A thyroid uptake scan is a diagnostic tool used to check how well the thyroid gland works and to understand the risks of a thyroid uptake scan before proceeding. It uses a small amount of radioactive material to see the gland’s structure and function.
Even though it helps diagnose, a thyroid uptake scan has risks. One is exposure to ionizing radiation. This worries patients and doctors about its safety and long-term effects.
The risks of thyroid uptake scans are not just about radiation. They also include the chance of misdiagnosis or needing more tests because of unclear results.
Key Takeaways
- Thyroid uptake scans involve exposure to ionizing radiation.
- The procedure is used to diagnose and monitor thyroid conditions.
- Potential risks include radiation exposure and misdiagnosis.
- Patients should discuss the benefits and risks with their healthcare provider.
- Alternative diagnostic methods may be available depending on the condition.
Understanding Thyroid Uptake Scans
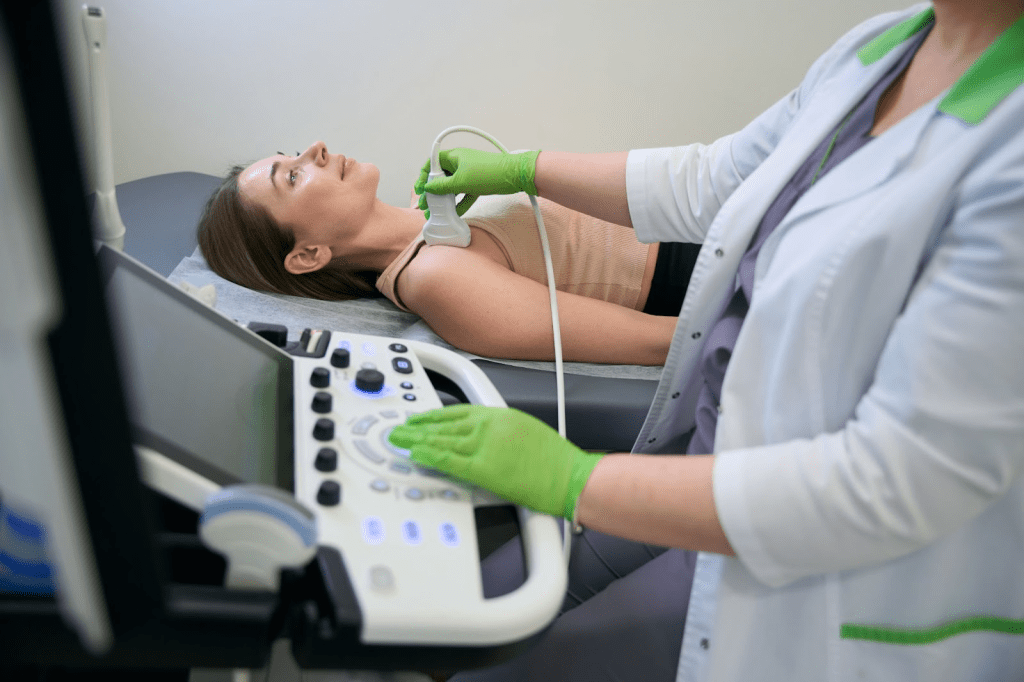
Definition and Purpose
The main goal of a thyroid uptake scan is to see how much radioactive iodine the thyroid gland takes in. This shows if the gland is working right or not. The test uses a small amount of radioactive iodine that the gland absorbs.
The scan’s results are very important for thyroid diagnosis. They help doctors find out why the thyroid isn’t working right. This could be because the gland is too active, has nodules, or other issues.
Types of Thyroid Scans
There are many types of thyroid scans, each with its own role in thyroid diagnosis. The main ones are:
- Thyroid Uptake Scan: This measures how much radioactive iodine the gland takes in. It shows if the gland is working well.
- Thyroid Imaging or Thyroid Scan: This creates pictures of the gland using radioactive material. It helps find nodules, inflammation, or other problems.
Knowing about the different thyroid scans and what they do is important. It helps both patients and doctors make better choices for thyroid care.
