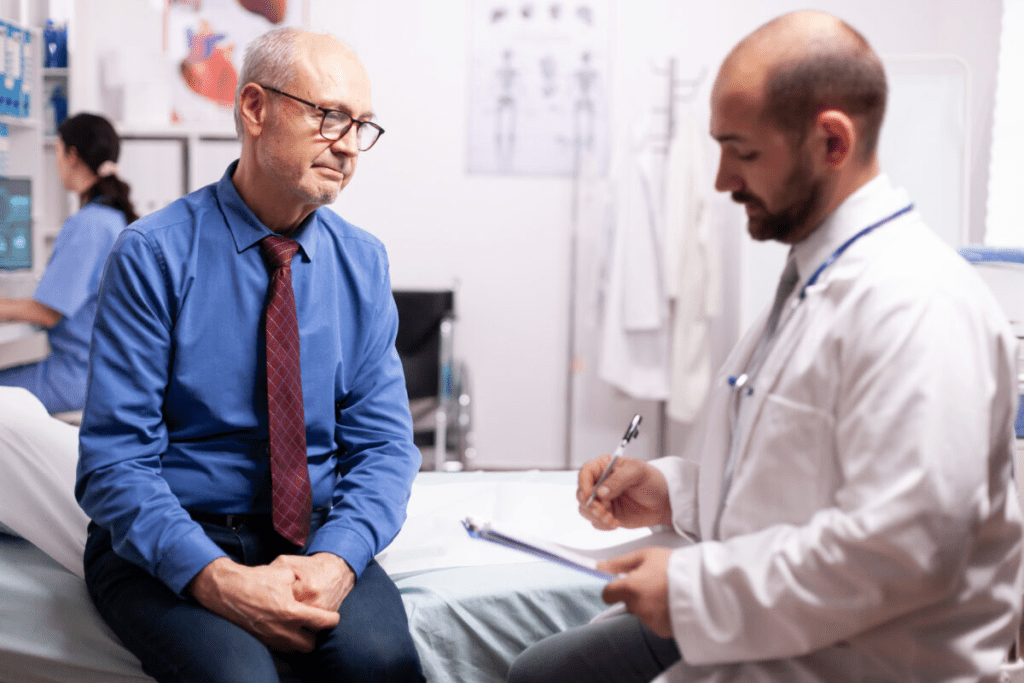
Prostate cancer is a big health worry for men everywhere. The American Cancer Society says it’s the second most common prostate cancer in men worldwide.
In the early stages, prostate cancer might not show any symptoms. But as the tumor grows, it can change how the body works. This includes changes in how you use the bathroom.
It’s very important to know the symptoms of prostate cancer early. If you ignore them, it can lead to serious problems.
Key Takeaways
- Prostate cancer is a common health issue among men globally.
- Early stages of prostate cancer may not show noticeable symptoms.
- Recognizing symptoms is key for early detection.
- Ignoring symptoms can lead to severe consequences.
- Understanding prostate cancer symptoms can save lives.
Understanding Prostate Cancer: An Overview
Prostate cancer is a common cancer in men. Knowing about it can help find and treat it early. It’s important to understand the basics.
What is the Prostate Gland and Its Function
The prostate gland is a small gland in men’s bodies. It’s about the size of a walnut. It makes seminal fluid, which helps sperm during ejaculation.
The gland is around the urethra. This is the tube for urine and semen.
The prostate gland is key for men’s health. Problems with it can cause urinary issues and pain.
How Prostate Cancer Develops
Prostate cancer starts when prostate cells grow out of control. These cells can form tumors. If not treated, they can harm nearby tissues and spread.
Many things can affect prostate cancer risk. These include genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Knowing these factors and early signs is vital for managing the disease.
| Aspect | Description |
| Prostate Gland Function | Produces seminal fluid to nourish and protect sperm |
| Prostate Cancer Development | Occurs when prostate cells mutate and grow uncontrollably |
| Potential Impact | Can damage surrounding tissue and spread if untreated |
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is key to managing prostate cancer well. Finding it early greatly increases the chances of successful treatment and survival. Prostate cancer often doesn’t show symptoms early on, making it hard to catch in time.
Survival Rates and Early Diagnosis
Early detection of prostate cancer leads to better survival rates. If caught early, the disease can be treated more effectively. This improves the patient’s life quality and chances of living longer. Studies have shown that early diagnosis can reduce mortality rates significantly. This highlights the need for regular screenings and check-ups, mainly for those at higher risk.
Challenges in Identifying Symptoms
One big challenge is that prostate cancer often doesn’t show clear symptoms early on. When symptoms do show up, they can be like those of less serious issues. This makes it hard to diagnose based on symptoms alone. Awareness and understanding of the risk factors and symptoms are key for both patients and healthcare providers. Regular screening is essential, even more so for men with a family history or other risk factors.
