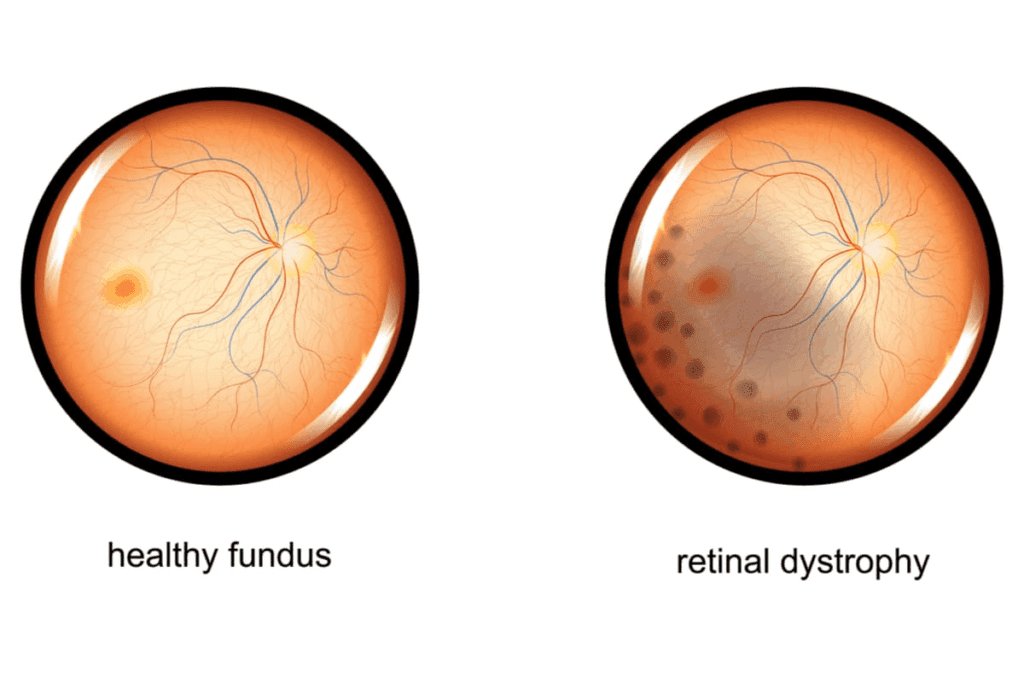
Do you see things that seem distorted or wavy? Epiretinal membrane (ERM), also known as macular pucker, is a condition. It happens when a thin layer of scar tissue forms on the macula. The macula is the part of the retina that helps us see clearly.What is a retinal membrane? This ultimate guide explains the epiretinal membrane (ERM), how serious it is, and treatment.
At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to catch ERM early and treat it right. We make sure our patients get the best care for their eyes. ERM affects millions globally, and knowing its effects is key to managing it well.
Key Takeaways
- Epiretinal membrane (ERM) is a condition characterized by the formation of scar tissue on the macula.
- ERM is also known as macular pucker and can cause distorted or wavy vision.
- Early detection and expert treatment are key to managing ERM and keeping your vision.
- Liv Hospital offers top-notch care for patients with ERM and other eye issues.
- Understanding ERM is vital for effective management and treatment.
Understanding Epiretinal Membrane (ERM)
Exploring epiretinal membrane means looking into its definition, structure, and how it’s made. We learn how it affects our vision and what it means for patients.
Definition and Anatomical Structure
An epiretinal membrane is a growth of cells at the back of the eye. It forms over the macula, causing a greyish, semi-clear layer. This layer is between the retina and the vitreous body.
The Fibrocellular Nature of ERM
ERM’s makeup is key to understanding it. It’s made of different cells, including myofibroblasts. These cells cause the membrane to contract, leading to vision problems.
Myofibroblasts are important because they make the membrane contract. This can cause macular pucker and vision issues.
