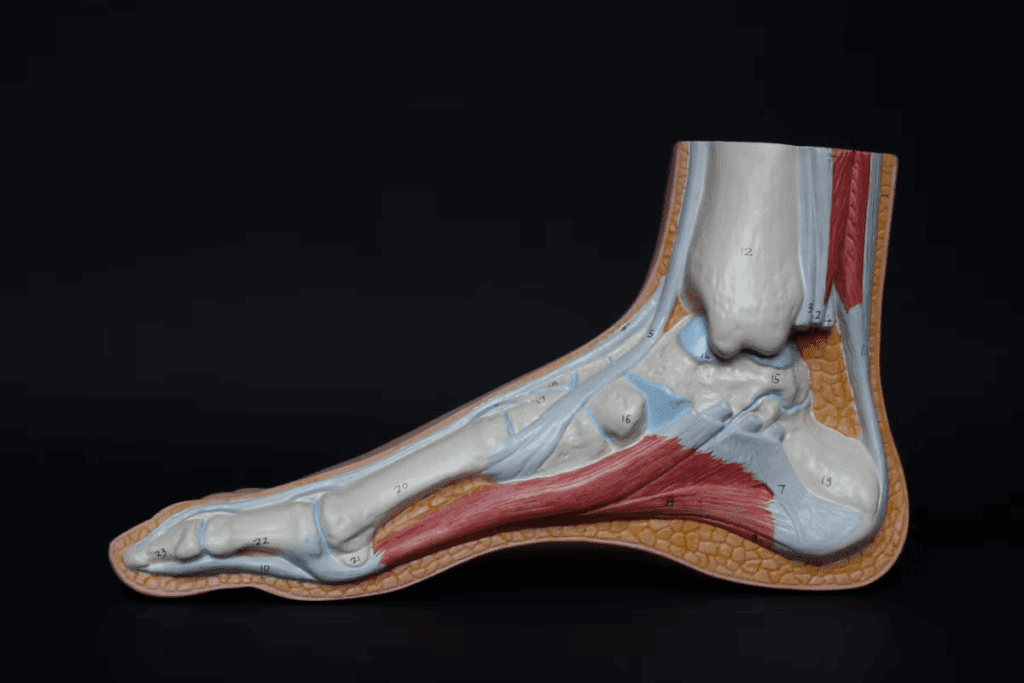
About 30% of adults will get tendinitis at some point. Stage4 Tendinitis is one of the worst kinds.
Stage4 Tendinitis is a serious condition. It causes long-lasting pain and makes it hard to move. Knowing about it is key to managing it well.
Key Takeaways
- Stage4 Tendinitis is a chronic and debilitating condition.
- It is characterized by persistent pain and limited mobility.
- Effective management and treatment require a thorough understanding.
- Advanced tendinitis can greatly affect a person’s life quality.
- Proper treatment can reduce symptoms and improve movement.
Understanding Tendinitis and Its Progression
It’s important to know about tendinitis and how it gets worse. Tendinitis is when tendons, which connect muscles to bones, get inflamed. If not treated, it can lead to serious tendon damage.
Definition of Tendinitis
Tendinitis is when a tendon gets inflamed, usually from too much strain. It can happen in any tendon but often affects the Achilles, rotator cuff, and patellar tendons. At first, tendinitis causes pain, swelling, and makes it hard to move.
Key characteristics of tendinitis include:
- Pain and tenderness
- Swelling or redness
- Warmth around the affected tendon
- Reduced strength or function
The Four Stages of Tendon Damage
Tendon damage goes through four stages, each getting worse. Knowing these stages helps find the right treatment.
| Stage | Description | Characteristics |
| Stage 1 | Inflammation | Pain, swelling, and inflammation |
| Stage 2 | Tendinosis | Chronic degeneration without inflammation |
| Stage 3 | Partial Tears | Partial tendon rupture, significant pain |
| Stage 4 | Complete Degeneration | Complete tendon rupture, severe pain and dysfunction |
Stage 4 tendinitis is very severe and often can’t be fixed. At this point, the tendon is completely damaged, causing a lot of pain and making it hard to move. Knowing how tendinitis gets worse is key to treating it early.
Managing tendinitis well can stop it from getting worse. Spotting the signs early and using the right treatment can prevent serious damage. This way, you can avoid getting to Stage 4 tendinitis.
