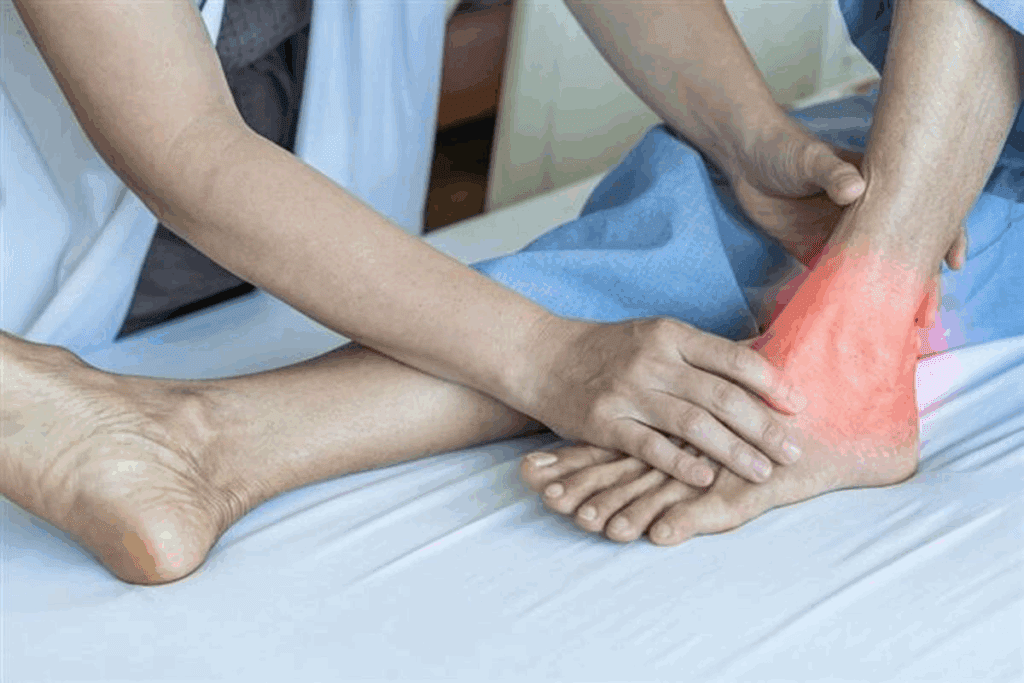
Soft tissue injuries happen a lot, affecting millions every year. Knowing the difference between a sprain and a strain is key for the right treatment. These injuries can be very painful and limit movement, but they affect different areas of the body. Sprain vs strain: The Crucial difference between the two injuries you Must know for Accurate self-care now.
A sprain usually hurts the ligaments, which link bones together. On the other hand, a strain affects the muscles or tendons, which connect muscles to bones. Knowing this can help you get the right care and heal faster.
Key Takeaways
- Sprains and strains are two different types of soft tissue injuries.
- Understanding the difference is key for the right treatment.
- Sprains hurt ligaments, while strains hurt muscles or tendons.
- Getting the right diagnosis helps in recovering better.
- It’s important to see the right doctor to heal.
Understanding Soft Tissue Injuries
It’s important to know about soft tissue injuries to get the right treatment. These injuries, like sprains and strains, are common. They can really affect how well you live your life.
Common Types of Musculoskeletal Injuries
Musculoskeletal injuries affect muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Sprains and strains are very common. A sprain happens when a ligament gets stretched or torn. A strain is when a muscle or tendon gets hurt.
Other injuries include:
- Tendonitis: inflammation of tendons
- Bursitis: inflammation of bursae
- Stress fractures: small cracks in bones
| Injury Type | Description | Common Locations |
| Sprain | Ligament stretch or tear | Ankle, wrist, knee |
| Strain | Muscle or tendon damage | Hamstring, back, neck |
Impact of Soft Tissue Injuries on Daily Life
Soft tissue injuries can really mess up your daily life. They can hurt, make it hard to move, and affect your mood. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons says millions go to the doctor each year for these injuries.
“The ability to prevent and effectively treat soft tissue injuries is key for staying active and avoiding long-term damage.”
