Did you know herniated discs are a big reason for back pain? The spine has bony vertebrae and soft discs that act as shock absorbers. They help keep the spine flexible. Severe slipped disc symptoms can stop you from walking. Learn how to treat the pain and find a successful path to mobility and health.
When a herniated disc happens, it can really hurt. It leads to lower back pain that makes simple tasks hard. Walking can become a big challenge.
We’ll look at how herniated discs affect movement. We’ll also cover the basics of the spine’s structure.
Key Takeaways
- Herniated discs are a common cause of radiating back pain.
- The spine’s intervertebral discs act as shock absorbers.
- A herniated disc can cause significant lower back pain.
- Mobility can be severely impacted by a herniated disc.
- Understanding the spine’s anatomy is crucial to addressing herniated disc issues.
Understanding Herniated Discs: Anatomy and Causes
The spine is a complex structure. Knowing its anatomy, especially the intervertebral discs, is key to understanding herniated discs. The spine has vertebrae, separated by discs that act as shock absorbers and help with flexibility.
Spinal Anatomy and Disc Function
The intervertebral disc has two main parts: the annulus fibrosus and the nucleus pulposus. The annulus fibrosus gives structure and support. The nucleus pulposus absorbs shock and helps with spinal flexibility. When a disc herniates, the nucleus bulges out through a tear in the annulus, often pressing on nerves.
It’s important to understand how these discs work. They cushion the vertebrae and allow the spine to twist and bend. A herniated disc happens when the nucleus pulposus bulges out through the annulus fibrosus, usually towards the spinal cord.
Common Causes of Disc Herniation
Several factors can lead to disc herniation. These include:
- Age: As we get older, our discs lose water, becoming drier and more likely to crack.
- Traumatic Events: Lifting heavy objects, sudden twisting, or a fall can cause a disc herniation.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some people may be more likely to have disc problems due to their genes.
- Repetitive Strain: Repeatedly straining the back can lead to disc herniation over time.
By knowing these causes and the spine’s anatomy, we can better understand why herniated discs happen. We can also learn how to prevent or treat them.
Slipped Disc Symptoms: From Mild Discomfort to Severe Pain
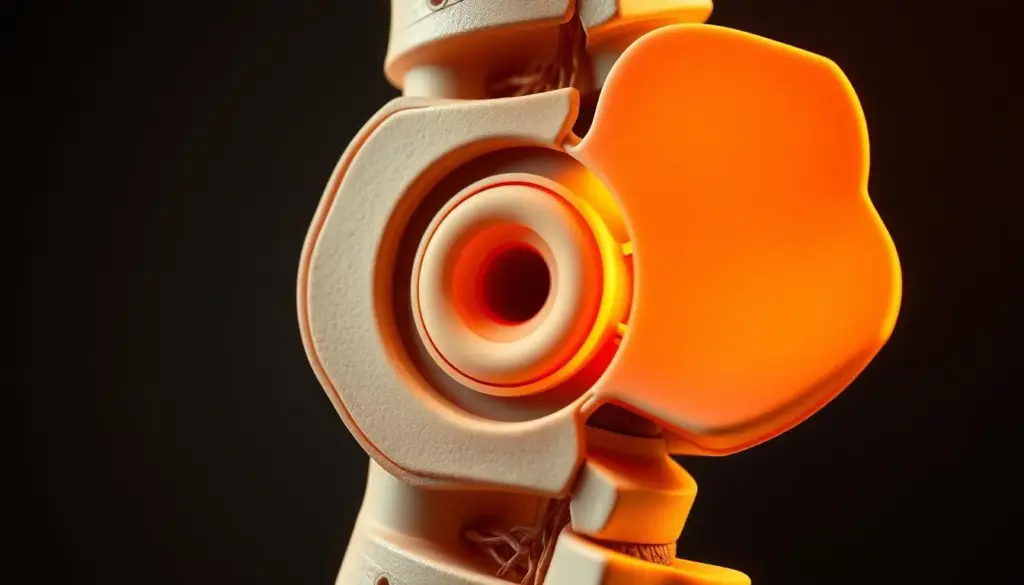

Slipped disc symptoms can range from a dull ache to sharp, severe pain. It’s important to know these symptoms to get the right medical care.
Early Warning Signs of Disc Problems
The first signs of a herniated disc include lower back pain that gets worse with movement. Some people feel radiating pain down their legs, known as sciatica.
Numbness or tingling in the legs or feet can also signal disc issues. Muscle weakness can make it hard to move and do daily tasks.