What is Stage4 Tendinitis?
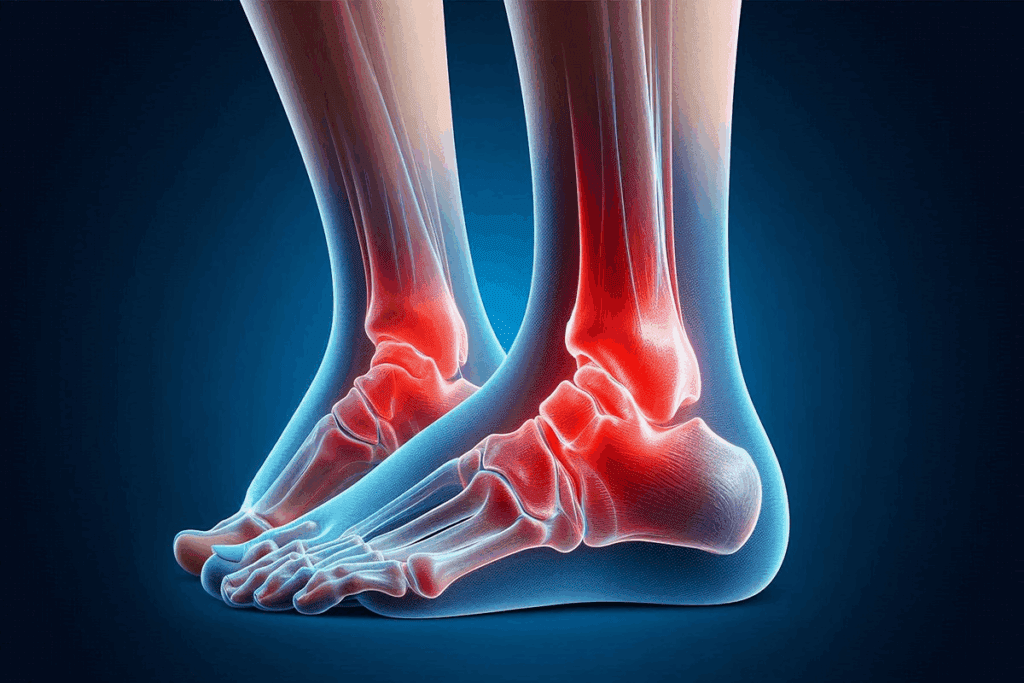
Tendon degeneration peaks in Stage 4 tendinitis. At this stage, the tendon’s structure is severely damaged. This affects its function and integrity greatly.
Clinical Definition
Stage 4 tendinitis is when the tendon completely degenerates. This results in a big loss of tendon function. The tendon can’t do its normal job because of the damage.
To diagnose Stage 4 tendinitis, doctors look at symptoms, patient history, and imaging. This helps them see how much damage there is.
Knowing what Stage 4 tendinitis is helps doctors choose the right treatment. They use physical exams, patient reports, and imaging to confirm it. This knowledge helps them tell Stage 4 apart from other tendon damage stages.
Pathophysiology of End-Stage Tendinitis
Stage 4 tendinitis involves complex changes at the cellular and molecular levels. The tendon degenerates, losing collagen fiber integrity and gaining ground substance. It may even calcify. These changes weaken the tendon, making it more likely to get injured or rupture.
The changes in Stage 4 tendinitis come from long-term tendon damage. This can be from overuse, poor healing, or past injuries. The tendon can’t handle stress anymore, causing pain and making it hard to function.
In Stage 4 tendinitis, the tendon’s repair processes fail. This leads to chronic degeneration. Treating this stage is tough because the tendon may not heal with simple treatments. More aggressive treatments might be needed.
Symptoms of Stage4 Tendinitis
Stage 4 Tendinitis shows up in many ways, like a lot of pain and trouble moving. Knowing these signs is key to figuring out and treating Stage 4 Tendinitis right.
