Did you know that nearly 80% of women may develop fibroid tumors by the time they reach menopause? If left unremoved, these growths can lead to severe symptoms that significantly impact daily life.
Research published on PubMed shows that not removing these growths can cause problems. This includes heavy menstrual bleeding and infertility issues. In some cases, these tumors can also lead to other health concerns that may need immediate medical attention.
Key Takeaways
- Fibroid tumors can cause severe symptoms if not removed.
- Leaving these growths untreated may lead to heavy menstrual bleeding.
- There is a possible link between fibroids and infertility.
- Failing to address fibroids can result in other health complications.
- Medical research supports the removal of fibroid tumors to prevent long-term health issues.
Understanding Uterine Fibroids: Types and Locations
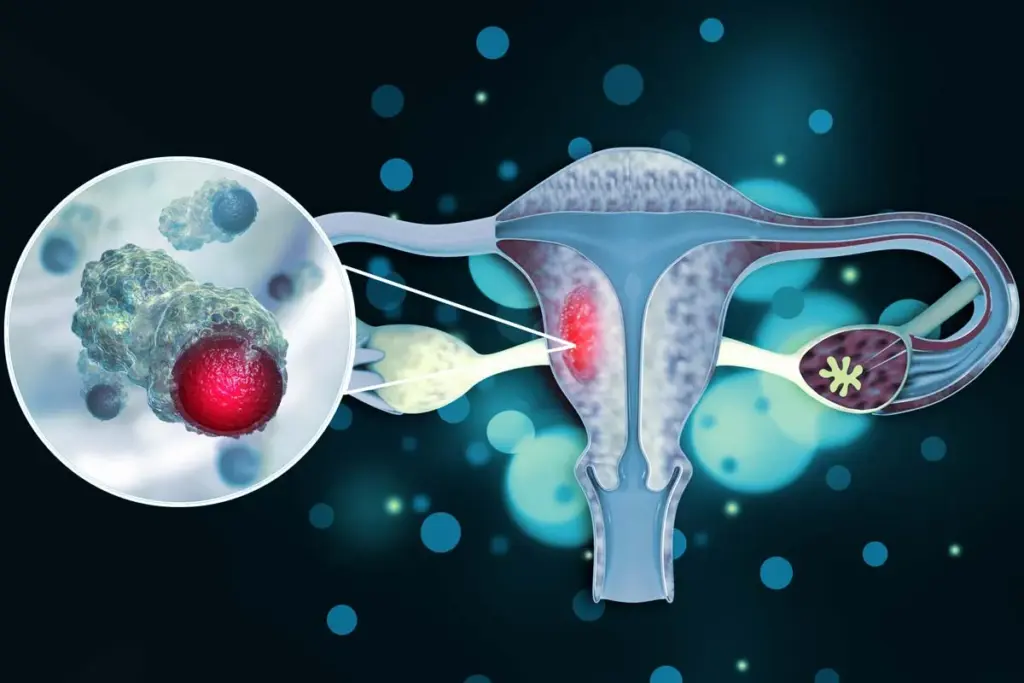
Uterine fibroids, or leiomyomas, are benign tumors that grow in or around the uterus. They are common among women of reproductive age. These growths can cause symptoms that affect daily life.
Definition and Classification of Fibroids
Fibroids are classified by their location in or around the uterus. Knowing this helps doctors understand symptoms and treatment options. Fibroids can be single or multiple, ranging from small to large.
Common Locations: Intramural, Subserosal, and Submucosal
Fibroids are mainly categorized into three types based on their location:
- Intramural fibroids grow inside the muscular wall of the uterus. They are the most common and can grow large.
- Subserosal fibroids grow outward from the uterus into the pelvic cavity. They can grow big and may be attached by a stalk.
- Submucosal fibroids grow just beneath the uterine lining. They can protrude into the uterine cavity, leading to heavy menstrual bleeding.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Fibroids are more common in some women, with certain risk factors increasing the chance of developing them. Fibroids are more common in women of African descent and tend to occur at a younger age in this group. Other risk factors include a family history of fibroids, early menstruation, and certain diets.
Understanding uterine fibroids is key for diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing the types, locations, and risk factors helps healthcare providers offer better care to women with fibroids.
The Natural Progression of Untreated Fibroids
Fibroids grow in the uterus and are influenced by hormones. They are benign tumors. Hormones play a big role in their growth.
