Heart diseases cause over 17.9 million deaths each year. Stent procedures are a common treatment for heart disease. But, many patients don’t know the risks involved. Assess risk of death during stent procedure. Get vital facts on life expectancy. See why stents are a best safe choice for long-term survival.
Getting a stent can be scary, and you might worry about the risks. In this article, we’ll talk about the risks of stent procedures. We’ll cover the chances of complications and how likely it is to die.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the risks associated with stent procedures
- Factors that influence the likelihood of complications
- Mortality rates associated with stent procedures
- Pre-procedure preparations to minimize risks
- Post-procedure care and follow-up
Understanding Stent Procedures
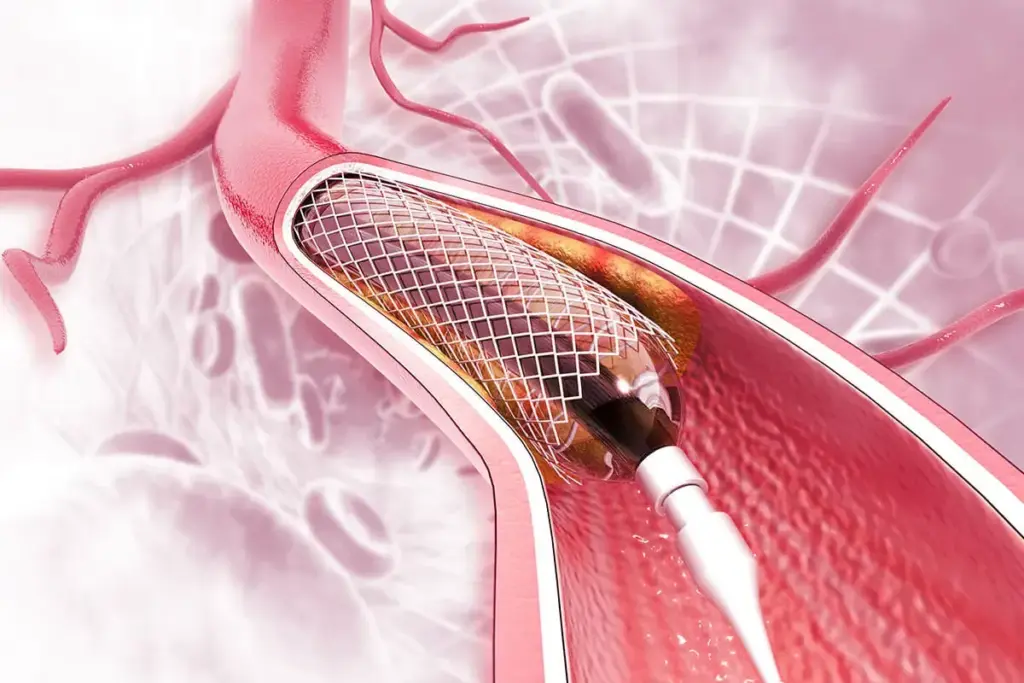
Learning about stent procedures is key for those thinking about this treatment. Stent placement is a common way to treat coronary artery disease. Knowing about it can ease worries and prepare patients for what’s ahead.
