Stem cell therapy side effects are seen as a hopeful treatment for many health issues. It makes people curious about its pain and side effects. This makes them very useful for healing.
Many patients worry about pain when considering stem cell therapy, but while it is generally safe, understanding potential side effects is essential. It helps patients decide if it’s right for them.
Key Takeaways
- Stem cell therapy is a promising treatment for various medical conditions.
- The therapy involves using stem cells that can self-renew and differentiate.
- Patients often wonder if stem cell therapy is painful.
- Understanding the side effects is important for making good choices.
- Stem cell therapy is generally safe when done by experts.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy?
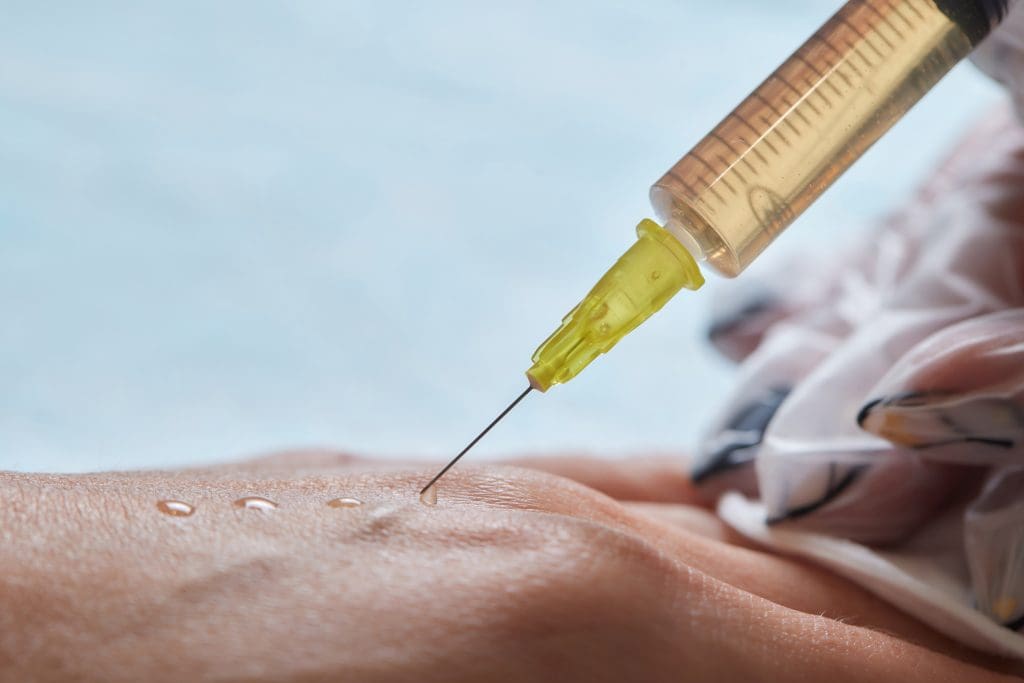
Stem cell therapy is a new way to heal the body. It uses stem cells to fix damaged tissues. This method is getting a lot of attention for treating many health problems.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Treatment
Stem cells come from embryos and adult tissues.This makes them great for fixing health issues. There are two main types used in therapy:
- Embryonic Stem Cells: These come from embryos and can become any cell type in the body.
- Adult Stem Cells: These are in adult tissues and can repair damaged tissues but are more limited.
Common Medical Applications
Stem cell therapy is used for many medical needs. It helps with blood disorders, degenerative diseases, and injuries. Here are some common uses:
- Orthopedic Treatments: It fixes damaged joints and bones.
- Neurological Disorders: Scientists are studying its use for brain conditions.
- Autoimmune Diseases: It’s being looked at as a treatment for diseases where the body attacks itself.
How Stem Cells Work to Heal the Body
Stem cells fix damaged tissues by turning into the needed cells. When used, they go to the injury or disease site. There, they help heal by releasing growth factors and signaling molecules.
Understanding how stem cells work helps patients decide if this therapy is right for them.
The Stem Cell Therapy Procedure Explained
Stem cell therapy is a complex treatment with several stages. It starts with harvesting stem cells, then processing them. Lastly, the cells are given back to the patient.
Harvesting Methods and Techniques
Stem cells come from different places like bone marrow, fat tissue, and blood. The method used depends on the patient’s needs and the condition being treated.