Macular Pucker: Alternative Terminology
ERM is also called macular pucker. This term describes the wrinkling of the macula caused by the membrane. It shows how ERM affects our vision.
Even though ERM and macular pucker are different names, they describe the same issue. It’s a membrane on the retina that can distort vision.
The Prevalence and Demographics of ERM
ERM affects many people worldwide. It’s a big issue in eye care. Studies show different numbers of people with ERM globally.
General Population Statistics
Research says 7% to 11.8% of people have ERM. This range comes from different studies and how they define ERM. Overall, ERM is quite common in eye care.
Age-Related Prevalence
Age plays a big role in ERM. After 50, more people get ERM. Over 75, it’s even more common, up to 20%. Older adults need regular eye checks.
ERM is more common with age. As more people get older, ERM will likely become more common. Eye care professionals need to focus on this.
Geographic and Ethnic Variations
There are different rates of ERM in different places and ethnic groups. But, the data isn’t always the same. More research is needed to understand these differences.
Knowing these differences helps in making eye care better for everyone. As we learn more about ERM, we can help those affected more.
Types of Retinal Membrane Conditions
Epiretinal membrane (ERM) comes in different types based on its cause. Knowing these types helps doctors diagnose and treat it better.
Idiopathic ERM
Idiopathic ERM makes up about 95% of cases and has no known cause. It’s more common in older people and linked to aging. The exact reasons for idiopathic ERM are not clear, but it’s thought to be related to changes in the vitreous gel and retina.
Medical Expert, a renowned ophthalmologist, says, “Idiopathic ERM is a big cause of vision loss in older adults.”
“The management of idiopathic ERM needs a full approach, including regular checks and surgery when needed.”
Medical Expert
Secondary ERM: Causes and Distinctions
Secondary ERM happens with other eye problems like diabetic retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion, and retinal detachment. It can also come from eye injuries or surgery. The causes of secondary ERM vary, and treatment often focuses on the main issue.
Causes of Secondary ERM | Characteristics |
Diabetic Retinopathy | Linked to diabetes, retinal damage |
Retinal Vein Occlusion | Caused by blocked retinal veins, leading to lack of blood flow |
Ocular Trauma | Caused by injury to the eye |
Relationship to Posterior Vitreous Detachment
Posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) happens when the vitreous gel pulls away from the retina. It’s common with age and often linked to ERM. While PVD itself usually doesn’t cause symptoms, it can lead to serious problems like retinal tears or detachment if not managed right.
It’s key to understand how ERM and PVD are connected for good management. As we dive deeper into ERM, it’s clear we need a detailed plan for the best results.
Risk Factors for Developing Epiretinal Membrane
Knowing the risk factors for Epiretinal Membrane is key for early detection and treatment. Several factors can lead to ERM. Identifying these can help in prevention and treatment planning.
Age and Gender as Primary Factors
Advanced age is a big risk for Epiretinal Membrane. Most people are diagnosed around 65 years old. This shows ERM is common in older adults.
Studies also show women are more likely to get ERM than men. So, gender is another major risk factor.
Systemic Conditions: Diabetes and Hypercholesterolemia
Diabetes and high cholesterol are key in ERM development. Diabetes can lead to retinal problems like diabetic retinopathy. This raises the risk of ERM.
Hypercholesterolemia, or high cholesterol, also increases ERM risk. This might be because it’s linked to vascular diseases.
Ocular Trauma and Previous Eye Surgeries
Ocular trauma or past eye surgeries can lead to ERM. Trauma can cause inflammation and scarring on the retina. This can lead to ERM.
Surgeries, though needed, can sometimes cause ERM as a complication.
Retinal Vascular Disorders
Retinal vascular disorders, like retinal vein occlusion and diabetic retinopathy, raise ERM risk. These disorders can change the retina’s structure and function. This makes it easier for membranes to form.
Understanding these risk factors helps doctors spot people at high risk for ERM. They can then closely watch these individuals to prevent or lessen the condition’s effects.