How Thyroid Uptake Scans Work
To understand thyroid uptake scans, we need to explore nuclear medicine and radioactive tracers. Nuclear medicine uses small amounts of radioactive materials to diagnose and treat diseases.
The Science Behind Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine uses radioactive tracers that are absorbed by specific organs or tissues. For thyroid uptake scans, the tracer is usually radioactive iodine. This iodine is taken up by the thyroid gland.
The amount of iodine absorbed helps doctors assess thyroid function. They can also spot any abnormalities.
Radioactive Tracers Used
The most common tracer for thyroid uptake scans is I-123 (Iodine-123). It has a short half-life and the right energy for imaging. This makes it safe for patients and accurate for assessing thyroid function.
Other tracers like Tc-99m (Technetium-99m) might be used too. They offer flexibility in diagnosing thyroid conditions based on patient needs.
Medical Conditions Diagnosed with Thyroid Scans
Thyroid scans are key in finding several thyroid issues, like hyperthyroidism and thyroid nodules. They give vital info on how the thyroid works. This helps spot any problems.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism means the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. Scans measure how much radioactive iodine the thyroid takes in. If it takes in a lot, it’s overactive.
Common causes of hyperthyroidism include:
- Graves’ disease
- Toxic multinodular goiter
- Thyroiditis
Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are growths on the thyroid gland. Scans check if these nodules are “hot” or “cold”. Cold nodules might be cancerous.
| Nodule Type | Characteristics | Malignancy Risk |
| Hot Nodules | Actively produce thyroid hormone | Low |
| Cold Nodules | Not producing thyroid hormone | Higher |
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer affects the thyroid gland. Scans show abnormal thyroid activity, helping spot cancer. More tests are needed to confirm cancer.
Knowing how thyroid scans help diagnose these conditions is key. They give detailed thyroid images. This helps doctors plan the best treatment.
Preparing for a Thyroid Uptake Scan
To get accurate results, it’s key to prepare well for a thyroid uptake scan. Good preparation ensures you get reliable data for diagnosis.
Dietary Restrictions
Before the scan, you might need to follow certain diet rules. You should avoid foods high in iodine. This is because iodine can mess up the test results. The specific diet rules depend on the scan’s needs and your health.
Foods to Avoid:
- Iodized salt
- Seafood
- Iodine-rich foods
Medication Adjustments
Some medicines can change how a thyroid uptake scan works. You might need to change or stop some medicines before the scan. Always tell your doctor about all the medicines you’re taking.
| Medication Type | Adjustment Required |
| Thyroid medications | Yes |
| Iodine supplements | Yes |
| Other medications | Consult your doctor |
What to Tell Your Doctor
Tell your doctor everything about your health before the scan. Share your medical history, allergies, past thyroid issues, and current meds. This helps make the scan fit your needs.
Be sure to discuss:
- Any previous thyroid scans or treatments
- Allergies to iodine or other substances
- Current medications and supplements
The Thyroid Uptake Scan Procedure Step by Step
Learning about the thyroid uptake scan can make patients feel less anxious. It’s a key test for checking how well the thyroid works. It has several important steps.
Initial Tracer Administration
The first step is giving a radioactive tracer. It’s usually taken orally as a capsule or liquid. Iodine-123 or Technetium-99m are common tracers. They help the scan measure thyroid function.
Waiting Period
After taking the tracer, there’s a waiting period. This lets the tracer absorb into the thyroid gland. The time needed varies but is usually a few hours to 24 hours. Patients can go home and come back for the scan.
The Scanning Process
The scanning process has the patient lying on a table. A gamma camera takes pictures of the thyroid gland. It detects the radiation from the tracer, showing detailed images for diagnosis. The scan is done in a nuclear medicine department and is painless.
Knowing the steps of the thyroid uptake scan helps patients prepare. It’s a simple process that gives important information for treating thyroid issues.
Brain SPECT Scan Duration and Procedure Time Compared to Thyroid Scans
Knowing how long different nuclear medicine scans take is key for getting ready and making the process smoother. Scans like brain SPECT and thyroid uptake scans need different times and steps.
