusted to meet the maker’s standards.
Key aspects of factory calibration include:
- Precision measurement tools
- Controlled environmental conditions
- Standardized calibration protocols
Factory calibration is important. It helps robots come ready to go, with less need for adjustments later.
In-Situ Calibration Procedures
In-situ calibration is done where the robot will work. It’s needed when factory conditions are different from real-world settings.
In-situ calibration offers several benefits, including:
- Compensation for environmental factors
- Adjustment for specific application requirements
- Enhanced system reliability
|
Calibration Method |
Advantages |
Limitations |
|---|---|---|
|
Factory Calibration |
Controlled conditions, standardized protocols |
May not account for field conditions |
|
In-Situ Calibration |
Compensates for environmental factors, application-specific |
Requires on-site expertise, potentially time-consuming |
Self-Calibrating Robotic Systems
Self-calibrating robots are a big step forward. They can change their settings on their own. This keeps them working at their best over time.
Features of self-calibrating systems include:
- Autonomous adjustment capabilities
- Continuous monitoring of system performance
- Adaptive compensation for wear and tear
These robots are great for places where precision is everything. This includes medical surgery and precise manufacturing.
Precision Standards and Measurement in Robotics
Setting and following precision standards is key for robotics to grow and be used in many areas. As robotics gets better, it’s more important to have standard ways to measure precision. This ensures robots work well together, safely, and perform well in different tasks.
Precision standards in robotics are about more than just being accurate. They also make sure robots can work well in different places and tasks. This means understanding how mechanical, electrical, and software parts affect a robot’s precision.
ISO and IEEE Standards for Robotic Precision
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) are big in setting robotic precision standards. They cover things like how well robots perform, safety, and how to test them.
- ISO 9283 gives guidelines for robot performance and testing, focusing on things like how accurately a robot can move and repeat its actions.
- IEEE standards, like those from the IEEE Robotics and Automation Society, help improve robotic technology. They set up common ways for innovation.
Testing Methodologies and Equipment
To follow precision standards, robots go through tough tests and use special tools. These tests check things like:
- How accurate and consistent a robot’s movements are.
- How well a robot follows paths and moves along them.
- How a robot reacts to things like temperature and shaking.
Tools like laser interferometers and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) help measure these things very precisely.
Certification and Compliance Requirements
Robots need to meet standards to be safe and work well. Manufacturers must follow these rules to make sure their robots are precise enough.
Being compliant means more than just passing a test at first. Robots also need regular checks and updates to keep working well over time.
By sticking to precision standards and measurement, we make sure robots are accurate and reliable. This improves their performance and safety in many fields.
Manufacturing Applications Demanding High Precision
In today’s manufacturing world, high precision is key, not just a need. This is true for industries like semiconductor production and aerospace fabrication. We look at the manufacturing areas that need high precision, why they’re important, and the tech used.
Semiconductor and Electronics Production
Semiconductor making is super precise. It needs exact control over steps like lithography, etching, and doping. We use cutting-edge tech like extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL) and atomic layer deposition (ALD) for this.
Being precise in making semiconductors is vital. Small mistakes can cause bad chips, which cost a lot. So, makers spend a lot on precision engineering and checking quality.
|
Process |
Precision Requirement |
Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
|
Lithography |
Nanometer scale accuracy |
EUVL |
|
Etching |
High selectivity and uniformity |
Plasma etching |
|
Doping |
Precise dopant concentration |
Ion implantation |
Automotive Manufacturing Precision Requirements
The car industry also needs high precision. This is for engine parts, transmission bits, and other key stuff. Precision making makes sure these parts are top quality and work well.
We use many precise making methods in car making. Like CNC machining, grinding, and honing. These help make complex parts with tight fits, making cars better and more reliable.
Aerospace Component Fabrication
Aerospace part making is also super precise. It’s about making aircraft and space parts with exact machining and assembly for safety and performance.
We use advanced materials and making ways, like 3D printing and CNC machining, for aerospace parts. These methods help make complex shapes and structures needed by the aerospace field.
High precision in aerospace making boosts safety and makes planes and spaceships better and more reliable. As aerospace grows, so will the need for precise making.
Medical and Surgical Robotics Precision
Medical robotics is getting better, making surgeries more precise and less invasive. This change is big, showing how surgical robots are now designed for micron-level precision.
Surgical Robot Design for Micron-Level Precision
Creating surgical robots for micron-level precision is a complex task. Microbot Medical’s LIBERTY® Endovascular Robotic System is a great example. It shows how robots can make medical procedures more accurate.
Key design considerations include high-resolution imaging and advanced control algorithms. These help robots move precisely during surgery.