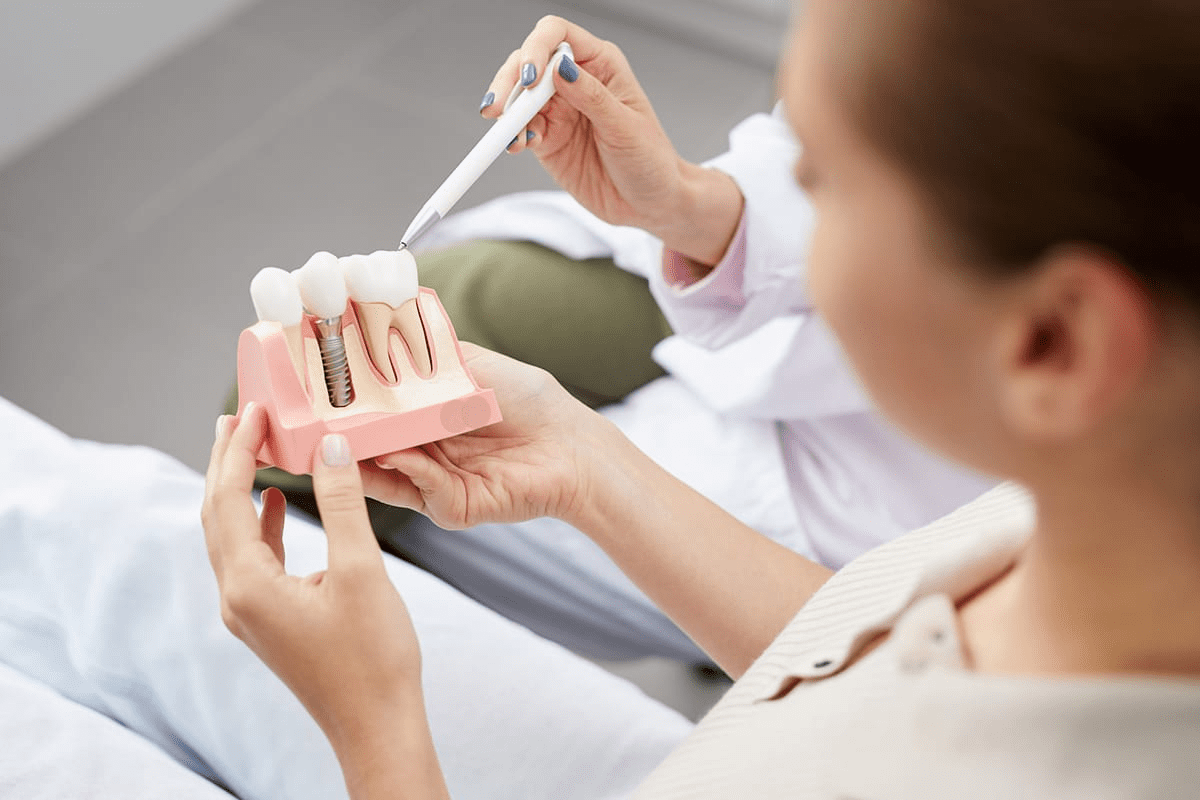
What is a Stent?
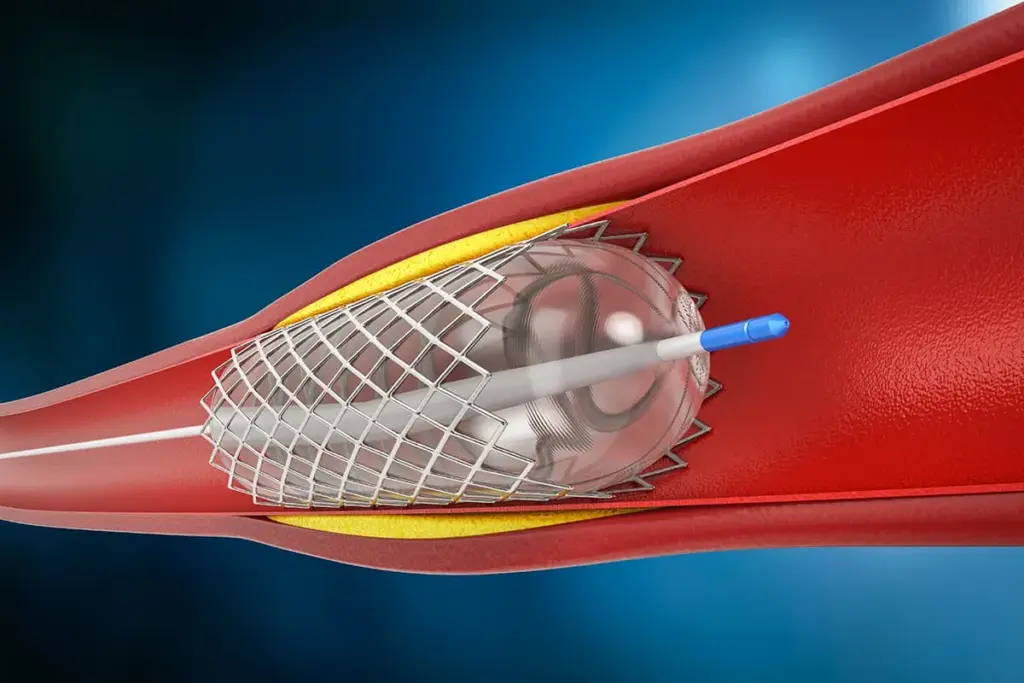
A stent is a small, mesh-like tube made of metal or other materials. It’s placed in a narrowed or blocked coronary artery to improve blood flow to the heart. Stents have changed how we treat coronary artery disease, making it less invasive than surgery.