Physical Manifestations
Stage 4 Tendinitis changes the tendon in clear ways. These changes include:
- Tendon thickening or swelling
- Nodule formation
- Tendon rupture or partial tear
- Crepitus or grinding sensation with movement
Functional Limitations
People with Stage 4 Tendinitis face big challenges. These challenges are:
- Reduced range of motion
- Weakness in the affected limb
- Difficulty performing daily activities
- Impaired athletic performance
| Functional Limitation | Description | Impact on Daily Life |
| Reduced Range of Motion | Decreased mobility in the affected joint | Difficulty with everyday movements |
| Weakness | Loss of strength in the affected limb | Challenges with lifting, carrying, or gripping |
| Impaired Athletic Performance | Decreased ability to perform sports-related activities | Impact on competitive or recreational sports participation |
Pain Characteristics
Pain is a big deal with Stage 4 Tendinitis. The pain is:
- Chronic and persistent
- Severe and debilitating
- Worsened by activity
- Relieved by rest, though not completely
Understanding Stage 4 Tendinitis symptoms is key to managing it well. Knowing the physical signs, how it affects movement, and the pain helps doctors create better treatment plans.
Common Locations for Stage4 Tendinitis
Knowing where Stage 4 tendinitis often occurs is key for prevention and treatment. This condition, marked by tendon degeneration, affects many tendons. Tendons under stress and strain are most at risk.
Achilles Tendon
The Achilles tendon is a common spot for Stage 4 tendinitis, mainly in runners and those in high-impact sports. The constant stress can cause degeneration and even rupture if not treated.
Rotator Cuff
Rotator cuff tendons are also often hit by Stage 4 tendinitis, mainly in those who do overhead motions a lot. This can really hurt shoulder function and movement.
Patellar Tendon
Stage 4 tendinitis can also hit the patellar tendon, common in jumpers. This tendon is vital for knee function. Its degeneration can cause a lot of knee pain and trouble.
Tennis and Golfer’s Elbow
Tennis elbow and golfer’s elbow can also lead to Stage 4 tendinitis. These affect the tendons on the elbow’s outside and inside. They’re linked to repetitive forearm actions.
All these conditions can lead to a lot of pain and trouble with moving. Knowing which tendon is affected is important for a good treatment plan.
Spotting Stage 4 tendinitis early can help stop it from getting worse. Treatment depends on the tendon and how bad the degeneration is.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several key factors contribute to Stage 4 Tendinitis. Knowing these causes and risk factors is key for prevention and treatment.
Overuse and Repetitive Strain
Overuse or repetitive strain on tendons is a main cause of Stage 4 Tendinitis. Activities like running, jumping, or throwing can cause chronic damage. Athletes and those with demanding jobs are at high risk.
Repetitive strain causes micro-tears in the tendon. This leads to inflammation and degeneration. If not treated, it can lead to Stage 4 Tendinitis with significant damage.
Previous Tendon Injuries
Previous tendon injuries are a big risk factor for Stage 4 Tendinitis. Incomplete healing or poor rehabilitation of initial injuries can weaken tendons. This makes them more prone to further damage.
Those with past tendon injuries should watch their tendon health closely. They should take steps to prevent re-injury.
Age-Related Factors
Age is a big factor in Stage 4 Tendinitis. As we age, tendons lose elasticity and blood flow. Older adults are more likely to experience tendon degeneration.
Years of repetitive strain and past injuries also increase risk in older people.
Medical Conditions Contributing to Tendon Degeneration
Certain medical conditions raise the risk of Stage 4 Tendinitis. Diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and obesity can harm tendon health.
Diabetes can slow tendon healing and increase degeneration risk. Rheumatoid arthritis causes chronic inflammation that affects tendons. Managing these conditions is vital to prevent Stage 4 Tendinitis.
Progression from Earlier Stages to Stage4 Tendinitis
Stage4 Tendinitis is the final stage of a process that starts with inflammation. It goes through several stages before reaching this point. Knowing how it progresses helps in treating it early and preventing serious damage.
Stage1: Inflammation
The first stage of tendinitis is inflammation. This stage is marked by pain, swelling, and warmth. It happens when there’s a sudden injury or too much strain on the tendon.
Stage2: Tendinosis
Stage2 is when the inflammation goes away, but the tendon starts to degenerate. This is called tendinosis. The tendon’s structure weakens because of collagen breakdown.
Stage3: Partial Tears
In Stage3, the tendon starts to tear partially. These small tears make the tendon more prone to damage. It’s a sign that the tendon is getting weaker.
Stage4: Complete Degeneration
Stage4 Tendinitis is when the tendon completely breaks down. This can lead to a full-thickness tear. At this stage, the tendon is severely damaged, causing a lot of pain and limiting function.