Haptic Feedback and Precision Control
Haptic feedback is key for precise control in surgical robots. It gives surgeons the feel of what they’re doing, making procedures more intuitive. This is vital for delicate surgeries.
Combining haptic feedback with advanced algorithms makes surgeons more confident. Research is ongoing to make these systems even better.
Clinical Outcomes Related to Robotic Precision
Robotic precision greatly improves patient outcomes. Studies show fewer complications, shorter recovery times, and better health. As technology advances, these benefits will grow.
Using the latest in medical robotics, healthcare can offer better care. Procedures will be more precise and less invasive. We’re dedicated to improving patient care through innovation.
Environmental Challenges to Robotic Precision
Robotic systems face many environmental challenges that impact their precision. As we explore new robotic capabilities, it’s key to tackle these challenges.
Temperature and Humidity Effects
Temperature and humidity greatly affect robotic precision. Thermal expansion can alter mechanical parts’ sizes, affecting their accuracy. For example, small temperature changes in high-precision manufacturing can cause big problems.
Humidity can lead to moisture issues like corrosion or electrical failures. Condensation from high humidity can damage electronic parts. We must think about these factors when designing and running robotic systems.
Vibration and External Disturbances
Vibrations and external disturbances also challenge robotic precision. Vibrations can stress mechanical parts and affect robotic stability, which is critical in precise tasks like assembly or surgery.
External disturbances, like seismic activity or nearby machinery, can also harm robotic systems. These can cause misalignments or disrupt robotic component calibration, reducing precision.
Compensation Strategies for Environmental Variables
To tackle environmental challenges, we use various strategies. For temperature and humidity, we might use climate-controlled environments or materials that expand less with temperature changes.
For vibrations and external disturbances, vibration isolation and strong design help keep robotic precision. Advanced sensors and real-time monitoring systems are also key in detecting and adjusting for environmental factors.
By understanding and addressing these challenges, we can improve robotic precision and reliability. This makes them more effective in many applications.
Software Algorithms for Precision Control
Advanced software algorithms are key to precision control in modern robotics. They help robots do complex tasks with great accuracy and reliability.
Advanced Control Algorithms
Control algorithms are vital for robots to work precisely. Model Predictive Control (MPC) and Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control are two top choices. MPC is great for complex systems with many rules. PID control helps control the robot’s movements with precision.
- MPC optimizes control inputs based on a system model.
- PID control adjusts outputs based on the difference between desired and actual states.
Real-time Computing Requirements
Real-time computing is key for precision in robotics. It makes sure the system can react quickly to changes and commands. Real-time operating systems (RTOS) are made for fast and predictable responses, which are vital for precise tasks.
- RTOS makes sure tasks are done on time.
- It’s important for robots to act consistently for precise operations.
AI and Machine Learning for Precision Enhancement
AI and machine learning are boosting precision in robotics. Machine learning algorithms get better with data, improving control over time. Reinforcement learning lets robots adapt to new situations and tasks, making them more precise.
- Machine learning enhances control with data insights.
- Reinforcement learning helps robots learn from their environment.
By combining advanced software, real-time computing, and AI/machine learning, we can greatly improve robotic precision. This mix is essential for high-performance robots in many industries.
Micro and Nano-Scale Precision Robotics
The world of micro and nano-scale precision robotics is changing fast. It’s bringing new levels of accuracy to many fields. We’re seeing big changes in how we do things at the tiny and teeny-tiny levels.
These robots need top-notch tech, like advanced sensors and control systems. This tech lets them do delicate tasks over and over again with great accuracy.
Micromanipulation Technologies
Micromanipulation is all about handling tiny objects. Tools like optical tweezers, atomic force microscopy, and microgrippers are key. They’re used in biological research, microassembly, and material science.
For example, optical tweezers use a laser to grab and move tiny particles. It’s super useful in biology for working with cells and studying how they interact.
Nanometer Precision Challenges and Solutions
Getting to nanometer precision is hard. It’s tough to avoid things like thermal drift and vibrations. But, advanced control algorithms and high-resolution sensing technologies help solve these problems.
Nanometer precision is key in making smaller and smaller parts for semiconductors. Closed-loop control and predictive modeling keep things precise.
|
Technique |
Application |
Precision Level |
|---|---|---|
|
Optical Tweezers |
Biological Research |
Nanometer |
|
Atomic Force Microscopy |
Material Science |
Sub-nanometer |
|
Microgrippers |
Microassembly |
Micrometer |
Applications in Biological and Material Sciences
Micro and nano-scale precision robotics are big in biology and material science. In biology, they let us work with cells and samples with precision. In material science, they help make and study tiny structures and materials.