How Fibroids Develop and Grow
Fibroids start in the uterus’s muscle layer, called the myometrium. We don’t know all about why they start, but hormones and genes are key. Estrogen and progesterone help them grow.
Fibroids grow at different rates in different women. Some stay small and don’t cause problems. Others grow fast and cause big symptoms.
Hormonal Influences on Fibroid Growth
Hormones are very important for fibroid growth. Estrogen is key because it makes fibroids grow. When women are younger, estrogen levels are higher, helping fibroids grow.
- Estrogen promotes fibroid growth.
- Progesterone also plays a role in fibroid development.
- Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can affect fibroid growth.
Typical Timeline for Fibroid Progression
Fibroids grow at different rates. Some grow slowly over years. Others may stop growing or even shrink after menopause, when hormone levels drop.
- Fibroids often grow during the reproductive years.
- Growth may slow or stop after menopause.
- In some cases, fibroids may shrink after menopause.
Knowing how fibroids grow is key to finding the right treatment. Regular check-ups and medical advice can help manage symptoms and prevent problems.
Can Fibroids Go Away on Their Own?
Many women wonder if fibroids can disappear without medical help. The chance of fibroids going away on their own depends on several factors. These include hormonal changes and how these growths naturally progress.
Spontaneous Regression Possibilities
Research shows that fibroids might shrink or go away by themselves in some cases. This isn’t fully understood but is linked to hormone level changes. A drop in estrogen, which helps fibroids grow, is thought to play a role.
Spontaneous regression means fibroids get smaller or disappear without treatment. While it happens, it’s not a sure thing for all women with fibroids.
Changes During Menopause
Menopause brings big changes in a woman’s hormones, like a drop in estrogen. This can make fibroids smaller or even disappear. Studies show that after menopause, women often feel less fibroid symptoms because of these hormonal changes.
The onset of menopause can be a turning point for women with fibroids. The drop in estrogen might make fibroids smaller and symptoms less. But, it’s important to keep an eye on fibroids even after menopause, as some might need medical care.
When “Wait and See” Is Appropriate
For women with small, symptom-free fibroids, waiting and watching might be okay. Regular check-ups with ultrasound and symptom tracking help see if fibroids are changing or causing problems.
This approach is often suggested for women close to menopause. Hormonal changes during this time might make fibroids smaller. But, women with big fibroids or bad symptoms might need a more active treatment plan.
- Regular monitoring is key to managing fibroids.
- Hormonal changes during menopause can affect fibroid size.
- A “wait and see” approach may not be suitable for all women.
Common Symptoms of Untreated Fibroids
Symptoms of untreated fibroids can affect a woman’s health and mood. They can make daily life hard and impact overall health.
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Patterns
One common symptom is abnormal uterine bleeding. This can be heavy periods, long periods, or bleeding between periods. It can cause discomfort and even anemia.
Pain, Pressure, and Pelvic Discomfort
Fibroids can cause pain and pressure in the pelvis. The pain can be mild or severe and may only happen during certain times. This can make it hard to do everyday things.
Urinary and Bowel Dysfunction
Big fibroids or those near the bladder or bowel can affect urination and bowel movements. Symptoms include frequent urination, constipation, and trouble with bowel movements. These symptoms can disrupt daily life.
Fatigue and Other Systemic Symptoms
Heavy menstrual bleeding can lead to anemia, causing fatigue and weakness. The pain and discomfort from fibroids can also affect mood and overall well-being.
|
Symptom |
Description |
Impact on Life |
|---|---|---|
|
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding |
Heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding |
Discomfort, anemia, and inconvenience |
|
Pain and Pressure |
Pelvic pain and pressure |
Limitations in daily activities |
|
Urinary and Bowel Dysfunction |
Frequent urination, constipation |
Disruption in daily routines |
|
Fatigue |
Anemia, weakness, shortness of breath |
Emotional distress, overall well-being |
It’s important for women to know these symptoms and seek medical help. Knowing about fibroids and their symptoms can help manage them better.
How Big Can Fibroids Get If Left Untreated?
If fibroids are not treated, they can grow quite large. This can lead to serious health issues. The way fibroids grow can differ a lot between women.
Growth Patterns and Possible Sizes
Fibroids can grow at different speeds. This is due to hormonal changes and genetics. Some stay small, while others can get very big.