Understanding how tendinitis progresses is key to treating it early. Knowing the difference between acute and chronic tendinitis helps in finding the right treatment.
Diagnosing Stage4 Tendinitis
To diagnose Stage 4 Tendinitis, doctors use a detailed method. This includes checking the patient’s symptoms, using imaging, and ruling out other conditions. Getting the diagnosis right is key to treating the patient well.
Clinical Evaluation
The first step is a thorough check-up. Doctors look at the patient’s medical history and do a physical exam. They check where the pain is, how long it lasts, and how bad it is. They also see how the patient moves and do tests to check the tendons.
Key components of the clinical evaluation include:
- Patient history: Understanding the onset and progression of symptoms
- Physical examination: Assessing pain, swelling, and tendon function
- Functional assessment: Evaluating the impact on daily activities and sports
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is a big help in diagnosing Stage 4 Tendinitis. Different tools give different views.
- X-rays: To rule out bone-related issues
- Ultrasound: To visualize tendon structure and detect tears
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): To assess tendon damage and surrounding tissue
Differential Diagnosis
It’s important to rule out other conditions that might look like Stage 4 Tendinitis. Doctors must think of other possibilities to make sure they’re treating the right thing.
Conditions to consider in differential diagnosis:
- Other types of tendinitis or tendinopathy
- Ligament sprains or tears
- Bursitis or other soft tissue disorders
- Degenerative joint diseases
By using clinical checks, imaging, and ruling out other conditions, doctors can accurately diagnose Stage 4 Tendinitis. Then, they can create a good treatment plan.
When to Seek Medical Help
Knowing when to get medical help is key for managing Stage 4 Tendinitis. This condition can really affect your daily life and quality of life if not treated quickly.
Warning Signs of Advanced Tendinitis
There are warning signs that mean you should see a doctor. These include:
- Persistent pain that doesn’t get better with rest or simple treatments.
- Significant swelling or bruising around the tendon.
- Decreased strength or function in the affected limb.
- Crepitus or a grating feeling when moving the tendon.
Emergency Symptoms
Some tendinitis symptoms are emergencies that need quick medical help. These are:
- Severe pain that suddenly gets much worse.
- Sudden loss of function in the affected limb.
- Deformity or a noticeable gap in the tendon.
If you have any of these symptoms, getting medical help right away is very important.
Choosing the Right Specialist
When you need help for Stage 4 Tendinitis, finding the right specialist is key. Orthopedic surgeons and sports medicine doctors are usually the best for treating this condition. Sometimes, a rheumatologist might also be needed, if there’s an underlying inflammatory issue.
Getting care from a specialist who knows a lot about tendinitis can really help your treatment plan work better.
Tendinitis vs. Tendinopathy: Understanding the Difference
The terms tendinitis and tendinopathy are often mixed up, but they mean different things for treatment. Knowing the difference is key for getting better.
Inflammatory vs. Degenerative Processes
Tendinitis is when the tendons get inflamed, usually from injury or too much use. It causes pain, swelling, and makes it hard to move. Tendinopathy, on the other hand, is long-term damage without much inflammation. It happens from repeated strain and wear on the tendons.
The main difference is inflammation. Tendinitis has it, while tendinopathy doesn’t. This matters because it changes how we treat it.
Implications for Treatment
Treatment for tendinitis aims to reduce inflammation and pain. It includes medicines, rest, and physical therapy. Tendinopathy treatment, though, focuses on healing and strengthening the tendon. This might include exercises, physical therapy, and sometimes PRP therapy.
Knowing if it’s tendinitis or tendinopathy is vital for the right treatment. Getting it wrong can lead to poor treatment and longer recovery times.
In summary, tendinitis and tendinopathy are both tendon issues, but they differ in how they affect the tendons. This difference is important for treatment. Getting the right diagnosis is essential for effective care.
Conservative Treatment Options for Stage4 Tendinitis
Stage4 Tendinitis can be managed with various treatments. These aim to reduce pain and improve function. They are key for those with severe tendinitis.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain management is vital for Stage4 Tendinitis. Several methods can be used, including:
- Pharmacological interventions, such as NSAIDs or corticosteroid injections
- Alternative therapies, including acupuncture and massage
- Topical treatments like creams or gels that contain anti-inflammatory agents
Effective pain management helps patients in rehabilitation.