Knowing what causes these injuries, their symptoms, and how to treat them is vital. By understanding the risks and taking steps to prevent them, you can lower your chance of getting hurt.
Sprain vs Strain: Key Differences Explained
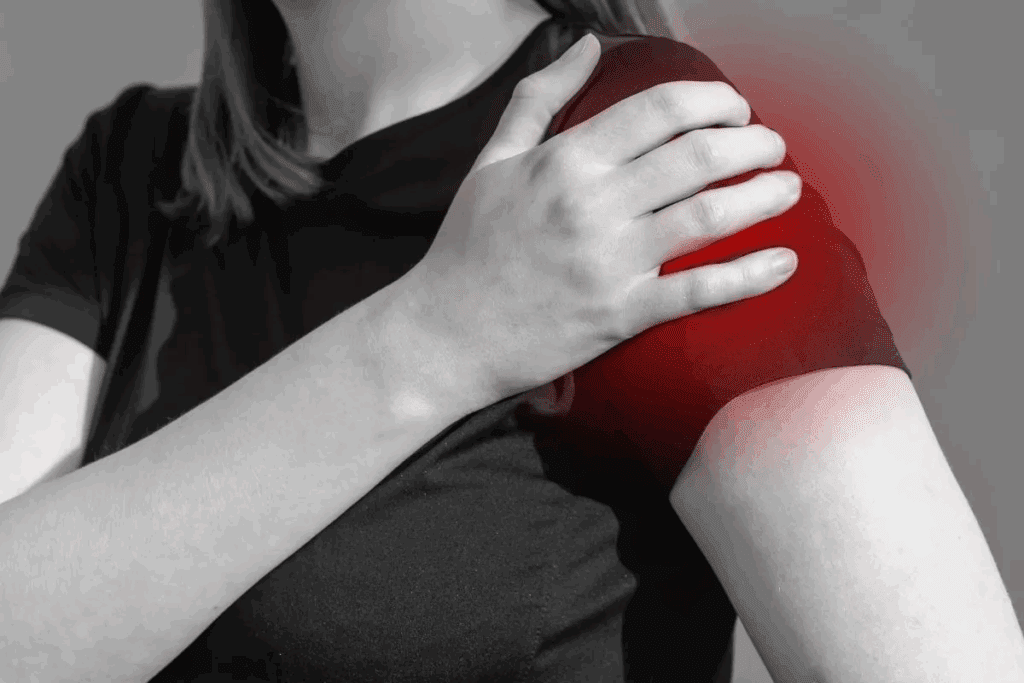

The terms sprain and strain are often mixed up, but they mean different things. Knowing the differences helps with diagnosis, treatment, and preventing more injuries.
Anatomical Differences
A sprain hurts the ligaments. These are tissues that link bones together, keeping joints stable. A strain, on the other hand, affects muscles or tendons. These connect muscles to bones.
The way sprains and strains affect the body is key to understanding their symptoms and how to treat them.
Injury Mechanisms
Sprains happen when a joint is twisted or bent wrong, hurting the ligaments. Strains, though, are from overstretching or tearing muscles or tendons. This usually happens from too much force, being tired, or using something the wrong way.
An athlete might get a sprain from sudden movements. A strain could happen from lifting heavy things without warming up or using the right technique.
Tissue Involvement Comparison
Sprains and strains affect different parts of the body. Sprains damage ligaments, which can make joints unstable. Strains hurt muscles or tendons, making it hard to move and weak.
Knowing which tissues are hurt is important for treating the injury right.