Key Differences in Nuclear Medicine Procedures
A brain SPECT scan usually lasts from 15 to 30 minutes. This depends on the specific method and technology used. On the other hand, a thyroid uptake scan is shorter, lasting about 5 to 10 minutes. But, it might take longer for preparation and for the tracer to take effect.
Brain SPECT scans use a radioactive tracer that builds up in brain tissue. This lets doctors see how the brain works. Because of this, the scan can take longer.
Why Timing Matters in Nuclear Imaging
Timing is very important in nuclear medicine. The quality of the images depends on when the radioactive tracer is best seen. For brain SPECT scans, when the scan happens after the tracer is given is very important.
Thyroid uptake scans also need to be timed just right. They measure how much of the radioactive tracer the thyroid gland takes in. The timing of the scan after the tracer is given can affect how accurate the results are.
The differences in how long each scan takes and when they should happen show we need to tailor each nuclear medicine procedure.
Radiation Exposure Risks
Radiation exposure is a big deal for people getting thyroid uptake scans. This test is key for finding thyroid problems, but knowing the risks is vital.
Amount of Radiation in a Thyroid Scan
The radiation from a thyroid uptake scan is small. The tracer used gives off a tiny bit of radiation. This is needed to make images that help find thyroid issues.
Typical Radiation Dose: The dose from a thyroid scan is usually 1-5 mSv. For comparison, we all get about 2.4 mSv of background radiation each year from nature.
Comparing to Other Medical Procedures
It’s good to know how much radiation a thyroid scan uses compared to other tests. Let’s look at some common ones.
| Procedure | Typical Effective Dose (mSv) |
| Thyroid Uptake Scan | 1-5 |
| Chest X-ray | 0.1 |
| CT Scan (Abdomen) | 10 |
| PET Scan | 7 |
Long-term Radiation Effects
Research is always going on about the effects of low-level radiation. Even though the dose is small, it’s important to talk about your risks with your doctor.
It’s important to understand the good and bad of thyroid scans. Patients should know about the steps taken to keep radiation low.
Allergic Reactions and Side Effects
Thyroid uptake scans are usually safe, but there are risks to know. Being aware of these can help make the test smoother.
Common Side Effects
Most people don’t feel much after a thyroid uptake scan. But, some might feel:
- Mild nausea or dizziness
- A metallic taste in the mouth
- Slight discomfort or pain at the injection site
These effects usually go away quickly without needing a doctor.
Rare Allergic Reactions
Some people might have an allergic reaction to the tracer used in the scan. Signs include:
- Hives or itchy skin
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Severe dizziness or trouble breathing
Tell your doctor about any allergies before the scan.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you have these symptoms after the scan, get help right away:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Severe headache or confusion
Quick medical help can lessen allergic reaction risks.
Knowing about possible side effects and allergic reactions helps prepare for the scan. Always talk to your doctor about any worries.
Special Considerations for Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
For pregnant and breastfeeding women, thyroid uptake scans need careful thought. The use of radioactive tracers in these scans is a big challenge for them.
Risks to the Fetus
The main worry with thyroid uptake scans during pregnancy is the fetus’s exposure to radiation. Even though the radiation from a thyroid scan is usually low, any radiation exposure during pregnancy is a concern. This is because it could increase the risk of childhood cancer and other developmental problems.
Pregnant women should talk to their healthcare provider about the risks and benefits. Sometimes, other tests that don’t use radiation are suggested instead.
Alternatives for Pregnant Patients
For pregnant women, ultrasound is often a safer choice for checking thyroid conditions. This method doesn’t use radiation, making it safer during pregnancy.
In some cases, the benefits of a thyroid uptake scan might outweigh the risks. If this is the case, the healthcare provider will try to use the least amount of radioactive tracer possible.
Guidelines for Breastfeeding After a Scan
For breastfeeding women, there are specific rules to follow after a thyroid uptake scan. Usually, breastfeeding should be temporarily stopped for a time set by the healthcare provider. This is usually between 24 to 48 hours to reduce the baby’s exposure to radioactive tracers through breast milk.