In biology, these robots are great for cellular injection and tissue engineering. In material science, they aid in making new materials with special properties.
Economic Considerations in Precision Robotics
The world of precision robotics is complex, with many economic factors to consider. These include the costs of starting up, the return on investment, and market trends. A clearer discussion of these economic aspects will help readers better understand the financial implications of adopting advanced robotics technologies.
Investment Costs for High-Precision Systems
Getting into high-precision robotics means a big initial investment. This investment covers several areas:
- Hardware and software expenses
- Installation and integration costs
- Training and personnel expenses
- Maintenance and upgrade costs
To better understand these costs, let’s look at a breakdown for a high-precision robotic system:
Return on Investment Analysis
The initial cost of precision robotics is high, but the return can be worth it. This return comes from increased productivity, less waste, and better product quality.
For example, a factory using precision robotics can make products faster and more consistently. This leads to happier customers and more sales.
Market Trends and Competitive Advantages
The market for precision robotics is changing fast, thanks to new tech and growing demand. Knowing these trends is vital for businesses wanting to stay ahead.
Some important trends include:
- More use in the automotive and electronics fields
- Increased need for collaborative robots (cobots)
- Improvements in AI and machine learning for better precision
By keeping up with these trends and using precision robotics, companies can outdo their rivals in the market.
Future Directions in Precision Robotics
Precision robotics is on the verge of big changes thanks to new technologies. These advancements will make robots more precise and useful in many fields.
Emerging Technologies for Ultra-Precision
New technologies are pushing ultra-precision robotics forward. Nanotechnology lets us work with materials at the atomic level. This is changing industries like semiconductors and biomedicine.
Advanced materials science is also key. It’s creating new materials that make robots more precise and long-lasting.
|
Technology |
Application |
Benefit |
|---|---|---|
|
Nanotechnology |
Semiconductor manufacturing |
Enhanced precision |
|
Advanced materials science |
Robotic components |
Increased durability |
Quantum Sensing and Control
Quantum sensing and control are big deals for precision robotics. Quantum sensors are super accurate, letting robots do tasks that were thought impossible.
“The integration of quantum sensing technologies into robotic systems represents a significant leap forward in precision robotics, enabling applications that were previously unimaginable.”
Quantum control is also being explored. It uses quantum mechanics to make robots more stable and reliable. This improves how well robots work.
Integration with Advanced Manufacturing Paradigms
Precision robotics is getting closer to advanced manufacturing like Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing. These systems use connected systems, data, and automation for better manufacturing.
Precision robotics will be key in these systems. It will help make complex products with great precision and reliability. Adding AI and IoT will make manufacturing even better.
Conclusion
Precision robotics has changed many fields, like manufacturing and healthcare. It makes movements very accurate and precise. We’ve looked at how it works, its uses, and why it’s important.
Robots now do complex tasks thanks to new tech like vision systems and AI. Soon, quantum sensing and control will make them even better.
The future of robotics is closely tied to precision robotics. It’s making new things possible. By learning about precision robotics, we can find new ways to grow and innovate. This will shape the future of many industries around the world.
FAQ
What is precision robotics?
Precision robotics combines robotics and engineering for exact movements. It’s used in healthcare, manufacturing, and aerospace.
How does precision differ from accuracy in robotics?
Accuracy is how close a robot hits its target. Precision is how consistent those hits are. A robot can be one without the other.
What role do sensors play in precision robotics?
Sensors like vision systems and force sensors help robots move precisely. They give feedback for better control.
What is the LIBERTY Endovascular Robotic System?
The LIBERTY System is a medical robot. It uses precision to improve endovascular procedures, giving precise control.
How is precision measured in robotics?
Precision is measured by standards like ISO and IEEE. Testing and certification also play a role.
What are some applications of precision robotics in manufacturing?
Precision robotics is used in making semiconductors, cars, and aerospace parts. High precision is needed here.
How do environmental factors affect robotic precision?
Things like temperature and vibration can mess with robot precision. But, there are ways to fix this.
What is the role of software algorithms in precision control?
Algorithms help robots move precisely. They use advanced computing and AI for consistent movements.
What are some emerging technologies in precision robotics?
New tech includes ultra-precision and quantum sensing. These will improve robot precision and capabilities.
What are the economic considerations of implementing precision robotics?
Costs and market trends are key when deciding on precision robotics. They help figure out if it’s worth it.
How is precision robotics used in medical and surgical applications?
In medicine, precision robotics helps with surgery. It uses haptic feedback for better results and care.
What are the challenges of achieving nanometer precision in robotics?
Getting to nanometer precision is hard. It needs advanced tech and control to overcome environmental issues.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10821852/