Activity Modification
Changing activities is essential. This means:
- Reducing the frequency or intensity of activities that aggravate the tendon
- Changing the technique or equipment used in sports or work-related tasks
- Incorporating regular breaks to rest the affected tendon
Modifying activities is a key part of managing Stage4 Tendinitis.
Bracing and Support
Braces or orthotics can offer extra support. They help reduce stress and aid healing.
Therapeutic Modalities
Several therapies can help with Stage4 Tendinitis recovery. These include:
| Therapy | Description | Benefits |
| Ultrasound Therapy | Uses sound waves to promote healing | Reduces inflammation, promotes tissue repair |
| Laser Therapy | Applies laser light to stimulate healing | Enhances tissue repair, reduces pain |
| Electrical Stimulation | Uses electrical currents to stimulate muscle contractions | Improves muscle strength, reduces atrophy |
These treatments offer a complete approach to managing Stage4 Tendinitis. They help improve life quality for those affected.
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is key in treating Stage4 Tendinitis. It uses various methods to ease symptoms and boost function. The main aim is to fix the tendon damage, improve its health, and get you moving better.
Eccentric Strengthening Protocols
Eccentric exercises are vital for Stage4 Tendinitis. They make the tendon longer under weight, helping it heal and get stronger. You might do 3 sets of 15 reps, twice a day.
Range of Motion Exercises
Range of motion exercises keep the tendon flexible and reduce stiffness. You can do different types of movements. The right amount and intensity depend on how you’re feeling and how far along you are in recovery.
Manual Therapy Techniques
Manual therapy, like massage and mobilization, helps with pain, blood flow, and tendon health. A skilled physical therapist can target specific tight spots or restrictions.
Progression and Timeline
How you progress in physical therapy depends on how you react to treatment. This includes changes in pain, how well you can move, and tendon health. Recovery times vary, often taking months of regular therapy.
| Treatment Phase | Interventions | Goals |
| Initial Phase | Pain management, gentle range of motion | Reduce pain, maintain flexibility |
| Strengthening Phase | Eccentric strengthening, progressive resistance exercises | Improve tendon strength, enhance function |
| Advanced Phase | Functional training, agility drills | Restore functional capability, return to activity |
Advanced Interventions for Stage4 Tendinitis
When simple treatments don’t work for Stage4 Tendinitis, more advanced options are needed. These treatments aim to fix the deep problems in tendons. They help those who haven’t seen improvement with basic therapies.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections
PRP injections use your own platelet-rich plasma. It’s injected into the tendon to help it heal. This method is being studied for its ability to reduce pain and improve function.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is another new approach for Stage4 Tendinitis. It uses stem cells to repair tendons. This treatment is being researched and is seen as a cutting-edge option.
Prolotherapy
Prolotherapy involves injecting a solution into the tendon to start healing. The solution, usually dextrose, causes inflammation and then healing. It’s been used for tendinitis and has shown promise for some patients.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive method. It uses shock waves to improve blood flow and repair tendons. It’s been used for many musculoskeletal issues, including Stage4 Tendinitis, with mixed results.
These advanced treatments offer hope for Stage4 Tendinitis patients who haven’t seen results with simple treatments. Each option has its own benefits. Choosing the right treatment should be done with a healthcare professional’s advice.
Surgical Options for End-Stage Tendinitis
When other treatments don’t work, surgery might be needed for end-stage tendinitis. Surgery aims to fix the tendon damage, ease pain, and help you move better.
Tendon Debridement
Tendon debridement removes damaged tendon parts. It helps the tendon heal by getting rid of the bad parts. This makes you feel less pain and move better.
Tendon Repair Techniques
There are different ways to fix a damaged tendon. For severe tendinitis, doctors might use special methods to fix or rebuild the tendon. This helps it work and feel strong again.
Tendon Transfer Procedures
If the tendon is too damaged to fix, a tendon transfer might be done. This moves a healthy tendon to the damaged area. It helps restore function.
The right surgery depends on how bad the tendinitis is, your health, and how active you are.
| Surgical Procedure | Description | Benefits |
| Tendon Debridement | Removal of damaged tendon tissue | Reduces pain, promotes healing |
| Tendon Repair | Repair or reconstruction of the tendon | Restores tendon function and strength |
| Tendon Transfer | Transfer of a healthy tendon to the affected area | Restores function in cases of severe tendon damage |
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
Rehab after surgery is very important. It includes physical therapy to get the tendon strong and flexible again. The rehab plan changes based on the surgery and the patient.