The stent is put on a balloon catheter and guided to the right spot under imaging. Once there, the balloon is inflated, expanding the stent against the artery walls. After the balloon is deflated and removed, the stent stays in place.
Types of Stents Used
There are many types of stents for cardiovascular interventions, each with its own benefits.
- Bare-metal stents: Simple metal mesh stents that support the artery.
- Drug-eluting stents: Stents coated with medication to prevent the artery from narrowing again.
- Bioresorbable stents: Stents made from materials that dissolve over time, potentially reducing complications.
The right stent depends on the patient’s condition, the blockage’s location and severity, and the patient’s overall health.
Purpose of Stenting
The main goal of stenting is to improve blood flow to the heart by opening blocked or narrowed arteries. This can greatly reduce symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath, improving life quality.
After stenting, cardiac rehabilitation is vital for recovery. It helps improve heart health, physical function, and managing heart risks. Understanding what cardiac rehabilitation entails and its benefits highlights the comprehensive care that patients receive.
Understanding stent procedures, including what stents are, the types available, and their purpose, helps patients make informed decisions about their care.
The Risks Associated with Stent Placement

Stent placement is usually safe, but knowing the risks is key. It’s important to weigh the benefits against the risks. For many, the benefits of stent placement are worth it.
Common Complications
Some common issues with stent placement include:
- Bleeding or bruising at the site of catheter insertion.
- Blood clots, which can lead to heart attack or stroke.
- Restenosis, or the re-narrowing of the arteries.
These problems can usually be handled with the right medical care. This includes inpatient cardiac rehab programs. They have shown good rehabilitation statistics.
Rare but Serious Risks
There are also rare but serious risks:
- Allergic reactions to the stent materials.
- Kidney damage from the contrast dye.
- Stroke or heart attack during or after the procedure.
It’s important for patients to know about these risks. This helps them make better choices about their care.
Risk Factors for Complications
Some factors can make complications more likely. These include:
- Pre-existing health conditions, like diabetes or kidney disease.
- Age, as older patients face higher risks.
- Lifestyle factors, such as smoking or not being active.
Healthcare providers can use this info to create better treatment plans. This can lead to better rehab stats.
Life Expectancy After Stent Placement
The impact of stent placement on life expectancy depends on several factors. These include the patient’s overall health, the severity of their cardiovascular disease, and the type of stent used. We will explore these factors in detail to provide a clear understanding of what to expect after stent placement.
Statistics on Life Expectancy
Studies show that patients who undergo stent placement generally have a good prognosis. They often see significant improvements in survival rates. A study found that many patients live for 10 years or more after the procedure.
To give you a better understanding, here are some statistics on life expectancy after stent placement:
|
Study |
Number of Patients |
Average Follow-Up |
Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Study A |
1,000 |
5 years |
85% |
|
Study B |
500 |
10 years |
70% |
|
Study C |
2,000 |
7 years |
80% |
Factors Affecting Longevity
Several factors can influence life expectancy after stent placement. These include:
- Age: Older patients may have a lower life expectancy compared to younger patients.