How Serious Is Epiretinal Membrane?
Understanding ERM’s seriousness means looking at its severity and vision impact. This condition can greatly affect a person’s life by changing how well they see and how they function daily.
Severity Spectrum of ERM
ERM’s severity can vary a lot. Some people might only notice mild symptoms that don’t really bother them. But others might see big changes in their vision.
The condition’s severity spectrum is wide. It can range from no symptoms at all to serious vision problems. This shows why it’s key to assess and watch each case closely.
Impact on Daily Visual Function
ERM can really affect how we see every day. Many patients say they see straight lines as wavy, a problem called metamorphopsia.
Even simple tasks like reading, driving, or seeing faces can get hard because of ERM’s effects on vision.
Progressive Nature of the Condition
ERM tends to get worse over time. The membrane can shrink or get thicker, making symptoms worse.
Knowing this helps set realistic goals and choose the right treatments.
When ERM Becomes Sight-Threatening
In severe cases, ERM can seriously harm vision. Though rare, it can cause big vision loss. This might make it hard to do everyday things without help.
Spotting when ERM is a serious threat is very important. Tools like Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) help track how bad it gets.
Signs and Symptoms of ERM
It’s important to know the signs and symptoms of Epiretinal Membrane (ERM) for early treatment. Understanding how ERM affects vision is key. Timely medical care is vital.
Metamorphopsia (Visual Distortion)
Metamorphopsia is a major symptom of ERM. It makes straight lines look wavy. This can make everyday tasks hard.
Common complaints include:
- Distorted vision
- Wavy lines
- Difficulty with tasks requiring precise vision
Central Vision Impairment
ERM can also cause central vision problems. This makes reading and driving harder. It affects the sharpness of your vision.
The progression of central vision impairment can vary among individuals, but it often worsens over time if left untreated.
Symptom Progression Timeline
Symptoms of ERM can start off mild. But as the condition gets worse, these symptoms can get more severe. This can really affect your daily life.
Symptom Stage | Common Symptoms | Impact on Daily Life |
Early Stage | Mild visual distortion, slight blurring | Minimal impact, may not notice significant changes |
Moderate Stage | Noticeable distortion, central vision impairment | Moderate impact, difficulty with tasks like reading |
Advanced Stage | Significant distortion, pronounced central vision loss | Significant impact, difficulty with daily activities |
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice symptoms like metamorphopsia or central vision problems, see a doctor. Early treatment can help a lot. It can also save your vision.
Key indicators to seek medical help include:
- Sudden changes in vision
- Increasing distortion or blurring
- Difficulty with daily tasks due to visual disturbances
Diagnostic Procedures for Epiretinal Membrane
Diagnosing ERM involves several steps. We use both clinical exams and advanced imaging. Accurate diagnosis is key to choosing the right treatment and improving patient care.
Comprehensive Ophthalmological Examination
The first step is a detailed eye exam. This includes a medical history, vision tests, and a retina check. We look for any vision problems and check the retina’s health.