Factors Influencing Fibroid Growth:
- Hormonal influences, like estrogen
- Genetic predisposition
- Other factors like diet and lifestyle
Record-Breaking Cases
There have been cases of very large fibroids. For example, a study in the Journal of Medical Case Reports reported a fibroid over 26 kg (57 lbs).
|
Size Comparison |
Weight |
Potential Complications |
|---|---|---|
|
Small (pea-sized) |
Less than 1 kg |
Often asymptomatic |
|
Medium (golf ball-sized) |
1-5 kg |
May cause discomfort, heavy bleeding |
|
Large (melon-sized or larger) |
Over 5 kg |
Can lead to severe anemia, pressure on surrounding organs |
When Size Becomes Medically Concerning
Big fibroids can cause serious problems. These include severe anemia from heavy bleeding, pressure on organs, and fertility issues.
Monitoring and medical intervention are key when fibroids get too big. This is to prevent or treat symptoms and complications.
Untreated Fibroids and Their Impact on Fertility
It’s important for women planning to have a baby to understand how untreated fibroids affect fertility. Fibroids can change how a woman gets pregnant and how the pregnancy goes.
How Fibroids Affect Conception
Fibroids can make it harder to get pregnant. They can change the shape of the uterus, making it hard for an embryo to stick. Submucosal fibroids are the worst because they can really mess up the uterus’s shape.
Studies show that removing fibroids can help women get pregnant. But, we don’t know all the reasons why. A study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that women with fibroids had lower pregnancy rates than those without.
Fibroids During Pregnancy: Risks and Complications
Fibroids during pregnancy can lead to serious problems. These include preterm labor, placental abruption, and fetal growth restriction. The size and where the fibroids are can make a big difference in the risk.
“Women with fibroids are at a higher risk of pregnancy complications, stressing the need for careful monitoring and management.”
Impact on Delivery and Postpartum Recovery
Fibroids can also make delivery and recovery after birth harder. Women with fibroids might need a cesarean delivery. Fibroids can also make it harder to stop bleeding after birth.
|
Fibroid Characteristic |
Potential Impact on Pregnancy |
|---|---|
|
Size: Large fibroids |
Increased risk of preterm labor and placental abruption |
|
Location: Submucosal fibroids |
Distortion of the uterine cavity, affecting implantation |
|
Number: Multiple fibroids |
Increased risk of pregnancy complications and possible preterm labor |
Fertility Preservation Considerations
Women with fibroids who want to get pregnant should think about how to protect their fertility. Talking to a healthcare provider about treatment options is key.
Options for preserving fertility include myomectomy or treatments to shrink fibroids. Women should talk to their doctor to find the best plan for them.
Serious Complications of Untreated Fibroids
If fibroids are not treated, they can cause severe and dangerous problems. These problems can greatly affect a woman’s life and health.
Severe Anemia from Chronic Blood Loss
One big problem is severe anemia from losing too much blood. Heavy bleeding from fibroids can lower red blood cells, causing anemia. Symptoms include feeling very tired, weak, and short of breath.
Consequences of Severe Anemia:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness and fainting
- Poor concentration and memory
Fibroid Degeneration and Necrosis
Fibroid degeneration happens when a fibroid grows too big for its blood supply. This can cause cell death and severe pain. It might need quick medical help, often during pregnancy or when blood supply is affected.
Symptoms of Fibroid Degeneration:
- Acute pelvic pain
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
Fibroid Rupture: A Medical Emergency
Rarely, a fibroid can burst, which is a serious emergency. This can lead to severe bleeding that needs immediate surgery. It’s important to know the signs of a ruptured fibroid to get help fast.
Signs of Fibroid Rupture:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Vaginal bleeding
- Dizziness or fainting
Urinary Tract Obstruction and Kidney Damage
Big fibroids can block the urinary tract, which can harm the kidneys if not treated. This can cause urine to back up into the kidneys, leading to damage if not fixed.
|
Complication |
Symptoms |
Consequences if Untreated |
|---|---|---|
|
Severe Anemia |
Fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath |
Poor quality of life, organ damage |
|
Fibroid Degeneration |
Acute pelvic pain, fever, nausea |
Infection, chronic pain |
|
Fibroid Rupture |
Severe abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding |
Life-threatening internal bleeding |
|
Urinary Tract Obstruction |
Urinary retention, pain |
Kidney damage, infection |
The Long-term Consequences of Untreated Fibroids
Untreated fibroids can have serious long-term effects. They can harm not just your body but also your overall happiness. If fibroids are not treated, they can cause many problems.