- Comorbidities: Presence of other health conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, can affect longevity.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adherence to a healthy lifestyle, including diet and exercise, can improve survival rates.
- Type of Stent: The type of stent used, such as drug-eluting or bare-metal stents, can impact outcomes.
Cardiac rehabilitation programs also play a key role in improving life expectancy after stent placement. These programs usually last from several weeks to a few months. How long is cardiac rehab and how long does cardiac rehab last are common questions. Generally, cardiac rehab programs are tailored to the individual’s needs and can last from 6 to 24 weeks.
Comparing Stent Procedures and Other Treatments
When considering treatment options for cardiovascular disease, it’s essential to compare stent procedures with other treatments. These include coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or medication therapy. Each treatment has its benefits and risks, and the choice depends on individual patient characteristics and the severity of their disease.
We will work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for your specific condition. By understanding the statistics on life expectancy, factors affecting longevity, and comparing different treatment options, you can make informed decisions about your care.
Evaluating Overall Health Before a Stent
Before a stent is placed, a full health check is key. It helps spot any issues and makes sure the patient does well. This check looks at the patient’s past health, current state, and lifestyle.
Importance of Pre-Procedure Assessments
Checking a patient’s health before a stent is very important. It includes looking at their medical history, doing a physical exam, and running tests like blood work and imaging. This helps find and fix any risks early on, making the procedure safer and more effective.
Research at the ESC Congress shows how vital these checks are. For example, finding out if a patient has kidney problems or diabetes helps doctors plan better. This can lower the chance of problems during the stent placement.
Impact of Existing Health Conditions
Health issues like high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease can affect stent outcomes. It’s important to manage these conditions well before the procedure.
For instance, keeping blood sugar in check for diabetics and blood pressure for hypertensives can lessen risks. Our team works with patients to get their health in the best shape possible before the procedure.
|
Health Condition |
Impact on Stent Procedure |
Pre-Procedure Management |
|---|---|---|
|
Diabetes |
Increased risk of complications |
Control blood sugar levels |
|
Hypertension |
Increased risk of cardiovascular events |
Manage blood pressure |
|
Kidney Disease |
Potential for contrast-induced nephropathy |
Hydration and careful contrast use |
Role of Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes is key to the success of stent placement and heart health. Cardiac rehabilitation programs help a lot. They include exercise, heart-healthy tips, and counseling. The benefits of cardiac rehabilitation are clear, like less sickness and death.
Places like Allen Hospital Cardiac Rehab offer great support. They help patients make healthy lifestyle choices. This can greatly improve their heart health in the long run.
- Smoking cessation
- Dietary modifications
- Regular physical activity
- Stress management
By focusing on health checks, managing health issues, and making lifestyle changes, we can greatly improve stent placement outcomes.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
Understanding the recovery process after a stent procedure is key. We’ll guide you through the typical recovery timeline, the importance of follow-up appointments, and the medications you can expect to be prescribed.
Recovery Timeline
The recovery time after a stent procedure varies. It depends on your health and the procedure specifics. Most people can get back to normal activities in a few days to a week.
Here’s what you can expect during recovery:
- Immediate Recovery (First 24-48 hours): Rest is recommended. Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting.
- Short-Term Recovery (2-7 days): Gradually resume normal activities. Follow the specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
- Long-Term Recovery (1-3 months): Continue to follow a heart-healthy lifestyle, including diet, exercise, and medication adherence.
Follow-Up Appointments
Follow-up appointments are key after a stent procedure. They help monitor your recovery and adjust treatments as needed. These appointments also help in early detection of any complications.
A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled within a few weeks after the procedure. Your healthcare provider will assess your overall health, check for any signs of complications, and adjust your medication regimen if needed.
|
Appointment Type |
Purpose |
Typical Timing |
|---|---|---|
|
Initial Follow-Up |
Assess recovery, check for complications |
2-4 weeks post-procedure |
|
Medication Review |
Review and adjust medication |
As needed, based on initial follow-up |
|
Long-Term Follow-Up |
Monitor overall heart health |
3-6 months post-procedure and beyond |
Medications to Expect
After a stent procedure, you’ll likely be prescribed medications. These are to prevent clot formation and manage heart health issues. Common medications include antiplatelet therapy, beta-blockers, and statins.