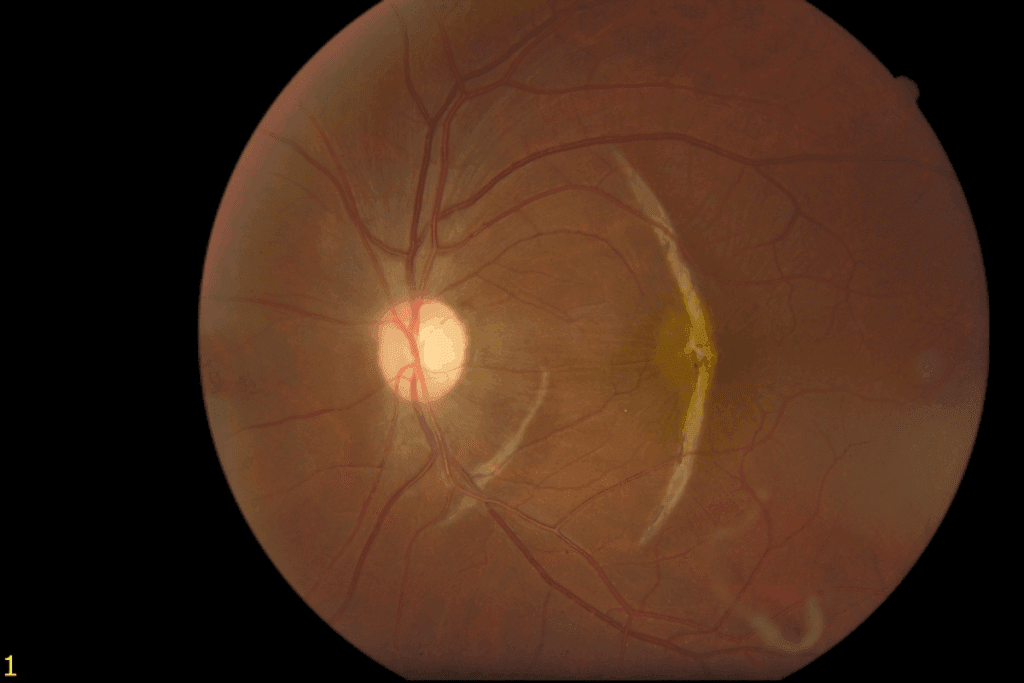
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): The Gold Standard
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is the top choice for ERM diagnosis. It gives clear images of the retina. This lets us see the membrane and its effect on the retina.
OCT has greatly helped in diagnosing and managing ERM. It lets us track the disease and plan surgeries if needed.
Retinal Photography and Angiography
Retinal photography and angiography are also important. Photography shows the retina’s details, and angiography checks the blood vessels. They help spot any ERM-related issues.
Grading Systems for ERM Severity
Grading systems help us measure ERM severity. They categorize the membrane’s extent and its impact. This helps us understand ERM’s progression and decide on treatment.
In summary, diagnosing ERM combines clinical exams and advanced imaging, with OCT being essential. These methods help us accurately assess ERM and plan effective treatments.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Epiretinal Membrane treatment has many options. It includes both conservative management and vitrectomy surgery. The right choice depends on how bad the symptoms are and how they affect the patient’s life.
Conservative Management Approaches
Many patients start with conservative management. This means regular checks with optical coherence tomography (OCT) to watch the membrane and its effect on vision. Conservative management is good for those with mild symptoms or no symptoms at all.
Vitrectomy Surgery: Procedure and Candidates
Vitrectomy surgery is for those with big vision problems and/or distortion. The surgery, pars plana vitrectomy (PPV), removes the membrane and reduces distortion. It aims to improve vision.
Who gets this surgery? Those with:
- Big vision problems that affect daily life
- Severe distortion
- ERM getting worse, shown by OCT
Membrane Peeling Techniques
Membrane peeling is key in vitrectomy surgery for ERM. It removes the membrane and any extra growth. Staining agents help see the membrane better during surgery.
Post-Surgical Care and Recovery
After surgery, patients need close follow-up. Post-surgical care includes antibiotics and steroids to prevent infection and swelling.
The recovery includes:
Timeframe | Care Instructions | Expected Outcomes |
Immediate Post-Surgery | Rest, avoid strenuous activities | Gradual improvement in vision |
1-2 Weeks | Follow-up appointments, medication as prescribed | Stabilization of vision |
1-3 Months | Continued follow-up, gradual return to normal activities | Improvement in visual acuity and reduction in distortion |
Living With Epiretinal Membrane
Living with ERM means getting medical care, making lifestyle changes, and finding support. It’s important to understand how ERM affects daily life.
Adapting to Visual Changes
Adapting to ERM’s visual changes is a big challenge. People often see straight lines as wavy or distorted, a condition called metamorphopsia. This can make everyday tasks like reading, driving, or recognizing faces hard.