What Is a Sprain? Ligament Injury Explained
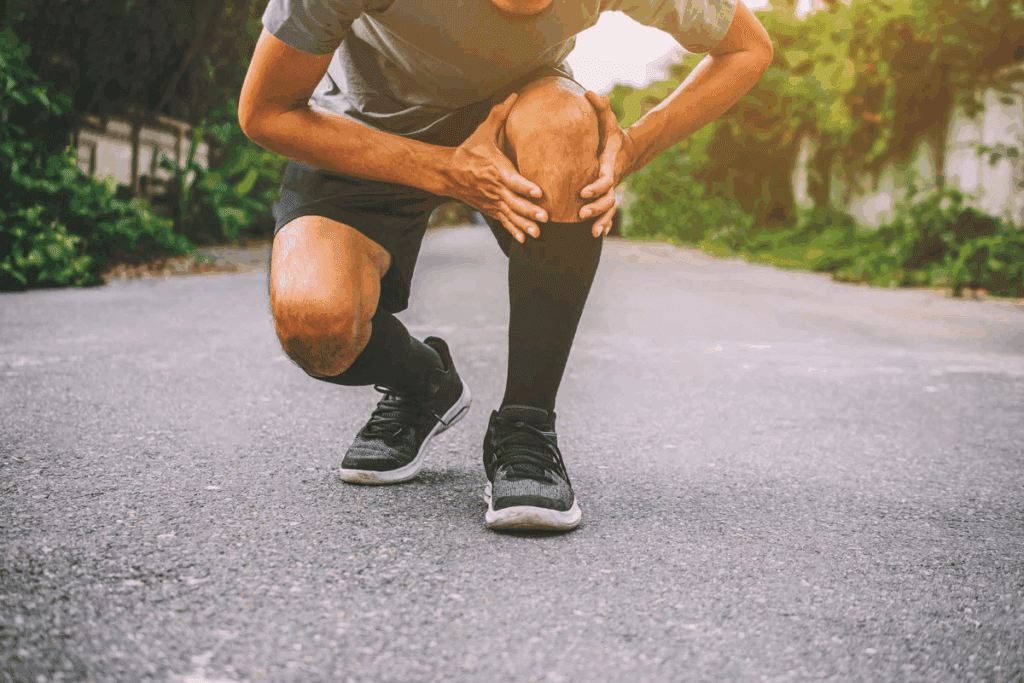

Sprains, or ligament injuries, happen often in sports and daily life. A sprain happens when a ligament, which connects bones, gets stretched or torn. This injury can really affect how well you move and do everyday things.
Definition and Anatomy of Ligaments
Ligaments are strong tissues that keep joints stable by linking bones. They help us know where our body is and how it’s moving. If a ligament gets hurt, it can cause pain and make joints unstable. Some ligaments are more likely to get injured than others.
Doctors say knowing about ligaments is important for treating sprains right. A top orthopedic surgeon notes, “Ligaments keep joints stable, and hurting them can cause long-term problems if not fixed.”
Grades of Sprains
Sprains are divided into three levels based on how bad they are:
- Grade 1: A mild injury with a bit of stretching or micro-tearing, causing little pain and no big joint problems.
- Grade 2: A bit worse, with a partial tear of the ligament, leading to more pain and some joint instability.
- Grade 3: The worst, with the ligament fully torn, causing a lot of pain, swelling, and big joint problems.
Knowing the grade of a sprain helps figure out the right treatment and how to get better. A medical journal says, “It’s key to accurately grade sprains to manage them well and avoid more harm.”
What Is a Strain? Muscle and Tendon Injury Detailed
Strains happen when muscles or tendons get stretched or torn. They are common in athletes and people who do a lot of physical activities.
Definition and Anatomy of Muscles and Tendons
Muscles and tendons are key parts of our body. Muscles help us move by contracting. Tendons are like strong cords that connect muscles to bones. When these get injured, it can cause pain and make it hard to move.
Muscles have many parts, like muscle fibers and connective tissue. Tendons, made of strong connective tissue, help muscles move bones.
Grades of Strains
Strains are divided into three levels based on how bad they are:
| Grade | Description | Symptoms |
| Grade 1 | Mild strain with minimal muscle or tendon damage | Mild pain, minimal swelling, and no significant loss of strength |
| Grade 2 | Moderate strain with partial muscle or tendon tear | Moderate to severe pain, swelling, and some loss of strength |
| Grade 3 | Severe strain with complete muscle or tendon tear | Severe pain, significant swelling, and substantial loss of strength or function |
Knowing the grade of a strain helps figure out the right treatment and how long it will take to get better.