Key parts of rehab include:
- Slowly getting stronger and more flexible
- Using tools like ultrasound to help heal
- Learning how to move right to avoid hurting it again
Good rehab is key to getting back to how you want to be. It helps you move well again.
Preventing Progression to Stage4 Tendinitis
Early action and lifestyle changes are key to stopping tendinitis from getting worse. Knowing the risks and acting early can help avoid serious tendon damage.
Early Intervention Strategies
Acting fast is important to stop tendinitis from getting worse. Spotting early signs and getting help quickly is essential. Early diagnosis leads to better treatment and less damage.
Some good early steps include:
- Rest and ice to reduce inflammation
- Physical therapy to improve tendon strength and flexibility
- Changing activities to avoid making it worse
Proper Training and Technique
Right training methods are key to stopping tendinitis. This means using the right body mechanics, not overdoing it, and doing strengthening exercises for tendons.
Coaches and trainers are important in teaching athletes the right ways to move. This helps lower the chance of tendon injuries.
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle can help your tendons a lot. Staying at a healthy weight, not smoking, and eating right are important. Nutritional supplements like omega-3s and vitamin D can also help.
Maintenance Exercises
Doing regular exercises helps keep tendons healthy. These exercises should make the muscles around the tendon stronger and more flexible.
A good exercise plan, made just for you, can keep your tendons strong and working well.
Conclusion
Understanding Stage4 Tendinitis is key to managing and treating it. This advanced tendon damage needs a detailed approach to ease symptoms and improve function.
A tendinitis management summary shows the value of acting early, getting the right diagnosis, and a custom treatment plan. For Stage4 Tendinitis, there are many advanced tendinitis treatment choices. These range from non-surgical methods to surgery.
The stage4 tendinitis conclusion is that a team effort is best. This includes physical therapy, pain control, and sometimes PRP injections or stem cell therapy. Knowing about tendinitis and its treatments helps people make better care choices.
Managing Stage4 Tendinitis well needs teamwork between doctors and patients. Together, they can help someone recover fully and get back to their activities.
FAQ
What is Stage4 Tendinitis, and how does it differ from other stages of tendinitis?
Stage4 Tendinitis is the most severe stage of tendon damage. It means the tendon has completely broken down. This stage is different because the tendon’s structure and function are completely lost.
What are the common symptoms of Stage4 Tendinitis?
Symptoms include severe pain and big limitations in how you can move. You might also see swelling or a deformity.
How is Stage4 Tendinitis diagnosed?
Doctors use a few methods to diagnose it. They look at your symptoms, use imaging like MRI or ultrasound, and rule out other conditions.
What are the causes and risk factors for developing Stage4 Tendinitis?
It can happen from overusing your tendons or having past injuries. Age and certain health conditions also play a role.
Can Stage4 Tendinitis be treated conservatively, or is surgery always required?
Not always. Some people might need surgery, but others can try pain management, changing how they move, bracing, and physical therapy first.
What are the advanced interventions available for Stage4 Tendinitis?
There are newer treatments like PRP injections, stem cell therapy, prolotherapy, and shock wave therapy.
How can progression to Stage4 Tendinitis be prevented?
You can prevent it by acting early, using the right training, making lifestyle changes, and doing regular exercises.
What is the difference between tendinitis and tendinopathy?
Tendinitis is inflammation, while tendinopathy is degeneration. Knowing this helps in choosing the right treatment.
What are the surgical options for end-stage tendinitis?
Surgery might include cleaning out the tendon, repairing it, or transferring tendons. After surgery, you’ll need to follow a rehabilitation plan.
How long does it take to recover from Stage4 Tendinitis with physical therapy?
Recovery time varies. It depends on the person and the treatment plan. It usually takes months, with exercises getting more challenging over time.
Can chronic tendinitis be managed without surgery?
Yes, many cases can be managed without surgery. This includes using pain management, physical therapy, and making lifestyle changes.
What are the implications of irreversible tendon damage?
If the tendon damage is permanent, like in Stage4 Tendinitis, you might need surgery. This is to get your function back and ease the pain.
References
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). Health care innovation and future models of care delivery. PubMed Central. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12059502/


