To cope, people can use magnifying glasses or adjust digital device settings. They can also rearrange their living space to reduce the impact of distorted vision.
Visual Rehabilitation Options
Visual rehabilitation is key for adapting to ERM. It involves working with a low vision specialist to use remaining vision effectively. Techniques include using specific lighting and assistive devices like telescopic lenses.
A good visual rehabilitation program can greatly improve life for ERM patients. It’s about learning to use what vision you have and finding new ways to do daily tasks.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Regular check-ups with an ophthalmologist are vital for ERM management. These visits help track the condition’s progress and adjust treatment plans as needed. For those with mild symptoms, regular monitoring is often enough.
During these visits, patients get a thorough eye exam, including OCT scans. This helps monitor the membrane’s effect on the retina. This ongoing care allows for early detection and timely treatment.
Support Resources for Patients
Living with ERM can be tough, both physically and emotionally. Support resources like counseling, support groups, and educational materials are very helpful. Connecting with others who face similar challenges can be very supportive.
Support Resource | Description | Benefits |
Support Groups | Groups where patients can share experiences and advice. | Emotional support, practical tips for managing ERM. |
Counseling Services | Professional counseling to cope with the emotional impact. | Reduced stress, improved mental well-being. |
Educational Materials | Resources providing information on ERM and its management. | Better understanding of the condition, empowerment through knowledge. |
By using these support resources and staying proactive, patients can lead fulfilling lives despite ERM’s challenges.
Conclusion
Understanding Epiretinal Membrane (ERM) is key to managing and treating it well. We’ve looked at what ERM is, how common it is, and how it affects daily life. We’ve also talked about the different types, risk factors, and signs that show it’s present.
Getting a clear diagnosis with Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and other tests is important. This helps figure out how serious ERM is. There are treatments like watching it closely or surgery, and knowing about these options helps patients make good choices.
In short, managing ERM needs a team effort. This includes quick diagnosis, the right treatment, and ongoing support. By knowing about ERM, patients can handle their treatment better and live a fuller life. Good ERM management helps people adjust to vision changes and stay independent.
FAQ
What is epiretinal membrane (ERM) in ophthalmology?
Epiretinal membrane, also known as macular pucker, is a condition. It forms a layer of fibrous tissue on the retina’s surface. This can cause visual disturbances.
How serious is epiretinal membrane?
The seriousness of ERM can vary. It can cause mild visual disturbances or significant vision impairment. This depends on the condition’s severity and progression.
What are the risk factors for developing epiretinal membrane?
Risk factors include age, gender, and certain health conditions. These include diabetes and high cholesterol. Ocular trauma and retinal vascular disorders also increase the risk.
What are the symptoms of epiretinal membrane?
Symptoms include visual distortion and central vision impairment. These symptoms can worsen over time if not treated.
How is epiretinal membrane diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a thorough eye exam. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is used to assess the severity of ERM.
What are the treatment options for epiretinal membrane?
Treatment options vary. They range from conservative management to vitrectomy surgery. The choice depends on the condition’s severity.
What is the prevalence of epiretinal membrane?
ERM affects 7-11.8% of the general population. This number increases to up to 20% in people aged 75 and above.
Can epiretinal membrane cause blindness?
ERM can cause significant visual impairment. It is not typically a cause of complete blindness. But, it can greatly affect daily vision.
How can I manage living with epiretinal membrane?
Managing ERM involves adapting to visual changes. Utilize visual rehabilitation options and follow up with care. Accessing support resources is also important.
Is epiretinal membrane related to posterior vitreous detachment?
Yes, ERM is often associated with posterior vitreous detachment. This is a condition where the vitreous gel separates from the retina.
What is the difference between idiopathic and secondary ERM?
Idiopathic ERM occurs without a known cause, making up about 95% of cases. Secondary ERM is linked to specific causes or conditions, such as trauma or previous eye surgeries.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560703/