Warning Sign #1: Urinary Changes
Urinary changes can be a warning sign of prostate cancer. The prostate gland is close to the urethra. As cancer grows, it can press on the urethra, changing how urine flows.
These changes can show up in different ways. You might notice changes in how often you urinate, how strong your urine is, or how easy it is to start or stop urinating. Spotting these signs early is key to getting the right treatment.
Frequent Urination
Frequent urination, or frequent urination, is a common sign. It can happen a lot at night, disrupting sleep and daily life. While many things can cause it, if it keeps happening, you should see a doctor.
Weak Urine Flow
A weak urine flow can also be a sign. The cancer can make the urethra narrower, making the urine stream weaker. This can make it hard to empty your bladder fully.
Difficulty Starting or Stopping Urination
Difficulty starting or stopping urination is another warning sign. The cancer can block the urethra, making it hard to start or stop urinating. You might feel like you’re straining during urination.
Having one or more of these symptoms doesn’t mean you definitely have prostate cancer. But, it’s very important to talk to a doctor. They can help figure out what’s going on and what to do next.
Warning Sign #2: Pain and Discomfort
Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area or back can be a sign of prostate cancer. This pain can happen in different ways. It depends on how the cancer grows and if it spreads.
Pain from prostate cancer can show up in many forms and places. Knowing these symptoms is key for catching the disease early.
Pelvic Pain
Pelvic pain is a symptom men should watch out for. It can feel like a dull ache or sharp pain in the pelvic area. This pain might be constant or come and go.
Back Pain
Back pain is also a symptom of prostate cancer, often when it spreads to the back bones. This pain can last a long time and get worse. It’s important to tell if it’s just back pain or something more serious.
Pain During Ejaculation
Pain during ejaculation is a less common but important symptom. It can feel like a sharp, stabbing pain or burning. If you experience this, you should see a doctor.
Remember, these symptoms don’t always mean prostate cancer. They can also be signs of other health issues. A doctor’s diagnosis is needed to figure out what’s causing the symptoms.
Warning Sign #3: Blood in Urine or Semen
Seeing blood in your urine or semen is scary. It could mean you have prostate cancer. This is a serious sign that needs attention.
What Causes Bleeding
Bleeding in urine or semen can have many causes. Prostate cancer is one of them. A growing tumor can make blood vessels weak and bleed easily.
- Infection or inflammation in the prostate or urinary tract
- Prostate cancer
- Trauma or injury to the prostate or urinary tract
When to Be Concerned
If you see blood in your urine or semen, see a doctor right away. This symptom can have many causes, but it’s important to check for prostate cancer or other serious problems.
Key factors to discuss with your doctor include:
- The frequency and duration of the bleeding
- Any accompanying symptoms such as pain or difficulty urinating
- Your medical history and risk factors for prostate cancer
Warning Sign #4: Erectile Dysfunction
Prostate cancer can show itself in many ways, with erectile dysfunction being a key sign. Erectile dysfunction (ED) means you can’t get or keep an erection for sex. It’s a big deal and can be linked to prostate cancer.
Connection Between Prostate Cancer and ED
Prostate cancer and ED are connected in many ways. The cancer can harm nerves and blood vessels needed for an erection. Treatments like surgery and radiation can also damage these areas, causing ED. Plus, the stress of having cancer can make ED worse.
Distinguishing Cancer-Related ED from Other Causes
It’s important to tell if ED is from prostate cancer or something else. ED can happen for many reasons, like diabetes or heart disease. But if ED starts suddenly or gets worse, it might be prostate cancer. Men with ED should see a doctor to check their health and see if they need to look for prostate cancer.
Warning Sign #5: Unexplained Weight Loss and Fatigue
Advanced prostate cancer can show signs like unexplained weight loss and fatigue. These happen when the cancer has spread a lot. It affects the body’s health and how it uses energy.
Systemic Symptoms of Advanced Cancer
In advanced prostate cancer, systemic symptoms include losing a lot of weight and feeling very tired. These aren’t just about the prostate. They happen because cancer affects the body’s systems.
Cancer can change how the body uses energy, leading to weight loss. It can also make it hard to get nutrients and energy, causing fatigue.
Other Accompanying Symptoms
Other symptoms can come with advanced prostate cancer too. These include loss of appetite, anemia, and general malaise. Spotting these signs early is key to managing advanced prostate cancer.
Recognizing the Signs of Prostate Cancer vs. Other Conditions
Prostate cancer symptoms can be hard to tell apart from other prostate issues. This makes finding the right diagnosis tricky. Knowing the differences between these conditions is key for the right treatment.
Prostate Cancer vs. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is when the prostate gland gets bigger but it’s not cancer. Both BPH and prostate cancer can cause problems with urination. But, BPH doesn’t raise the risk of prostate cancer.
BPH usually doesn’t hurt, but prostate cancer can cause pain in the pelvic area. Tests like a digital rectal exam (DRE) and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test can tell them apart.