- Bone Marrow Aspiration: This method takes stem cells from the bone marrow, usually from the hip area. It’s done under local anesthesia.
- Adipose Tissue Extraction: This method uses fat tissue, often taken through liposuction. It’s less invasive than bone marrow aspiration.
- Peripheral Blood Collection: This method moves stem cells from the bone marrow into the blood. It’s good for those who want a less invasive option.
Processing of Stem Cells
After getting the stem cells, they are processed to focus on the cells needed for treatment. This step is key to making the treatment work well.
| Processing Technique | Description | Benefits |
| Centrifugation | Separates components based on density | High cell yield |
| Cell Culture Expansion | Expands cell numbers in a controlled environment | Increased cell count for therapy |
| Magnetic Separation | Isolates specific cell types using magnetic beads | High purity of stem cells |
Administration and Injection Procedures
The processed stem cells are given back to the patient through injection or infusion. The choice depends on the condition being treated.
Direct Injection: Cells are injected directly into the affected area, like joints or muscles, to help heal.
Systemic Infusion: Cells are infused into the blood, letting them reach injured or inflamed areas.
The details of the stem cell therapy process can change based on the treatment plan and the patient’s situation. Knowing these steps is important for those thinking about this treatment.
Pain During Stem Cell Harvesting
Harvesting stem cells can worry patients because of possible pain. This process gets stem cells from places like bone marrow, fat tissue, and blood.
Bone Marrow Aspiration Discomfort Levels
Bone marrow aspiration is a common way to get stem cells. Patients might feel some pain before and after, but doctors use pain medicine to help.
Adipose Tissue Extraction Pain Experience
Getting stem cells from fat tissue can also cause some discomfort. How much pain varies by person and the method used. Doctors often use local anesthesia to lessen pain during the procedure.
Blood-Derived Stem Cell Collection Sensation
Collecting stem cells from blood is less invasive than bone marrow aspiration. Some patients might feel a little discomfort during the blood draw, but it’s usually minor.
Anesthesia Options During Harvesting
To lessen pain during stem cell harvesting, different anesthesia options are available. Local anesthesia is often used to numb the area, making it less painful. Sometimes, conscious sedation or general anesthesia is used, based on the patient’s anxiety and the procedure’s complexity.
Pain During Stem Cell Injection and Administration
It’s important for patients to know about the pain from stem cell injections. This therapy involves putting stem cells into the body. This can cause different levels of pain.
This pain can be managed with pain relief medicine. The pain level can change based on where the injection is and how sensitive you are.
Localized Injection Site Pain
Many people feel pain at the injection site during stem cell therapy. This pain can be mild or moderate. Pain relief medication is usually suggested to help with this.
Deep Tissue Injection Discomfort
Injecting stem cells into deeper tissues can be more painful. The pain can differ based on the location and how sensitive you are.
Duration of Procedural Pain
The pain from stem cell injections doesn’t last long. It usually goes away soon after the procedure. Some people feel better right away, while others might take a few days.
Immediate Post-Injection Sensations
After the injection, you might feel soreness, swelling, or bruising. These feelings are usually mild and go away in a few days.
Post-Procedure Pain and Recovery Timeline
Knowing about post-procedure pain and recovery is key for those thinking about stem cell therapy. The recovery time can change based on several things. These include the treatment type, the area treated, and the patient’s health.
First 24-48 Hours After Treatment
Right after stem cell therapy, some discomfort, pain, or swelling might happen at the injection site. The Institute for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine says this is normal. The pain usually goes away in a few days.
Common symptoms during this period include:
- Mild pain or soreness
- Swelling or bruising
- Redness at the injection site
One Week Post-Treatment
By the end of the first week, most people start feeling better. The pain gets less, and swelling or bruising starts to go away. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s post-procedure instructions for the best recovery.
Long-Term Recovery Expectations
The recovery time can vary based on the condition treated and the patient’s health. Generally, people see more improvement over weeks to months after the procedure. It’s important to have realistic hopes and be patient during this time.