It’s important for breastfeeding mothers to talk to their healthcare provider about their feeding options. This includes the possibility of expressing and discarding milk during the waiting period.
Risks for Patients with Specific Medical Conditions
Some health issues can make thyroid uptake scans less safe or effective. People with certain medical conditions need a careful check before they get scanned.
Kidney Disease
Those with kidney disease face risks because some thyroid scan agents can harm their kidneys more. Kidney disease patients should tell their doctors about their condition. This helps decide if the scan is safe for them.
Here’s a quick guide for kidney disease patients getting thyroid scans:
| Condition | Risk | Precaution |
| Mild Kidney Disease | Low | Monitor kidney function |
| Moderate Kidney Disease | Moderate | Consider alternative scans |
| Severe Kidney Disease | High | Avoid contrast agents |
Iodine Allergies
People allergic to iodine or contrast media might have an allergic reaction during a scan. Telling healthcare providers about any allergies is key. This way, they can prevent problems or find other ways to diagnose.
Other Medical Contraindications
Pregnancy and some thyroid issues can also make scans unsafe. It’s vital for patients to share their full health history with their doctors.
Knowing these risks and taking steps to avoid them helps doctors use thyroid scans safely. This ensures they work well for diagnosis.
Post-Procedure Safety Precautions
After a thyroid uptake scan, it’s key to follow safety steps. These steps help lower the risk of radiation exposure for you and others. They are about the radioactive tracer used in the scan.
Radiation Safety Guidelines
Keeping safe from radiation is very important after a thyroid uptake scan. The tracer used in the scan gives off radiation. This radiation can be detected by people close to you. Even though the amounts are small, following guidelines can help lower exposure.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding post-scan precautions.
- Understand that the radiation will decrease over time as the tracer is eliminated from your body.
Hydration and Elimination
Drinking lots of water is very important. It helps your body get rid of the radioactive tracer faster. Drinking water can also reduce radiation exposure to you and those around you.
| Hydration Tips | Benefits |
| Drink plenty of water | Helps in flushing out the radioactive tracer |
| Avoid diuretics | Reduces loss of fluids and electrolytes |
Contact Precautions with Others
Even though the radiation from a thyroid uptake scan is usually safe, it’s wise to take precautions. This is true for vulnerable people like pregnant women and children.
- Sleeping in a separate bed from your partner for a night or two.
- Maintaining distance from pregnant women and children for a recommended period.
- Following good hygiene practices, like washing your hands thoroughly.
By following these safety steps, you can reduce radiation exposure for yourself and others. This ensures a safe recovery after your thyroid uptake scan.
Modern Developments in Thyroid Scan Safety
New technologies have greatly improved thyroid scan safety. These changes have made scans more accurate and safer for patients.
Advancements in Imaging Technology
New imaging tech has been key in making thyroid scans safer. Modern scanners take clearer pictures, helping doctors make better diagnoses. Software updates have also improved how images are processed, making scans safer and more effective.
Strategies for Minimizing Risks
Several steps have been taken to lower risks in thyroid scans. These include using less radioactive material, better shielding to cut down on radiation, and precise calibration of equipment.
| Risk Reduction Strategy | Description | Benefit |
| Lower Doses of Radioactive Tracers | Using the minimum necessary dose for effective imaging | Reduced radiation exposure |
| Improved Shielding | Enhanced protective measures to minimize radiation leakage | Increased safety for patients and staff |
| Equipment Calibration | Regular and precise calibration of scanning equipment | More accurate diagnostic results |
Healthcare providers are using these new technologies to make thyroid scans safer and more effective. This leads to better diagnoses and treatments for patients.
Balancing Risks and Benefits
It’s important for both patients and doctors to understand the risks and benefits of thyroid uptake scans. This knowledge helps in making smart choices about when and how to use this tool.
Diagnostic Value vs. Possible Risks
Thyroid uptake scans are great for checking thyroid function and structure. But, there are risks like radiation exposure and allergic reactions to the tracer. It’s important to think about these risks and the benefits of getting a clear diagnosis.