Common Locations for Sprains
Knowing where sprains often happen can help prevent and treat them. Sprains are injuries to the ligaments, which can occur in many body parts. They usually happen when there’s sudden twisting or bending.
Ankle Sprains
Ankle sprains are very common, often from sports or activities that involve running, jumping, or quick turns. The ligaments on the outside of the ankle are usually affected.
Wrist Sprains
Wrist sprains can happen when falling onto an outstretched hand, straining the wrist ligaments. This is common in sports like gymnastics or skateboarding.
Knee Sprains
Knee sprains involve injuries to the ligaments around the knee joint. They can happen in sports that involve cutting, pivoting, or jumping, like soccer or basketball.
Thumb and Finger Sprains
Thumb and finger sprains are common in sports that involve catching or throwing, like baseball or basketball. These sprains occur when the ligaments around the thumb or finger joints are stretched or torn.
Knowing where sprains often happen can help prevent them and get the right treatment when they do occur.
Common Locations for Strains
It’s important to know where strains often happen to prevent and treat them well. Strains can affect many muscles and tendons in the body. But some areas are more likely to get strained because of how we use them or sudden injuries.
Hamstring Strains
Hamstring strains are common in athletes, mainly those who sprint or need quick starts. The hamstring muscles at the back of the thigh work hard during sports. This makes them more likely to get strained.
Symptoms of hamstring strains include: pain in the back of the thigh, swelling, and trouble walking or bending the knee.
Back Strains
Back strains are also common, often from lifting heavy things, bending, or sudden twists. The muscles in the lower back are very vulnerable.
Prevention strategies for back strains include good posture, lifting right, and exercises that strengthen the back.
Neck Strains
Neck strains can happen from bad posture, like when using digital devices, or sudden neck movements. Symptoms include pain, stiffness, and less ability to move.
“Maintaining a neutral spine and taking regular breaks when working on computers or smartphones can significantly reduce the risk of neck strains.”
Calf and Achilles Tendon Strains
Calf and Achilles tendon strains are common in athletes who run or jump a lot. These injuries can come from overuse, sudden direction changes, or direct hits to the area.
Treatment for calf and Achilles tendon strains usually means rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Physical therapy is also used to help regain strength and flexibility.
Common Causes of Sprains and Strains
It’s important to know why sprains and strains happen. These injuries can come from many things. They affect different people and activities.
Sports-Related Injuries
Sports injuries are a big reason for sprains and strains. Running, jumping, quick turns, or contact sports can cause these injuries. Sports like soccer, basketball, and football are often linked to these injuries because they are so demanding.
Everyday Activities That Lead to Injuries
Even everyday tasks can lead to sprains and strains. Overexertion or bad lifting can cause these injuries. Simple things like lifting heavy objects, slipping on a wet floor, or falling can lead to them. Being careful with how we move during daily tasks helps prevent these injuries.
Occupational Risk Factors
Some jobs are more likely to cause sprains and strains because of the physical demands. Construction, manufacturing, and healthcare workers are often at risk. Heavy lifting, repetitive motions, or awkward postures are common causes. Employers can help by setting up safety rules and training workers.
Age and Fitness Level Considerations
Age and fitness level also play a big part in getting sprains or strains. Older people might be more at risk because of less flexibility and strength. Those who are less active are also at higher risk. Staying active and keeping a healthy weight can help lower these risks.
| Risk Factor | Description | Prevention Strategies |
| Sports-Related Injuries | High-intensity activities, contact sports | Proper warm-up, use of protective gear |
| Everyday Activities | Lifting heavy objects, slipping, falling | Mindful lifting, safety at home |
| Occupational Hazards | Heavy lifting, repetitive motions, awkward postures | Safety protocols, workplace training |
| Age and Fitness Level | Decreased flexibility, strength, physical inactivity | Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight |
Symptoms: How to Identify a Sprain vs a Strain
It’s important to know the signs of sprains and strains to get the right medical help. Both can hurt a lot and make it hard to move. But knowing the symptoms helps doctors figure out what’s wrong and how to fix it.