Progression of Symptoms Over Time
As the problem gets worse, symptoms can turn from mild to severe pain that affects daily life. Even simple actions like walking or sitting can be hard because of the pain.
Sometimes, symptoms stay the same for a while before getting much worse. It’s key to watch for any changes in your symptoms.
When Symptoms Indicate an Emergency
In serious cases, a herniated disc can cause cauda equina syndrome, needing quick medical help. Look out for sudden, severe back pain, trouble walking, loss of bladder or bowel control, and numbness or weakness in the legs.
If you have these severe symptoms, get medical help right away. This can prevent serious long-term damage.
Why a Herniated Disc Can Make Walking Difficult
Walking can become hard for those with a herniated disc. This is because of nerve compression and muscle weakness. A herniated disc happens when the soft center of the disc leaks out, irritating nearby nerves.
Nerve compression can cause many symptoms that affect how we move. When nerves get compressed or irritated, they can lead to pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs. This makes walking hard.
Nerve Compression and Mobility Issues
Nerve compression is a big reason why walking is hard for those with a herniated disc. When a disc herniates, it can press on nerves that control leg muscles. This can disrupt normal nerve function, causing pain, numbness, or tingling in the legs.
These symptoms can really affect how well someone can walk. For example, pain or numbness in the legs can make it hard to balance or feel sensations in the feet. This increases the risk of falls.
Muscle Weakness and Instability
Muscle weakness is another big factor that affects walking. When nerves are compressed, they can’t send the right signals to muscles. This leads to weakness, especially in the legs.
Muscle weakness can make walking unstable. It’s hard to keep balance or do daily activities without help. In bad cases, you might need to use canes or walkers.
It’s important to understand how a herniated disc affects walking. By tackling nerve compression and muscle weakness, people can improve their mobility and feel less pain.
Lumbar Herniated Discs: The Most Common Culprit
Herniated discs in the lumbar spine often cause back pain and mobility problems. The lumbar region, which bears weight, is more likely to have disc herniations. We will look into why lumbar herniated discs are so common and how they affect people.
L4-L5 and L5-S1 Herniations
The L4-L5 and L5-S1 levels are where herniations most often happen. These spots face a lot of stress because of their location and the weight they carry. Nerve compression can lead to pain, numbness, and weakness in the lower legs.
Research shows that the L4-L5 level is especially at risk for herniation. This is because of its structure and the forces it deals with. The L5-S1 level, where the lumbar spine meets the sacrum, also faces a lot of stress, making it another common spot for herniations.
Slipped Disc in Lumbar Region: Symptom Patterns
Symptoms of a lumbar herniated disc can differ from person to person. Common signs include lower back pain, sciatica, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. The severity and type of symptoms depend on the herniation’s size and location, and the nerves it affects.
- Pain that radiates down one leg (sciatica)
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the legs or feet
- Muscle weakness, particularly in the legs
- Loss of bladder or bowel control in severe cases (Cauda Equina Syndrome)
Knowing these symptom patterns is key to diagnosing and treating lumbar herniated discs. We will delve deeper into diagnosis and treatment options in the next sections.
Diagnosing a Herniated Disc When You Can’t Walk
Diagnosing a herniated disc in patients with limited mobility is complex. It needs a careful and multi-faceted approach. When symptoms are severe, using a mix of diagnostic tools is crucial. This helps confirm a herniated disc and rule out other causes of symptoms.
Physical Examination Techniques
A thorough physical examination is the first step. Healthcare providers check muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation. They look for any neurological deficits.
Specific tests, like the straight leg raise test, are used. They stretch the sciatic nerve and can reproduce pain or discomfort. This helps diagnose lumbar disc herniations.
Key Components of Physical Examination:
- Muscle strength testing to assess weakness
- Reflex testing to evaluate nerve function
- Sensation testing to identify areas of numbness or tingling
Imaging Tests for Confirmation
Imaging tests are often needed to confirm the diagnosis. The most common ones are:
|
Imaging Test |
Description |
Usefulness in Diagnosing Herniated Disc |
|---|---|---|
|
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) |
Provides detailed images of soft tissues, including discs and nerves |
Highly effective for visualizing disc herniations and nerve compression |
|
CT (Computed Tomography) Scan |
Offers detailed images of bone structures and can detect disc issues |
Useful for assessing bone spurs and disc height, but less sensitive for soft tissue |
|
X-ray |
Primarily used to evaluate bone alignment and detect fractures |
Limited in directly diagnosing herniated discs, but can show indirect signs |
Ruling Out Other Conditions
It’s important to tell a herniated disc from other conditions. These include spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, or vertebral fractures. A detailed medical history and imaging help make an accurate diagnosis.