For many, the benefits of a thyroid uptake scan are worth the risks. The scan can spot issues like hyperthyroidism, thyroid nodules, and cancer. Doctors should talk about these points with their patients.
Alternative Diagnostic Procedures
There are other tests that can be used to lower risks. These include ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans, depending on the condition. Each option has its own benefits and risks, and the right one depends on the patient’s needs.
Ultrasound is a safe, non-radiation option for checking thyroid nodules. But, it might not give the same detailed info as a thyroid uptake scan.
Making an Informed Decision
Deciding on a thyroid uptake scan involves looking at several things. This includes the risks, benefits, and other test options. Patients should talk to their doctor about their medical history, worries, and questions.
By knowing the risks and benefits, patients can choose what’s best for them. It’s also key to follow the instructions before and after the scan to reduce risks.
Conclusion
It’s important to know the risks and benefits of a thyroid uptake scan. This test is key for diagnosing thyroid problems, like hyperthyroidism and thyroid cancer. Nuclear medicine is a big part of this.
The scan uses tiny amounts of radioactive tracers to see the thyroid gland. Even though there’s a risk of radiation, the scan’s accuracy is often worth it.
Thyroid uptake scans differ from other tests, like brain SPECT scans. They require special preparation and follow certain safety steps after the test. Knowing this helps patients make better choices about their health.
Deciding to have a thyroid uptake scan should be a thoughtful choice. It’s best to talk it over with a doctor first. This way, patients can get the right test for their health needs.
FAQ
What is a thyroid uptake scan, and how does it work?
A thyroid uptake scan is a test that checks how much radioactive iodine the thyroid gland takes in. It uses a small amount of radioactive iodine. This iodine is absorbed by the thyroid gland. Then, a special camera detects the radiation to create images of the thyroid.
How long does a thyroid uptake scan take?
A thyroid uptake scan can take a few hours. It starts with giving you a tracer, then you wait, and then the scan happens.
What are the risks associated with radiation exposure during a thyroid uptake scan?
The scan uses low amounts of radiation. This might slightly increase the risk of cancer over time. But, the risk is generally low.
Are there any allergic reactions or side effects associated with thyroid uptake scans?
Yes, some people might have allergic reactions or side effects. These can include hives, itching, or swelling. But, these are rare. Most side effects are mild and short-lived.
Can pregnant or breastfeeding women undergo a thyroid uptake scan?
Pregnant women should avoid this scan because of the risk to the fetus. Breastfeeding women might be able to have the scan. But, they must follow specific guidelines for breastfeeding after.
How do I prepare for a thyroid uptake scan?
To prepare, you might need to follow certain diets or adjust your medications. Also, tell your doctor about any allergies or medical conditions you have.
What are the benefits of a thyroid uptake scan compared to other diagnostic tests?
A thyroid uptake scan gives important information about the thyroid gland. It can help diagnose conditions like hyperthyroidism, thyroid nodules, and cancer. It’s often used with other tests to fully understand thyroid health.
Are there any alternative diagnostic procedures to a thyroid uptake scan?
Yes, other tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans are available. But, they might not give the same info about thyroid function as a thyroid uptake scan.
What are the post-procedure safety precautions after a thyroid uptake scan?
After the scan, you’ll need to follow safety guidelines. Stay hydrated and avoid close contact with others, like pregnant women and children, for a while.
How do modern developments in thyroid scan safety impact the procedure?
Modern tech and safety measures have made thyroid scans safer and more effective. This reduces risks to patients.
How do brain SPECT scans compare to thyroid uptake scans in terms of duration and procedure time?
Brain SPECT scans and thyroid uptake scans are both nuclear medicine tests. But, brain SPECT scans are shorter, both in waiting time and scanning duration.
What are the risks for patients with specific medical conditions undergoing a thyroid uptake scan?
People with certain conditions, like kidney disease or iodine allergies, might face higher risks. It’s key to tell your doctor about any health issues before the scan.