Sprain Symptoms
Sprains show up as pain and swelling near the joint. The pain’s intensity depends on how bad the sprain is. A mild sprain might just hurt a little, while a bad one can really hurt and swell up a lot.
Also, the joint might feel unstable, making it hard to move it.
Doctors say sprains can really hurt, not just the joint but also the tissues around it.
“Pain, swelling, and bruising are hallmark signs that require immediate attention to prevent further injury.”
Strain Symptoms
Strains show up as muscle or tendon pain and spasms. You might also see swelling and have trouble moving. The pain and weakness can vary, with more severe strains causing more harm.
When Symptoms Overlap
Sometimes, sprains and strains can look the same, making it hard to tell them apart. Both can hurt, swell, and make it hard to move. But knowing how the injury happened can help figure out if it’s a sprain or strain.
Red Flags That Require Immediate Attention
Some symptoms need you to see a doctor right away. These include a lot of pain, swelling, or if you can’t move the limb. Also, if there’s an open wound or signs of infection, get help fast. Prompt treatment helps avoid bigger problems and speeds up healing.
Diagnosis of Sprains and Strains
Diagnosing sprains and strains involves a few steps. First, a doctor will do a physical check. Then, they might use imaging tests if needed. Getting the diagnosis right is key to healing properly.
Physical Examination Techniques
A doctor will start by checking the injured area. They look for:
- Pain location and intensity
- Swelling and bruising
- Range of motion and stability
- Muscle strength
They might use specific tests like the anterior drawer test for ankle sprains. Or the straight leg raise test for hamstring strains. These tests help figure out how bad the injury is.
Imaging Tests
Even with a physical check, imaging tests are often needed. They help confirm the diagnosis or check for more serious injuries. Common tests include:
- X-rays: To check for fractures or bone problems
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): To see soft tissue damage like ligament or tendon injuries
- Ultrasound: To look at tendon and ligament injuries, and find fluid or blood
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
It’s important to rule out other possible causes of pain or injury. Doctors need to think about things like:
- Fractures
- Tendinopathies
- Other soft tissue injuries
- Underlying conditions that might make injury more likely
A detailed check helps make sure the diagnosis is correct. This way, the treatment plan can be just right.
Treatment Approaches for Sprains and Strains
Treating sprains and strains requires a few steps. First, you need to take care of it right away. Then, manage the pain and help it heal. This way, you can get back to normal faster.
Immediate Care (RICE Protocol)
The RICE method is key for quick care of sprains and strains. RICE means Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
- Rest: Stay away from activities that make it worse.
- Ice: Ice helps lessen pain and swelling.
- Compression: A bandage can help shrink swelling.
- Elevation: Keep the injured area higher than your heart to reduce swelling.
Medications for Pain and Inflammation
There are medicines to help with pain and swelling. You can buy these at a drug store. Ibuprofen and acetaminophen are common ones.
| Medication | Dosage | Purpose |
| Ibuprofen | 200-400 mg every 4-6 hours | Pain relief and anti-inflammatory |
| Acetaminophen | 325-1000 mg every 4-6 hours | Pain relief |
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is very important for healing sprains and strains. It helps make the area stronger and more flexible.
Bracing and Support Options
Bracing and support can help the injured area heal faster. You can use elastic bandages, orthotics, and splints.
Choosing the right support can really help your recovery. It gives the area the stability it needs and lowers the chance of more injury.
Recovery Timeline: Sprain vs Strain
Knowing how long it takes for sprains and strains to heal is key. It helps manage expectations and ensures proper recovery. The healing time depends on the injury’s severity, treatment success, and personal factors like age and health.
Typical Healing Time for Sprains
Sprains can take weeks to months to heal. Mild sprains usually heal in 2-4 weeks. But, severe sprains might need 6-8 weeks or more.
For example, a mild ankle sprain might heal quickly. But a severe one could take months to recover from.
Typical Healing Time for Strains
Strains also have different healing times. Mild strains can heal in a few weeks. But severe strains might take months.
A mild hamstring strain might heal in 2-3 weeks. But a severe one could take up to 6 months.