By combining physical examination findings with imaging test results, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose a herniated disc. They can then develop an effective treatment plan, even when mobility is significantly impaired.
Immediate Relief Strategies for Severe Disc Pain
Managing severe disc pain needs a mix of safe moves, heat and cold therapy, and medicine. When facing a herniated disc, it’s key to find ways to ease pain and help healing.
Safe Positioning and Movement Techniques
First, focus on safe moves and positions. This means:
- Keeping good posture to ease spine stress
- Using tools like lumbar rolls or back supports
- Staying away from heavy lifting or bending
- Doing gentle stretches to boost flexibility
Ice and Heat Therapy Applications
Thermal treatments, like ice and heat, are great for disc pain. Ice therapy cuts down swelling, and heat therapy eases muscles and boosts blood flow.
- Use ice packs for the first 48-72 hours after pain starts
- Move to heat therapy after the swelling goes down
- Try a warm bath or shower to relax muscles
Switching between ice and heat can really help many people.
Over-the-Counter Pain Management Options
OTC pain meds are key in handling severe disc pain. You can try:
- NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen to lessen inflammation and pain
- Acetaminophen for pain relief
Always stick to the right dose and talk to a doctor before starting any new meds.
Conservative Treatment Approaches for Herniated Discs
Conservative treatments are key in managing herniated disc symptoms. They aim to lessen pain, boost function, and prevent surgery. These methods are designed to help you avoid surgery whenever it’s possible.
Physical Therapy Interventions
Physical therapy is a vital part of treating herniated discs. Personalized exercise programs are made to strengthen the spine’s muscles. They also improve flexibility and posture.
Techniques like massage and joint mobilization help ease pain and improve movement. Physical therapists teach patients how to move right and keep good posture. This helps reduce pain and boosts spinal health.
Medication Options for Bulging Disc in Back
There are many medicines to help with herniated disc symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers, like NSAIDs, are often suggested. They help reduce inflammation and pain.
Muscle relaxants might be given for muscle spasms. For severe pain, stronger medicines might be prescribed. Always follow your doctor’s advice when taking medication.
Alternative Therapies with Evidence
Some alternative therapies also help with herniated disc symptoms. Chiropractic care involves spinal manipulation. It can improve spinal alignment and reduce disc pressure.
Acupuncture is another option. It’s a traditional Chinese medicine that uses thin needles to stimulate healing and pain relief.
When trying alternative therapies, talk to your healthcare provider. They can make sure the treatments are safe and right for you.
Advanced Treatments for Persistent Symptoms
Advanced treatments offer new hope for those with ongoing symptoms from a herniated disc. When simple treatments don’t work, these options can help.
Epidural Steroid Injections
Epidural steroid injections are a common treatment for herniated discs. They put corticosteroids near the spinal cord to reduce inflammation and pain.
The procedure is done under a special X-ray to place the injection correctly. While these injections can help a lot, they work differently for everyone.
Benefits of Epidural Steroid Injections:
- Reduced inflammation
- Pain relief
- Minimally invasive
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive procedures are another option for herniated discs. They aim to reduce pain and inflammation with less damage.
Some common techniques include:
- Discectomy: Removing the herniated disc material
- Nucleoplasty: Using radiofrequency energy to decompress the disc
- Laser discectomy: Using a laser to remove disc material
|
Procedure |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Discectomy |
Removal of herniated disc material |
Pain relief, reduced inflammation |
|
Nucleoplasty |
Decompression using radiofrequency energy |
Minimally invasive, quick recovery |
|
Laser Discectomy |
Removal of disc material using a laser |
Precise, less damage to surrounding tissue |
When Surgery Becomes Necessary
In some cases, surgery is needed for a herniated disc. This is usually when other treatments haven’t worked and symptoms are severe or getting worse.
The most common surgery is a discectomy, which removes the herniated part of the disc. Sometimes, spinal fusion is also done to stabilize the spine.
Surgical Considerations:
- Severity of symptoms
- Failure of conservative treatments
- Progressive neurological deficits
Choosing surgery is a big decision. It’s important to talk about the risks and benefits with a healthcare professional to find the best treatment for you.
Recovery Timeline: From Immobility to Normal Function
Knowing the recovery timeline for a herniated disc can make the healing process clearer and more confident. Everyone’s recovery is different, but there are common steps many people take.