It’s important to follow your medication regimen as prescribed. This helps minimize the risk of complications and keeps the stent open.
Participating in cardiac rehabilitation programs can significantly improve outcomes. It reduces the risk of future heart problems and improves overall heart health.
Patient Stories and Testimonials
Patients who have had stent procedures share their recovery journeys. Their stories help us understand the process and its challenges. These personal accounts show how stenting affects lives and the importance of cardiac rehab in recovery.
Success Stories
Many patients have seen big improvements after getting stents. They talk about being able to do normal activities again. Cardiac rehabilitation benefits include better heart health, more energy, and lower heart problem risks.
One patient’s story is about how cardio rehab helped them a lot. It included exercise, heart-healthy tips, and stress management. This approach helped them feel better and enjoy life again.
Challenges Faced by Patients
Recovery isn’t always easy. Patients might feel uncomfortable or face complications. It’s important for doctors to know these challenges to help better.
For example, sticking to a new diet and exercise can be hard. But, cardiac rehabilitation benefits help patients manage their health and make lasting changes.
Lessons Learned from Experiences
Patients’ experiences teach us a lot. A key lesson is the need for a good recovery plan that includes cardiac rehab. Knowing what is cardio rehab helps patients on their recovery path.
Patients also learn the value of following their medication, going to check-ups, and making lifestyle changes. These lessons show the importance of a supportive care environment for recovery and heart health.
“The cardiac rehabilitation program was instrumental in my recovery. It not only helped me physically but also provided emotional support during a challenging time.”
A patient reflecting on their experience
We share these stories to encourage and offer insight to those going through stent procedures. Recovery is unique, but with the right support, many patients can fully recover.
Advances in Stenting Technology
Stenting technology has evolved, making heart procedures safer and more effective. These advancements are changing how we care for patients with heart issues.
Stent technology has improved a lot. New stent designs and ways to place them are key. They help lower risks and speed up recovery.
New Techniques in Stenting
New stenting methods aim to be less invasive and more effective. Drug-eluting stents, for example, cut down on restenosis. Better imaging helps place stents more accurately, leading to better results.
Bioresorbable stents are another big step. They dissolve over time, aiming to avoid long-term stent problems. These changes focus on better patient care, improving both short-term and long-term health.
The Future of Cardiovascular Interventions
The future of heart treatments will see more stenting tech and a big push for cardiovascular rehabilitation. Rehab programs are key for full recovery and preventing future heart issues.
Rehab stats show great progress, with many patients seeing big health gains. Combining new stenting tech with rehab will be essential for top-notch care.
By using these new technologies and focusing on patient care, we’re set to make big leaps in heart disease treatment. The future of heart treatments looks very promising, with new tools and methods coming up all the time.
Real-World Outcomes and Studies
It’s important to know how stent procedures work in real life. This helps us see their good points and possible downsides. Studies show us how stents really do in the real world.
Key Research Findings
Many studies have looked into stent outcomes. For example, rehabilitation statistics show that inpatient cardiac rehab helps a lot. A study found that those in cardiac rehab had fewer heart problems later on.
Some key points from these studies are:
- The value of inpatient cardiac rehab in better recovery.
- How lifestyle changes can help patients live longer after a stent.
- Comparing different stents to see which works best for whom.
How Studies Inform Risks and Benefits
Studies on stents give us a clear view of their effects. They help us understand the risks and benefits. By looking at real-world data, researchers find patterns that help doctors make better choices.
For instance, rehabilitation statistics help doctors plan care better for each patient. This might lower the chance of problems. Studies also lead to new tech and treatments, making care better for everyone.
In the end, studies on stents help doctors make smart choices. They balance risks and benefits to get the best results for their patients.
Talking to Your Doctor About Stents
Talking to a cardiologist is key when thinking about stents. This talk can clear up the good and bad of stents. It also helps know what to expect when you get better.