Factors Affecting Recovery Speed
Many things can affect how fast sprains and strains heal. These include the injury’s severity, treatment success, any health conditions, and age and fitness level. For more info, visit MassGeneralBrigham’s article on sprains and strains.
Signs of Proper Healing
Signs of healing include less pain, better mobility, and stronger muscles. It’s important to watch for these signs and adjust treatment as needed for the best recovery.
Rehabilitation Exercises and Techniques
A good rehabilitation program is key for healing from sprains and strains. It uses different exercises and techniques to help the body recover.
Rehabilitation plans vary a lot. This depends on the type of injury, how severe it is, and the person’s health and fitness.
Rehabilitation for Sprains
For sprains, the goal is to make ligaments strong again and improve joint stability. The program starts with simple exercises and gets harder as the person gets stronger.
- Range of Motion Exercises: These are gentle movements that keep or improve joint mobility.
- Strengthening Exercises: These exercises make the muscles around the injured ligament stronger, helping the joint stay stable.
- Balance and Proprioception Exercises: These exercises help the body stay balanced and understand the position of the joint.
For example, someone with an ankle sprain might start with toe raises and ankle circles. Then, they might do single-leg balances and heel-to-toe walks.
Rehabilitation for Strains
For strains, the focus is on getting muscles and tendons to work right again. The program includes exercises to improve flexibility, strength, and ability to do daily and sports activities.
- Stretching Exercises: These are gentle stretches to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension.
- Strengthening Exercises: These exercises make the affected muscle and tendon stronger.
- Eccentric Training: This focuses on the lengthening phase of muscle movement, which is good for tendon injuries.
A rehabilitation program for a hamstring strain might include hamstring stretches, strengthening exercises with resistance bands, and eccentric training like Nordic hamstring curls.
| Exercise Type | Sprains | Strains |
| Range of Motion | Essential for maintaining joint mobility | Beneficial for maintaining muscle flexibility |
| Strengthening | Critical for ligament and joint stability | Important for muscle and tendon strength |
| Eccentric Training | Not typically emphasized | Beneficial, specially for tendon strains |
Return to Activity Guidelines
Going back to activity after a sprain or strain should be done slowly. It depends on how the person feels, their strength, and how well they can function. It’s important to make sure the injured area can handle the activity without getting worse.
“The key to successful rehabilitation is a gradual and well-planned return to activity, ensuring that the injured tissue is not subjected to undue stress too quickly.” – Sports Medicine Expert
Criteria for returning to activity include:
- Minimal pain and inflammation
- Sufficient strength and flexibility
- Adequate functional ability for the desired activity
By following a structured rehabilitation program and sticking to return to activity guidelines, people can recover better from sprains and strains. This helps lower the chance of getting hurt again.
Real-World Examples: Common Sprain and Strain Injuries
Sprains and strains happen to everyone, from athletes to regular folks. They can occur during sports, at work, or even doing everyday tasks. This shows why we need to be aware and take steps to prevent them.
Notable Sports Injuries
Sports injuries are a big deal for athletes and fans. Ankle sprains are common in sports like soccer and basketball. These injuries can affect athletes’ performance and careers.
- Ankle sprains in soccer players
- Knee ligament sprains in football players
- Wrist sprains in gymnasts
Everyday Case Studies
Sprains and strains happen outside of sports too. Simple things like lifting heavy objects or slipping on a wet floor can cause these injuries. Knowing these risks helps us find ways to prevent them.
- Lifting heavy objects improperly, leading to back strains
- Slipping on wet floors, resulting in wrist or ankle sprains
- Overexertion during exercise, causing muscle strains
Lessons Learned from High-Profile Cases
High-profile cases teach us a lot about sprains and strains. For example, how professional athletes recover and rehabilitate can help others. These examples show the importance of proper treatment and prevention.
“Proper rehabilitation is key to preventing re-injury and ensuring a full recovery.” –
A Sports Medicine Specialist
Looking at real-world examples and learning from famous cases helps us understand how to manage and prevent sprains and strains. This knowledge can make a big difference in our daily lives.