First Days: Managing Acute Pain
The first part of recovery is all about managing pain and discomfort. It’s key to rest and avoid activities that make things worse. Always follow your doctor’s advice on managing pain, which might include medicine, physical therapy, or other treatments.
Good pain management is crucial in the first days. This might include resting, using ice or heat, and taking medication to ease pain and swelling.
Weeks 1-4: Gradual Improvement Milestones
As the initial pain goes away, people start to feel better. This time is marked by more mobility and less pain. Starting gentle exercises and physical therapy can help your back muscles get stronger and more flexible.
It’s important to keep track of how you’re doing and change your treatment if needed. Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help find the best recovery plan for you.
Protruding Disc Recovery Time Expectations
The time it takes to recover from a protruding disc varies a lot. It depends on how bad the condition is, how well the treatment works, and your overall health and how well you follow treatment.
Usually, you’ll see big improvements in a few weeks to a few months. Staying healthy, exercising regularly, and keeping good posture can help you recover fully and prevent future problems.
Signs Your Bulging Disc is Getting Worse
It’s important to know the signs of a worsening herniated disc. This condition can cause a lot of pain and make it hard to move. Knowing when it’s getting worse is key to managing it well.
Red Flags That Require Immediate Attention
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
- Increasing pain that doesn’t get better with treatment
- Neurological deficits, like numbness, tingling, or weakness in your limbs
- Changes in bladder or bowel function, such as losing control or trouble starting
- Severe pain that goes down your legs
If you notice any of these signs, get medical help fast. They can mean your condition is getting worse and needs stronger treatment.
Tracking Symptom Progression
Watching your symptoms over time can show patterns and if they’re getting worse. Keeping a journal of your symptoms can help. Note how bad the pain is, how often it happens, and any changes in how you move or feel.
By keeping track of your symptoms, you can:
- Find out what makes your condition worse
- See if your current treatment is working
- Give your doctor the info they need to make better treatment plans
Being active in tracking your condition can really help you manage a herniated disc better.
Preventing Recurrence and Future Disc Problems
To avoid the effects of a herniated disc, it’s key to keep your spine healthy. We’ll look at how to prevent problems, like using proper body mechanics and doing core exercises. We’ll also talk about making lifestyle changes.
Proper Body Mechanics for Spine Protection
Keeping your body mechanics right is important for your spine. This means:
- Lifting objects correctly by bending at the knees and keeping the object close to your body
- Maintaining good posture during daily activities, such as standing, sitting, and sleeping
- Avoiding twisting or bending movements that can put unnecessary stress on your spine
By following these tips, you can lower the chance of spine injury and herniated discs.
Core Strengthening Exercises
Doing core exercises is key for spine support and preventing disc issues. A strong core includes muscles in your abdomen, back, and pelvis. Exercises like planks, bridges, and pelvic tilts can boost your spinal stability.
|
Exercise |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Plank |
Strengthens abdominal and back muscles |
|
Bridge |
Targets gluteal and lower back muscles |
|
Pelvic Tilt |
Engages core muscles and improves flexibility |
Lifestyle Modifications for Spine Health
Changing your lifestyle can also help prevent herniated disc problems. This includes:
“A healthy lifestyle is the foundation of a healthy spine. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking are crucial.” – Spine Health Expert
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce the strain on your spine
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, to keep your spine flexible and strong
- Avoiding smoking, as it can reduce blood flow to the discs and accelerate degeneration
By adding these habits to your daily routine, you can lower the risk of herniated disc problems. This helps keep your spine healthy.
Living with Chronic Disc Issues: Management Strategies
Managing chronic disc issues is key to a good life. People with these problems face many challenges. They need a full plan to handle symptoms and stay active.
Long-term Pain Management Techniques
Managing pain over time is vital. We suggest a mix of medicine, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Pain management strategies must fit each person’s needs. This might include medicines, physical therapy, and even acupuncture or chiropractic care.
It’s important to work with doctors to create a personalized pain management plan. This plan should be checked and updated often. It must keep up with any changes in symptoms or health.
Adaptive Equipment and Ergonomics
Adaptive equipment and ergonomic changes can help a lot. This includes special furniture, tools for daily tasks, and changes to your home or work space. These changes help avoid back strain.
Using ergonomic practices in daily life can also help. Small changes, like using a back support or adjusting computer monitors, can make a big difference.