When Pain May Indicate Complications
While some pain is normal after stem cell therapy, severe or getting worse pain could mean complications. It’s good to know the risks, like infection or immune reactions. If you have severe pain, fever, or swelling, call your healthcare provider right away.
| Recovery Stage | Common Symptoms | Expected Outcome |
| First 24-48 Hours | Pain, swelling, bruising | Discomfort subsides within a few days |
| One Week Post-Treatment | Improving symptoms, reducing pain | Noticeable improvement |
| Long-Term Recovery | Continued improvement | Optimal results over weeks to months |
Understanding the post-procedure pain and recovery timeline helps patients prepare for what’s ahead. Always talk to a healthcare professional for personalized advice and care.
Common Stem Cell Therapy Side Effects
It’s important to know about the side effects of stem cell therapy. This treatment uses stem cells to fix or replace damaged tissues. While it’s mostly safe, it can cause different side effects, from mild to severe.
Mild Side Effects
Mild side effects are common and include swelling, bruising, and soreness at the injection site. Common Mild Side Effects:
- Swelling at the injection site
- Bruising
- Soreness
Moderate Side Effects
Some people might have moderate side effects like inflammation and stiffness. These can be managed with the right care and medication after the procedure.
Moderate Side Effects May Include:
| Side Effect | Management Strategy |
| Inflammation | Anti-inflammatory medication |
| Stiffness | Physical therapy |
Severe Side Effects
Severe side effects, though rare, can happen. These include infection and immune reactions. It’s key for patients to be watched closely after the procedure to spot severe side effects early.
Frequency of Pain-Related Side Effects
Pain-related side effects are common after stem cell therapy. How often and how severe these effects are can differ from person to person and the area treated.
Knowing about the side effects of stem cell therapy helps patients make better choices. It’s vital to talk to a healthcare provider about any worries to get the best results.
Factors That Influence Pain Levels in Stem Cell Therapy
It’s important to know what affects pain levels when thinking about stem cell therapy. Pain can be different for everyone during and after the treatment. This is because of several key factors.
Treatment Area and Tissue Type
The body area treated and the tissue type greatly affect pain levels. For example, treatments in joints or areas with many nerve endings can be more painful. This is compared to softer tissue areas.
- Treatments in areas with more nerve endings tend to be more painful.
- Joint and bone treatments can be more uncomfortable than those in fatty tissue.
Individual Pain Tolerance
Everyone’s pain tolerance is different. Age, health, and past pain experiences can change how much pain someone feels. This is true during and after stem cell therapy.
Key factors influencing individual pain tolerance include:
- Genetic predispositions to pain sensitivity.
- Previous experiences with medical procedures.
- Psychological factors, such as anxiety or stress levels.
Pre-existing Conditions
Medical conditions before treatment can also affect pain levels. Conditions that change how pain is felt or cause chronic pain can alter a patient’s experience.
For example, patients with fibromyalgia may feel pain differently than those without it.
Practitioner Skill and Technique
The skill and technique of the practitioner can greatly impact pain levels. More experienced practitioners might use methods that cause less discomfort.
Techniques that can reduce pain include:
- Using ultrasound guidance for precise injections.
- Employing local anesthesia or sedation when appropriate.
- Utilizing gentle and precise injection methods.
Pain Management Strategies for Stem Cell Therapy
pain management strategies
Knowing about pain management is key for those thinking about stem cell therapy. Good pain management can make the treatment better and more effective.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Getting ready for the procedure is important for pain management in stem cell therapy. This includes looking at the patient’s health history, current pain, and past pain management experiences.
Pre-procedure preparation may involve:
- Reviewing current medications and supplements
- Discussing anesthesia or sedation options
- Understanding the procedure’s specifics and possible pain triggers
During-Procedure Pain Control Options
During the stem cell therapy, there are ways to control pain. These include local anesthesia, sedation, or other methods based on the patient’s needs and the procedure.
| Pain Control Measure | Description | Typical Use Case |
| Local Anesthesia | Numbing the specific area where the procedure is performed | Minor procedures or injections |
| Sedation | Relaxing the patient to reduce anxiety and discomfort | More invasive procedures or when extra comfort is needed |
Post-Procedure Pain Relief Methods
After the procedure, it’s important to manage pain well for a smooth recovery. This might include medication, rest, and other care strategies.
Post-procedure pain relief methods may include:
- Prescribed pain relief medication
- Applying ice or heat to the affected area
- Rest and avoiding strenuous activities
By understanding and using these pain management strategies, patients can greatly improve their stem cell therapy experience. It’s vital to follow the healthcare provider’s advice on pain management for the best results.