Prevention Strategies for Sprains and Strains
To lower the chance of sprains and strains, knowing and using good prevention methods is key. These injuries can really affect our daily lives and sports performance. So, preventing them is very important for our health and well-being.
Proper Warm-up and Stretching
Starting with a good warm-up and stretching is essential. It gets the muscles and joints ready for activity. This can include some cardio, dynamic stretches, and drills specific to the activity or sport.
Key components of a warm-up routine:
- Light cardio to increase blood flow
- Dynamic stretching to improve flexibility
- Mobility drills to enhance range of motion
Strengthening Exercises
Building muscle around the joints helps support them and lowers injury risk. Focus on exercises for major muscle groups like legs, core, and upper body.
| Muscle Group | Example Exercises |
| Legs | Squats, Lunges, Leg Press |
| Core | Plank, Russian Twists, Leg Raises |
| Upper Body | Push-ups, Pull-ups, Dumbbell Rows |
Proper Technique and Body Mechanics
Using the right technique and body mechanics during activities can greatly lower injury risk. This means learning the correct way to move and not pushing too hard.
“Proper technique is not just about avoiding injury; it’s also about optimizing performance.” – Fitness Expert
Protective Equipment
Wearing protective gear is very important in many sports and activities to prevent injuries. This includes braces, tape, and other support items for vulnerable areas.
By adding these prevention strategies to our daily routines and training, we can greatly reduce the risk of sprains and strains. It’s all about being prepared, using the right technique, and wearing protective gear.
Conclusion
It’s important to know the difference between sprains and strains to manage and prevent injuries. Sprains hurt ligaments, while strains affect muscles or tendons. Getting the right diagnosis and treatment is key to healing and avoiding more harm.
Managing sprains and strains well means taking care of them right away, rehabilitating, and preventing them. Using the RICE method, taking the right medicine, and doing physical therapy helps a lot. This way, people can heal faster and get back to normal.
Preventing injuries is also vital. This can be done by warming up and stretching, doing strengthening exercises, and wearing protective gear. Taking these steps helps lower the chance of getting hurt and keeps muscles and bones healthy.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a sprain and a strain?
A sprain hurts a ligament, which links bones together. A strain hurts a muscle or tendon, which connects muscles to bones.
How can I tell if I have a sprain or a strain?
Sprains and strains share similar symptoms. But, sprains often cause joint pain and instability. Strains lead to muscle or tendon pain and stiffness.
What are the common causes of sprains and strains?
Sprains and strains can happen from sports injuries, daily activities, work risks, and aging.
How are sprains and strains diagnosed?
Doctors use a physical check-up, medical history, and sometimes X-rays or MRI scans to diagnose.
What is the RICE protocol, and how does it help with sprains and strains?
The RICE protocol (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is a first aid method. It helps reduce pain, swelling, and promotes healing in sprains and strains.
Can sprains and strains be prevented?
Yes, you can prevent them. Warm up, stretch, do strengthening exercises, use proper techniques, and wear protective gear.
How long does it take to recover from a sprain or strain?
Recovery time varies by injury severity. Most sprains and strains heal in a few weeks with proper care and rehab.
What are some common locations for sprains?
Common sprain spots include the ankle, wrist, knee, and thumb or fingers.
What are some common locations for strains?
Common strain spots include the hamstring, back, neck, and calf or Achilles tendon.
When should I seek medical attention for a sprain or strain?
See a doctor if you have severe pain, swelling, or instability. Also, if walking or bearing weight is hard on the affected area.
Can I continue to exercise with a sprain or strain?
It’s best to rest and avoid activities that make the injury worse. But, gentle exercises and rehab can aid in recovery.
How can I prevent re-injury after a sprain or strain?
To avoid re-injury, strengthen, use proper techniques, and wear protective gear. This reduces injury risk.
What is the difference between a grade 1, 2, and 3 sprain or strain?
Grade severity of a sprain or strain ranges from mild (grade 1) to severe (grade 3).
Can sprains and strains be treated with medication?
Yes, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage pain and swelling from sprains and strains.
References
- HealthDirect Australia. (2025). Sprains and strains. https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/sprains-and-strains