Mental Health Considerations with Chronic Pain
Chronic disc issues can really affect mental health. Pain and limited movement can cause frustration, anxiety, and depression. It’s important to deal with these mental health issues as part of the overall plan.
We recommend talking to mental health experts, doing stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga, and staying connected with friends. These steps help with the emotional side of chronic disc issues.
When to Seek Emergency Care for Disc Problems
Knowing when to seek emergency care is crucial. It can make a big difference in managing disc problems. Some conditions related to herniated discs need immediate attention to avoid serious damage.
Cauda Equina Syndrome is a medical emergency. It happens when nerves in the lower spine get compressed. This can cause permanent damage if not treated fast. It’s important to recognize its signs to act quickly.
Cauda Equina Syndrome Warning Signs
The symptoms of cauda equina syndrome vary. They often include:
- Severe lower back pain
- Numbness or tingling in the legs
- Weakness or paralysis of the legs
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Numbness in the groin or genital area
If you or someone you know has these symptoms, seek emergency care right away.
Severe Neurological Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
Other severe neurological symptoms also need emergency care. These include:
|
Symptom |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Progressive weakness |
Increasing weakness in the legs or arms |
|
Loss of reflexes |
Diminished or absent reflexes |
|
Sudden numbness |
Unexpected numbness or tingling, especially if it’s severe or unilateral |
These symptoms can mean serious nerve compression or damage. They need quick evaluation and treatment.
It can be hard to recognize these signs. But knowing them is the first step to getting the right care. If you’re experiencing severe neurological symptoms, don’t wait. Seek emergency medical care right away.
Conclusion: Moving Forward After a Herniated Disc
Recovering from a herniated disc takes time, the right treatment, and sometimes changes in how we live. Knowing about the condition and how to manage it helps people feel more confident. A good recovery plan includes medical care, physical therapy, and making lifestyle changes.
Learning about herniated discs, their causes, symptoms, and treatments is a big step. It helps people start to move better and live better. We suggest that those dealing with herniated discs work with their doctors to create a recovery plan that fits them.
With the right help and support, managing symptoms and avoiding future problems is possible. As people get better, they can look forward to being more independent and enjoying a better life.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of a herniated disc?
Symptoms include lower back pain and sciatica. You might also feel numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness in your legs. The pain can range from mild to severe.
How does a herniated disc affect walking ability?
It can cause nerve compression and muscle weakness. This makes walking hard. The nerves can get compressed, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness in the legs.
What are the most common levels for lumbar herniated discs?
The most common levels are L4-L5 and L5-S1. These areas are more prone to herniation due to the stress and strain on the lower back.
How is a herniated disc diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, medical history, and imaging tests like MRI or CT scans. These tests confirm the herniated disc and rule out other conditions.
What are the immediate relief strategies for severe disc pain?
Immediate relief includes safe positioning, ice and heat therapy, and over-the-counter pain meds. These methods help manage pain and aid in recovery.
What are the conservative treatment approaches for herniated discs?
Treatments include physical therapy, medication, and alternative therapies like chiropractic care and acupuncture. These are tailored to individual needs and preferences.
When is surgery necessary for a herniated disc?
Surgery is needed when conservative treatments fail or if there are severe symptoms like cauda equina syndrome. Surgical options include discectomy and minimally invasive procedures.
How long does it take to recover from a herniated disc?
Recovery time varies, but most see improvement in weeks to months. Factors include the herniation’s severity, treatment effectiveness, and overall health.
How can I prevent the recurrence of a herniated disc?
Prevent recurrence by maintaining proper body mechanics and doing core strengthening exercises. Lifestyle modifications like a healthy weight and avoiding smoking also help.
What are the warning signs of cauda equina syndrome?
Warning signs include severe lower back pain, numbness or tingling in the legs, and loss of bladder or bowel control. Weakness or paralysis in the legs is also a sign. Seek emergency care if you experience these symptoms.
How can I manage chronic disc issues?
Manage chronic issues with long-term pain management, adaptive equipment, and ergonomics. Addressing mental health is also key. A comprehensive approach can improve your quality of life.
What does a herniated disk feel like?
A herniated disk can cause sharp pain, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. The sensations vary based on the herniation’s location and severity.
What are the symptoms of a bulging disc in the lower back?
Symptoms include lower back pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Some may also feel radiating pain, numbness, or tingling in the legs.
Can a slipped disc in the lumbar region cause severe pain?
Yes, a slipped disc in the lumbar region can cause severe pain. The pain can be sharp, stabbing, or burning and may spread to the legs.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19303959/