Preparing for Your Consultation
Getting ready for your talk with the doctor is smart. Here’s how:
- Write down your questions and concerns so you don’t forget.
- Bring any medical records, like test results and what meds you take.
- Have a family member or friend there for support and to help remember.
Questions to Ask Your Cardiologist
Asking the right questions is important. Here are some to think about:
- What are the risks and benefits of a stent for me?
- How will the stent be put in, and what kind will it be?
- How long will I need to recover, and what follow-up care will I get?
- How will cardiac rehab fit into my recovery, and how long does it last?
Understanding Your Options
Your doctor can explain the different treatments you have. This includes the good and bad of each. You might talk about other options, like medicine or lifestyle changes, and how they compare to stents.
Cardiac rehab is a big part of getting better. It includes exercise, learning about heart health, and support. It helps you recover and manage your heart condition.
|
Program Component |
Description |
Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|
|
Exercise Training |
Supervised exercise to improve heart health |
Several weeks to a few months |
|
Education |
Classes on heart health, nutrition, and stress |
Ongoing, with sessions over several weeks |
|
Support |
Counseling and groups to manage your condition |
Ongoing, with varying support |
Knowing your options and what cardiac rehab includes helps you make a good choice. It lets you take an active part in getting better.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
As we wrap up our talk on stent procedure risks, it’s key to look at both sides. Knowing how stents work and what happens after is important for your heart health. This knowledge helps you make smart choices about your heart.
Balancing Risks and Advantages
Stent procedures have changed how we treat heart diseases. They offer a less invasive way to open blocked arteries. While there are risks, the benefits like better blood flow and fewer symptoms often win out for many. Cardiac rehab programs can also boost recovery, adding to your heart health.
Ongoing Care and Monitoring
After a stent, it’s important to keep up with care and watch for problems. This means taking your meds, changing your lifestyle, and going to check-ups. Cardiac rehab also helps, improving heart function and lowering future heart risks. Understanding these points helps patients take charge of their heart health.
Being well-informed and involved in your care helps you handle stent procedures better. This leads to better health results in the long run.
FAQ
What is a stent and how is it used in cardiovascular procedures?
A stent is a small, mesh-like device. It’s inserted into a narrowed or blocked artery. This improves blood flow and reduces heart attack risk. Stents keep arteries open and are often used with angioplasty.
What are the different types of stents available?
There are several stent types, like bare-metal, drug-eluting, and bioresorbable stents. Each has its own benefits and risks. The right stent depends on the patient’s needs.
What are the risks associated with stent placement?
Stent placement risks include bleeding, infection, and material reactions. Serious risks are heart attack, stroke, and death, though rare.
How long does cardiac rehabilitation typically last after a stent procedure?
Cardiac rehab lasts weeks to months, based on patient needs. It includes exercise, education, and support to aid recovery and condition management.
What are the benefits of cardiac rehabilitation after a stent procedure?
Cardiac rehab helps patients recover faster and improves health. It reduces future heart risks. Benefits include better exercise tolerance, reduced symptoms, and a better quality of life.
What factors affect life expectancy after stent placement?
Life expectancy after stent placement varies. It depends on health, lifestyle, and underlying conditions. Patients with multiple conditions or unhealthy habits face higher risks.
How can I prepare for a consultation with a cardiologist about stent placement?
To prepare, gather medical records and list medications. Write down questions for your cardiologist. Discuss your medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle habits.
What questions should I ask my cardiologist about stent placement?
Ask about stent risks and benefits, the type of stent, and what to expect. Discuss post-procedure care, recovery, and follow-up appointments.
What are the latest advances in stenting technology?
New stent materials, designs, and delivery systems are being developed. These aim to improve safety, efficacy, and patient outcomes.
How do studies inform the risks and benefits associated with stent procedures?
Studies provide insights on stent risks and benefits. They help guide treatment decisions and improve outcomes. Research also informs new treatments and technologies.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25173339/