Prostate Cancer vs. Prostatitis
Prostatitis is when the prostate gland gets inflamed, often from an infection. It can cause pain in the pelvic area and trouble with urination, just like prostate cancer. But, prostatitis usually starts quickly and comes with fever and chills.
To tell prostatitis apart from prostate cancer, doctors use physical exams, urine tests, and sometimes a prostate biopsy. It’s important for men to get checked if they have symptoms.
Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer
Knowing the risk factors for prostate cancer is key to catching it early. Several things can raise a man’s chance of getting prostate cancer. Being aware of these can help in making better health choices.
Age and Family History
Age is a big risk factor, with most cases found in men over 65. Family history also matters a lot. Men with a dad or brother who had prostate cancer are at higher risk. This risk goes up if the relative was diagnosed young.
Race and Ethnicity
Race and ethnicity are also key risk factors. African American men face the highest risk of prostate cancer. They are also more likely to be diagnosed late. Genetic factors are thought to play a role in this difference.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices, like diet and exercise, can affect prostate cancer risk. Dietary habits, like eating a lot of fat, and obesity can increase risk. It’s good to stay active.
When to See a Doctor About Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Men should know when to talk to a doctor about their symptoms. This is key for early detection and treatment of prostate cancer. Spotting symptoms early can save lives.
It’s important to know when to go to the doctor. This means knowing the right ages for screenings and spotting urgent signs that need quick medical help.
Recommended Screening Ages
The American Cancer Society says men should talk to their doctor about prostate cancer risk at 50. If you’re at higher risk, like having a family history or being African American, start these talks at 45 or 40.
| Risk Category | Recommended Age to Start Screening Discussions |
| Average Risk | 50 |
| High Risk (Family History, African American) | 45 |
| Very High Risk | 40 |
Emergency Warning Signs
Prostate cancer can grow slowly, but some symptoms need quick attention. Look out for severe pain, trouble urinating, or blood in urine or semen.
Seek help right away if you have severe pelvic or back pain, can’t urinate, or have a lot of bleeding.
Conclusion: Taking Action for Prostate Health
Knowing the signs of prostate cancer is key to catching it early. This can lead to better treatment options. By spotting symptoms and understanding risks, you can help keep your prostate healthy.
Early detection and treatment are vital for prostate cancer patients. Regular health checks and screenings are important. This is true for those with a family history or other risk factors.
Protecting your prostate health means staying informed and alert. Also, don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor when you need to. This way, you can lower your risk and have a better chance of successful treatment.
Prostate health is a big part of your overall well-being. Taking steps to protect it can lead to better health. Stay informed, get screened, and make your prostate health a priority.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of prostate cancer?
Symptoms of prostate cancer include changes in urination and pain in the pelvic area. You might also feel pain in your back or during ejaculation. Other signs are blood in urine or semen, trouble getting an erection, and feeling very tired or losing weight without trying.
What is the prostate gland and its function?
The prostate gland is a small gland below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It makes fluids that are part of semen. These fluids help and protect sperm during ejaculation.
How does prostate cancer develop?
Prostate cancer starts when abnormal cells in the prostate gland grow too much. This forms a tumor. These cancer cells can harm nearby tissue and spread to other parts of the body.
What are the risk factors for prostate cancer?
Risk factors for prostate cancer include age, family history, and race. Lifestyle choices like diet and exercise also play a role.
What is the importance of early detection in treating prostate cancer?
Finding prostate cancer early is key to treating it well. It can greatly improve your chances of survival. Regular check-ups can catch cancer early, when it’s easier to treat.
What are the warning signs of advanced prostate cancer?
Signs of advanced prostate cancer include unexplained weight loss and fatigue. You might also feel bone pain or have trouble urinating or have a weak urine flow.
Can prostate cancer be mistaken for other conditions?
Yes, prostate cancer can be confused with other issues like BPH or prostatitis. A doctor’s diagnosis is needed to figure out what’s causing your symptoms.
When should I see a doctor about prostate cancer symptoms?
See a doctor if you notice unusual symptoms like changes in urination, pain, or trouble getting an erection. If you have a family history or other risk factors, talk to your doctor about screening.
What are the recommended screening ages for prostate cancer?
The American Cancer Society suggests talking to your doctor about screening at age 50. If you have a family history or other risk factors, you might need to start screening earlier.
Is prostate cancer painful?
Early prostate cancer might not hurt. But as it grows, it can cause pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, back, or during ejaculation.
How can I reduce my risk of developing prostate cancer?
There’s no sure way to prevent prostate cancer. But living a healthy lifestyle, with a balanced diet and regular exercise, may help lower your risk.
References
Chen, F., Xie, H., & Zhang, L. (2013). Prostate cancer:Current treatment and prevention strategies. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology, 88(1), 1-19.




