Chronic Pain and Its Impact
Chronic pain is a big issue from untreated fibroids. This pain can make everyday tasks hard and lower your quality of life. It can also make you feel very tired because your body is always fighting pain.
Progressive Symptoms Over Time
As time goes by, untreated fibroids grow and symptoms get worse. You might experience heavier periods, more pelvic pressure, and severe cramps. Growing fibroids can also press on other organs, causing problems with your bladder or bowel.
Potential for Emergency Interventions
In some cases, untreated fibroids can cause emergencies. This includes severe bleeding or a twisted fibroid that needs quick medical help. This shows why it’s key to watch and manage fibroids closely.
Can Untreated Fibroids Become Cancerous?
Many people worry if fibroids can turn into cancer if not treated. The link between fibroids and cancer is complex. Medical research has explored this topic deeply.
Understanding the Relationship Between Fibroids and Cancer
Fibroids, or uterine leiomyomas, are usually not cancerous. They grow in the uterus. But, there’s a concern about their possible link to cancer. Studies show that the chance of a fibroid becoming cancer is very low.
Key Findings:
|
Condition |
Cancer Risk |
Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
|
Fibroids (Leiomyomas) |
Extremely Low |
Benign tumors, common in women of reproductive age |
|
Leiomyosarcoma |
High |
Rare, malignant tumor of the smooth muscle |
Leiomyosarcoma: Rare but Serious
Leiomyosarcoma is a rare cancer in the uterus’s smooth muscle. It’s different from benign fibroids and can grow fast. Even though it’s rare, knowing the symptoms is important.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Medical Attention
Some symptoms mean you should see a doctor right away. These include:
- Rapid growth of a fibroid
- Severe pain or pressure
- Abnormal or postmenopausal bleeding
- Fever or other signs of infection
Women should watch their symptoms closely. If something seems off, tell your doctor. Early action can make a big difference.
Diagnosing and Monitoring Untreated Fibroids
To diagnose and monitor untreated fibroids, doctors use imaging and lab tests. Knowing the size, number, and location of fibroids is key. This information helps decide the best treatment.
Imaging Techniques: Ultrasound, MRI, and CT Scans
Imaging is essential for finding fibroids. Ultrasound is often the first choice because it’s easy to get and works well. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) gives detailed pictures and is great for seeing fibroid size and location. CT scans are sometimes used, but not as often.
Each imaging method has its own benefits. Ultrasound is safe because it doesn’t use radiation. MRI, though, gives very detailed images. These are useful for planning surgery.
Laboratory Tests for Fibroid Assessment
Laboratory tests add to what imaging shows. They check for anemia from heavy bleeding and thyroid issues. These tests help rule out other problems that might cause similar symptoms.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
- Thyroid Function Tests
- Other relevant blood tests
Frequency of Monitoring Recommendations
How often to check on fibroids varies. It depends on the fibroids’ size, symptoms, and the patient’s health. Doctors use research to decide when to check in.
Women with small, symptom-free fibroids might not need to be checked as often. But those with big symptoms or large fibroids might need more visits. Regular checks help catch any changes early. This way, doctors can act fast if needed.
Quality of Life Impact of Living with Untreated Fibroids
Untreated fibroids affect more than just physical health. They impact daily life and overall happiness. Women with untreated fibroids face many challenges that affect their quality of life.
Physical Limitations and Daily Activities
Untreated fibroids cause a lot of discomfort and limit daily activities. Women may feel chronic pain, heavy bleeding, and pressure that makes simple tasks hard. Even basic actions like exercising or bending can be tough.
Psychological and Emotional Effects
The mental effects of untreated fibroids are significant. Dealing with symptoms can lead to anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation. This emotional burden can be as tough as the physical symptoms, harming a woman’s mental health.
Sexual Function and Relationship Impacts
Fibroids can also harm sexual health and relationships. Pain during sex, low libido, and emotional stress from symptoms can strain relationships. This can lead to feelings of inadequacy and more emotional pain.
Work and Social Life Disruptions
Symptoms of untreated fibroids can disrupt work and social life. Frequent absences and emergency visits can hurt career and reputation. Social activities may also decrease due to unpredictable symptoms, causing isolation and a lower quality of life.