Patient Experiences and Pain Testimonials
Stem cell therapy is becoming more popular, and patient feedback is key. People getting this treatment share different stories about pain and how they feel after it.
Neurological Treatment Experiences
People with Parkinson’s or multiple sclerosis have mixed feelings about pain and discomfort. Some see their symptoms improve, while others don’t feel much change in pain.
Autoimmune Condition Patient Perspectives
Those with rheumatoid arthritis share their stem cell therapy experiences. Some say they feel less pain and inflammation, but others don’t notice a big difference.
Pain Versus Benefit Analysis from Patients
Every patient’s story is unique, showing the need for personalized care in stem cell therapy. Understanding these experiences helps doctors tailor treatments to fit each person’s needs.
Pain Comparison: Stem Cell Therapy vs. Alternative Treatments
pain comparison stem cell therapy
When comparing pain levels, stem cell therapy often stands out. It’s seen as a better option than some traditional treatments. This is because it might offer less pain and quicker recovery times.
Comparison with Surgical Interventions
Surgeries can lead to a lot of pain and a long recovery. Stem cell therapy, being less invasive, might cause less pain. Studies show it can lead to faster recovery times than surgery for some conditions.
Comparison with Medication-Based Treatments
Medications like corticosteroids or opioids can have serious side effects. They might not even fix the pain’s root cause. Stem cell therapy, by healing at the cellular level, could offer relief without as many side effects. The pain from stem cell injections is usually mild and short.
Comparison with Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a gentle approach but might not work for severe cases. It’s not painful but can take a lot of time and sessions. Adding stem cell therapy to physical therapy could help repair tissues faster, reducing pain.
Recovery Pain Duration Differences
The time it takes to recover from pain varies a lot. Surgeries can take weeks or months to heal. But, stem cell therapy usually means a quicker return to normal life, in just a few days to a week. Knowing these differences helps manage patient expectations and pain better.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy is seen as a hopeful treatment for many health issues. It has both good and bad sides. While it’s mostly safe, it can cause pain and side effects.
Knowing what affects pain, like where the treatment is and how sensitive you are, helps. There are ways to manage pain before and after the treatment. This can make you feel less uncomfortable.
If you’re thinking about stem cell therapy, talk to your doctor first. They can help you understand the good and bad parts. This way, you can make a smart choice for your health.
As scientists keep studying, stem cell therapy will likely get better. It’s important to stay up-to-date and talk to your doctor. This helps you make the most of this new treatment.
FAQ
Are there any risks associated with stem cell therapy?
Yes, like with any treatment, there are risks. These include infection, allergic reactions, or other problems. But, these can be lowered by choosing a qualified doctor and following the right steps.
What pain management strategies are used during stem cell therapy?
To manage pain, doctors might prepare you before the treatment, use anesthesia during it, and give you medicine or physical therapy after. This helps you feel better.
What factors influence pain levels during stem cell therapy?
Several things can affect how much pain you feel, like where the treatment is, your pain threshold, any health issues you have, and the skill of the person doing the treatment.
How does stem cell therapy compare to other treatments for pain?
It’s different because it tries to fix the cause of pain, not just cover it up. It might be a better option than surgery, medicine, or physical therapy for some people.
Can stem cell therapy be used to treat chronic pain?
Yes, it can help with chronic pain from conditions like joint or nerve problems. It aims to heal and grow new tissue, which can reduce pain and improve function.
How long does it take to recover from stem cell therapy?
Recovery time can differ. You might feel sore or stiff for a day or two. Then, you’ll start to feel better over the next few days or weeks.
What are the possible side effects of stem cell therapy?
You might feel some swelling, bruising, or soreness after treatment. Rarely, you could have a serious reaction or infection.
Is stem cell harvesting painful?
The pain from harvesting stem cells can vary. Bone marrow aspiration might hurt a bit, but it can be managed. Taking stem cells from fat or blood might be a bit uncomfortable, but it’s usually not bad.
What are the different types of stem cells used in therapy?
Adult stem cells, like those from bone marrow or fat, are often used. Embryonic stem cells are used too, but less because of ethical issues.
What is stem cell therapy and how does it work?
Stem cell therapy is a way to fix damaged cells and tissues in the body. It uses stem cells, which can turn into different types of cells. This helps in healing and growing new tissue.