In summary, untreated fibroids have a wide-ranging impact on life. They affect physical comfort, emotional well-being, sexual health, and social and professional life. It’s important to understand these effects to make informed decisions about managing fibroids.
Treatment Options Beyond Surgical Removal
Uterine fibroids can be treated in many ways, not just surgery. This is good news for women dealing with fibroids. Knowing about these options helps them make better choices for their health.
Medication-Based Approaches
Medicines are a common choice for fibroid symptoms. Hormonal treatments can lessen bleeding and pain. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists can even shrink fibroids by making the body think it’s in menopause. But, they can’t be used for too long because of side effects like bone loss.
Tranexamic acid helps control heavy bleeding from fibroids. Progestin-releasing IUDs can also reduce bleeding and act as birth control.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Some women choose less invasive methods than surgery. Myolysis and cryomyolysis use heat or cold to destroy fibroids. These methods can lessen symptoms without harming the uterus.
Uterine Artery Embolization and Focused Ultrasound
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) stops blood flow to fibroids, making them shrink. It’s a less invasive option that can greatly reduce symptoms. Focused ultrasound surgery (FUS) uses sound waves to heat and destroy fibroids, guided by MRI.
Lifestyle Modifications That May Help
Changing your lifestyle can also help with fibroid symptoms. Eating well and staying active can prevent fibroids from growing. Eating lots of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is also good. Stress management, like yoga or meditation, can also help.
It’s important for women to talk to their doctors about these options. This way, they can find the best treatment for their situation.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Fibroid Management
To manage fibroids well, you need to know all about the treatment options. Research shows how important it is to educate patients about fibroids.
It’s key for women to understand the different fibroid management options. This knowledge helps them choose treatments that fit their health goals and likes. Options include medicines, small surgeries, and changes in lifestyle.
Knowing what each treatment can do helps women make better choices. This way, they can be more involved in their care. It leads to better symptom control and a better life quality.
Success in managing fibroids comes from working together with your doctor. This ensures your treatment fits your unique needs.
FAQ
What are fibroids and how do they develop?
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths in or around the uterus. Hormones play a role in their growth. They can get bigger over time.
Can fibroids go away on their own?
Sometimes, fibroids can shrink, like after menopause. But this doesn’t always happen. Many things can be affected if they shrink.
What are the common symptoms of untreated fibroids?
Untreated fibroids can cause bleeding, pain, and pressure. They can also affect your bladder and bowel. These symptoms can really disrupt your life.
How big can fibroids get if left untreated?
Fibroids can grow to different sizes. Sometimes, they can get very large. Their size can be a concern if they cause a lot of symptoms.
Can untreated fibroids affect fertility?
Yes, fibroids can affect fertility. Their size, location, and number can impact getting pregnant. Treatment options can help preserve fertility.
What are the serious complications of untreated fibroids?
Untreated fibroids can lead to severe anemia and rupture. They can also block the urinary tract and damage the kidneys. These problems can be very serious and need quick medical help.
Can untreated fibroids become cancerous?
While rare, fibroids can turn into a serious cancer called leiomyosarcoma. It’s important to watch for warning signs that need immediate medical care.
How are untreated fibroids diagnosed and monitored?
Doctors use ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans to diagnose and monitor fibroids. They also use lab tests. How often you need these tests depends on your situation and medical guidelines.
What is the impact of living with untreated fibroids on quality of life?
Untreated fibroids can limit your physical abilities and daily activities. They can also affect your mental and emotional health, sex life, and relationships. Work and social life can also be impacted.
Are there treatment options beyond surgical removal for fibroids?
Yes, there are many treatment options. These include medicines, minimally invasive procedures, and focused ultrasound. Lifestyle changes can also help manage symptoms.
Can fibroids cause diarrhea?
Yes, fibroids can cause bowel problems like diarrhea. This is because of their size and location.
Can fibroids cause urinary incontinence?
Yes, large fibroids can put pressure on the bladder. This can lead to urinary incontinence.
Should fibroids be removed?
Whether to remove fibroids depends on your situation. This includes your symptoms, the size and location of the fibroids, and if they affect fertility. Talk to your healthcare provider to decide the best treatment for you.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Uterine fibroids: Learn More – Surgery for fibroids. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279531/



































